Mod 1- Radiographic Appearances
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key radiographic appearances and diagnostic criteria for various esophageal and gastric pathologies.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
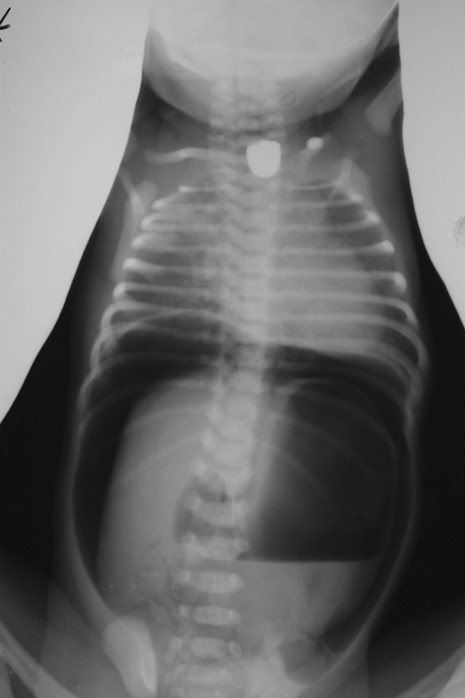
What is the key plain-film finding in esophageal atresia?
NG/OG tube coils in the proximal esophageal pouch and does not reach the stomach.
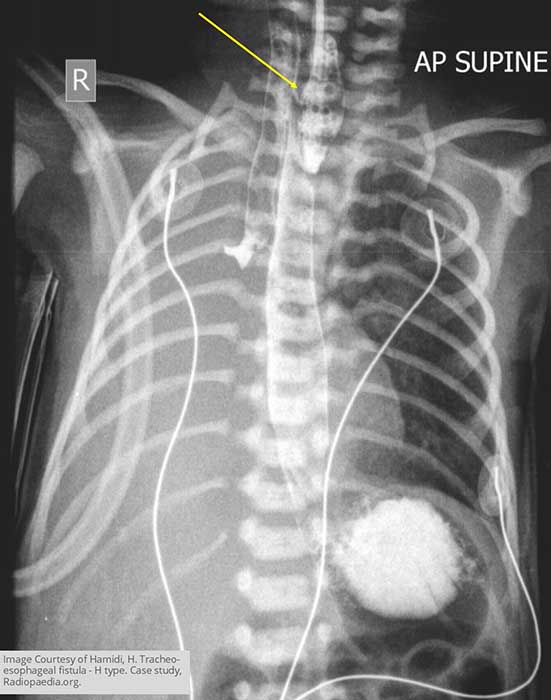
What does abdominal gas pattern indicate in TEF?
Presence or absence of bowel gas helps determine the type of TEF.
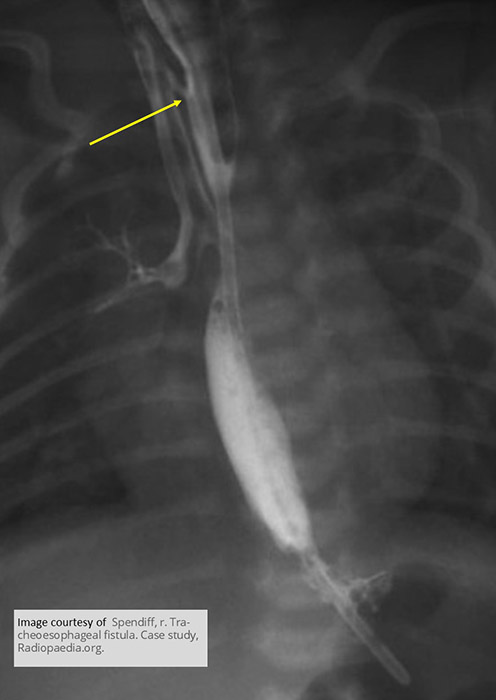
What contrast should be used if fluoroscopy is required for TEF?
Water-soluble contrast only (high aspiration risk).
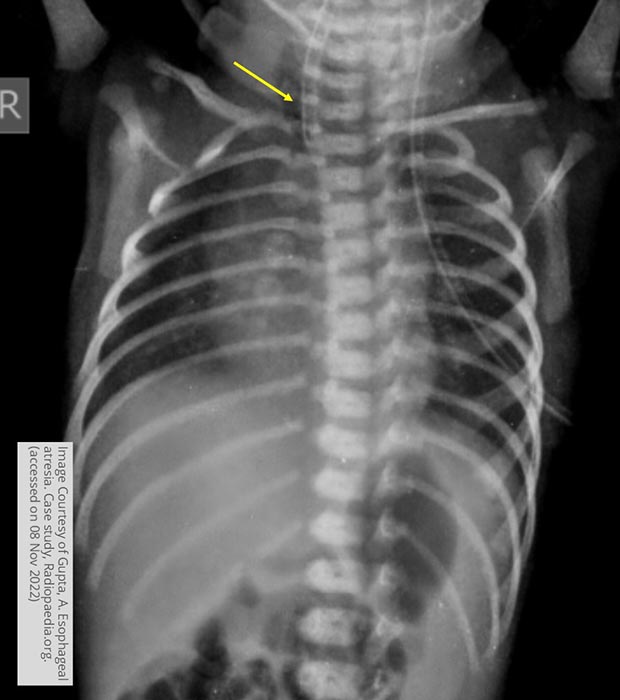
What may be seen on a plain chest X-ray for acquired tracheoesophageal fistula?
Air in the mediastinum, especially if caused by malignancy.
What is the best imaging modality to identify the fistula in acquired TEF?
Fluoroscopy with water-soluble contrast.
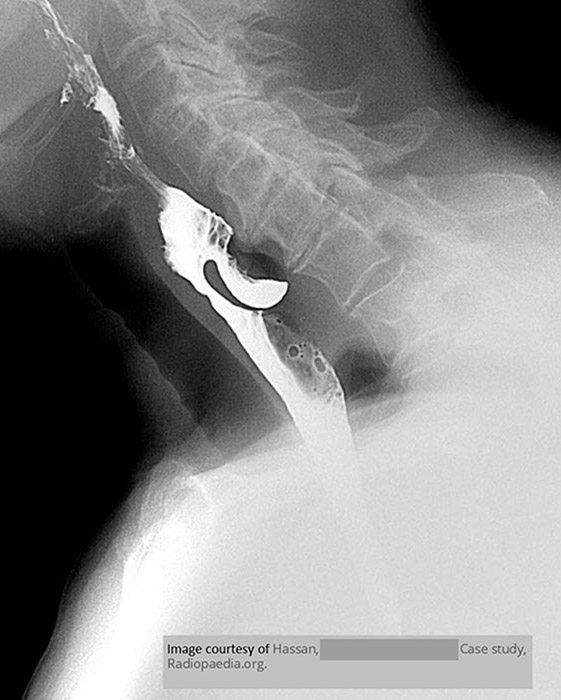
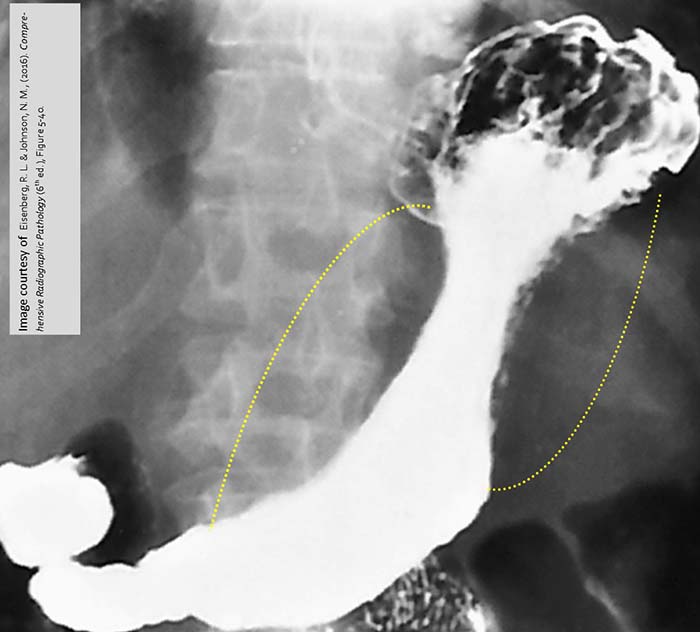
What is the gold-standard imaging study for Zenker’s diverticulum?
Barium swallow.
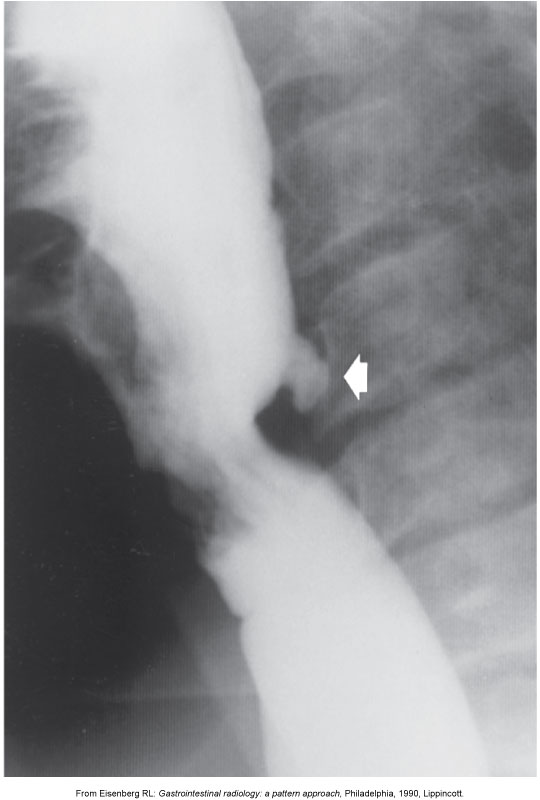
What is the typical radiographic appearance of Zenker’s diverticulum?
Posterior outpouching at the pharyngoesophageal junction.
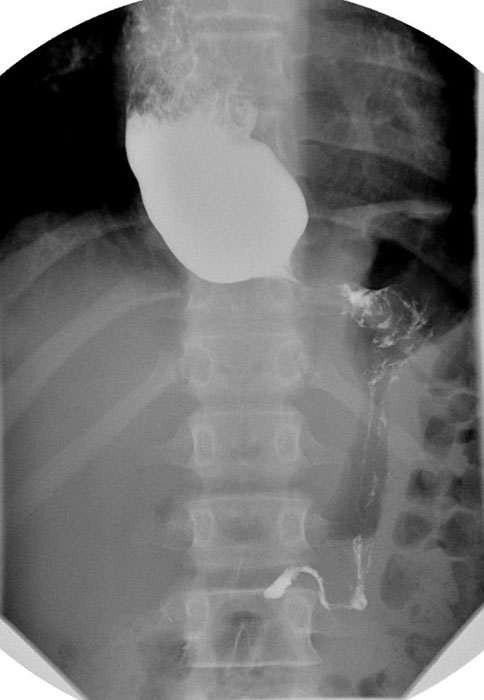
What may be seen on chest X-ray for achalasia?
Widened mediastinum with an air-fluid level.
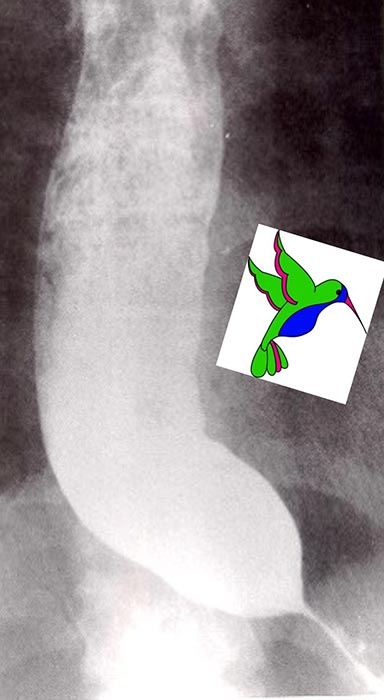
What are the classic barium swallow signs of achalasia?
Bird’s beak sign, string sign, corkscrew esophagus.
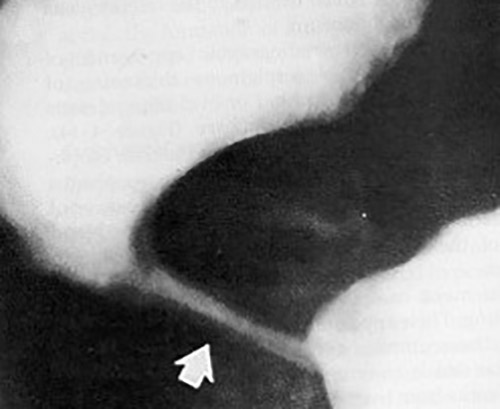
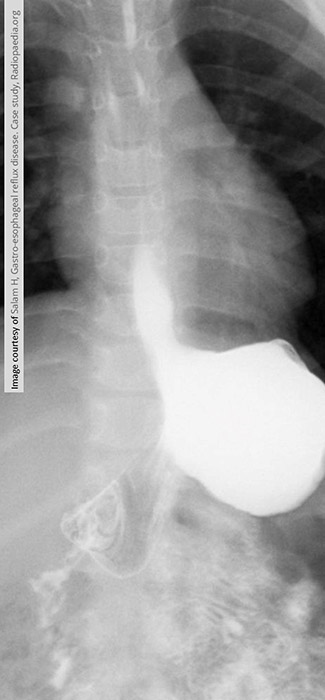
What is the standard imaging study for GERD?
Fluoroscopic barium swallow with UGI.
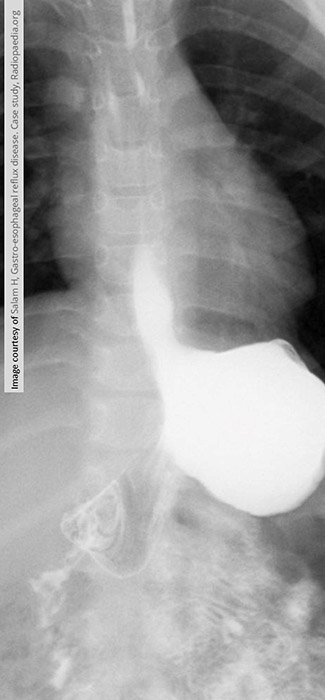
What are the early radiographic changes in GERD?
Mild esophageal dilation and reduced peristalsis.
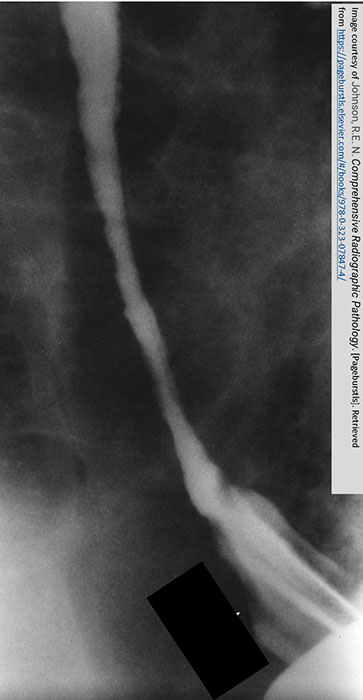
What is the late-stage radiographic appearance of GERD?
Smooth, tapered narrowing of distal esophagus due to scarring; Barrett’s esophagus appears stomach-like.
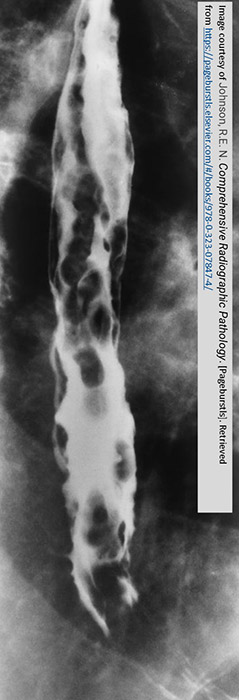
What does a barium swallow show in esophageal varices?
Irregular, serpiginous filling defects within the esophagus.
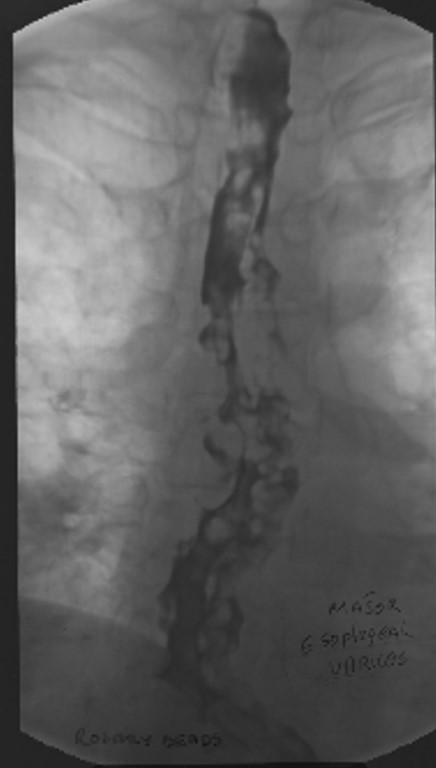
What is the role of CT in esophageal varices?
Not diagnostic, but shows extent of disease.
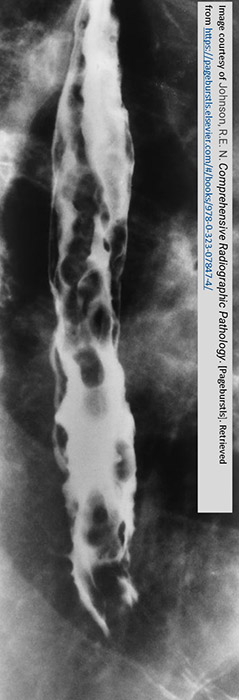
What is an additional modality for diagnosis of esophageal varices?
Endoscopic ultrasound.
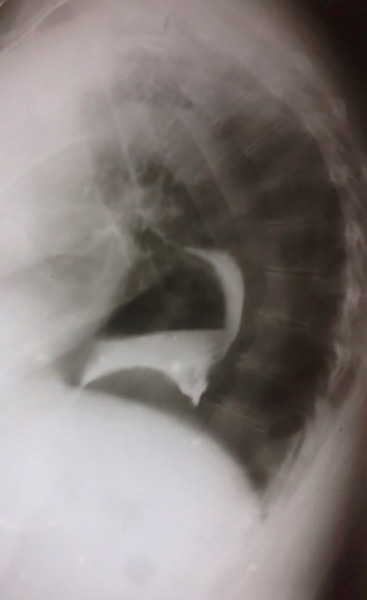
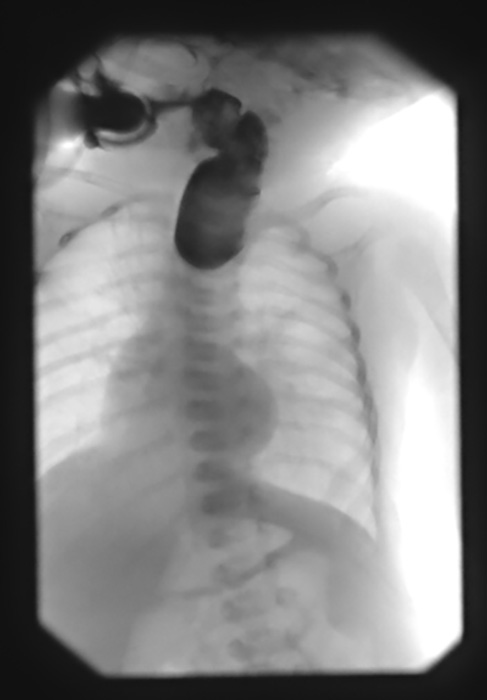
What may be seen on chest X-ray with a large hiatus hernia?
Retrocardiac soft-tissue mass with an air-fluid level.
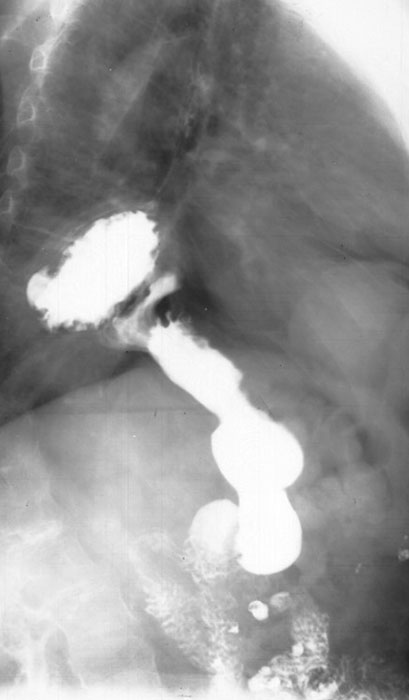
How do you differentiate the esophagus from the stomach on a barium study?
Esophagus = smooth; stomach = rugal folds.
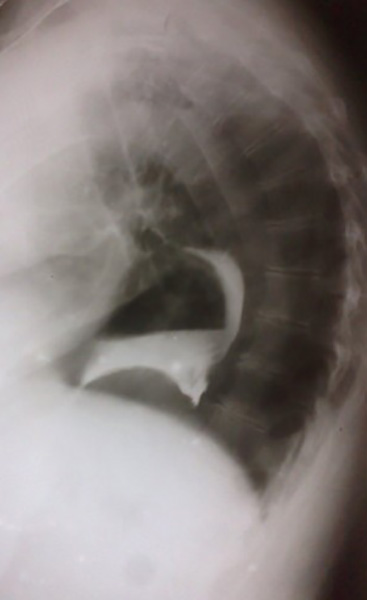
What is the key landmark to identify in a hiatus hernia?
Diaphragm.
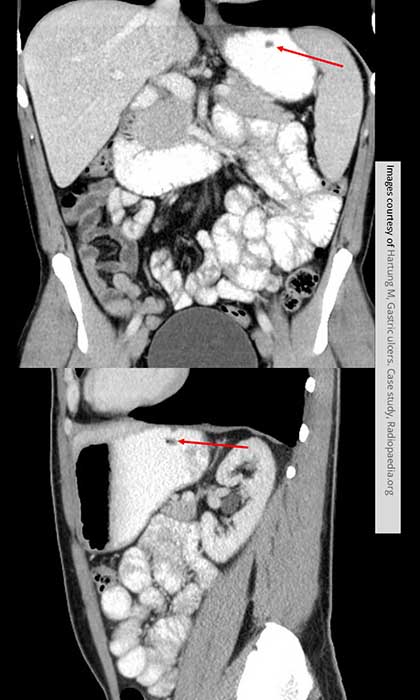
How do ulcers appear on contrast studies?
Appear as outpouchings due to surrounding mucosal edema (not true outpouchings).
How are ulcers classified by location?
Gastric (stomach) vs duodenal (duodenal bulb or pylorus).
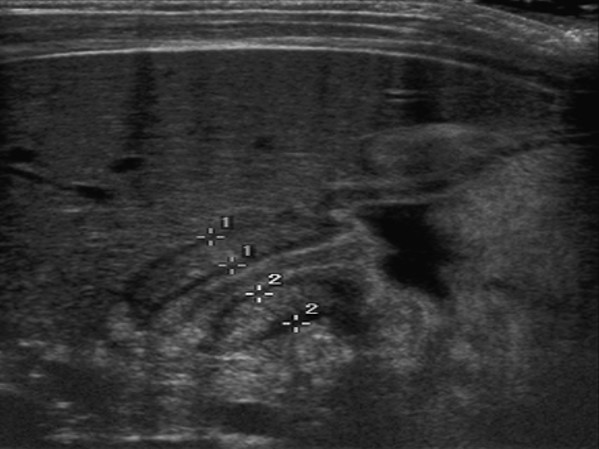
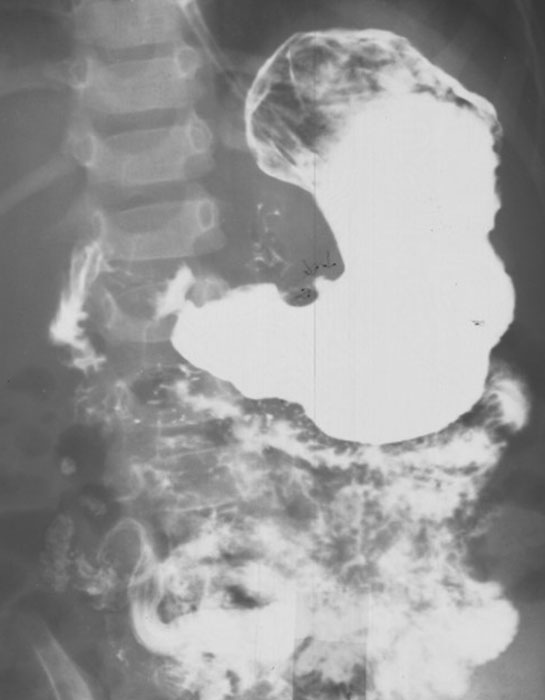
What is the modality of choice for diagnosis of pyloric stenosis?
Ultrasound (accurate muscle thickness and length measurements).
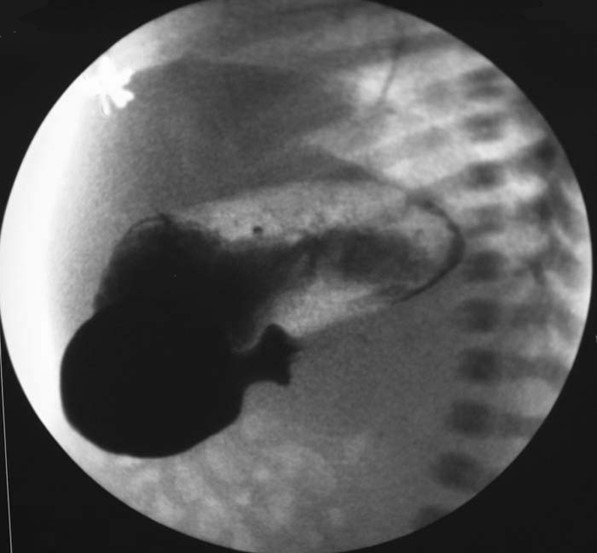
What are the upper GI radiographic findings for pyloric stenosis?
Delayed or absent gastric emptying; impression of enlarged pylorus on distal stomach.
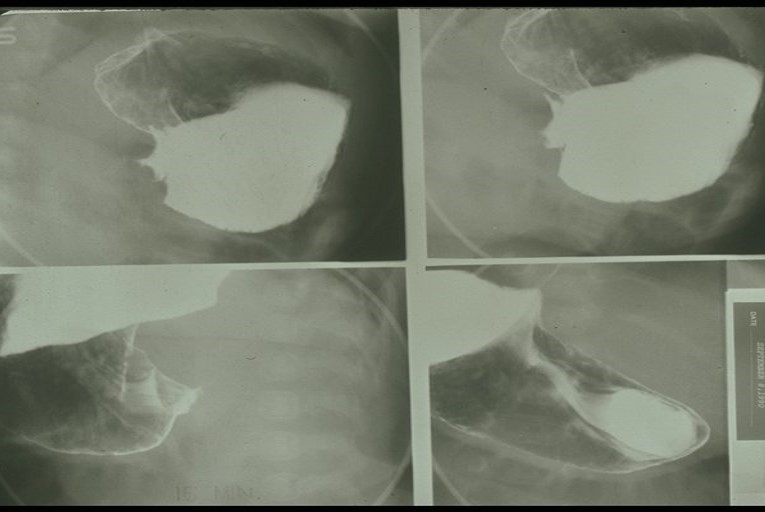
What may an abdominal X-ray show for pyloric stenosis?
Gastric distention (limited diagnostic value).
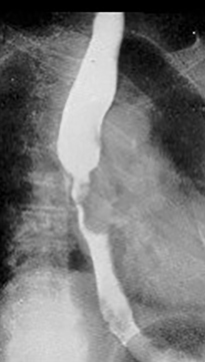
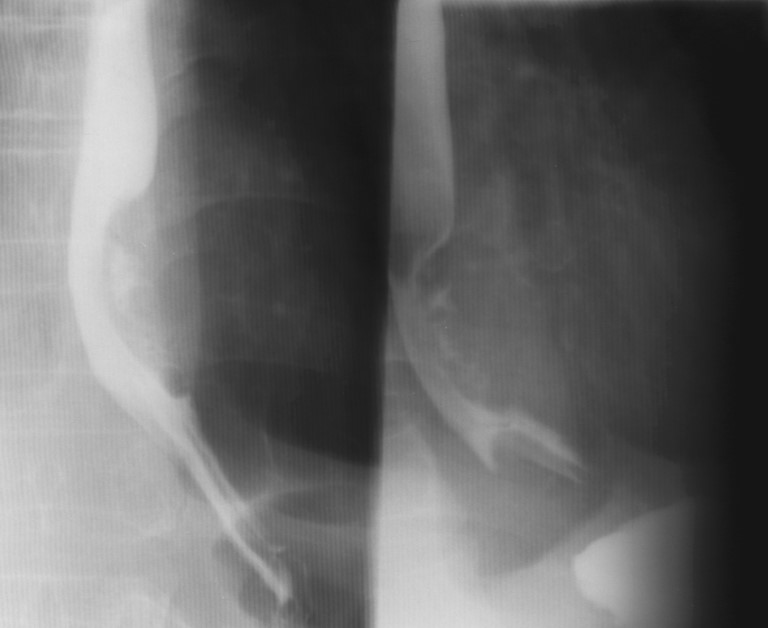
What are the two growth patterns of esophageal carcinoma?
Infiltrating and proliferating.
What is the radiographic appearance of the infiltrating type of esophageal carcinoma?
Irregular narrowing, mucosal destruction, esophageal dilation above lesion.
What is the radiographic appearance of the proliferating type of esophageal carcinoma?
Plaque-like lesions causing filling defects.
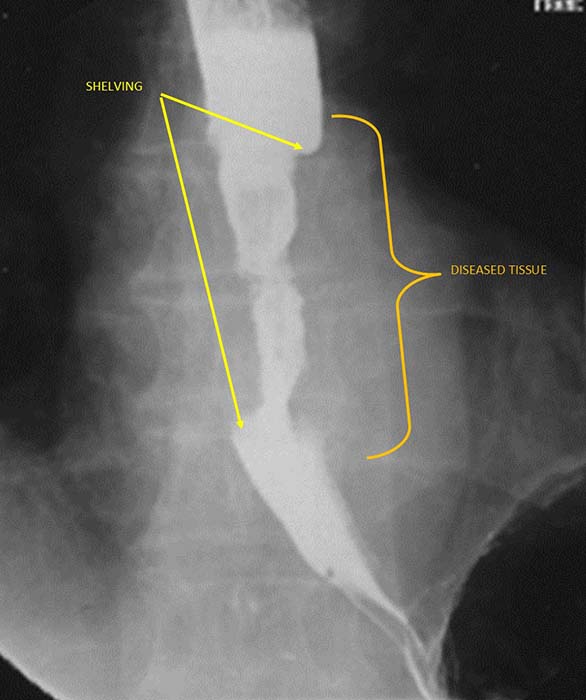
What is 'shelving' in esophageal carcinoma?
Sharp, shelf-like demarcation between normal and diseased esophagus (classic infiltrative sign).
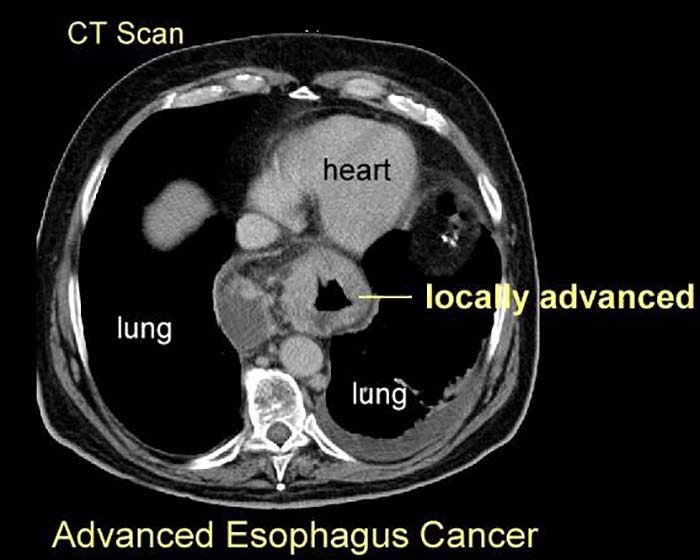
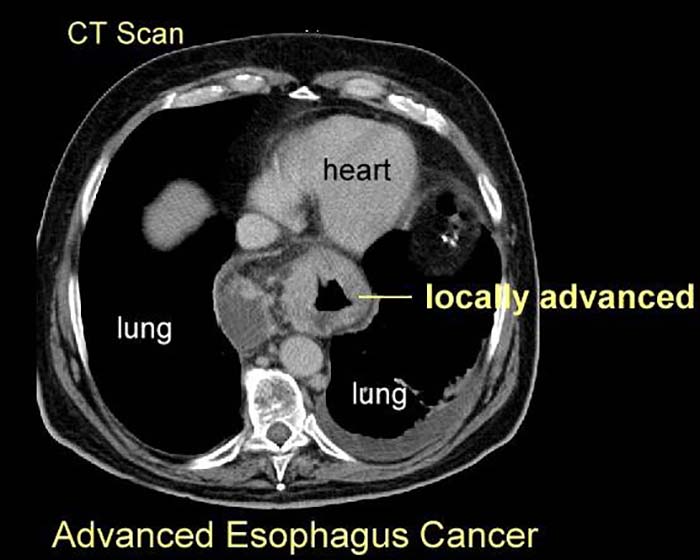
What are the best imaging studies for esophageal carcinoma?
Barium swallow (if patient can swallow); CT for staging and treatment planning.
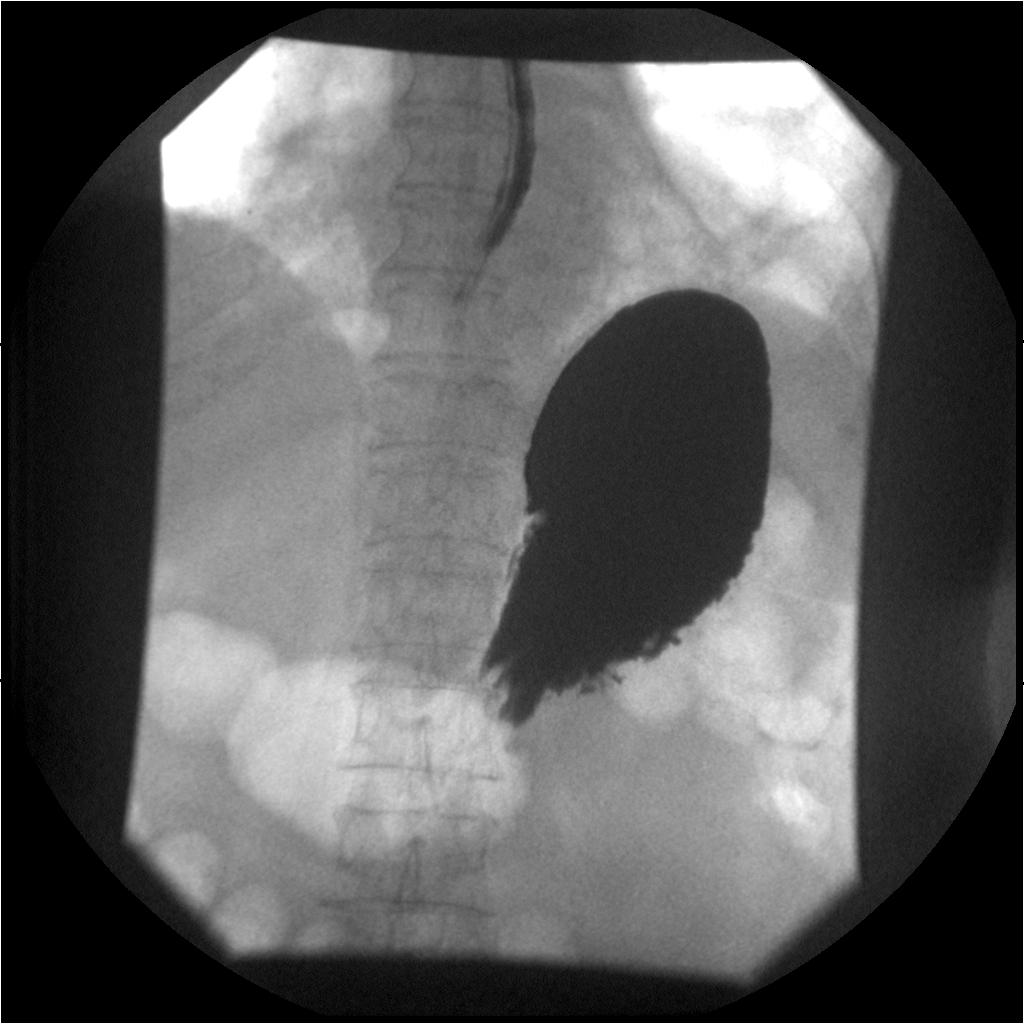
What is the radiographic appearance of infiltrative gastric carcinoma?
Thickened walls, narrowed lumen, rigid non-contracting 'fixed stomach', loss of rugal folds.
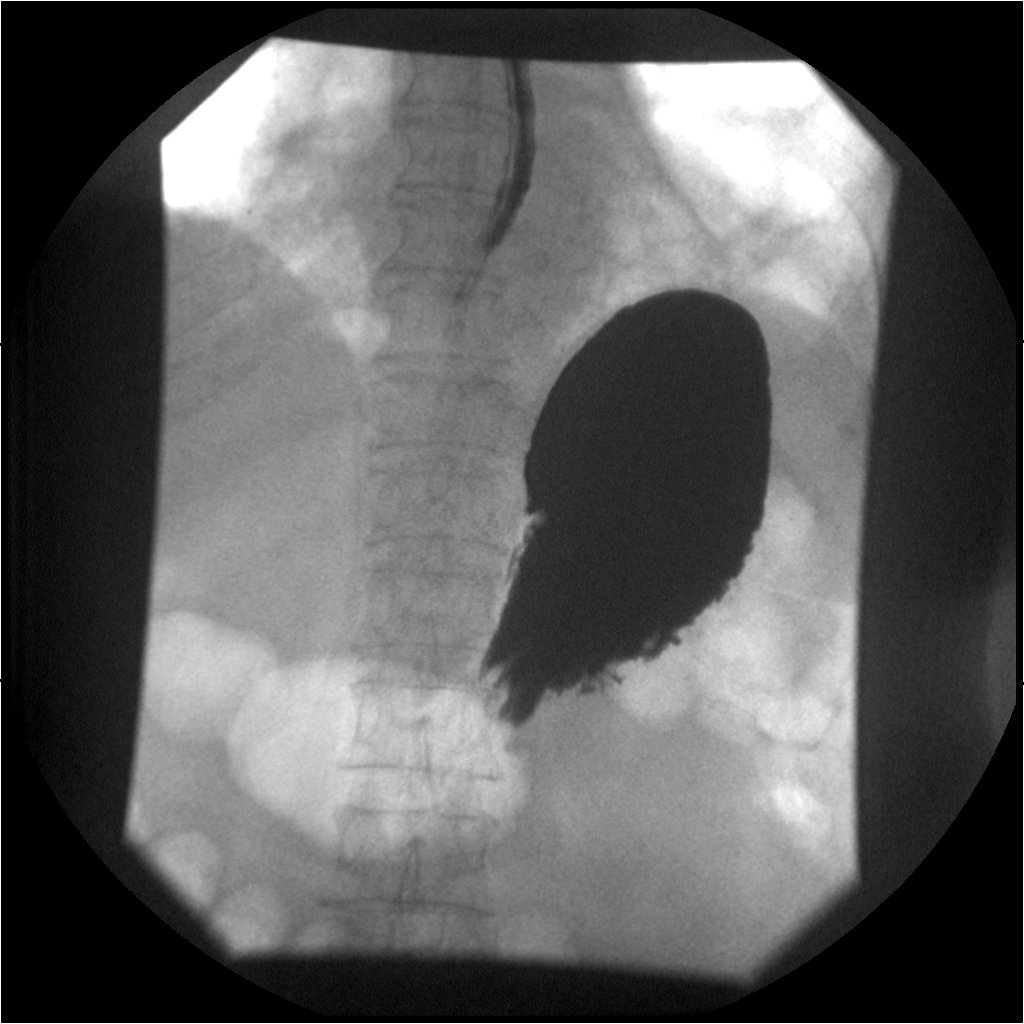
What is the hourglass stomach?
Circumferential involvement causing mid-gastric narrowing.
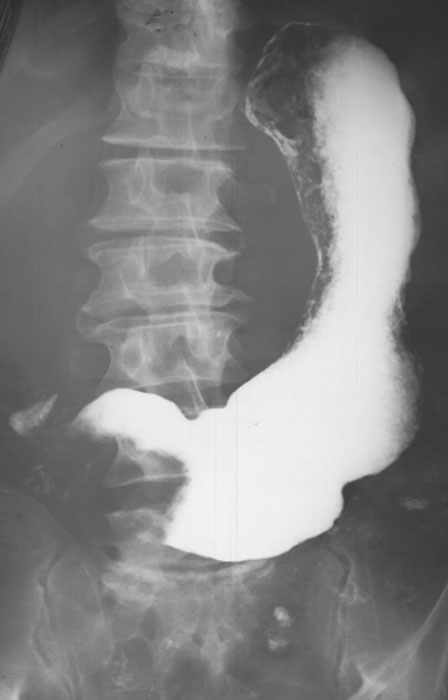
What is the radiographic appearance of proliferative type of gastric carcinoma?
Polypoid mass projecting into the lumen; may mimic ulcer.
What are the best imaging studies for gastric carcinoma?
UGI for detection; CT for staging, treatment, and follow-up.