bio1111 - lab exam review #1
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
109 Terms
polymers
all of these are a type of what?
1. proteins
2. lipids
3. carbohydrates
4. nucleic acids
monomers
all of these are a type of what?
1. amino acids
2. N/A
3. monosaccharides
4. nucleotides
black
in the molecular model kit, what colour is CARBON?
white
in the molecular model kit, what colour is HYDROGEN?
purple
in the molecular model kit, what colour is PHOSPHORUS?
red
in the molecular model kit, what colour is OXYGEN?
blue
in the molecular model kit, what colour is NITROGEN?
alcohol or hydroxyl group
what is this functional group?
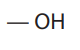
amino group
what is this functional group?
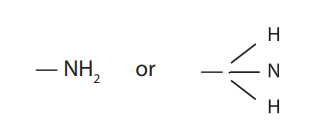
acid or carboxyl group
what is this functional group?
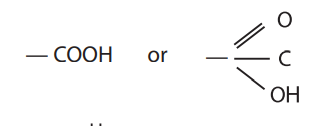
methyl
what is this functional group?

false
TRUE OR FALSE: most of the world’s population can digest milk-based food?
they lack the lactase enzyme
why are people lactose intolerant?
lactose intolerance
> a relatively recent mutation in the human genome
> survival advantage for human cultures with milk and dairy products available year-round
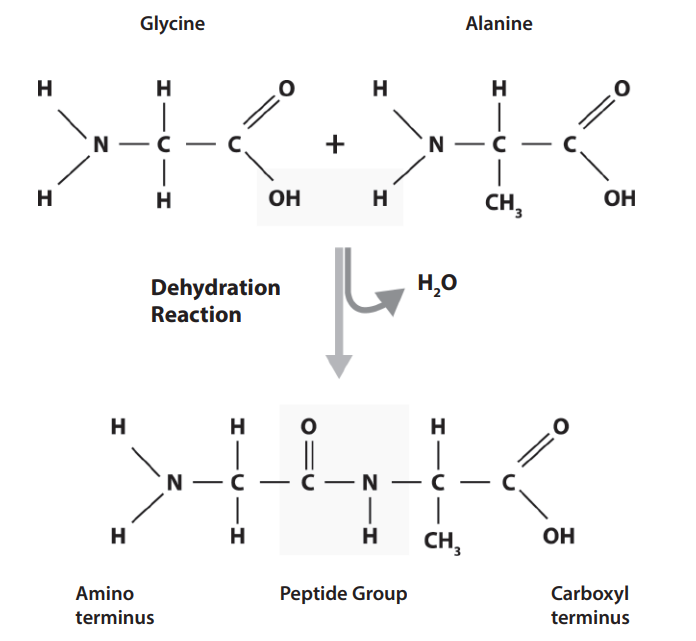
dehydration synthesis
monomers are linked together to form polymers through ____________, (removes water)
hydrolisis
polymers are broken apart by __________, the addition of water
peptide bond
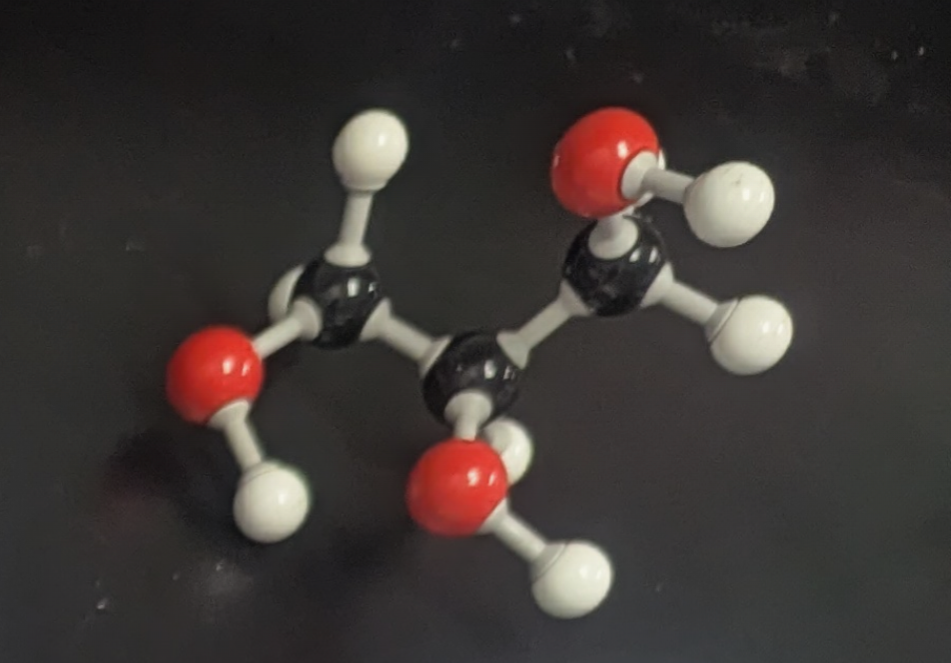
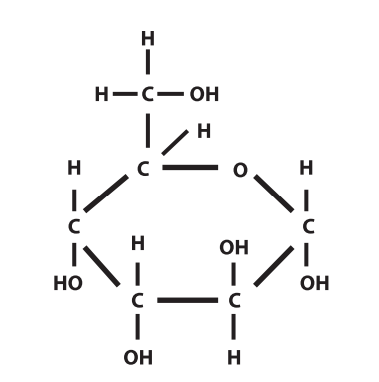
glucose
what is this molecule?
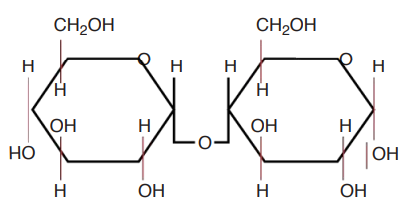
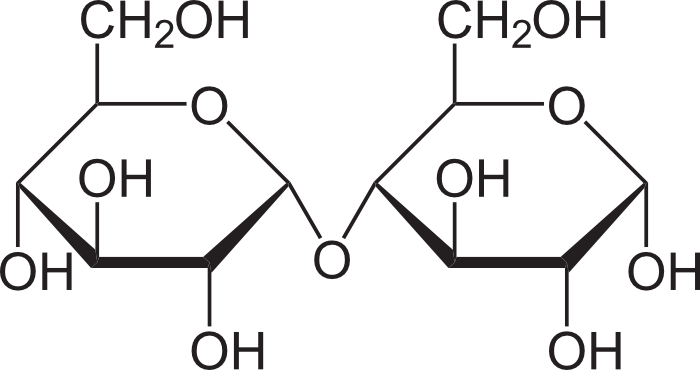
maltose
what is this molecule?
peptide bonds
what does this represent?
enzymes
reactions of hydrolysis/dehydration are mediated by _______, specialized proteins that speed up chemical reactions, serve as catalysts, regulate virtually all chemical reactions within cells
oxygen
what is this molecule?
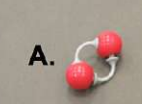
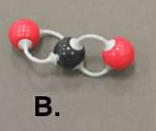
carbon dioxide
what is this molecule?
hydrogen
what is this molecule?
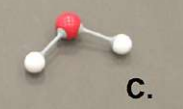
methane
what is this molecule?
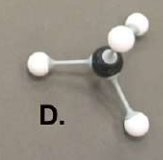
alanine
name this organic molecule
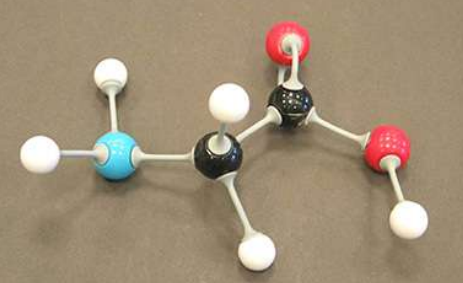
glucose
name this molecule
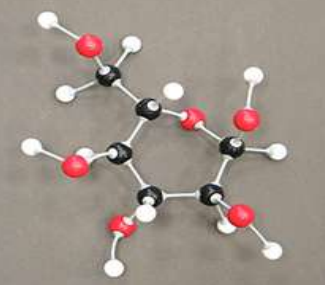
dissarcharide
two monosaccharides can bond to form a ____________ by a dehydration reaction
glucose, glucose
maltose = ________ + _________
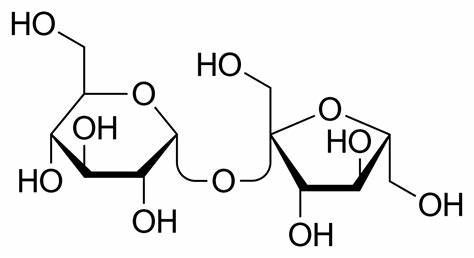
glucose, fructose
sucrose = ______ + _________
methyl
what is this functional group?

hydroxyl
what is this functional group?

carboxyl
what is this functional group?

amino
what is this functional group?

polysaccharides
_________ function as:
> storage molecules
> structural compounds
starch
used by plants for energy storage
glycogen
energy storage in the animal liver
cellulose
forms plant cell walls
chitin
exoskeleton component in insects & crustaceans (also found in the cell walls of fungi)
carbohydrates
polymer names for _________:
> polysaccharides, complex ____________
lipids
polymer names for _________:
> triglycerides, steroids
protein
polymer names for _______:
> polypeptide, _________
nucleic acids
polymer names for _________:
> polynucleotides
carbohydrate
_________ purpose:
> short-term energy, energy storage, structure
lipids
_________ purpose:
long-term energy storage, plasma membrane, pigments, cell membranes (plants)
protein
_________ purpose:
> biological catalyst, muscle contraction, structure
nucleic acids
_________ purpose:
> genetic information
carbohydrates
examples of _______:
> sucrose, glucose, fructose, lactose, starch, cellulose, glycogen
lipids
examples of _______:
> phospholipids, cholesterol, fats, oils, waxes, chlorophyll (plants)
proteins
examples of _______:
> Insulin, hemoglobin, actin & myosin, enzymes, collagen, structure, cell messaging, etc
nucleic acids
examples of _______:
> DNA, RNA
Benedict’s solution
what solution do you use to test for simple sugars?
blue
In the Benedict’s Solution, what colour is the test tube if there are no simple sugars?
green
In the Benedict’s Solution, what colour is the test tube if there are traces of simple sugars?
yellow
In the Benedict’s Solution, what colour is the test tube if there are low amounts simple sugars?
orange
In the Benedict’s Solution, what colour is the test tube if there is a moderate amount of simple sugars?
red
In the Benedict’s Solution, what colour is the test tube if there is a high amount of simple sugars?
iodine
what solution do you use to test for starch?
yellow
in iodine solution, what colour does the test tube change to when there is no starch?
black/purple
in iodine solution, what colour does the test tube change to when there is starch?
sudan iv
to test for lipids, what solution do you use?
yellow with a red line
what does the test tube colour change to when there are lipids? (sudan iv)
yellow
what does the test tube colour change to when there are no lipids? (sudan iv)
fat
____ is a large lipid made from two kinds of smaller molecules linked by a dehydration rection
triglycerides
one glycerol linked to 3 fatty acids, therefore often referred to as _________________
Biuret reagent
to test for proteins, what solution do you use?
blue
what colour does the test tube change to when there are no proteins? (Biuret reagent)
purple
what colour does the test tube change to when there are proteins present? (Biuret reagent)
pink
what colour does the test tube change to when there are peptides present? (Biuret reagent)
unsaturated fats
contain one or more double bonds which can cause kinks; preventing them from packing together tightly
saturated fatty acids
contain only one single bonds; most animal fats are this
unsaturated fats, saturated fats
hydrogenated vegetable oils are _________________ that have been converted to ________ by adding hydrogen
trans fats
partial hydrogenation creates _________, which are associated with health risks
LDL
= BAD
HDL
= GOOD
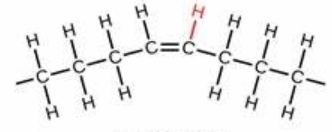
cis-fat molecule
what fat is this?
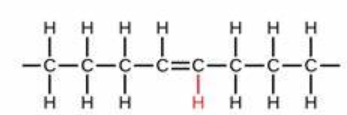
trans-fat molecule
what fat is this?
phospholipids
the major component of all cell membranes
hydrophilic head
what part of the phospholipid is attracted to water?
it also contacts with:
the water of the environment, the internal part of the cell
hydrophobic tail
what part of the phospholipid is afraid of water?
it also clusters together in the center of the bilayer
proteins
> involved in nearly every dynamic function of the body
> 20 amino acid monomers
central dogma
DNA → RNA → Protein
amino acids
____________ all have:
> amino group
> carboxyl group
> symbolized by R, which determines the specific properties of each of the 20 __________ to make proteins
true
true or false:
when a protein’s shape is altered, it can no longer function
denaturation
when a protein unfolds
peptide bond
joining the carboxyl group of one amino acid to the amino group of the next amino acid makes a ____________
polypeptide
chain of amino acids is called _____________
primary protein structure
sequence of a chain of amino acids
secondary protein structure
hydrogen bonding of the peptide backbone causes the amino acids to fold into a repeating pattern
tertiary protein structure
three-dimensional folding pattern of a protein due to side chain interactions
quarternary protein structure
protein consisting of more than one amino acid chain
deoxyribonucleic acid
scientific name for DNA
DNA
> genes consist of _______
> inherited
> provides directions for its own replication
> programs a cell’s activities by directing protein synthesis
ribonucleic acid
scientific name for RNA
nucleotides
____________ has three parts:
1) a five-carbon sugar called ribose in RNA and deoxyribose in DNA
2) a phosphate group
3) a nitrogenous base
negative
DNA and RNA have a ___________ charge
DNA
sugar: deoxyribose
structure: double helix
nucleotides: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), cytosine (C)
A - T ; G - C
RNA
sugar: ribose
structure: single helix
nucleotides: uracil (U), adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C)
A - U ; G - C
true
true or false: hydrogen bonds hold together the strands of DNA
glycerol
what model is this?
