Lecture 13: Development and Molting
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Insect grows
Everytime they molt
Pre-insects — Ametabolous — NO Metamorphosis
- Immature stage: egg —> nymph —> adult
- Growth: nymphs and adults look the same, just different sizes, no wings
- Adult stage: same structures as immatures —> just change in size, no wings
- EX: Bristletails
Hemimetabolous — Terrestrial — Incomplete Metamorphosis
- Immature stage: egg —> nymph —> adult
- Growth: nymphs resemble adults, but adults have wings
- Adults: nymphs and adults have similar habits and habitats, wings
- EX: Cockroaches
Hemimetabolous — Aquatic
- Immature stage: egg —> naiad —> adult
- Growth: naiads distinct from adults
- Adult stage: naiads and adults closely related, different habitats
- EX: damselfly, mayfly
Holometabolous — Complete Metamorphosis
- Immature stage: egg —> larva —> pupa —> adult
- Growth: larvae don't resemble adults
- Adult stage: larvae and adults don't have similar habits
- EX: Fleas, Coleoptera, Lepidoptera, Flies
Holometabolous Advantages
- leads to reduced competition between immatures and adults
- permits adults to feed on different food sources
- permit adults to exploit different habitats
Larval Forms
- Polypod larvae
- Oligopod larvae
- Apod
Polypod larvae
- 3 pairs of thoracic legs
- up to 5 pairs of unjointed abdominal legs = prolegs
Oligopod larvae
- thoracic legs are well developed
- abdominal legs are absent
Apod Larvae
No legs
Pupal Forms
- Obtect (Chrysalis)
- Exarate
- Coarctate (Puparium)
Obtect (Chrysalis)
- Often see the inside
- Developing appendages (antennae, wings, legs, etc.) held tightly against body by a shell like casing. Often found enclosed within a silken cocoon
- EX: Butterflies and Moths
Exarate
- No coverings
- All developing appendages free and visible externally
EX: Beetles and Lacewings
Coarctate (Puparium)
- Hard case, can't see developing parts
- Body encased within the hard exoskeleton of the next-to-last larval instar
- EX: Flies
Oviposition
Females lay eggs
Eclosion
Eggs hatch
Molting Stages — 1: Apolysis
- Beginning
- Epidermal cells separate from old cuticle
Molting Stages — 2: Epidermal Cells
- Epidermal cells secrete molding fluid
- inactive
Molting Stages — 3: Epidermal Cell/Old Cuticle
- Epidermal cells secrete new epicuticle, separates epidermal cells from molting fluid
Molting Stages — 4: Endocuticle
- Molting fluid becomes active and breaks down old endocuticle
Molting Stages — 5: Absorption
- Old endocuticle is absorbed by epidermal cells
- 90% used to form new endocuticle
- Exocuticle and epicuticle not broken down —> allows insect to keep safe
Molting Stages — 6: New Cuticle
- New cuticle is wrinkled under old cuticle
- Insects need to expand
Molting Stages — 7: Sutures Form
- Ecdysial structures form — places in the cuticle where there is no exocuticle.
- When endocuticle dissolved away, weakens at these sutures
- Places where there is no exocuticle
- Insects takes in or pumps air to blow up, splits old cuticle at sutures
Molting Stages — 8: Ecdysis
- Ending
- Insect then emerges from old skin
Molting Stages — 9: Following Ecdysis
- Following ecdysis, insect may be light in color and soft
- Hardens with time
- May eat leftover exocuticle —> for nutrients
- Sclerotization (tanning)
Define Molting BY:
- Apolysis (Beginning)
- Ecdysis (Ending)
Adults no longer Molt — Disadvantage
- Disadvantage of exoskeleton: exoskeleton rigid, molting process expands overtime
- Epidermis: cells attach to basement membrane
- Exo/Endo cuticle: together create procuticle covered by epicuticle compromised of multiple layers
Teneral
- First emerging from its old skin
- Exoskeleton has not hardened, it is soft
Larval Instar
- Feed first instar until it is ready to molt
- Next instar will feed and molt (apolysis and ecdysis)
Instar
When emerges from the end of ecdysis until the next end of ecdysis
Stadium
End of ecdysis to the beginning of apolysis
Insect Brain
- Triggers prothoracic gland which stimulates ecdysome which is the pro-molting hormone in the insect larva (Ecdysteroid)
Hormones
- Juvenile hormone
- Ecdysteroid
Juvenile hormone (JH)
- Hormone comes from corpus allatum
- What is keeping insect as an immature and is present at each one of the molts, but the JH is changing
- Keeps insect immature until it is ready to pupate, decreases once molting begins
- Important for pest management—> used to keep insects out of adult stage
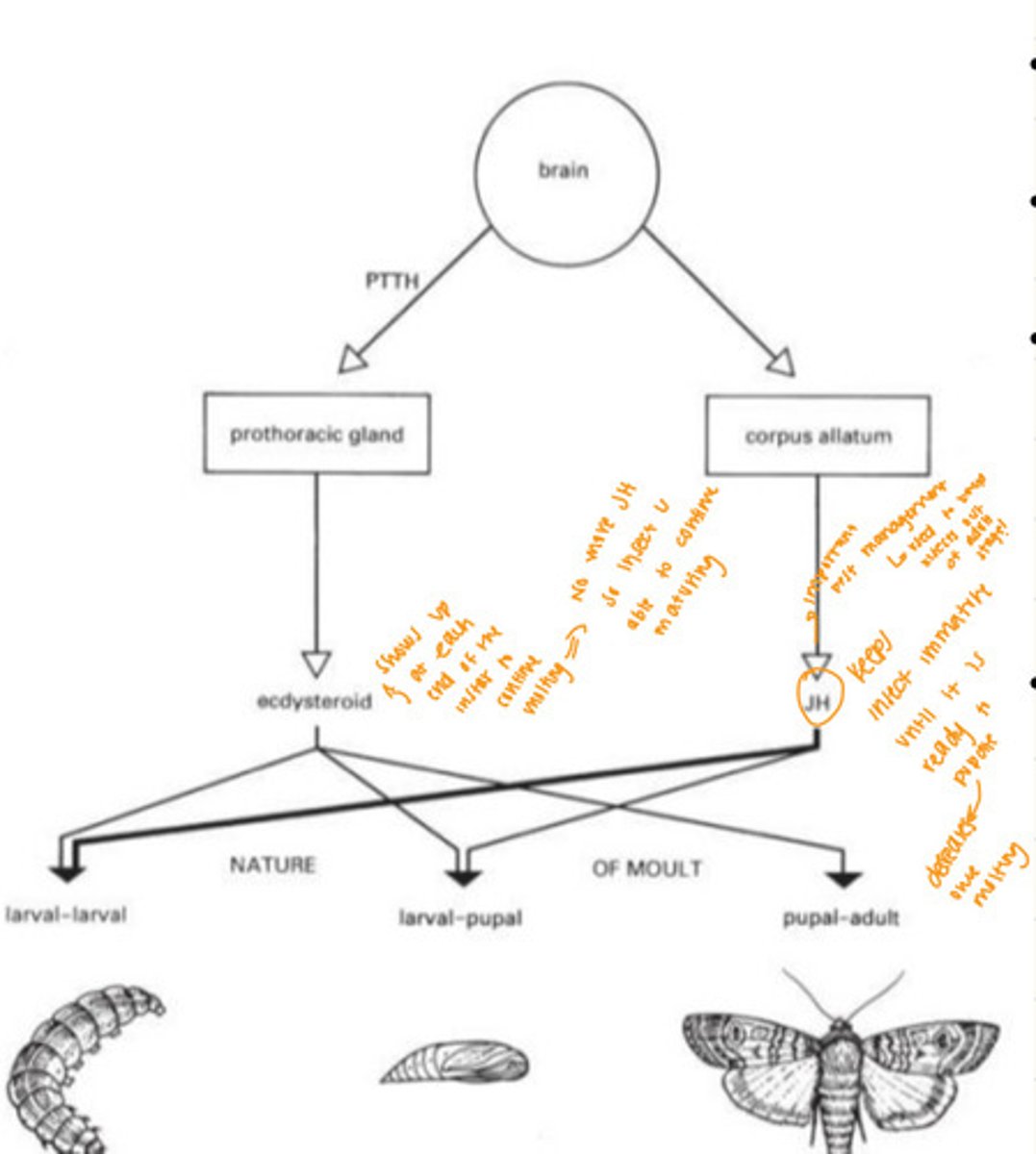
Ecdysteroid Hormone
- Comes from prothoracic gland
- Shows up at each end of the instar to continue molting
- No more JH, so insect is able to continue maturing
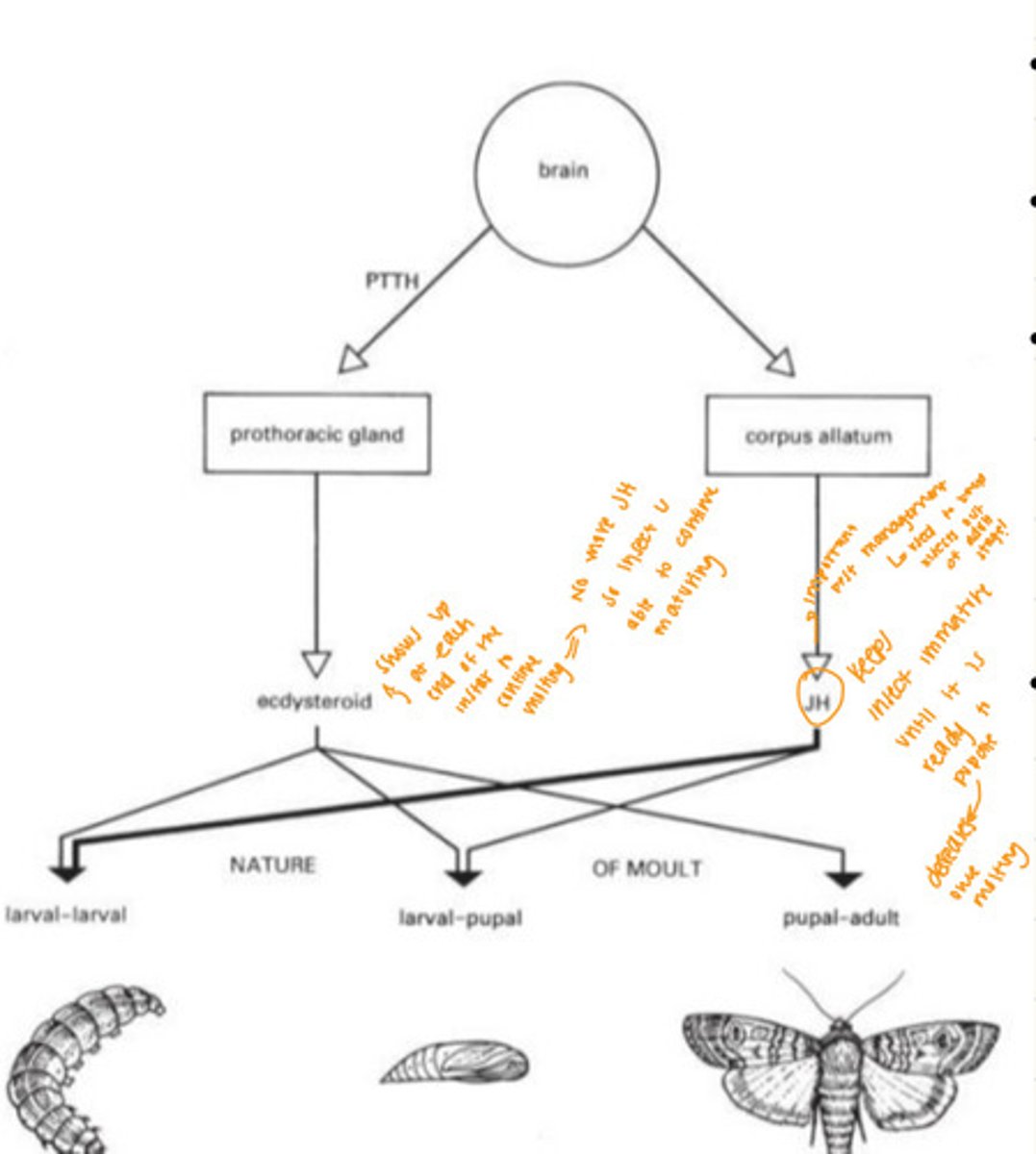
Similar Pattern with Hormones
- See similar pattern in Hemimetabolous insects —> insect molts every time it needs to grow
Voltanism
- Number of generations per year
- Univoltine
- Bivoltine
- Multivoltine
Univoltine
One generation
Bivoltine
Two generations
Multivoltine
Many generations
Dealing with unsuitable environmental conditions
- Quiescence
- Diapause
Quiescence
Slowed development, resumes upon favorable conditions
Diapause
- Slowed development and physiological change, resumes only after proper stimuli
- Aestivation: hot/dry = summer
- Diapause: cold = winter
Major Environmental Cues
- Photoperiod
- Temperature
- Food quality
- Moisture
- pH
- Chemicals: O2, urea, 2 degree plant compounds
Steps to molting according to assignment — Use to study
1. Apolysis: separation of old exoskeleton from epidermis
2. Secretion of inactive molting fluid by epidermis
3. Activation of molting fluid
4. Digestion and absorption of old endocuticle
5. Epidermis secretes new procuticle
6. Ecdysis: shedding of old exoskeleton