S + P Chapter 13
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Touch
mechanical displacement of the skin
determined by receptors in the skin and other internal tissues
touch information travels through the spinal cord
Kinesthesia
perception of the position and movement of our limbs in space
Propriception
perception mediated by kinesthetic and internal receptors
Somatosensation
collectively, sensory signals from the skin, muscles, tendons, joints, and interval receptors
Nociception
pain perception
Interoception
perception of internal organs
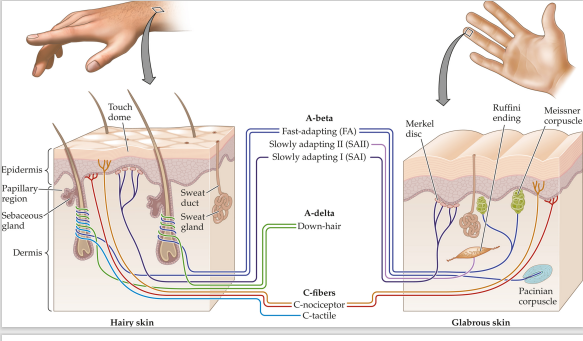
A-beta fibers
wide-diameter, myelineated sensory nerve fibers that transmit signals from mechanical stimulation
A-delta fibers
intermediate-sized, myelinated sensory nerve fibers that transmit pain and temperature signals
C fibers
narrow-diameter, unmyelinated sensory nerve fibers that transmit pain and temperature signals
Layers of the Skin
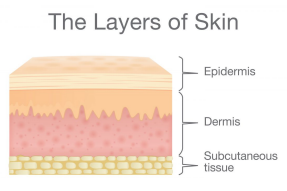
Layers of the Skin
epidermis
dermis
subcutaneous tissue
Each receptor can be categorized by two criteria
size of the receptive field
rate of adaptation
Touch receptors are called
mechanoreceptors, because they respond to mechanical stimulation (pressure, vibration, or movement)
A-beta fibers
wide diameter, myelinated sensory nerve fibers that transmit signals from mechanical stimulation
How many types of mechanoreceptors are there?
Meissner corpuscles
Merkle Cell Neurite Complexes
Pacinian corpuscles
Ruffini Ends
Merkel (SA I)
small receptive field
slow adaptation rate
sustained pressure, very low frequency (<~5 Hz)
coarse texture and pattern
Meissner
small receptive field
fast adaptation rate
temporal changes in skin deformation (~5 - 50 Hz); skin slip
Low-frequency vibration; grasp stability
Ruffini
large receptive field
slow adaptation rate
sustained downward pressure; lateral skin stretch (~ 5 - 50 Hz)
finger position
Pacinian
large receptive field
fast adaptation rate
temporal changes in skin deformation ( ~50 - 700 Hz)
high frequency vibration; fine texture
Diagram
Kinesthetic Receptors
mechanoreceptors in muscles, tendons, and joints
play an important role in sense of where limbs are, what kinds of movements
Muscle Spindle
sensory receptor located in a muscle that senses its tension
receptors in tendons signal tension in muscles attached to tendons
receptors in joints react when joint bent to an extreme angle
Thermoreceptors
signal information about changes in skin temp
two distinct populations of thermoreceptors: warmth fibers, cold fibers
C fibers (unmyelinated) and A-delta fibers (myelinated)
Response Rate of Thermoreceptors
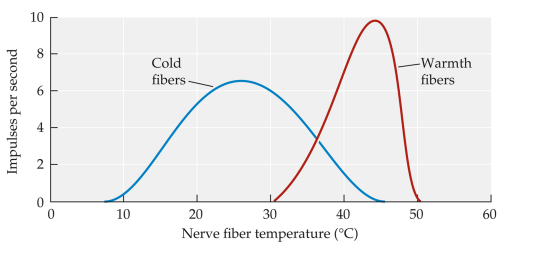
Thermoreceptors (2 of 2)
body is constantly regulating internal temperature
thermoreceptors respond when you make contact with an object warmer or colder than your skin
Nociception Pain
determine perception of pain
sensory receptors that transmit information about noxious stimulation that causes damage or potential damage to skin
A-delta fibers (nociceptors)
intermediate-sized, myelinated sensory nerve fibers that transmit pain and temperature signals
C fibers (nociceptors)
Narrow-diameter, unmyelinated sensory nerve fibers that transmit pain and temperature signals
Two stages of pain processing (receptor level)
quick and sharp
dull throbbing
difference in pain quality is due to
Labeled Lines
a theory of sensory coding in which each nerve fibers carries a particular stimulus quality
Dorsal Horn
axons from tactile fibers enter the spinal cord in the dorsal horn
organized into multiple layers, or laminae
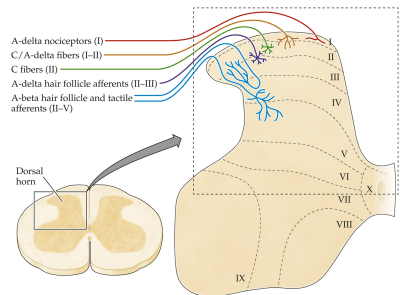
Somatopical Organization
inputs to spinal cord organized somatotopically—adjacent areas of the skin project to adjacent areas in the spinal cord. (very important)
complex calculations that enrich touch sensations occur in the dorsal horn
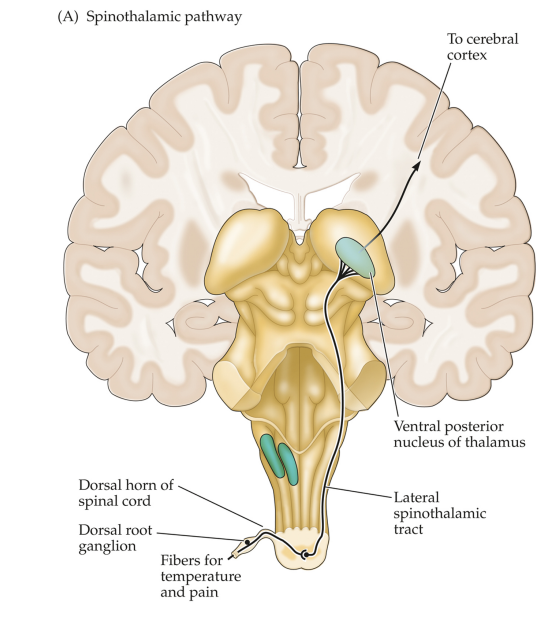
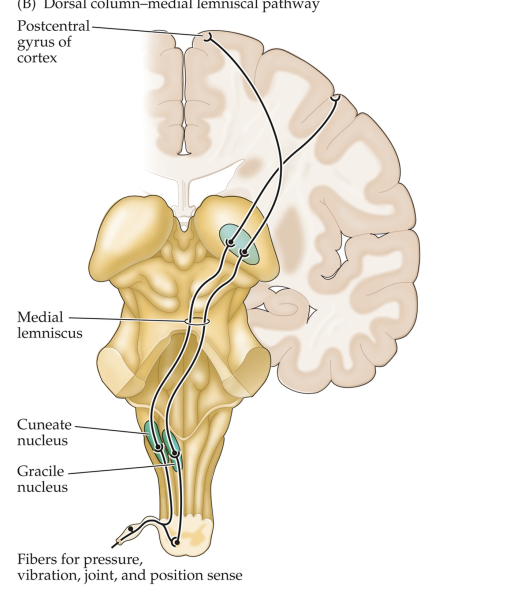
Two pathways to brain
spinothalamic pathway
dorsal column-medial lemniscal DCML
spinothalamic pathway
carries most of the information about skin temperature and pain (slower)
Dorsal column-medial lemniscal (DCML)
carries tactile and kinesthetic information (Faster)
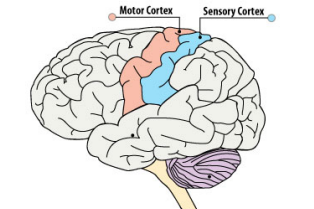
Primary Somatosensory Cortex
S1
Secondary Somatosensory
S2
Sensory Homunculus
maplike representation the amount of somatosensory cortex devoted to each part of the body
Sensorimotor system
motor and somatosensory cortex interact to produce movement
Phantom Limb Pain
neural plasticity
sudden loss of input to somatosensory cortex
other areas will take over
false stimulation = pain
no response = pain
Treating phantom limb pain
some have received transplants from donor cadaver
when successful the somatosensory cortex will rewire to respond to the new hand
other amputees have received prosthetic limbs with biomimetic feedback, which mimics biological signals
in some cases, users feel sensations emanating from the hand
Body image
phantom limb pain represents a disruption in the body image
which is: the impression of our bodies in space
Gate Control Mechanisms
pain information relayed from nociceptors to the substantia gelantinosa of the spinal cord
excitation (nociceptors) and inhibition (neurons in substantia gelantinosa and a-beta fibers)
Analgesia
decreasing pain sensation during conscious experience
can occur thru
stimulation of the gate-control mechanism
release of endogenous opiates
external substances like morphone, heroin, opium
Hyperalgesia
heightened response to normally painful stimulus
nociceptors signal that damage is ongoing, cranking up the pain signal
Tactile Sensitivity
sensitivity to mechanical pressure is known as mechanical touch
How would we measure tactile spatial acuity?
two point threshold
Two pint threshold
lab day
varies across the body, fingers/face/toes show the highest acuity
Haptic perception
knowledge of the wrold that is derived from sensory receptors in skin, muscles, tendons, and joints, usually involving active exploration
receptors in the skin help us maintain grasp
Exploratory procedures
stereotypical hand movement pattern used to contact objects in order to perceive their properties; each exploratory procedure is best for determining one or more object properties
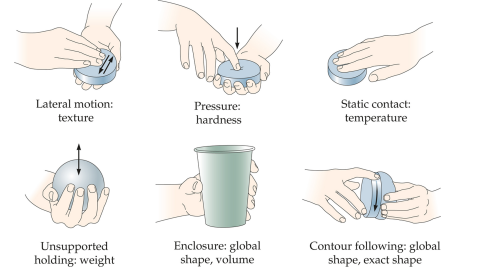
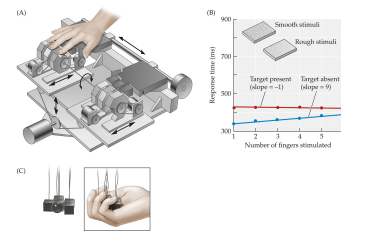
Haptic Search
some material properties “popout” in haptic search tasks
rough among smooth, hard among soft, cool among war, edged surfaces among smooth
horizontal lines among vertical lines