World Issues Unit 1+2 Test
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Mercator Projection
developed in 1569, this projection is still widely used today for navigation, however it is no longer popular in atlases
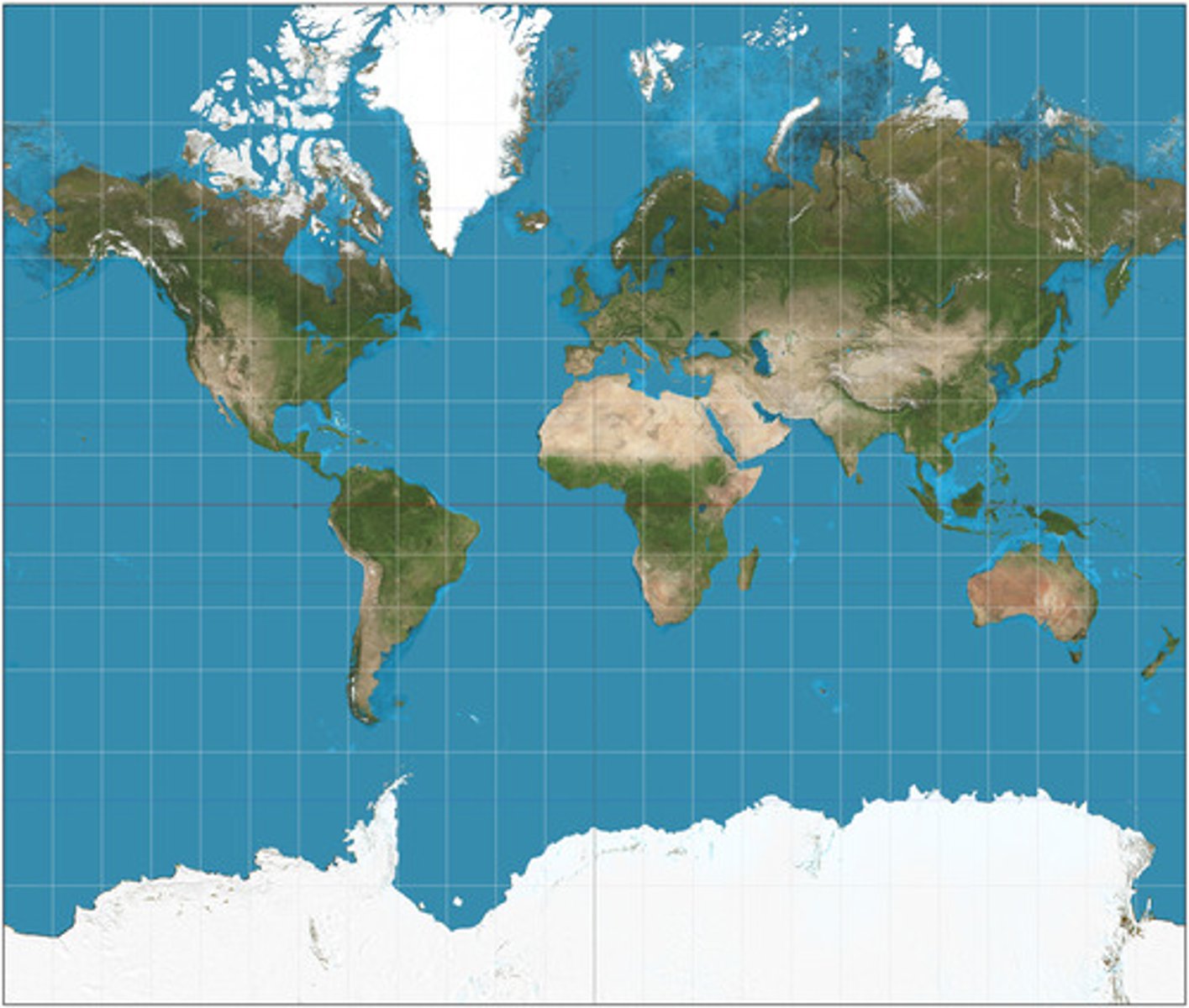
What are the benefits of Mercator Projections?
it preserves compass bearings and distances on maps
What are the problems with Robinson Projections?
minimizes and distorts the shape and size of most regions, particularly bad in the polar regions
What are the problems of Gall Peters Projections?
certain areas appear stretched, horizontally near the poles and vertically near the Equator
Winkel Tripel Projection
developed by __ in 1921. prime meridian and equator are straight lines while all other parallels and meridians are curved
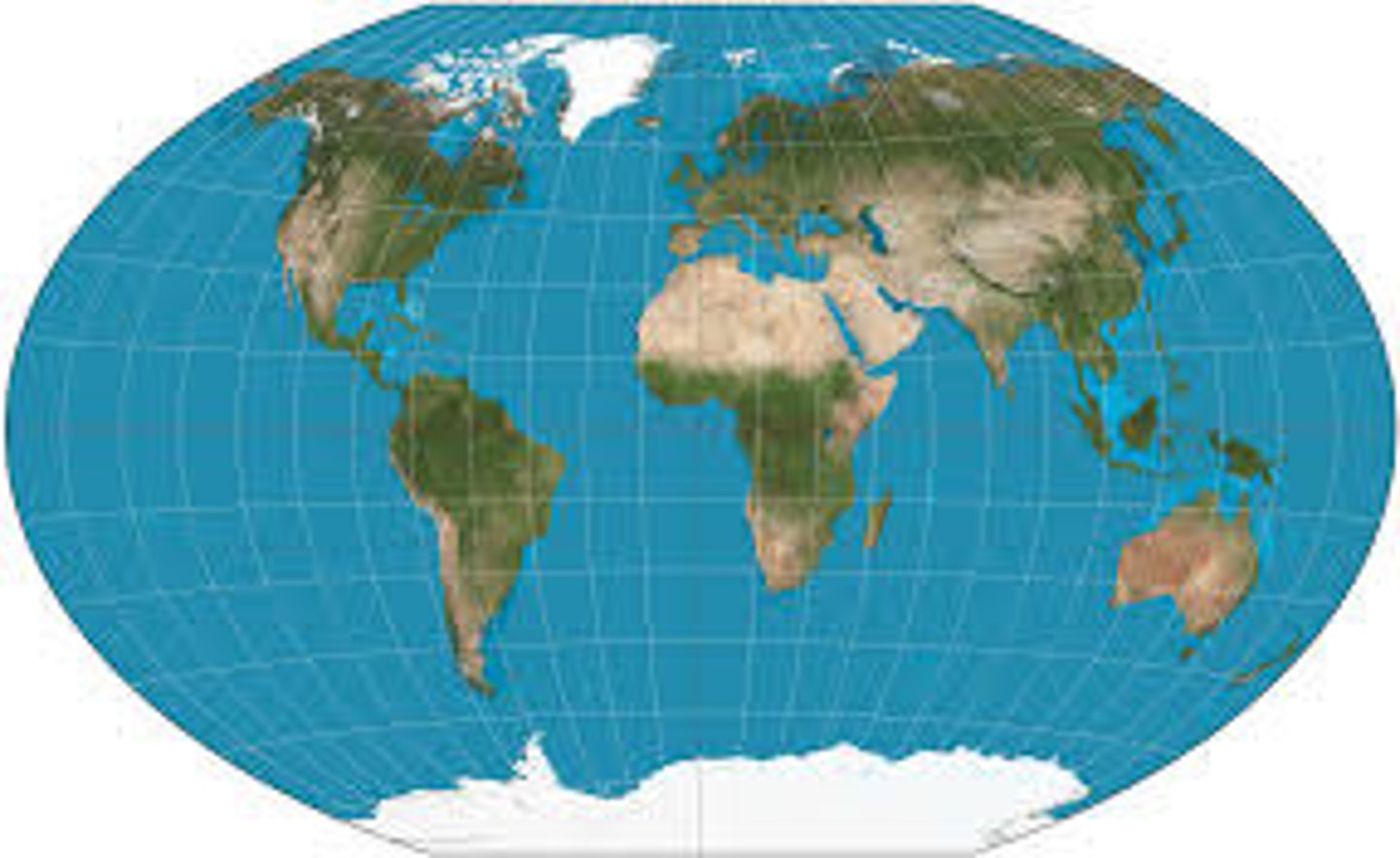
What is good about Winkel Trippel?
Adopted by the National Geographic in 1998 as it better represents the size and shape of Earth features, especially in the polar regions. It preserves compass bearings and distances
What is the problem with map biases?
Distortion - unfair representation of countries
North-South World Classification
- most developed nations in the northern hemisphere, temperate zone
- nations in the southern hemisphere dependent on agriculture (tropical zone)
- exceptions: australia, new zealand, argentina and south africa (economy - partly north and south)
North-South: Environmental determinism
- south = hot, work slower, more breaks, lazy
- north = cooler, variable temperatures led to more determined and driven work ethic, inside inventing
outdated: First world
capitalist, industrialized, democratic, urbanized, north
Second world
communist, command economy, not as developed or urbanized as the first world
Political framework
the focus is on the power and control governments and international organizations have because they design, administer and make judgments, e.g. the sustainable development goals
Social framework
the focus is cultural - the customs, values, and other forms of human endeavour characteristic of a particular community or group within a community, e.g position of women in Iraq
Economic Framework
the focus is financial - the cost of the situation and its remedy or the monetary benefits from its solution, e.g NAFTA trade disputes
Environmental Framework
the focus is the natural environment and the way people interact with that environment either locally or globally, e.g global warming
What are the disadvantages of Mercator Projections?
it distorts shape and sizes of regions (polar regions larger, equatorial regions smaller)
Robinson Projection
developed as a compromise between all of the distortions in an attempt to accurately project the earth onto a map
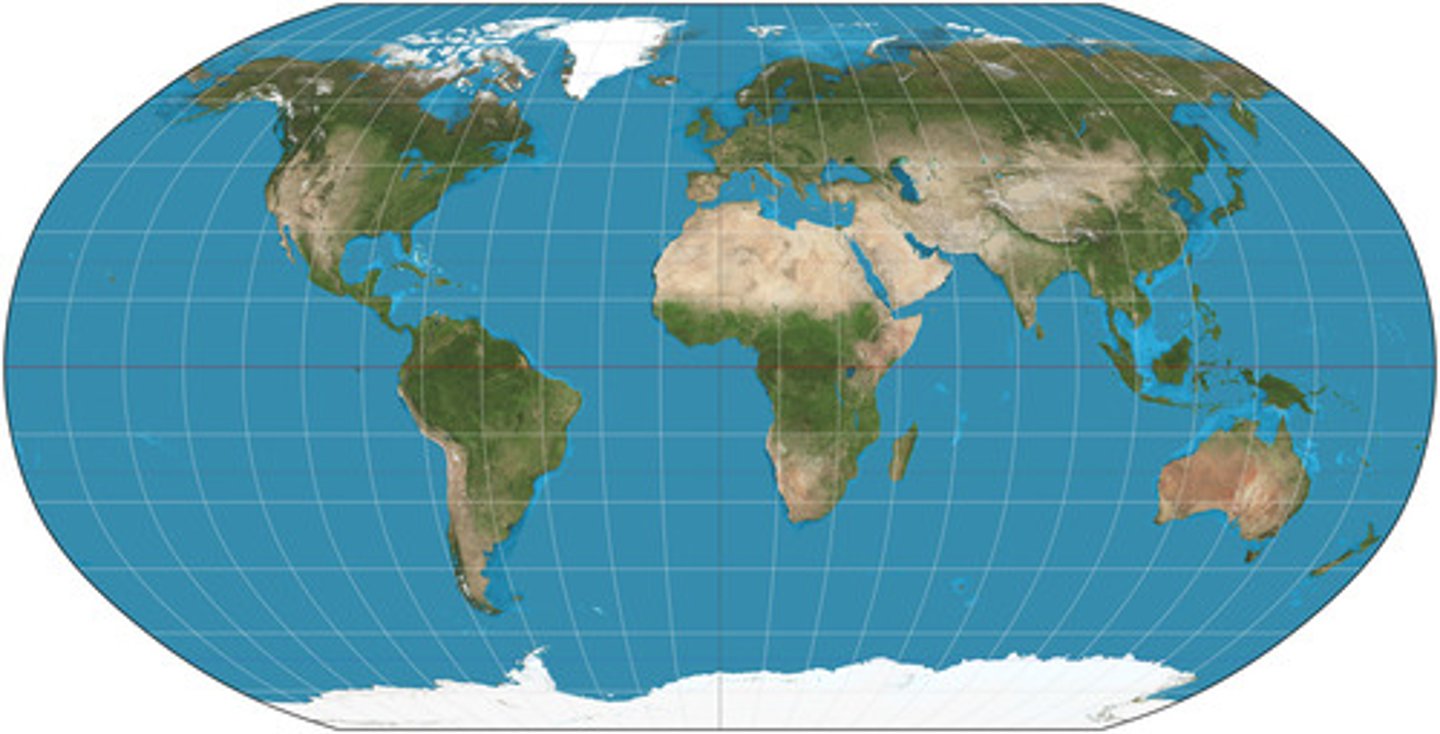
What are the benefits of the Robinson Projection?
size and shapes near the eastern and western edges of the map are accurate
Gall Peters Projections
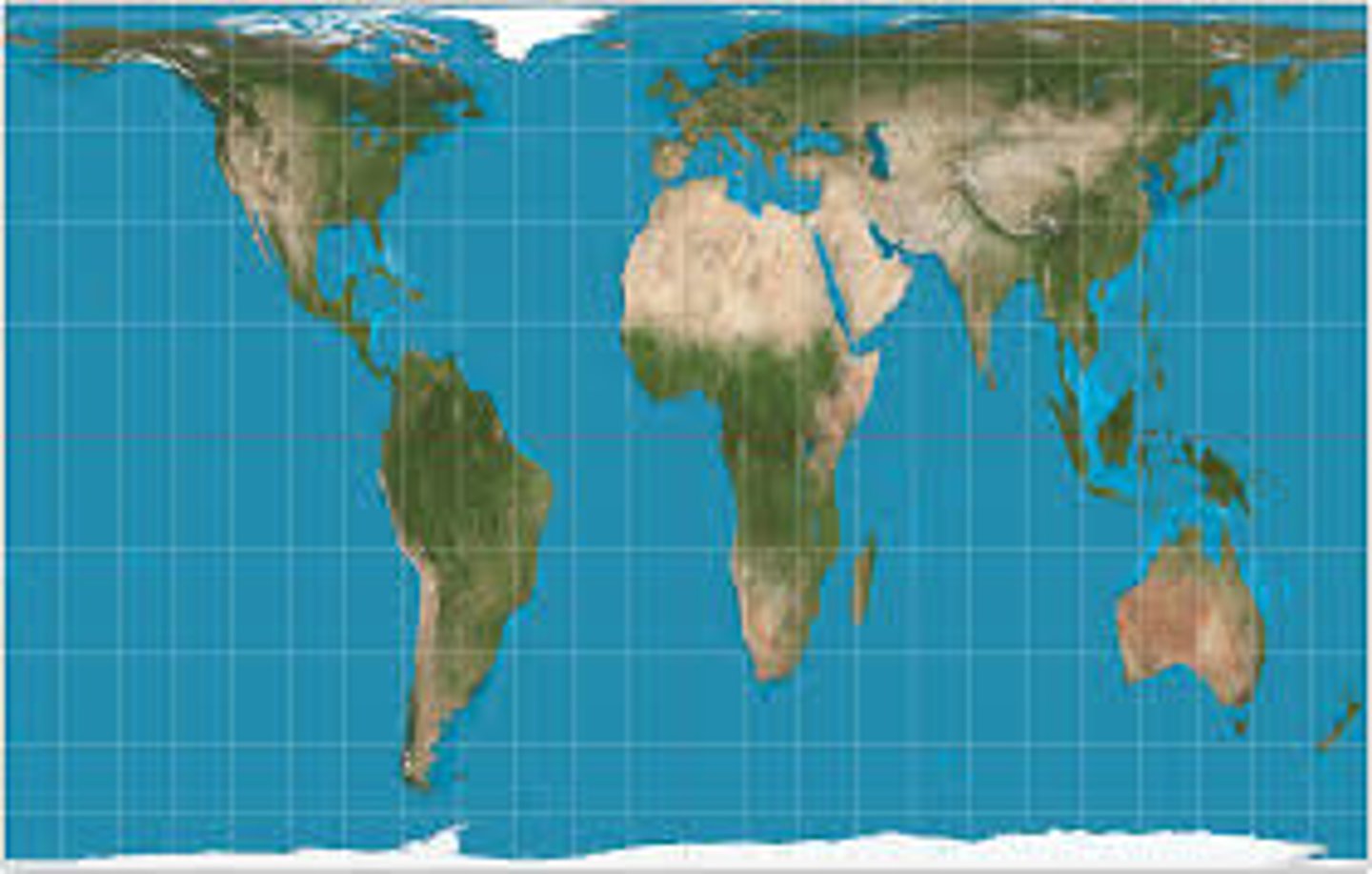
What are the benefits of the Gall Peters Projections?
Accurate with size but not shape. Offers a representation of the nations in their true proportion to one another
third world
- unstable governments (some autocratic, democratic, communist)
- varied and weak economies
- low standard of living
- large percentage of the population engaged in farming
- rural, south
developed countries
- industrialized, stable government, strong economies - free market/mixed
- democratic
- wealthy
- high GDP and GNP
- high standard of living
nearly industrialized countries
moving from developing to developed by expanding their economy from agriculture to industry/manufacturing
increased social freedoms and civil rights
developing countries
economy is based on few products, not industrialized
high % in agriculture.
demographic transition model
used to describe the change from a high birth rate and high death rate demographic patterns to a low birth rate and low death rate pattern
human development index
summary measure of average achievement in key dimensions of human development
focuses on people and their capabilities as criteria for assessing the development of a country
fertility rate
average number of children born to a woman in her lifetime
replacement fertility
the total fertility rate that will result in a stable population. the __ is usually considered to be 2.1 children per woman (2 children born to replace two parents dying - the 0.1 is required to make up for women who choose not to or are unable to have children, or who dies before having children)
population implosion
a dramatic decline in population, the opposite of population explosion
demographic momentum
the phenomenon of continued population increase despite reduced reproductive rates. even in the face of extreme measures aimed at lowering reproductive rates, the population will continue to grow due to a large proportion of its population entering its reproductive years
dependency ratio/load
a demographic measure of the ratio of the number of dependents to the total working-age population in a country or region
dependency ratio formula
# dependents/population aged 15 to 64 x 100
zero population growth
theoretical goal in which the number of people entering a population through birth or immigration is equal to the number of people leaving via death or emigration
population composition
a snapshot of of the demographic profile of a population based on fertility, mortality, and migration rates
malthusian theory
a theory asserting that population is controlled through positive checks (war, famine, disease) and preventive checks (measures to reduce fertility)
carrying capacity
the amount of people that can live in a given area considering the amount of available resources
cornucopian theory
asserts that human ingenuity will rise to the challenge of providing adequate resources for a growing population
crude death rate
number derived from the number of deaths per 1000 people per year
population growth formula
(births + immigration) - (deaths + emigration)
net reproductive rate (r)
r = (births-deaths) / population size)
OECD the better life index
more to life than cold numbers of GDP and economic statistics. this index allows you to compare well-being across countries, based on 11 topics of the __ has identified as essential in the ares of material living conditions and quality of life