Biological Bases of Behaviour in Dentistry
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Sensory Neurons
Transmit information from sensory receptors to the brain (afferent).
Motor Neurons
Transmit commands from the brain to the muscles and glands of the body (efferent).
Interneurons
Interconnect neurons, most common type of neuron.
Neurotransmitters
Chemicals that transmit information from one cell to another.
Presynaptic Cell
The cell that releases neurotransmitters in response to an action potential.
Synaptic Cleft
The space between the presynaptic and postsynaptic cells where neurotransmitters diffuse.
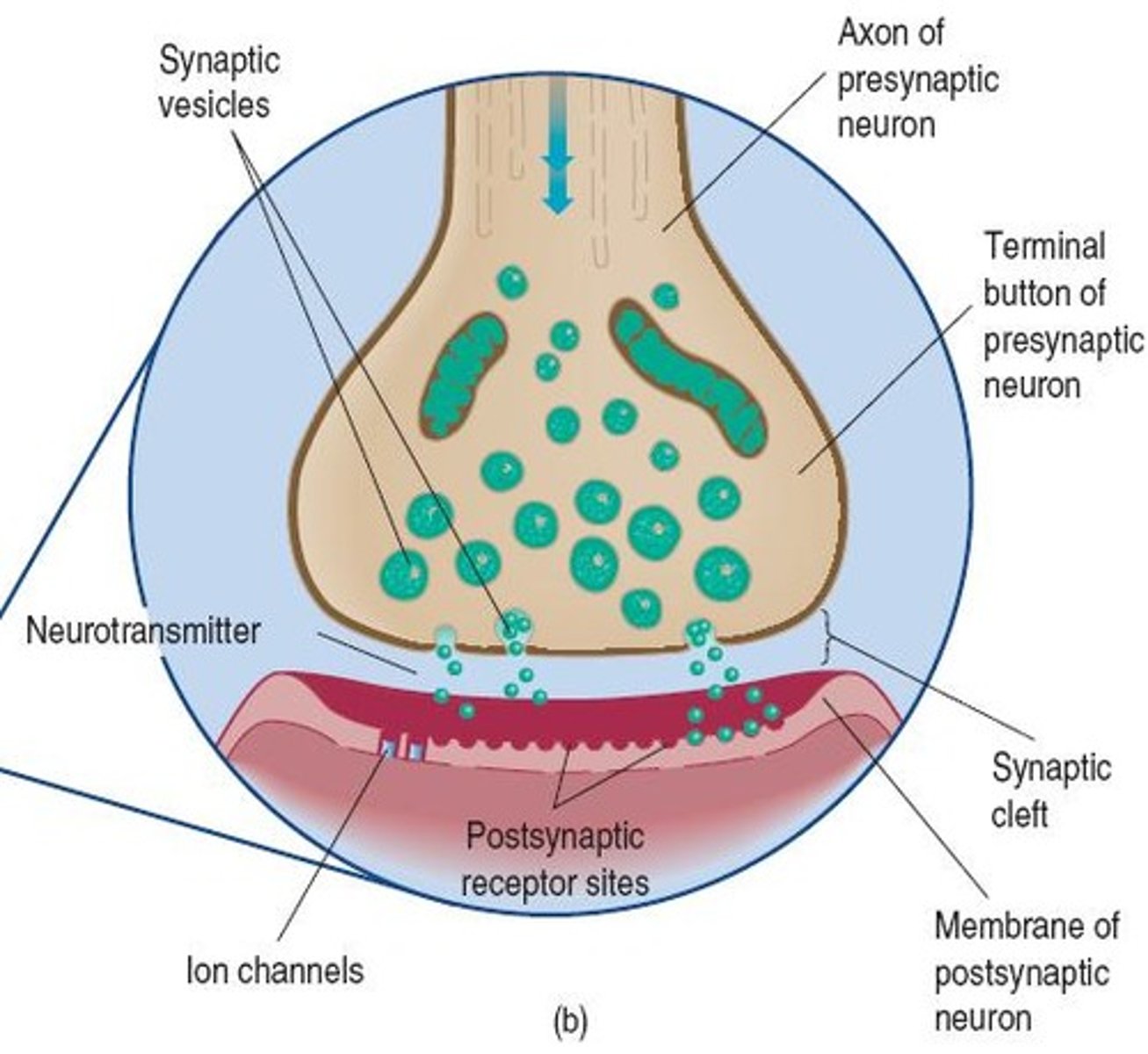
Postsynaptic Receptors
Receptors that bind neurotransmitters and produce a graded potential in the next cell.
Vesicles
Small membrane-bound sacs in the presynaptic cell that store neurotransmitters.
Autonomic nervous system (ANS)
The ANS has two divisions: Sympathetic (Emergency system, typically activated in face of a threat e.g., fight or flight) and Parasympathetic (Vegetative functions e.g., digestion, 'business as normal').
Sympathetic nervous system
Emergency system, typically activated in face of a threat (e.g., fight or flight).
Parasympathetic nervous system
Vegetative functions (e.g., digestion), 'business as normal'.
Cranial nerves
The 12 pairs of cranial nerves are arranged in groups along the longitudinal axis of the brainstem.
Trigeminal Nerve (Cranial Nerve V)
Key role in pain perception (e.g., dental pain, temporomandibular disorders), motor control of mastication muscles, basis for local anesthesia targeting.
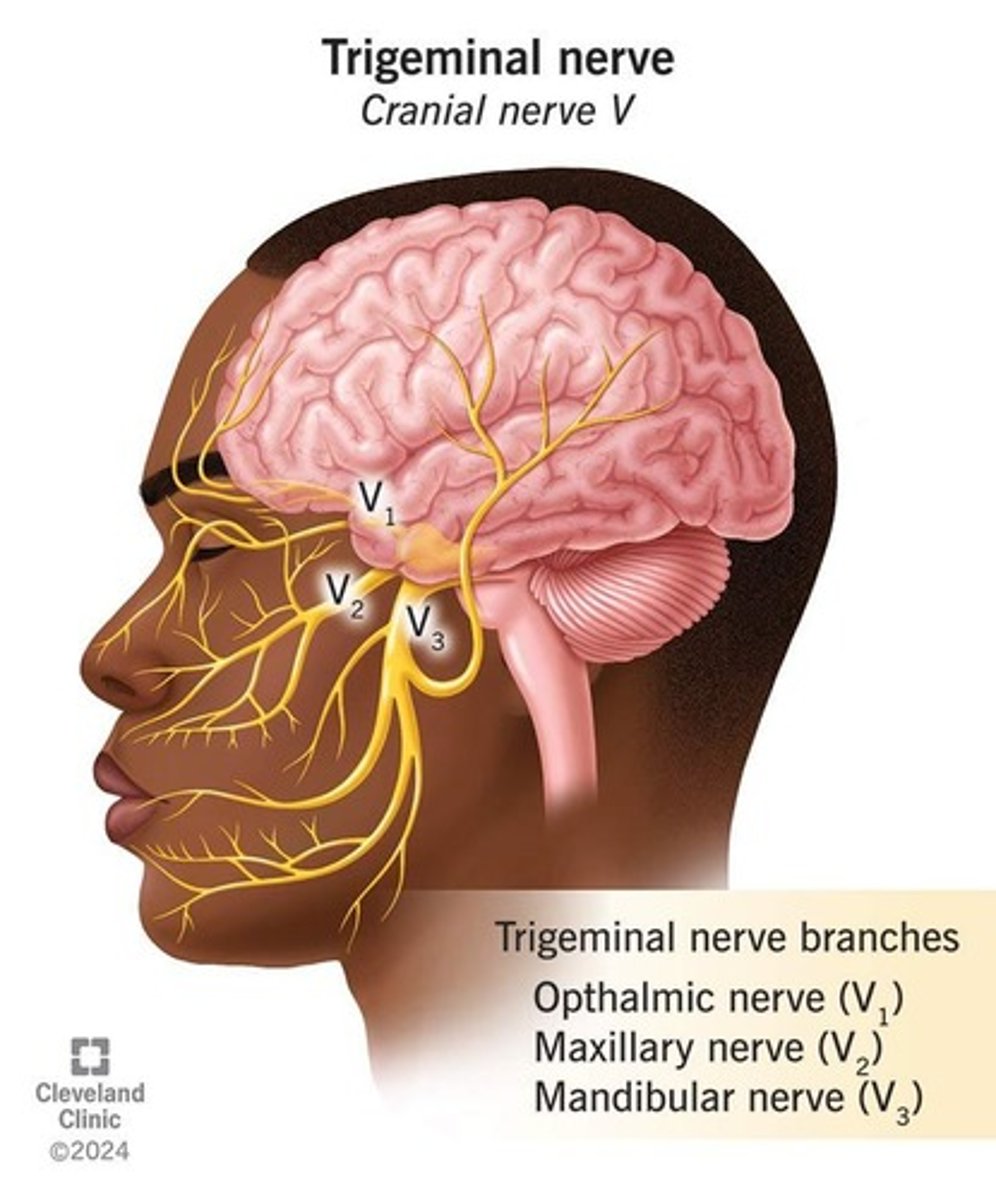
Branches of the Trigeminal Nerve
Ophthalmic, Maxillary, Mandibular.
Central nervous system
The Central nervous system is composed of the brain and spinal cord.
Parts of the brain
Forebrain, Midbrain, Hindbrain.
Medulla Oblongata
Extension of spinal cord that regulates heartbeat, circulation and respiration.
Cerebellum
Involved in movement, learning and sensory discrimination.
Reticular Formation
A network of neurons involved in consciousness and arousal.
Pons
Links Medulla Oblongata and Cerebellum with upper part of brainstem.
Tectum
Involved in orienting to visual and auditory stimuli.
Tegmentum
Involved in movement and arousal, plays an important role in learning to produce behaviours that minimise unpleasant (aversive) consequences and maximise pleasant (rewarding) consequences.
Hypothalamus
Helps regulate eating, sleeping, sexual activity and emotional experiences.
Thalamus
Processes incoming sensory information and transmits it to higher brain areas.
Basal Ganglia
Involved in the control of movement and also plays a part in 'automatic' responses and judgements.
Limbic System
Involved in pleasure, relief from pain, emotionally-significant learning.
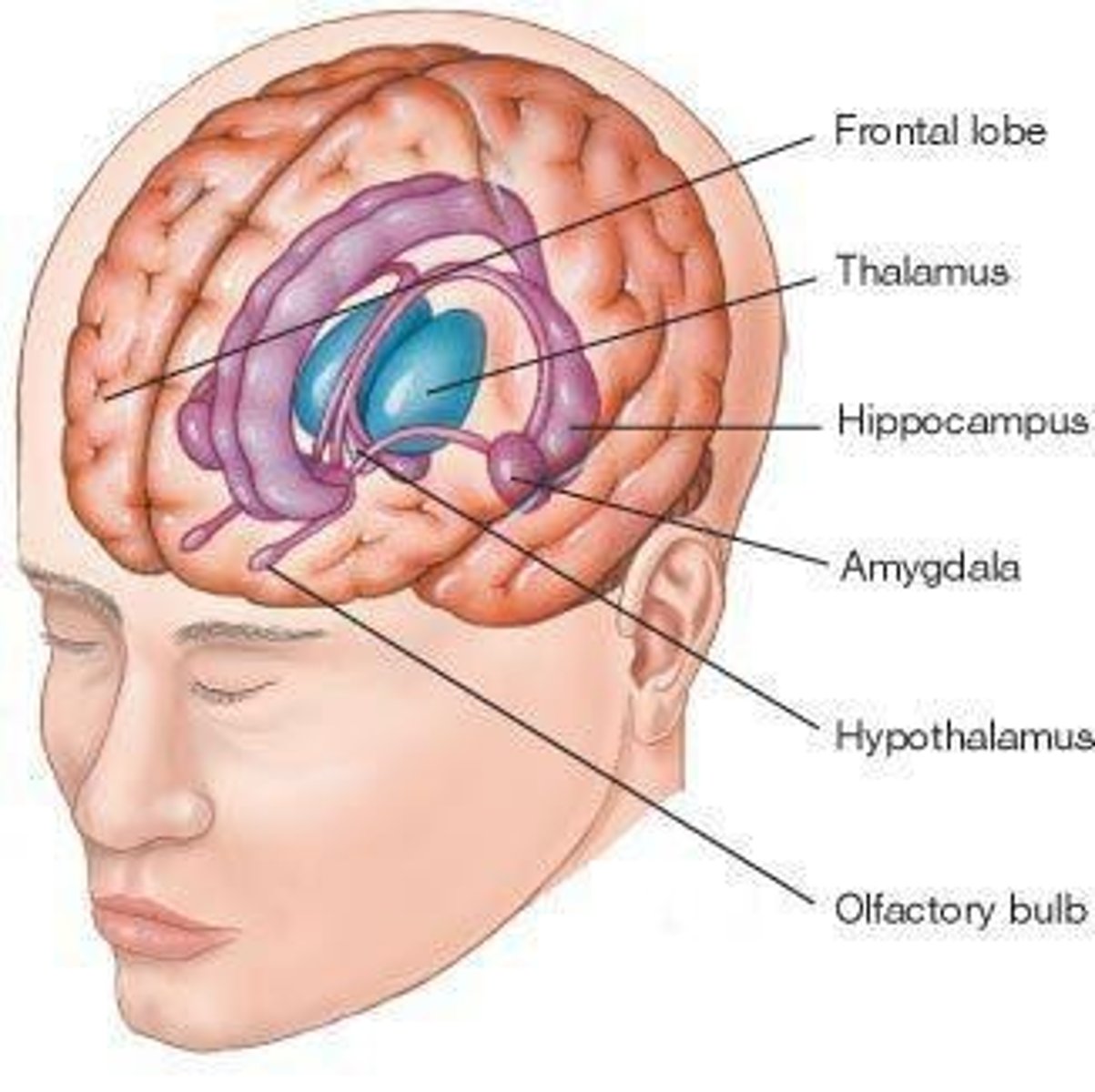
Amygdala
Involved in learning and remembering emotionally significant events, and recognition of fear.
Hippocampus
Involved in the storage of new memories.
Amygdala Activation
Triggers the fight-or-flight response in patients.
Fear of Pain
Anxiety related to the anticipation of pain, needles, or loss of control during dental procedures.
Limbic System
Comprises the amygdala and prefrontal cortex, processes fear and regulates emotional responses.
Hippocampus
Stores past traumatic dental experiences, making the amygdala hyperactive during future visits.
Prefrontal Cortex
Regulates fear and can help patients reframe their dental experiences through relaxation techniques.
Cerebral Cortex
Part of the brain that provides flexible control of movement patterns and complex sensory discrimination.
Frontal Lobes
Responsible for coordinating movement, attention, planning, social skills, abstract thinking, memory, and personality.
Temporal Lobes
Important for hearing, language, object recognition, and memory.
Parietal Lobes
Involved in sensation, perception of movement, and location of objects in space.
Occipital Lobes
Specialized for vision and visual recognition.
Primary Somatosensory Cortex
Processes touch, pain, temperature, and pressure sensations, relevant for detecting oral and facial pain.
Primary Motor Cortex
Controls voluntary muscle movements, regulating chewing, biting, and swallowing.
Prefrontal Cortex Function
Involves decision-making, problem-solving, pain perception regulation, and emotional control.
Limbic System Function
Explains dental phobia and anxiety, influencing future responses to dental visits.
Temporal Lobe Function
Processes hearing and language, and stores memories relevant to past dental experiences.
Parietal Association Cortex
Integrates sensory inputs to create body awareness, allowing accurate perception of dental pain.
Cerebral Cortex
The part of the brain that governs decision-making, problem-solving, and motivation.
Prefrontal Cortex
Encourages rational thinking, allowing patients to make informed decisions about oral hygiene and treatment.
Frontal Lobes
Involved in personality, as evidenced by the case of Phineas Gage.
Somatosensory Cortex
Processes dental pain.
Amygdala
Part of the brain that is involved in the emotional response to pain, such as fear and anxiety.
Limbic System
Involved in the emotional response to pain.
Pain Perception
The brain processes pain signals from other parts of the body, including the teeth and oral structures.
Trigeminal Nerve (CN V)
Transmits dental pain.
Motor Cortex
Controls chewing and speech.
Amygdala and Fear Responses
Stores fear responses, making past negative dental experiences increase patient anxiety.
Neurotransmitters
Chemicals like serotonin, dopamine, and endorphins that influence pain tolerance and stress levels.
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
Regulates involuntary bodily functions; includes sympathetic (fight-or-flight) and parasympathetic (relaxation) systems.