physio- thyroid hormones
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
TRH (thyrotropin releasing hormone)
what does the hypothalamus release to the anterior pituitary in order to stimulate the thyroid gland?
TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone)
what does the anterior pituitary release to the thyroid gland stimulate the production of hormones?
TRH (thyrotropin releasing hormone)
what is 1?
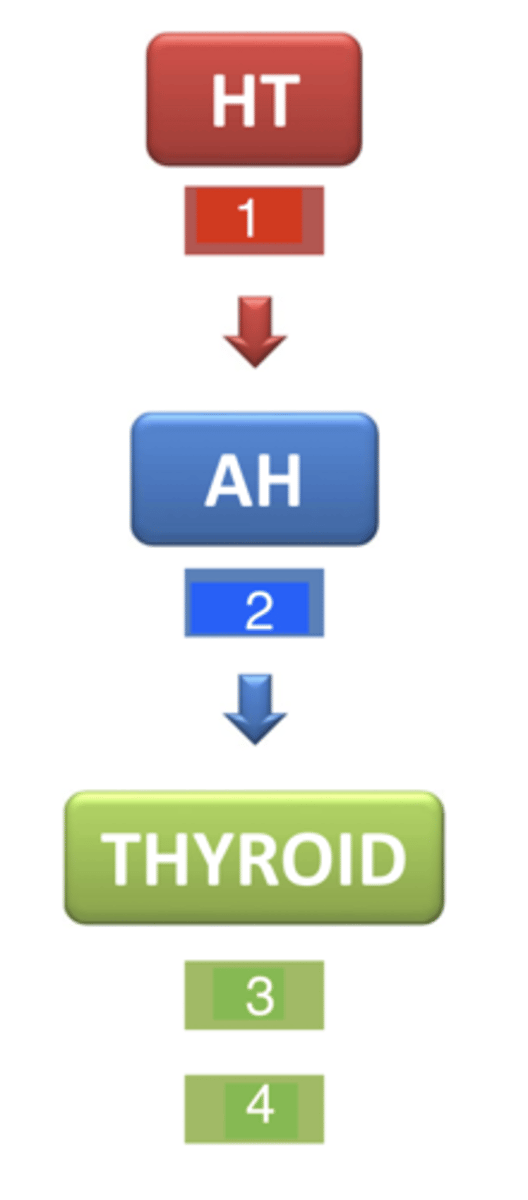
TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone)
what is 2?
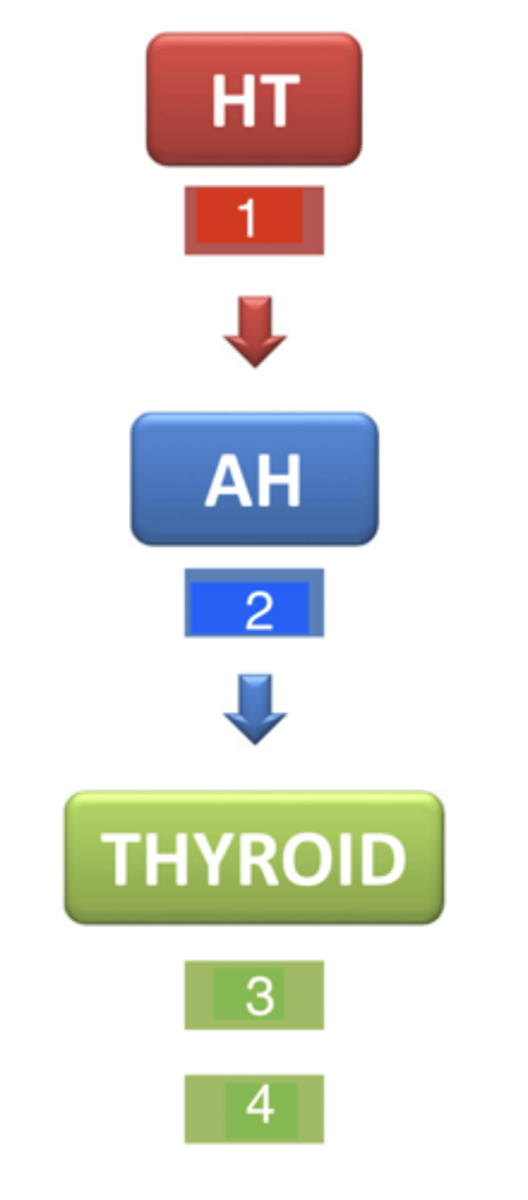
T3 and T4
what are 3 and 4?
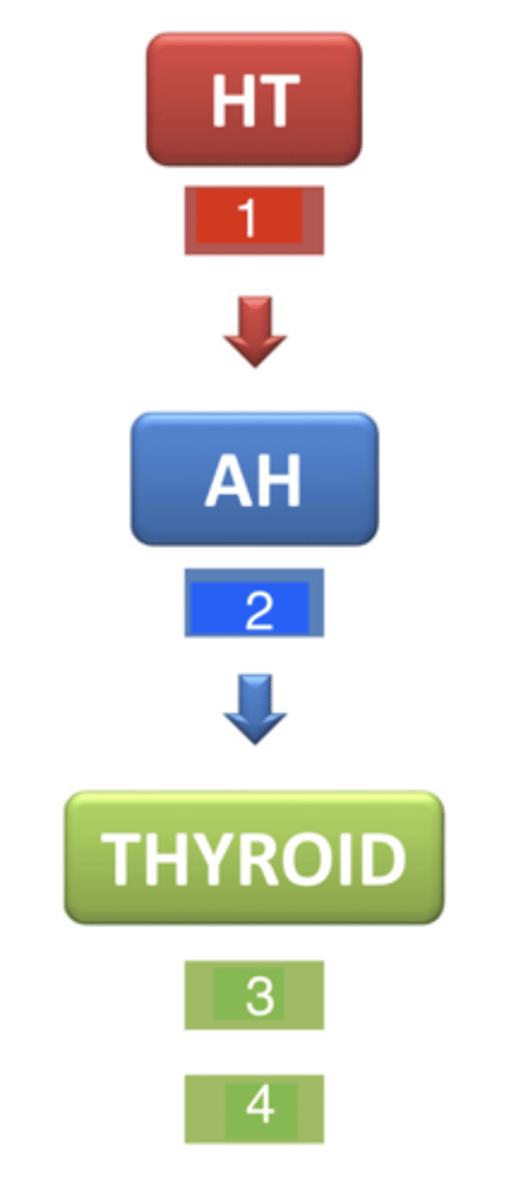
next to the trachea
where is the thyroid gland located?
follicle cells
what part of the thyroid gland produces thyroglobulin (Tg)?
thyroglobulin (Tg)
what do the follicle cells in the thyroid gland produce?
triiodothyronine (T3)
tetraiodothyronine (T4)
calcitonin
what are the 3 hormones released by the thyroid gland?
tyrosine
T3 and T4 are derived from the modification of _____
amine hormones
what type of hormones are thyroid hormones (T3, T4, calcitonin)?
liposoluble
are thyroid hormones hydrosoluble or liposoluble?
hours
how long is the half life of thyroid hormones?
follicular cells
what cells in the thyroid gland synthesize, store, and release T3 and T4?
parafollicular cells
what cells in the thyroid gland synthesize, store, and release calcitonin?
with TBG (type of binding proteins)
also can be transported with albumin and prealbumin
how are thyroid hormones transported in the plasma?
metabolic regulation
thyroid hormones contribute to the __________ of all tissues during development
inside of the cell- on the nucleus (because they are liposoluble)
where are the receptors for thyroid hormones (on cell membrane or inside of the cell)?
T4
which, T3 or T4 is secreted more?
T4
which, T3 or T4, acts as a circulating prohormone?
T3
which, T3 or T4, exerts almost all hormonal activity in target cells?
tyrosine, iodine
what are the 2 molecules necessary for the synthesis of T3 and T4?
1. collection and concentration of iodide in thyroid gland
2. oxidation and incorporation of iodine to phenol ring of tyrosine
3. coupling of 2 molecule of iodine-tyrosine to form T3 or T4
what are the 3 steps in the synthesis of thyroid hormones?
thyroid cells capture iodide (first step of synthesis)
what is occurring here?

1. the iodide is oxidized to iodine by an enzyme
2. the cells synthesize thyroglobulin
3. iodine is added to thyroglobulin (specifically, the tyrosine residues of the thyroglobulin)
explain what is happening here, in the process of synthesizing thyroid hormones
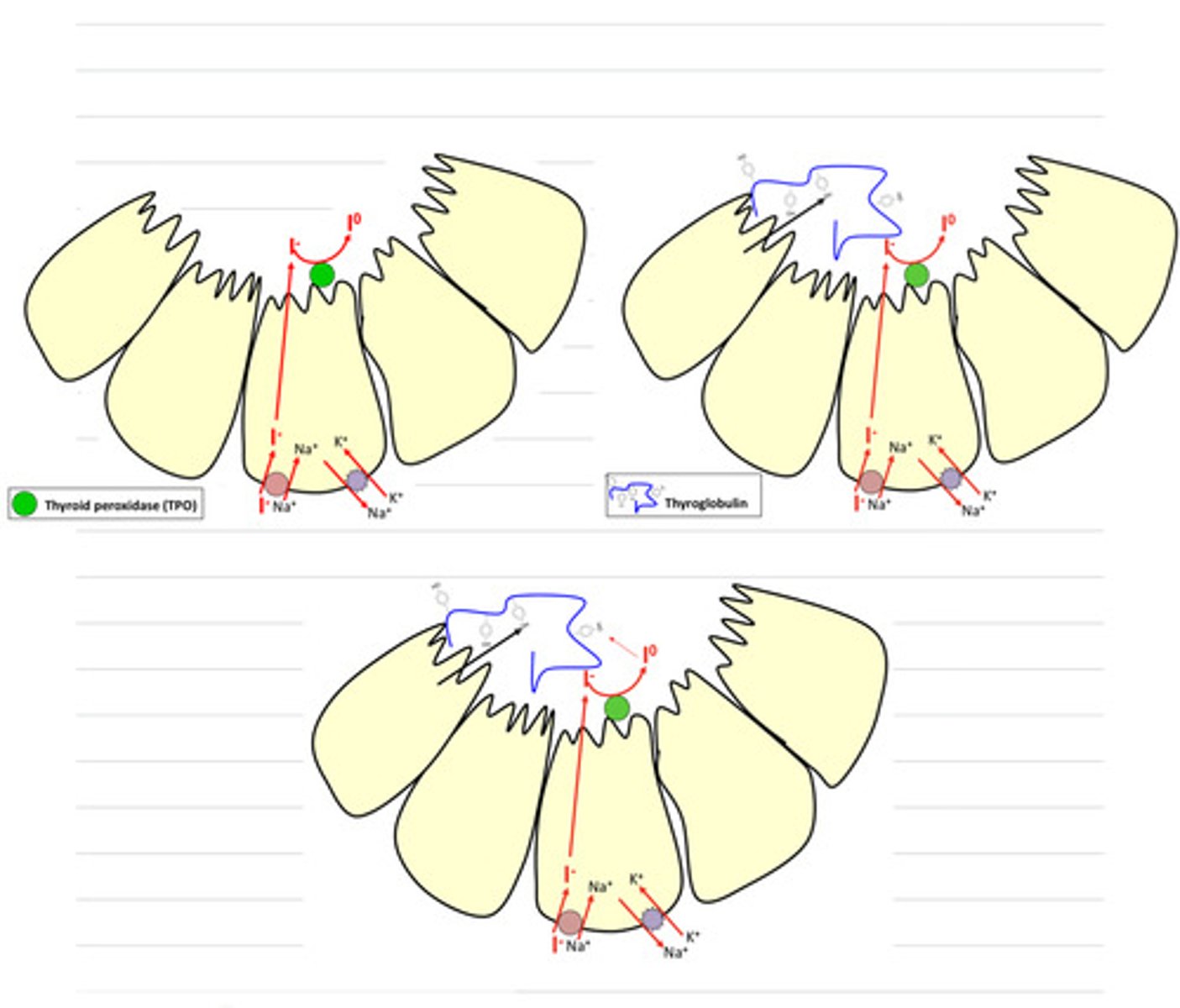
it is oxidized, turning into iodine, and then added to the tyrosine residues of the thyroglobulin
in the synthesis of thyroid hormones, what happens to the iodide after it is captured by the follicular cells?
1 or 2
1- monoiodidotyrosine
2- diiodidotyrosine
how many iodines can be added to a tyrosine residue?
the tyrosine residues are linked together, making couples
in the synthesis of thyroid hormones, what happens after the iodine is added to the tyrosine residues of thyroglobulin?
iodine is added to the tyrosine residues of thyroglobulin
what step of thyroid hormone synthesis is this?
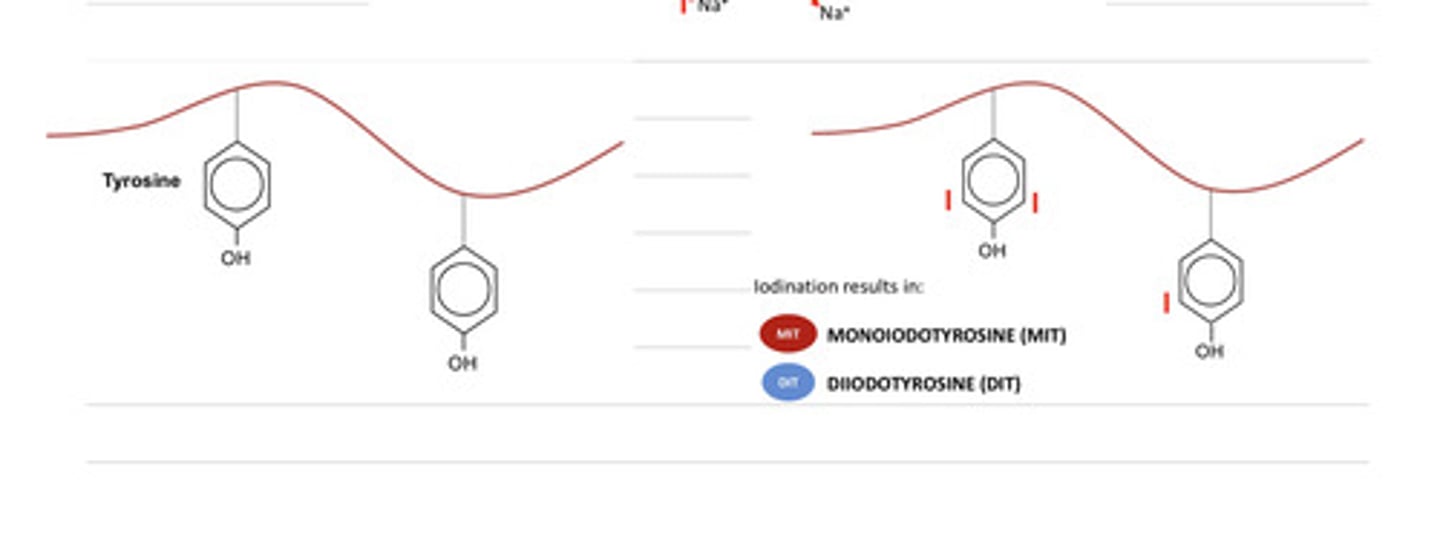
(after the iodine is added) the tyrosine residues are linked together, making couples
in the synthesis of thyroid hormones, what is occurring here?
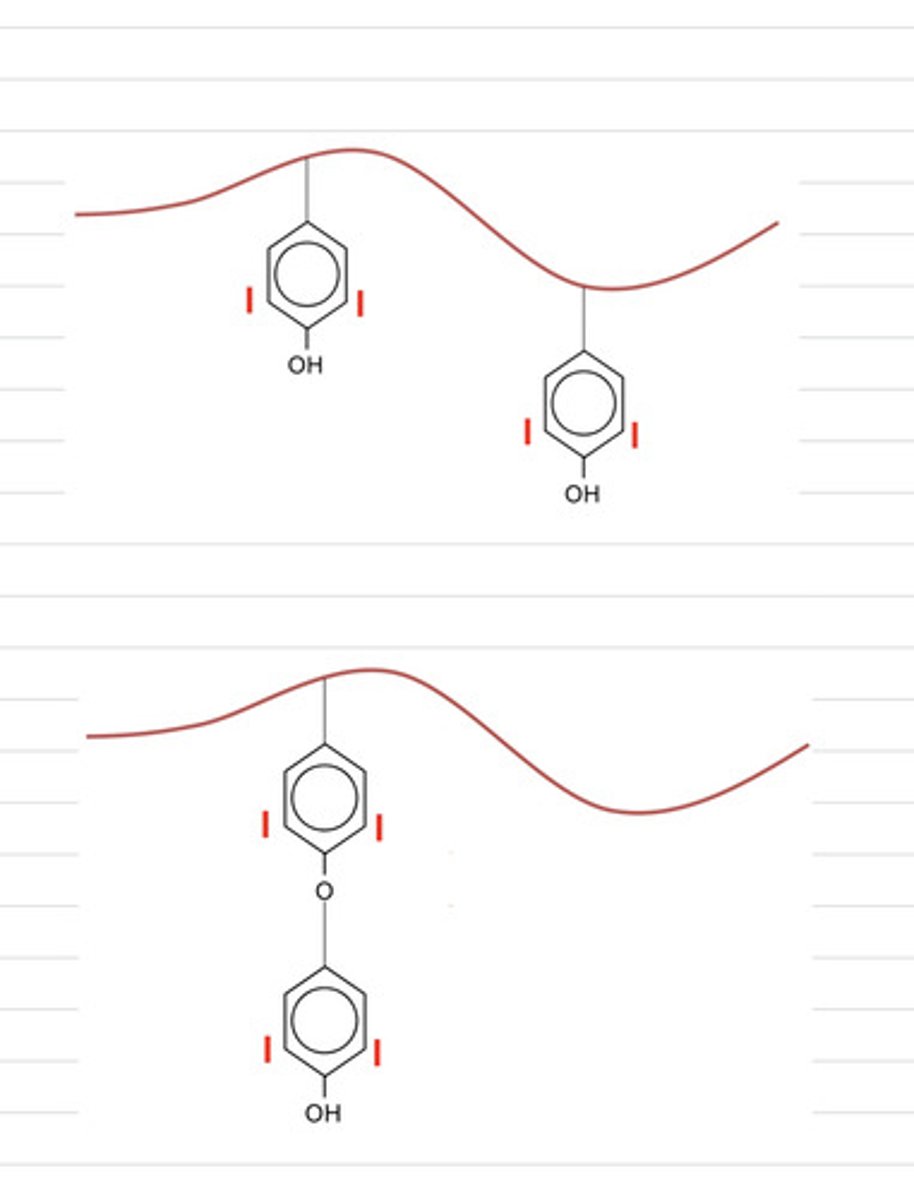
hydrosoluble
are the immature coupled tyrosines hydrosoluble or liposolible?
secretion-
first, cells take up portions of thyroglobulin, and then once the protein is ruptured (hydrolized) because of TSH from the anterior pituitary, T3 and T4 become liposoluble and are released
in the synthesis of thyroid hormones, after the coupling of tyrosine, what occurs?
TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone)
what signals trigger the hydrolization of thyroglobulin, which ultimately causes the maturation of T3/T4?
it triggers the hydrolization of thyroglobulin, which causes the maturation of T3/T4- making them liposoluble and able to leave the cell
what exactly is the mechanism of TSH to the thyroid gland?
T3
(T4 has to convert into T3 before going to the nucleus)
which, T3 or T4, can go directly to the nucleus of the target cell?
deiodinase (it removes an iodine)
what enzyme converts T4 into T3?
gene expression is modified
once T3 is bound to the nucleus of the target cell, what is the result?
increased cell metabolism, increasing production of energy
what is the general effect of T3 and T4?
TBG (thyroid binding globulin)
prealbumin
albumin
what are the binding proteins that allow thyroid hormones to be transported in plasma?
less than 1%
what % of thyroid hormone circulates freely(before binding to a transporter)
T4
which, T3 or T4, has more affinity for binding proteins?
T4- because it is protected by TBG
which, T3 or T4, has a longer half-life?
T4
which, T3 or T4, is synthesized more?
T3- because it binds better to the receptors
which, T3 or T4, has more activity?
the free hormone (without binding protein)
what is the active form of the thyroid hormone?
TBG
which of the binding proteins, TBG, prealbumin, or albumin, is least concentrated in the blood (least amount)?
TBG
which of the binding proteins, TBG, prealbumin, or albumin, has the most binding strength?
albumin
which of the binding proteins, TBG, prealbumin, or albumin, has the weakest binding strength?
albumin
which of the binding proteins, TBG, prealbumin, or albumin, is the most concentrated in plasma (most amount)?
no
is there a large concentration of TBG in the blood?
bound to a transport protein (TBG, pre-albumin, albumin)
when the thyroid hormone is _______, it is inactive
liver and kidneys
where does deiodination of T4 (to convert it into T3) take place in the body?
reverse T3
when T4 is converted to T3, an equal amount of ______ is also formed
a form of T3 that does not work, made when metabolism does not need increasing
what is reverse T3, and why is it made?
short stature and mental deficits (cretinism)
the lack of thyroid hormones during development causes...
increases and stimulates it
what do thyroid hormones do to metabolism?
nervous system tissues
thyroid hormones are essential for the normal growth of tissues, especially __________
growth hormone and prolactin
thyroid hormones are necessary for the production and secretion of what other 2 hormones?
increases their glucose reabsorption
what effect do thyroid hormones have on intestines?
increase
what effect do thyroid hormones have on ATP production?
increases its production of adrenaline and noradrenaline
what effect do thyroid hormones have on the adrenal medulla?
increase
do thyroid hormones increase or decrease the production of adrenaline and noradrenaline?
increases protein degradation
what effect do thyroid hormones have on proteins?
catabolic effect- increases breakdown of glycogen into glucose to use for energy
what effect do thyroid hormones have on carbohydrates?
T3 increases the number of Na/K+ ATPase pumps, which increases ATP consumption
what effect do thyroid hormones have on the Na/K+ ATPase pumps?
makes the mitochondria produce more ATP- making more energy and heat
what effect do thyroid hormones have on mitochondria?
kidneys, liver, skeletal muscle
where are thyroid hormones degraded?
it decreases the production
how does an iodine deficiency effect thyroid hormones?
decrease (negative feedback)
an increase in thyroid hormones has what effect on TSH/TRH production?
hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism
what 2 diseases are associated with thyroid problems?
hypothyroidism
which, hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism is more common in dogs?
LOW metabolism
this causes:
less heat production
laziness, lethargy
skin issues
decreased appetite but increased weight
nonregenerative anemia
hyperlipidemia
what are the problems caused by hypothyroidism?
swollen thyroid gland
what is goitre?
because metabolism is so low, that the thyroid gland is overstimulated to work better
why does hypothyroidism cause goitre?
the baby will have cretinism, decreased mental and physical growth
what happens if a pregnant animal is hypothyroidic?
hypothyroidism
what disease do these animals have?

hyperthyroidism
what disease do these animals have?

hyperthyroidism
which endocrinopathy related to metabolism is more common in cats?
increased metabolism
this causes-
increased appetite but decreased weight
increased heat production
lots of urination and drinking
increased heartrate and cardiac output
increased red blood cells (erythrocytosis)
decreased/weak muscle
decreased cholesterol levels
nervousness, aggressiveness
what is caused by hyperthyroidism?
because the thyroid gland is working too hard
why does hyperthyroidism cause goitre?
hypothyroidism
which, hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism, causes fatigue and laziness?
hyperthyroidism
which, hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism, causes nervousness and aggressiveness?
hypothyroidism
which, hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism, makes the animal fatter?
hyperthyroidism
which, hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism, makes the animal lose weight?