Polysaccharides: Cellulose and Chitin
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What is cellulose made of?
Cellulose is a complex carbohydrate made of a polymer of β-glucose molecules.
What type of glycosidic linkages are present in cellulose?
β-1,4 glycosidic linkages.
In a cellulose chain, how are adjacent glucose molecules oriented?
Adjacent glucose molecules are rotated 180° relative to each other.
Why don't hydrogen bonds form within the same cellulose chain?
Because hydrogen bonds form between glucose molecules in different chains, not within the same chain.
What structural feature of cellulose provides high tensile strength?
Hydrogen bonds form cross-linkages which hold the chains together.
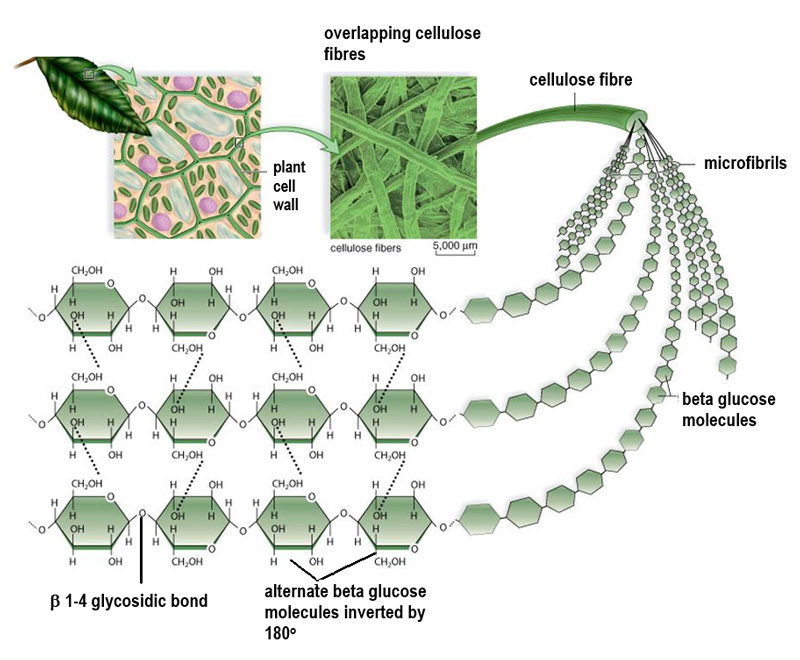
What are the long threads formed by cellulose called?
Microfibrils.
Is cellulose soluble or insoluble?
Cellulose is completely insoluble.
What role does cellulose play in plant cell walls?
Cellulose provides structural support and resistance to osmotic lysis.
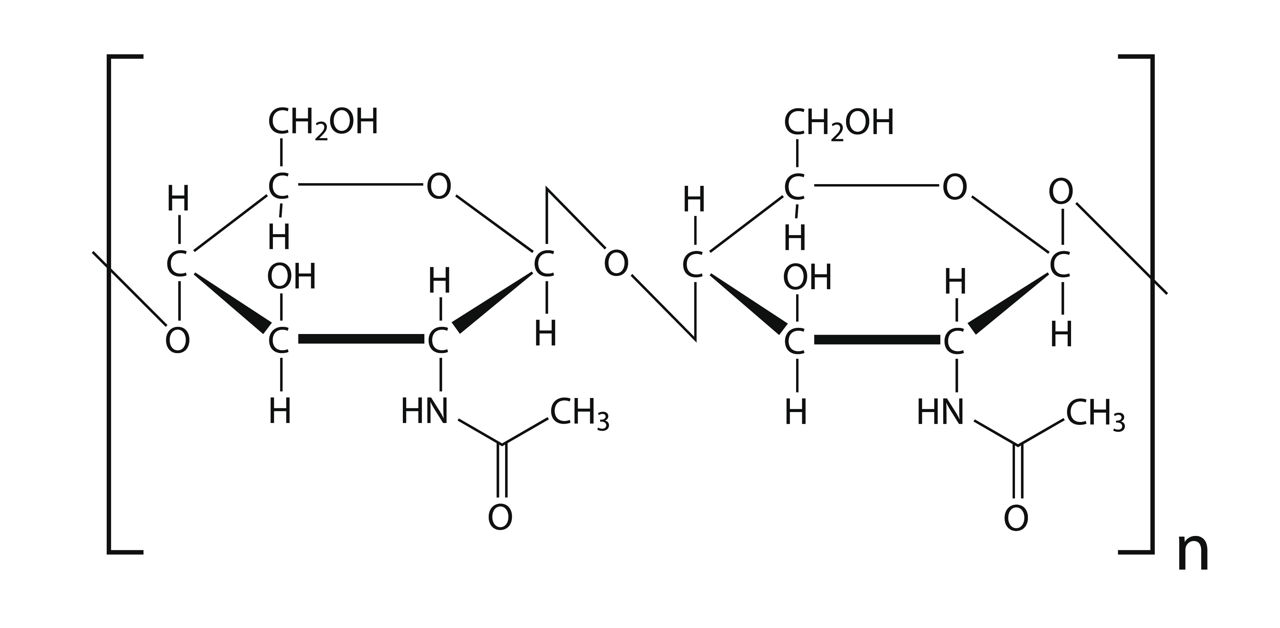
What is chitin and where is it found?
Chitin is found in the cell walls of fungi and in the exoskeletons of insects.
Why is chitin classified as a heteropolysaccharide?
Because it contains the element nitrogen.
What is the relationship between chitin and cellulose?
Chitin has a similar structure and function as cellulose but forms more hydrogen bonds due to nitrogen-containing side groups.
What type of bond joins the monosaccharides in chitin?
β-glycosidic bond.