Tutorial Questions for Management accounting
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Which of the following is not a role for a system of cost and management accounting?
(a) Planning within the organisation.
(b) Information for management decision-making on investment in fixed assets.
(c) Information for shareholder decision-making on when to buy more shares.
(d) Control within the organisation.
(c) It is concerned with internal aspects of management, not information provided directly to shareholders.
Which of the following questions is an example of using management accounting to direct attention?
(a) Who is responsible for achieving this month’s cost reduction?
(b) How do we carry out this activity?
(c) Where are the stocks of good held in store?
(d) What are the strategic aims of the business?
(a)
Which of the following questions is an example of using management accounting to solve problems?
(c)
An architect has asked for a management accountant to help identify the costs of each architectural contract, in order to arrive at the best estimates for contract prices.
What is the best description of the role of management accounting in this case?
(a) Directing attention
(b) Decision-making
(c) Keeping the score
(d) All of the above
(d) There are elements of all three aspects in this case.
Which of the following statements is the best description of strategic management accounting?
(a) Management accountants must have a strategy in preparing cost information.
(b) Management accountants must identify, measure and communicate data on the company relative to data for other similar companies.
(c) Management accountants must know the cost of the enterprise’s strategy.
(d) Management accountants must focus on the strategy of the enterprise and not be distracted by data for other similar companies.
(b)
Which of the following will not use the services of a system of cost and management accounting?
(a) A manager planning an investment in fixed assets for a department.
(b) A director proposing to begin a new marketing activity.
(c) A shareholder making a decision on when to buy more shares.
(d) A supervisor controlling the work of a team of agents
(c) This is an external decision-maker, the rest are internal
Which of the following is the best statement of a control activity?
(a) Measuring and correcting the difference between a stated objective and the
actual outcome of an activity.
(b) Deciding to change supplier so that a cheaper material may be used.
(c) Closing down a profitable production facility because there is insufficient demand.
(d) Preparing a forecast of sales for the month ahead.
(a)
Which of the following describes a fixed cost?
(a) Any overhead cost that is incurred in the factory of a manufacturing company.
(b) Any selling, general or administrative cost incurred in a manufacturing company.
(c) A total cost that remains constant within the relevant range of output.
(d) A total cost which fluctuates with changes in output.
(c)
Which of the following is the best description of a variable cost?
(a) Cannot be estimated with any great degree of accuracy.
(b) Does not change over time.
(c)Varies with the level of activity.
(d) Varies in proportion to the level of fixed cost incurred.
(c)
Which of the following is the best definition of product costs?
(a) Product costs are the costs associated with unsold products retained in stock.
(b) Product costs are those costs associated with goods or services purchased, or produced, for sale to customers.
(c) Product costs are those costs which change with changes in the level of product activity, over a defined period of time.
(d) Product costs are overhead costs which are allocated over a number of products of the business for which costs are to be determined.
( b)
Which of the following is the best definition of product costs?
(a) Product costs are those costs which are directly related to a cost centre in the period in which they are incurred.
(b) Product costs are a measure of the performance of the person responsible for the cost centre.
(c) Product costs are those costs associated with goods or services purchased, or produced, for sale to customers.
(d) Product costs are not affected by changes in the level of activity, over a period of time.
( c)
Which of the following is the best definition of a profit centre?
(a) A profit centre is a unit of the organisation which is required to make a profit.
(b) A profit centre is a unit of the organisation which is operated by the management accounting department.
(c) A profit centre is a unit of the organisation in respect of which a manager is responsible for both revenues and costs under his or her control.
(d) A profit centre is a unit of the organisation in respect of which a manager is responsible for costs under his or her control.
( C)
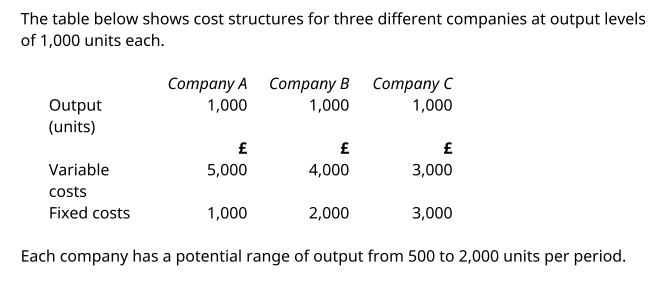
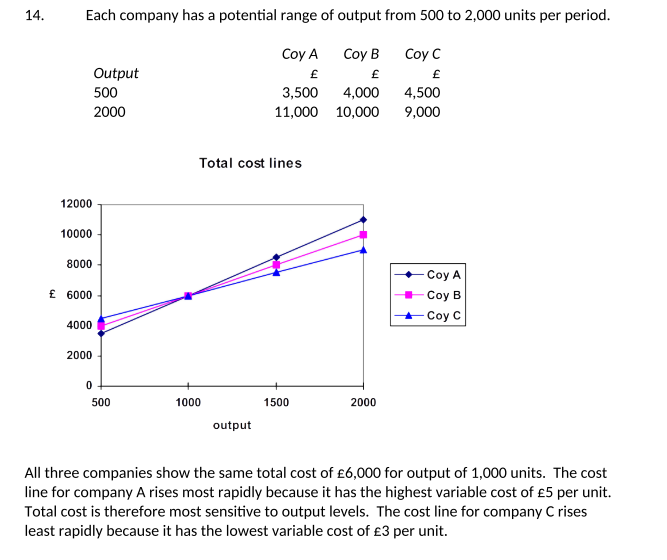
Each company has a potential range of output from 500 to 2,000 units per period.
Required: Draw a graph showing the total cost of each company over the range from 500 to 2,000 units of output and comment on the graph.
All three companies show the same total cost of £6,000 for output of 1,000 units. The cost line for company A rises most rapidly because it has the highest variable cost of £5 per unit.
Total cost is therefore most sensitive to output levels. The cost line for company C rises least rapidly because it has the lowest variable cost of £3 per unit.
Is a Salespersons’ weekly wage a fixed or variable cost and is it a direct or indirect cost with respect to the number of bicycles sold?
-Fixed cost and Indirect cost
Is a Salespersons’ commission a fixed or variable cost and is it a direct or indirect cost with respect to the number of bicycles sold?
-Variable and Direct cost
Is a Pre-sale service and check of each bicycle sold a fixed or variable cost and is it a direct or indirect cost with respect to the number of bicycles sold?
-Variable and Direct cost
Is a officer clerk a fixed or variable cost and is it a direct or indirect cost with respect to the number of bicycles sold?
-Fixed and Indirect cost
Is a shop managers monthly salary a fixed or variable cost and is it a direct or indirect cost with respect to the number of bicycles sold?
-Fixed and Indirect cost
Is a Free Helmet with each bicycle sold a fixed or variable cost and is it a direct or indirect cost with respect to the number of bicycles sold?
-Variable and Direct cost
Is a Shop Cleaners Weekly wage a fixed or variable cost and is it a direct or indirect cost with respect to the number of bicycles sold?
-Fixed and Indirect cost
Is a Weekly advertising in local newspaper a fixed or variable cost and is it a direct or indirect cost with respect to the number of bicycles sold?
-Fixed and Indirect cost
Is a Fire insurance premium for shop a fixed or variable cost and is it a direct or indirect cost with respect to the number of bicycles sold?
-Fixed and Indirect cost
Is theft insurance premium based on estimate in advance of the total value of bicycles to be purchased and sold a direct or indirect cost with respect to the number of bicycles sold?
-Fixed and Indirect cost
Is the cost of purchasing bicycles from supplier a fixed or variable cost and is it a direct or indirect cost with respect to the number of bicycles sold?
-Variable and Direct cost
Is the cost of transporting bicycles from supplier a fixed or variable cost and is it a direct or indirect cost with respect to the number of bicycles sold?
-Variable and indirect cost
Is Purchase of new history textbooks controllable or non-controllable for the history unit cost centre.
-Controllable
Is replacement of history textbooks damaged during teaching time controllable or non-controllable for the history unit cost centre
-Controllable
Is replacement of history textbooks damaged during break in controllable or non-controllable for the history unit cost centre
-Non-controllable
Is Payment of salary to temporary teacher to replace full-time teacher under stress from teaching junior class controllable or non-controllable for the history unit cost centre
Non-Controllable
Is Payment of travel expenses to visiting speaker for senior history class controllable or non-controllable for the history unit cost centre
Controllable
In most companies, direct labour is treated as:
(a) Product cost.
(b) Period cost.
(c) Fixed cost.
(d) Sunk cost.
( a) Product Cost
Which of the following is a direct labour cost?
(a) The wages of an operative paid on the basis of output achieved.
(b) A bonus paid to the storeman.
(c) Costs of the payroll accounting section.
(d) Supervisors' salaries in the factory.
(a) The wages of an operative paid on the basis of output achieved.
Which of the following types of cost would not form part of the prime cost of a product?
(a)The factory overhead costs
(b) The direct labour costs
(c) The direct expense costs
(d) The direct material costs
(a)The factory overhead costs

.
( b)
In Week 2, the budgeted labour hours for normal activity are 10,000 hours. The budgeted fixed cost is £15,000. The fixed overhead cost rate is calculated on the basis of budgeted cost and budgeted normal activity. At the end of the week it is found that 11,000 hours were worked in practice. What is the amount of fixed overhead overapplied or underapplied to jobs in Week 1?
(a) £1,500 overapplied
(b) £1,500 underapplied
(c) £16,500 overapplied
(d) £16,500 underapplied
Budgeted rate = £1.50 per hour. Applied to 11,000 hours = £16,500. Assumed that the actual fixed cost is the same as the budgeted fixed cost at £15,000, the fixed overhead is overapplied compared to actual cost. so answer is (a) £1,500 overapplied
The accounts department investigates all applications from new customers for credit sales. It has incurred a cost of £2,500 in January to investigate 100 customer applications. The accounts department has apportioned the cost as £1,250 each to divisions A and B because each has the same level of sales. The manager of division A has claimed that this is unfair because she only asked for 20 investigations while division B asked for 80 investigations. Which of the following statements is/ are correct?
(i) Activity based costing would charge £500 to division A and £2,000 to division
B.(ii) Activity based costing forecasts that the customer investigation costs for February will be £500 for division A and £2,000 for division
B.(it is a model of allocation, not a model of prediction)
(iii) Activity based costing makes managers more aware of the costs incurred by their operations.
(i) and (iii) only Cost is £25 per customer application (assuming all are similar).
Applied to actual investigations splits the cost £500 to A and £2,000 to B.
Which of the following is the best description of cost drivers?
(a) Cost drivers are a new name for cost centres.
(b) Cost drivers are the factors that most closely influence the cost of an activity.
(c) Cost drivers represent the difference between a budgeted cost and actual cost.
(d) Cost drivers are the direct product costs of output.
(b) Cost drivers are the factors that most closely influence the cost of an activity.
An organisation has 3 cost centres. Production overheads are absorbed into production units by the use of overhead cost rates. Which of the following best describes how the overhead cost rate should be calculated?
(a) Total indirect costs for the business divided by the total number of units produced.
(b) Overhead costs for each cost centre divided by activity levels of the relevant cost centre.
(c) Number of units produced divided by the total cost centre overheads.
(d) Number of units produced multiplied by the unit overhead cost.
(b) Overhead costs for each cost centre divided by activity levels of the relevant cost centre.