cman 380 exam 2
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
123 Terms
principles of disaster management
1. Prevent disaster
2. Minimize casualties
3. Prevent further casualties
4. Rescue victims
5. Provide first aid
6. Evacuate injured
7. Provide medical care
8. Promote reconstruction of lives
how do critical rescue workers use the principles of disaster management?
critical rescue workers apply these principles in proper sequence, or they will be ineffective and possibly detrimental to disaster victims
disaster risk reduction (drr)
aims to reduce the damage caused by natural hazards like earthquakes, hurricanes, floods, droughts, cyclones, and disease through an ethic of prevention
what does disaster severity depend on?
how much a hazard impacts the vulnerable society and environment
direct victim definition
individual immediately affected by event
indirect victim definition
family member, friend of the victim, or first responder.
displaced person definition
are those who evacuate their homes, schools, or businesses due to disaster
refugees definition
are those who fled their country due to famine, drought, natural disaster, war, or civil unrest
categories of disasters
- mass casualty event
- multiple casualty event
define disaster
-occurrence: natural or man-made
-must causes human suffering
-must creates human needs that victims CANNOT alleviate without assistance
define mass casualty event
- Usually >3-100 casualties
A mass casualty incident (MCI) is an incident where the number of patients exceeds the amount of healthcare resources available. This number varies widely across the country...but is typically greater than 10 patients.
define multiple casualty event
<2 persons injured
what are dimensions of a disaster?
-Predictability (natural/man-made)
-Frequency (impacted more often)
-Controllability (prevent/reduce damage)
- Time (period of warning)
- Scope (geographical area)
- Intensity (ability to inflict damage $$$ and injury)
factors that impact the scope & severity of disasters
- vulnerability of population
- environmental conditions: chemical, physical, biological, social
- warning duration & proximity to disaster
- individual perception & response
effects of a disaster on a community
•Public service personnel overworked
•Lifelines are disrupted (phone/TV/water/sewer)
•Resources depleted (food/medicine)
•Public/private buildings are damaged
•($)
•Impacting the role of a disaster response nurse
what are the three phases of a disaster?
1. pre-impact: mitigation & preparedness
- efforts to reduce risk, checking supplies/resources, warning the public at first possible sign of danger
2. impact:
- initial assessment of disaster, estimating needed resources, rescue efforts, injured people undergoing triage, morgue facilities.
3. post-impact: emergency phase (begins end of impact phase until there is no longer any immediate threat from the destruction)
- rescue & first aid, recovery (from emergency to full recovery), evaluate and debrief
what is the nurse's role during the impact phase of a disaster?
nurse's role: assess health needs and provide physical/mental support to victims.
federal agencies responsible for disaster management
- federal emergency management agency (FEMA): supports state and local governments. involved in mitigation, preparedness, response, and recovery activities.
how are different levels of government involved in disaster management?
- local government responds first
- followed by state
- federal government provides support
FEMA emergency cycle
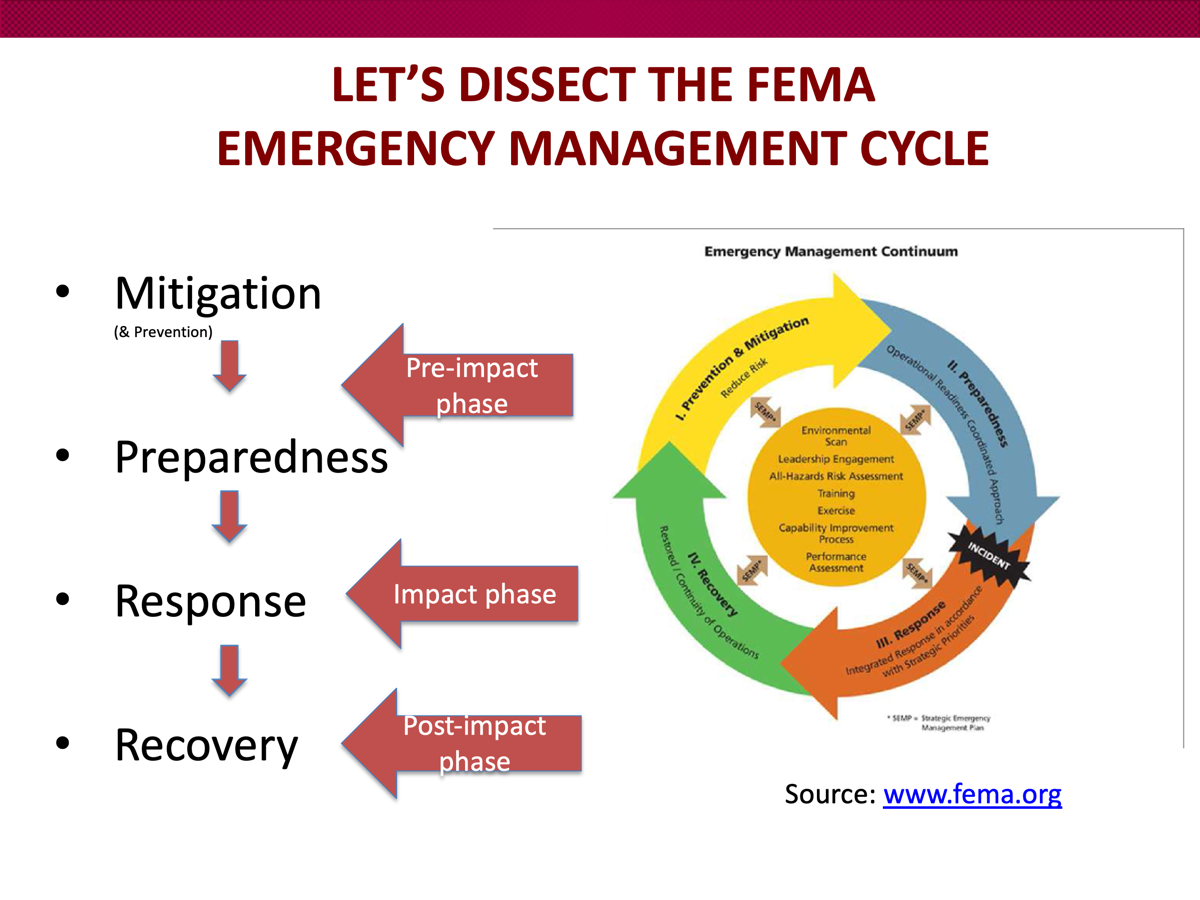
purpose of prevention & mitigation efforts
to reduce loss of life and property by decreasing impact of disaster by assuming that disaster is inevitable.
mitigation phase? and types
mitigation: reducing severity of human and material damage caused by the disaster. takes place before and after emergencies.
structural mitigation: actions to change characteristics of buildings or environment (i.e. raising building elevation, flood control projects, etc.)
non-structural mitigation: most of the time adopting or changing building codes (minimum standards & requirements for building structures)
preparedness phase of the emergency cycle
takes place before a disaster
a continuous cycle of planning, organizing, evaluating, training, etc. to focus on readiness to respond to disasters.
response phase of the emergency cycle
occurs immediately after a disaster. during this phase operations do not function normally. duration of the response phase depends on the level of preparedness.
recovery phase of the emergency cycle
restoration efforts occurring with regular operations and activities'
recovery period can take a while
who has the power to declare a disaster?
FEMA
what level of government is FEMA?
federal
responsibility of state agencies for disaster management
state governor (after making a request to president to declare disaster) coordinates state’s Emergency Operations Plan (EOP) & opens Emergency Operations Center (EOC)
Emergency Operations Center (EOC)?
state agencies work together to direct agency’s functions for disaster relief
Emergency Operations Plan (EOP)?
aka all-hazards plan
plans and assigns resources to other organizations
sets up lines organizational relationships and how each organization operates in emergencies
responsibility of local agencies for disaster management
also has EOP
involves fire dept, police, nurses, volunteers, hospitals
performs mock disaster drills & exercises
focused on providing direct care
community reactions to disasters
follows a pattern
heroic phase: help people survive
honeymoon phase: drawing people together
disillusionment phase: disappointment with delays to aid
reconstruction phase: belief in community & restoration
emotional responses to disaster
victims go through:
denial
strong emotional response
acceptance
recovery
nursing implications for patients of long-term disaster experiences
• Lead to interpersonal or social problems
• Some turn to alcohol or drugs to relieve stress
• Others might have difficulty resuming their usual routines and relationship patterns
• Long-term respiratory syndromes such as asthma and bronchitis and mental health problems such as post traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and depression
• Children: mental or behavioral problems years after the event
what symptoms are indicative of PTSD?
two or more symptoms indicative of PTSD:
hyper-alertness
exaggerated startle response
sleep disturbance
survivor guilt
decreased concentration
impaired memory
avoidance behavior.
nursing responsibilities in disaster management
adapting nursing skills to meet needs of community from a disaster
CHN & PHN from state and local levels
American Red Cross Nurses (>20,000)
what is triage?
prioritizing victims of disaster for treatment
color coded tags to assign care: black → red → yellow → green
“START” is the most common Mass Casualty Triage algorithm.
what is START?
the most common Mass Casualty Triage algorithm
BLACK: (Deceased/expectant) injuries incompatible with life or without spontaneous respiration; should not be moved forward to the collection point
RED: (Immediate) severe injuries but high potential for survival with treatment; taken to collection point first
YELLOW: (Delayed) serious injuries but not immediately life-threatening
GREEN: (Walking wounded) minor injuries
triage in a mass casualty incident (MCI)
disaster triage: greatest good for the greatest number in the shortest time
sorting system of patients
fast sorting: 30sec-60sec → Tag → next person
1st triage station: first contact, quick assessment, assign tag (left upper arm or leg)
2nd station: victims move to color coded area (treatment/holding) or move patients to casualty collection point (CCP)
3rd station: receive ongoing care (until transported)
what does a red tag mean?
1st priority
life-threatening injuries that need immediate care
experiencing or near hypoxic
CAN BE HELPED BUT NEED MEDICAL ATTENTION WITHIN MINUTES OR UP TO 60 MINUTES
what does a yellow tag mean?
2nd priority
care can be delayed until all reds are transported
not yet hypoxic or in shock
can wait 2 hours without immediate risk
what does a green tag mean?
“walking wounded”
can survive >2+ hours without treatment
assign to casualty collection point (CCP) to get them out of the way
what does a black tag mean?
hopelessly injured patients/dead
would not survive under the best of circumstances
present the greatest difficulty to nurses because conflicts with nursing ethics to not treat these patients
hazmat tag?
might be color coded or triangle tag
contaminated with hazardous bacterial/viral OR chemical substances
need to be decontaminated
eliminate hazards before additional treatment provided
clinical parameters in START
focusing on respiration, profusion, and mental status assessments (RPMs)
involves:
ability to walk
presence or absence of breathing
respiratory rate greater OR less than 30 per min
perfusion assessment (cap refill, radial pulse)
mental status assessment (ability to obey commands)
how to assess respirations during RPM
not breathing = reposition airway
no breathing = black tag
breathing = assess quality of breaths
>30 = red (indicates respiratory distress
how to assess pulse (RPM)
cap refill >2 seconds or no radial pulse = RED (signs of shunting)
cap refill <2 seconds or radial pulse present = check mental status
how to assess mental status (RPM)
unable to answer/follow commands = red
able to follow commands = yellow
mnemonic for RPM
30-2-can do
what to do for pediatric patients who are apneic in RPM
if they have a pulse, give 5 rescue breaths
what organization developed the World Health Organization?
United Nations
what does WHO do?
promotes health on a global basis
direct and coordinate authority for international health work & collaboration with UN and other organizations
mobilizes resources of governments and financial institutes
what is WHO the best source for?
global morbidity and mortality data
what is the World Bank?
global financial & health-related org that collaborates with WHO to:
lend money to low-income countries with lower interest rates
provide resources
reinsurance
what is PEPFAR?
President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief
national org launched in 2003 by Bush to combat HIV/AIDS
at the time was “the largest commitment by any nation to combat a single disease in history”
GOAL: increase % of HIV+ individuals receiving antiretroviral therapy
what is an NGO and what is an example of it?
Non-governmental organization: private health company driven by a health goal
Global Grand Challenge is an NGO
other examples: Global Health Council, Feed My Starving Children, International Council of Nurses
What is Global Challenges?
launched by Bill & Melinda Gates in 2003
focuses attention and efforts to unsolved global problems that are hard to address
offers grants for research projects in 33+ countries
what do all agencies have in common? (global health related)
strive to fulfill countries’ health-promoting priorities
protect rest of the world from the spread of diseases
develop a reliable global incidence report to make sound policy decisions
what environmental hazards are killing children worldwide?
inadequate drinking water
indoor air pollution & accidents
injuries & poisoning
what are the top 10 leading causes of death globally?
1)Ischemic Heart Disease
2)Stroke
3)Chronic Obstructive
4)Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
5)Neonatal Conditions
6)Trachea, Bronchus, and Lung Cancers:
7)Diabetes Mellitus
8)Alzheimer’s Disease and Other Dementias
9)Diarrheal Diseases:
10)Tuberculosis (TB)
trends in causes of death in developed vs developing nations
developing: more causes related to communicable, maternal, neonatel, or nutritional conditions
developed: more noncommunicable diseases (stroke, ischemic heart disease)
throughout all nations: lower respiratory infections & road injuries are remain some of the most common reasons of death
#1 global cause of death
cardiovascular disease
caused often by smoking, making smoking “hidden” cause of death
how have health organizations impacted health outcomes?
over the past 25 years, children who died before their 5th birthday has fallen dramatically
why do we need to know the reasons people die?
to understand how diseases and injuries affect people
assess the country’s health system
what groups can receive social security?
retirees, disabled, survivors (of deceased workers)
what is social security?
a program that uses public funds to provide some economic security for the public.
what role does SSA have in medicare/medicaid?
determines eligibility for medicare/medicaid
independent from HHS
how much does medicare cover?
80% of medical expenses. patients pay 20% of bill after meeting annual deductible
does NOT cover most long-term care
what role does HHS have in medicare/medicaid?
oversees and administers Medicare & Medicaid as CMS (Centers for medicare/medic
what is medicare and who does it cover?
public health insurance from federal government for people 65 and older. Includes disabled and end-stage renal disease
must also be a US citizen or permanent US resident, having lived in the US for 5 continuous years
DO NOT have to be retired to receive medicare benefits
parts of medicare
2 parts: part A (hospital) + part b (medical)
***part c (medicare advantage) and d (prescription drug) are choices you can buy
medicare costs for original
parts a +b
monthly premium with yearly deductible
some people may not have to pay monthly premium based on income
after meeting your annual deductible, you pay 20% of the bill for the medicare-approved amount
medicare part A deadline
must apply 3 months before age 65 or receive penalty
medicare part A coverage
all services free for a limited time (w monthly premium)
covers first 20 days of each benefit period (time spent in the hospital). coverage restarts if you stay out of the hospital for 60 days
provider must “certify the need” for care
Inpatient care in a hospital (including nursing services)
Skilled nursing facilities (rehabilitation/cardiac rehab)
Short-term nursing home care (inpatient care in a skilled nursing facility/not custodial or long-term care)
Hospice care (6 months-can recertify if live >6mos.)
Some home health care and PT (short-term and discharged from the hospital)
***pays nurses***
how can retirees get SS benefits
age >65-67
work hx needed (10 years/40 credits)
amount of money received is affected by age of retirement and earned income
SS benefits for spouse/family of retirees
eligible spouse
children can get up to half of the parent’s full retirement benefits if:
unmarried
under 18 OR 19 in high school or two months after HS graduation
SSA definition of disability
inabiltiy to engage in ADL’s due to medically diagnosable physical or mental impairment that can be lead to death
OR lasted or can be expected to last for >12 months
types of disability programs
social security disability insurance (SSDI
supplemental security income (SSI)
eligibility for SSDI
worker with disability under retirement age
cant work do to medical condition that lasts >12 months
must meet earnings tests (aka insured status)
“recent work” test: based on age at start of disability
“duration of work” test: show that a person worked long enough to earn benefits under SS
at retirement age- pulled from retirement funds at same rate
SSDI for children and young adults
SSDI can also pay benefit throughout adulthood (whole life) if disability started <22
paid through parents’ social security record
to be eligible at least ONE parent must:
be receiving SS benefits OR
have died + worked long enough to meet earnings test
eligibility for SSI
little or no income
disability OR >65
benefits NOT based on prior work experience
if eligible for SSI, also eligible for Medicaid
SSI for disabled children
age <18 with disability
based on family income
conditions that qualify for immediate SSI payments to child (or else takes 3-5 months to come to decision)
HIV
total blindness
total deafness
cerebral palsy
down syndrome
muscular dystrophy
severe intellectual disorder
birth weight <2lbs 10oz
SS benefits for survivors
available for family members of deceased eligible persons (like parents)
children under 18 (or 19 if still in highschool)
any age if disabled before 22 (can receive up to 75% throughout life)
widows + full retirement age (receive 100% of deceased spouse’s benefits)
widows under retirement age receive reduced amount
widow, any age, caring for child <18 OR disability (75%)
can you collect your deceased spouse’s SS and your own at the same time?
no, SS will pay the higher of the two
what does medicare part b cover?
covers 80% expenses on:
provider services inpatient
out patient provider services (primary care visits)
will cover visits focusing on treating specific problem
will NOT cover yearly physical or exams focusing on preventative care
ER visits (for emergencies only)
some home health services (“contract goals'“)
durable medical equipment
preventative vaccines
what is not covered by part A&B
annual physical exams
dental care
eye exams
acupuncture
dentures
hearing aids
long term care
what is part c of medicare?
medicare advantage plans
offered by private insurances that cover services that a+b does not
includes part d (medications)
out of pocket add on
types of medicare advantage plans
HMO
PPO: more flexible
medicare part d
covers prescription drugs
different tiers of copy (tiers 1-4, 4 being most expensive)
two ways to get part d:
buying part d
buying part c (which includes part d)
***buying part d will not include part c, however
what is medigap?
a medicare “supplement insurance” that helps fill the gaps of original medicare (a+b)
sold by private companies but plan approved by The Office of Medicare
cannot have part c if you buy medigap
hospital acquired “never events”
policy medicare made that says Medicare will no longer reimburse hospitals for preventable errors in healthcare (i.e. performing surgery on the wrong patient)
readmissions reduction program
established by ACA that penalizes hospitals for patients that are readmitted to a hospital within 30 days of discharge
who is medicare overseen by
center for medicare & medicaid services (CMS) that is under HHS
eligibility for medicare through SSA
what is medicAID?
established as extension of the Social Security Act to provide health insurance for the poor
eligibility follows federal poverty guidelines
funded by both state & federal government through tax revenues
who administers and regulates medicaid?
by individual states
therefore benefits vary by state
medicaid benefits
federal government requires minimum coverage similar to medicare a+b
states can “expand” and add more coverage
MAY cover prescription drugs, dental, eye care, long term nursing care
can you have both medicare & medicaid?
yes!
can be dual eligible for medicare-medicaid
for low income medicare recipients (both retirees and disabled), medicAID pays for medicare part B “premium” + part D
acts like medigap
illinois medicaid requirements
must be resident of illinois
in need of health insurance assistance and has low income or very low income (poverty line)
adults must be US national or have satisfactory immigration status
components to medicaid in illinois
All Kids
Moms and Babies
Family Care
Aid to Aged, Blind, and Disabled
ACA Adults “The Marketplace”
All Kids
covers children 0-18, not matter who they live with
does NOT have to be a citizen or be legal immigrant