Ovarian function, pregnancy, and contraception
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Progesterone is needed to support a pregnancy, what anti-progestrone is given to terminate a pregnancy
Mifepristone
How does progesterone turn into oestrogen
Progesterone is converted into oestrogen through a series of enzymatic reactions involving aromatase, which transforms androgens into estrogens, primarily in the ovaries.
What is the metabolic screwdriver of pregnancy (prioritises nutrients to developing foetus)
Human Placental Lactogen (hPL)
Human Placental Lactogen (hPL) function and place of production
Human Placental Lactogen (hPL) is produced by the placenta and functions to prioritize nutrients for the developing fetus by altering maternal metabolism and promoting glucose availability.
Prolactin function
Prolactin is a hormone produced by the pituitary gland that stimulates milk production in breastfeeding mothers and plays a role in regulating the menstrual cycle.
How is prolactin produced
Prolactin is produced by lactotroph cells in the anterior pituitary gland in response to oestrogen,
When does the oestrogen:progesterone ratio increase?
At term, to increase oxytocin receptor levels to cause myometrial contractions
Where is oxytocin synthesised and secreted
Oxytocin is synthesised in the hypothalamus and secreted from the posterior pituitary gland and decidual tissue
Why doesn’t prolactin produce until baby delivery?
Oestrogen and progesterone inhibit milk secretion until parturition by making cells unresponsive to prolactin
Name 5 types of contraception
Hormonal
Barrier
IUDs
Permanent
Natural
what is the Pearl index?
Number of failures/100 women years of exposure
e.g 100 women using a contraceptive for 1 year or 10 women using it for 10 years
How does the morning after pill work, what is its active ingredient
The morning after pill works primarily by preventing ovulation or fertilization. Its active ingredient is usually levonorgestrel or ulipristal acetate.
How do hormonal methods of contraception work
Mimicking hormonal levels during pregnancy (e.g. progesterone)
Constant exposure to progesterone suppresses ovulation
Progesterone also causes thickening of cervical mucus and decreases endometrial receptivity
Oestrogenfurther suppresses ovulation and stabilizes the endometrium.
What primordial cells give rise to gametes in early embryonic development
Primordial germ cells (PGCs)
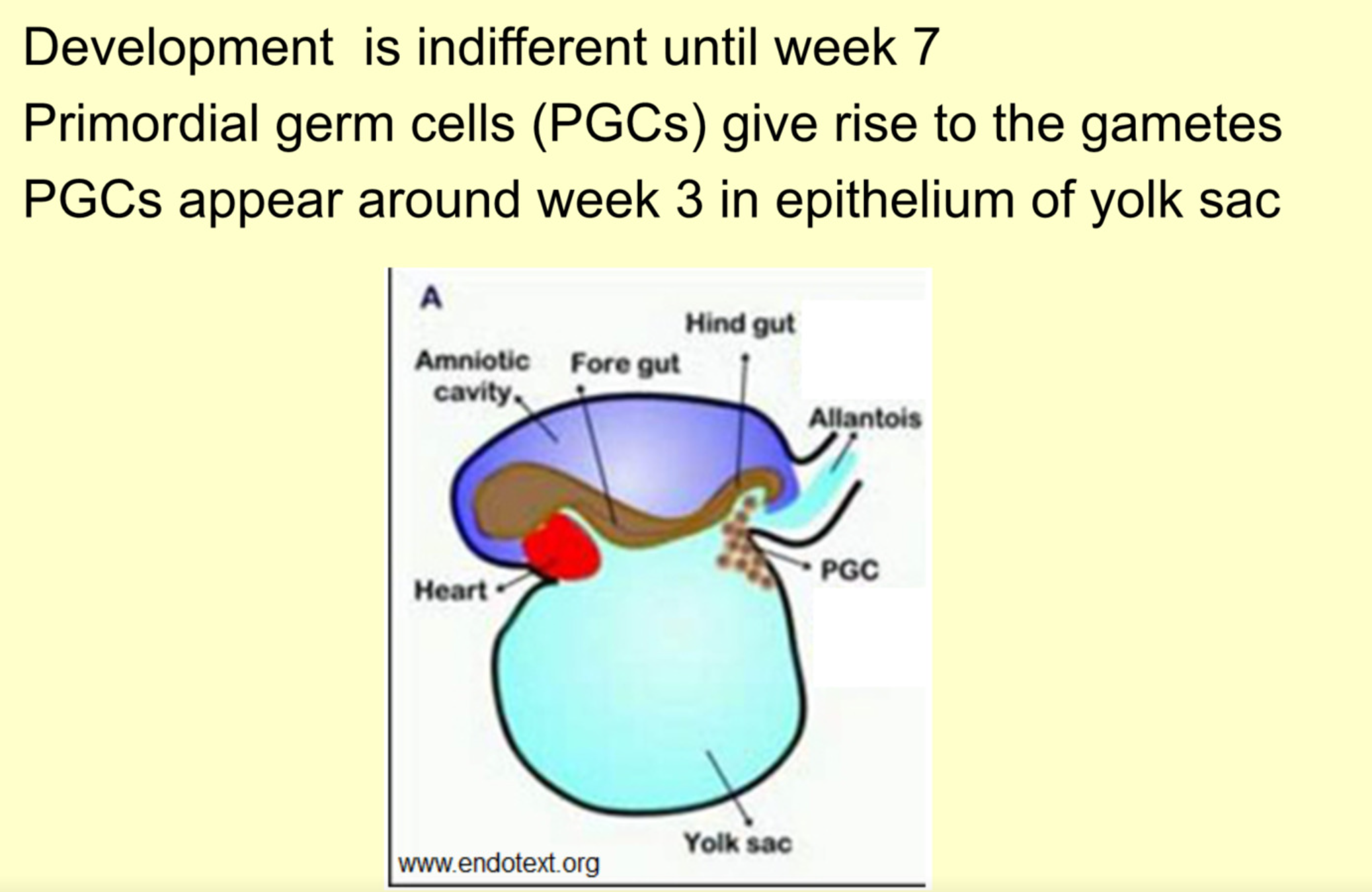
How is the motion of primordial germ cells controlled?
Guided by chemotaxis
What do sex cord cells do in week 7 of embryonic development
Form granulosa, which cluster around primordial germ cells (PGCs). Which then forms oogonia, which then forms primordial follicles
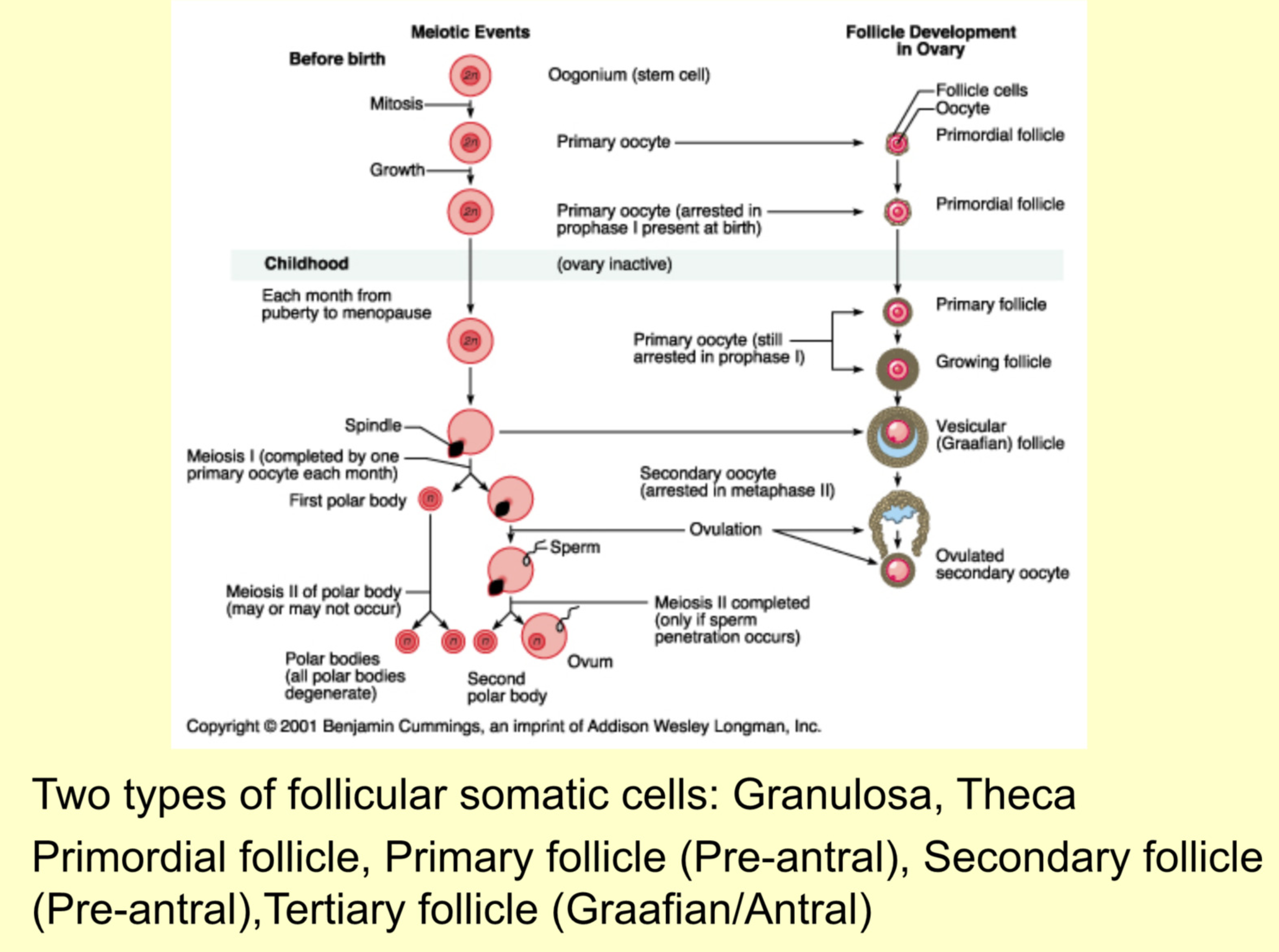
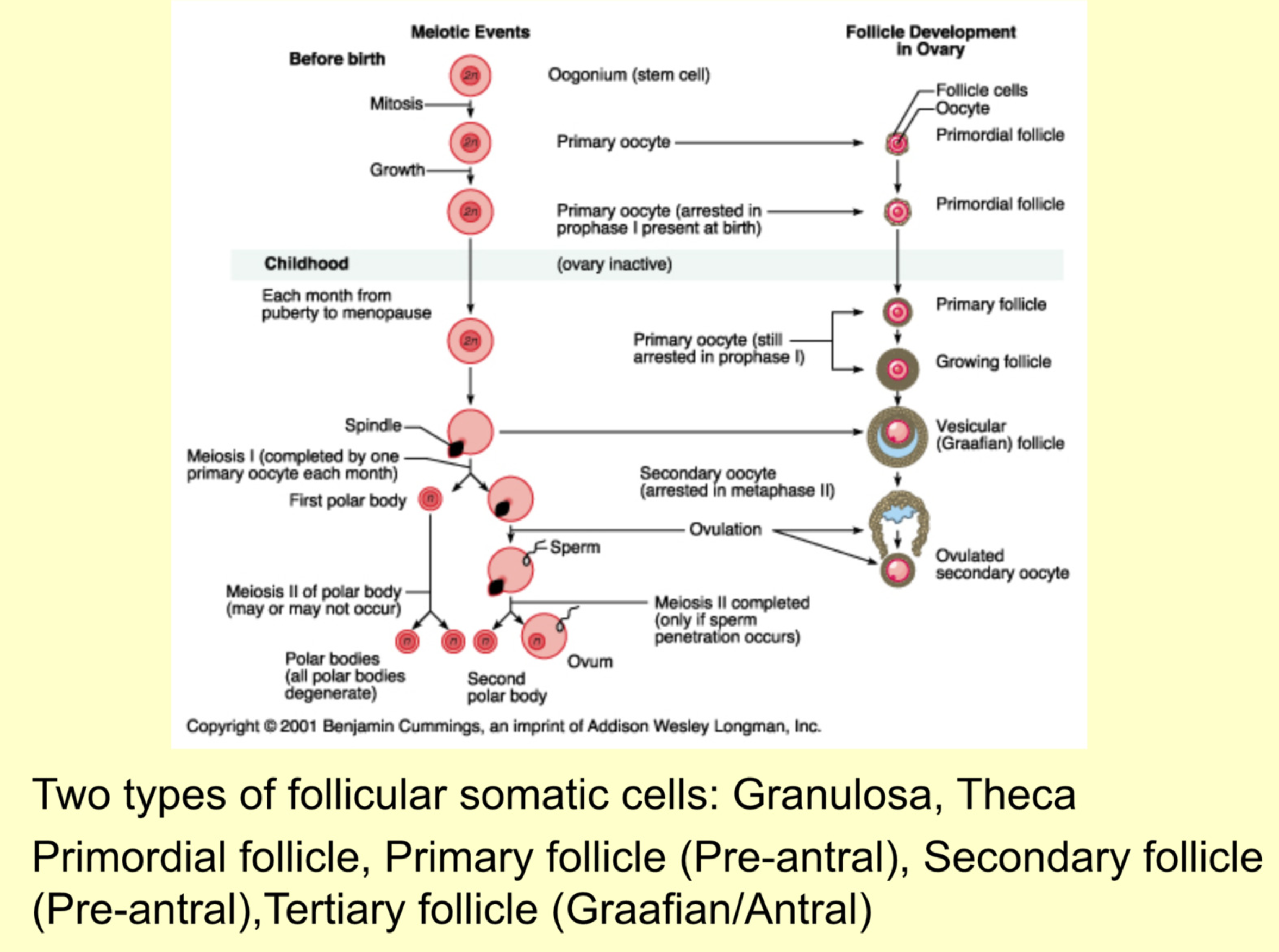
Steps of oocyte formation (include cell type and what type of division)
Primordial germ cells - mitosis
Oogonium - mitosis
Primary oocyte - 1st meiotic division
Secondary oocyte - 2nd meiotic division
Mature oocyte - becomes haploid (due to meiosis)2
What gene regulates the start of meiosis
Stra8 - Stimulated by retinoic acid
Women - retinoic acid builds up in foetal period, stimulating production of all oocytes they’ll ever have
Men - can metabolise retinoic acid via cytochrome p450, and only allows levels to build at puberty
When do primary oocytes become secondary oocytes
Primary oocytes complete meiosis I to go from prophase I to secondary oocytes at metaphase II just before the oocyte is ovulated
When do secondary oocytes become mature oocytes
When a sperm penetrates the secondary oocyte, it finishes meiosis II, and become fully mature
What are polar bodies
Discarded genetic material that is a by-product of meiotic division. Divides this way so the mature oocyte can have the lion’s share of cytoplasm
Overview of ovary
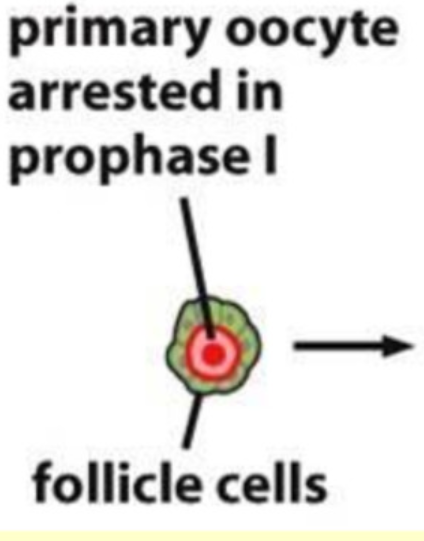
Describe the structure of a primordial follicle
Primary oocyte surrounded by a single layer of flattened granulosa
Describe the structure of a primary follicle
Granulosa go from flat to cuboidal
theca and zona pellucida become visible
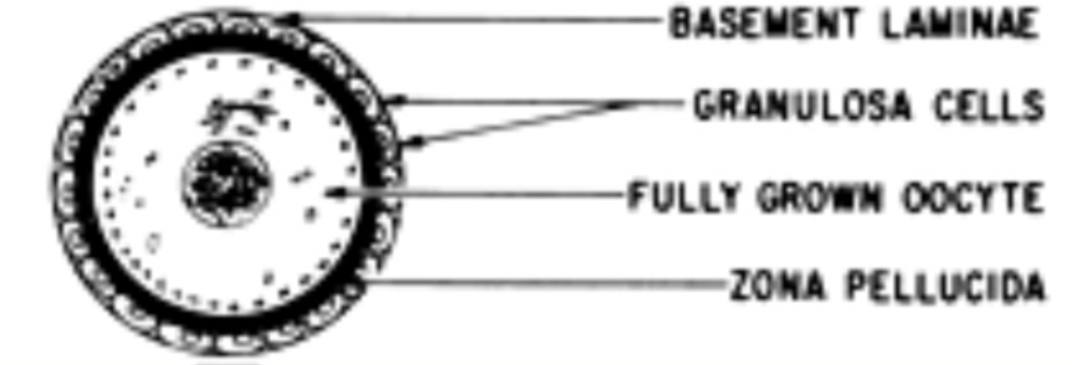
Functions of the zona pellucida
Provides a sperm binding site
Induces acrosome reaction (reaction where acrosome vesicle on sperm head breaks through outer layer of ovum)
Prevents polyspermy
Protects early embryo
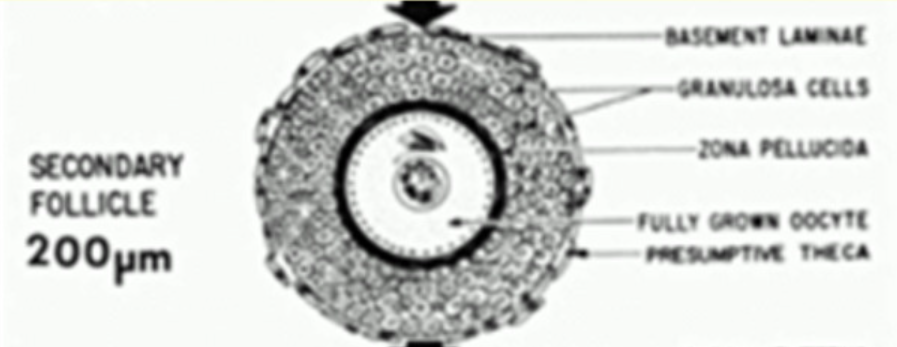
Describe structure of the secondary follicle
Granulosa proliferate, and become a stratified cuboidal layer
Theca now has two distinct layer - external, internal
Now requires gonadotrophin to develop to tertiary follicle
Describe structure of the tertiary follicle
Granulosa secrete follicular fluid
Oocyte surrounded by a layer of corona radiata
What Neuropeptide triggers the start of puberty
kisspeptin-1 (KISS-1) Matches GnRH pulses
Why does GnRH have do be released in pulses?
Continuous GnRH secretion leads to downregulation of GnRH receptors on surface of gonadotroph cells, and FSH and LH are no longer stimulated to release
FSH function and location of action
Acts on ovary to stimulate follicular development
Function and location of action of LH
Acts of ovary to stimulate follicle maturation, ovulation and development of corpus luteum [[luteum - luteinising hormone]]
3 Families of sex steroids and their main functions
Progestogens - Pregnancy
Androgens - Maleness
Oestrogens - Femaleness
Functions of oestrogens
Growth of body and sex organs at puberty
Development of secondary sexual characteristic
Follicular maturation
Preparation of endometrium for pregnancy
Thinning of cervical mucus (just before ovulation)F
Functions of progesterone
Completes the preparation of and maintains endometrium for pregnancy
Produced by corpus luteum post-ovulation
The whole menstrual cycle in a diagram
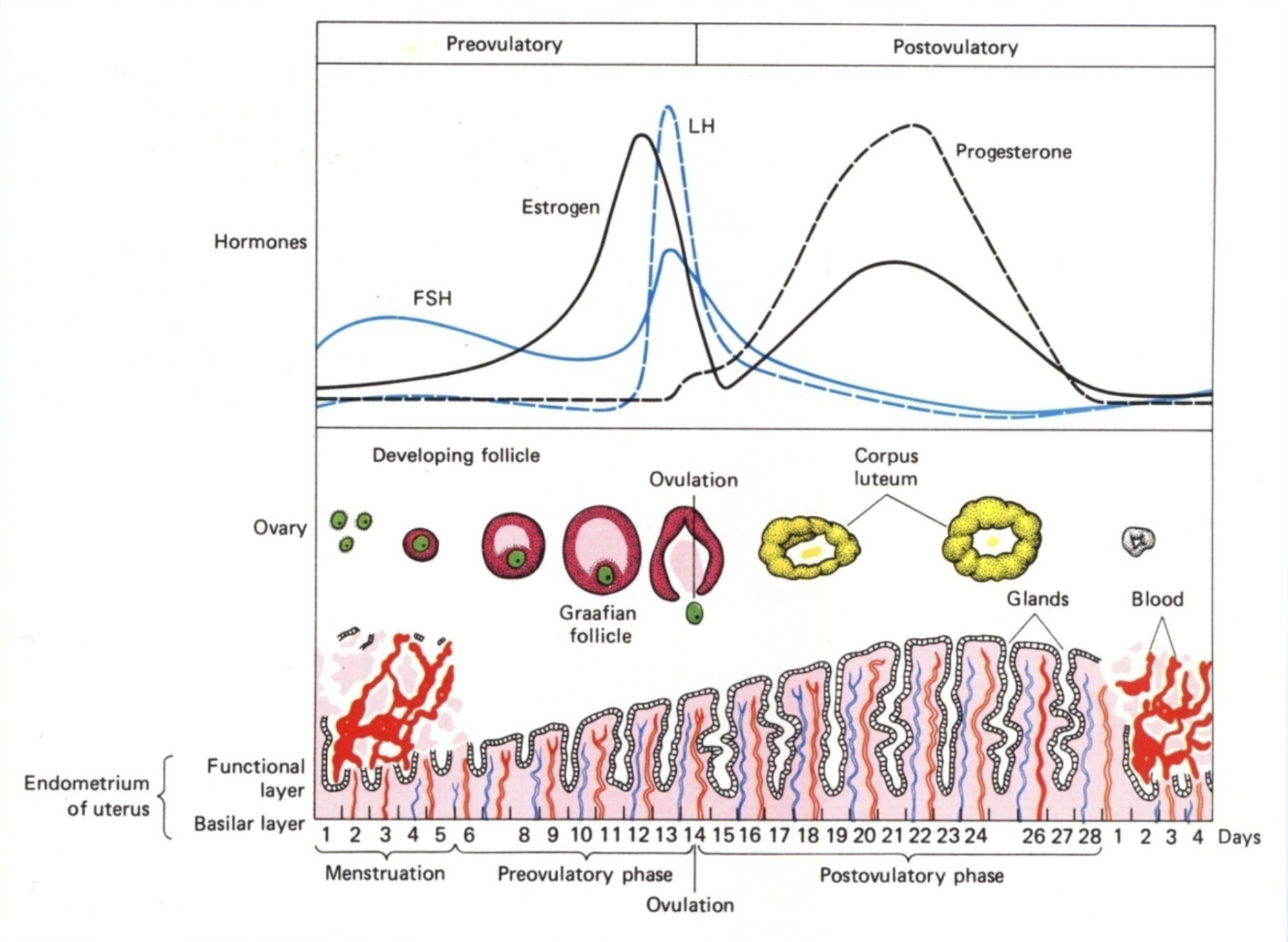
What happens in the follicular/proliferative phase (day 1-10)
Shedding occurs in days 1-5
Hypothalamus secretes GnRH
Medium pulses, so most FSH and a little bit of LH released
Up to 15 follicles are ‘rescued’ - their granulosa and theca cells develop
In days 5-10, the endometrium tries to rebuild after menstrual shedding
Theca cells produce testosterone, which is converted by granulosa to oestrogen
Oestrogen thickens endometrium and thins cervical mucus
Oestrogen also suppresses FSH production via -ve feedback on HPG axis
Only one of the 15 follicles are selected to develop further
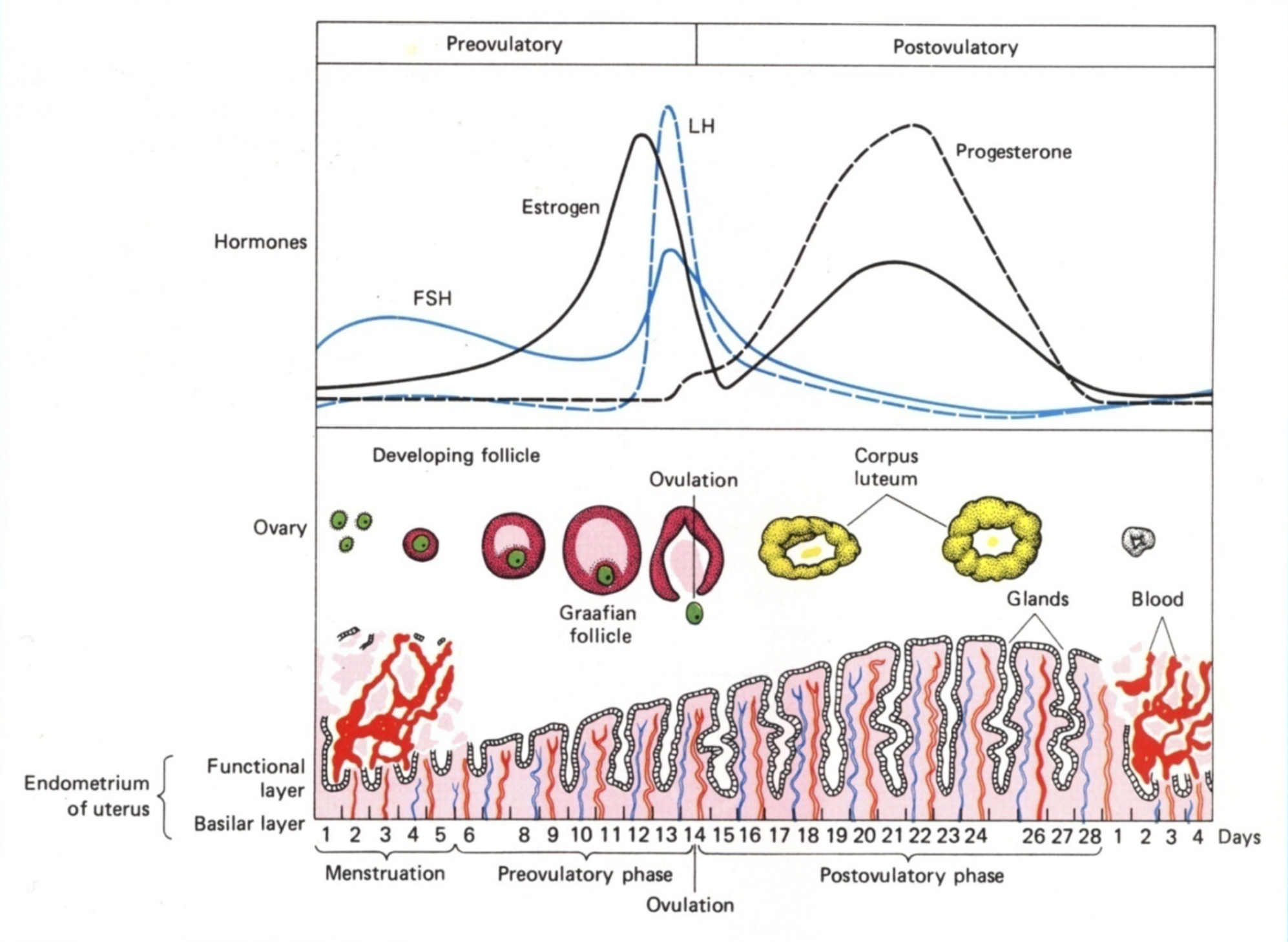
Days 10-14 of menstrual cycle
Granulose in dominant follicle express LHCG receptors
High levels of oestrogen at mid cycle cause LH surge from ant.pit
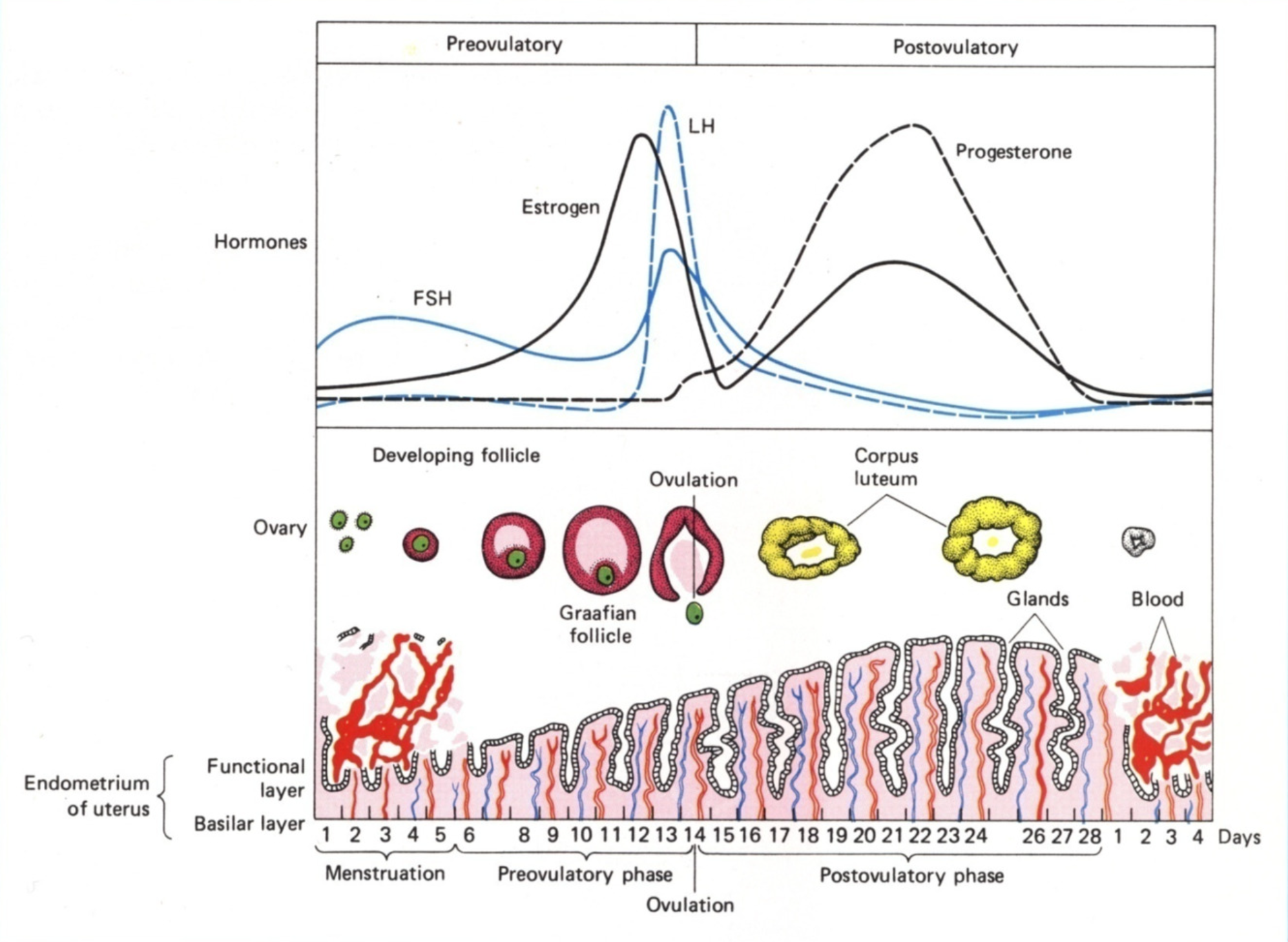
Day 14 of menstrual cycle (ovulation)
Primary follicle completes meiosis I, and secondary oocyte enter meiosis II and stops at metaphase II.
Increase in follicular fluid and number of granulosa
Cumulus oophorus (stalk thing) loosens
Follicle wall weakens due to proteases
Follicle wall is broken through due to pressure buildup, releasing cumulus-oocyte complex
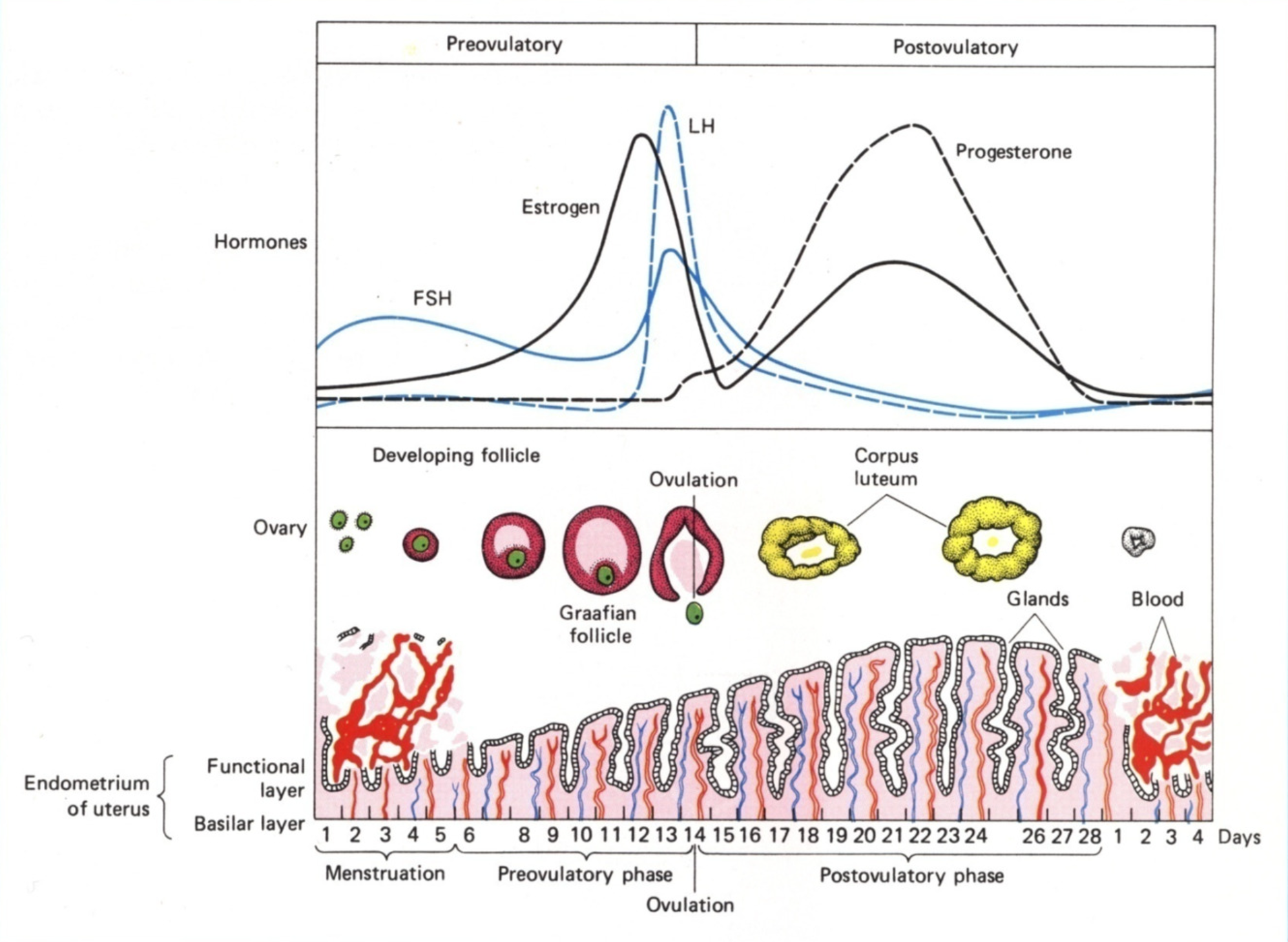
Luteal (secretory) phase - Days 14 - 21
Corpus luteum forms, producing progesterone
Granulosa turn into large lutein cells, which produce progesterone and oestrogen
Many theca cells disperse to stromal tissue
Some stay as lutein cells, which produce progesterone and androgens (which then converts to oestrogen)
High levels of progesterone and oestrogen provide negative feedback on FSH and LH production, so levels are low
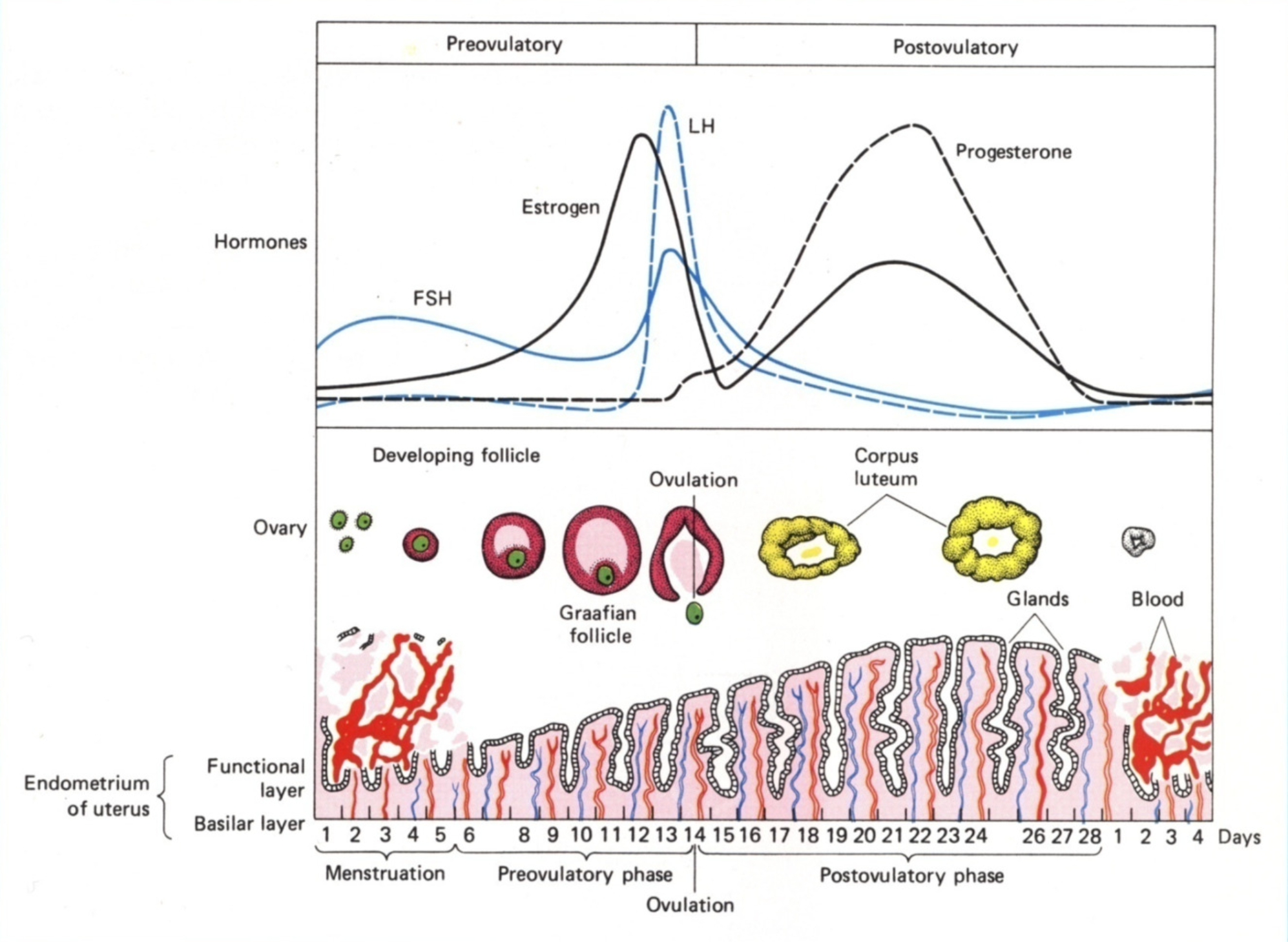
What hormone is produced when pregnancy occurs
hCG - chorionic gonadotrophin
Function of hCG (chorionic gonadotrophin)
Binds to LHCGR on lutein cells, which maintains the corpus luteum, thus upkeeping progesterone production and suppressing ovulation