Overview of the Autonomic Nervous System Organization
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Autonomic Nervous System
Controls involuntary bodily functions subconsciously.
Somatic Motor
Involves voluntary control of skeletal muscles.
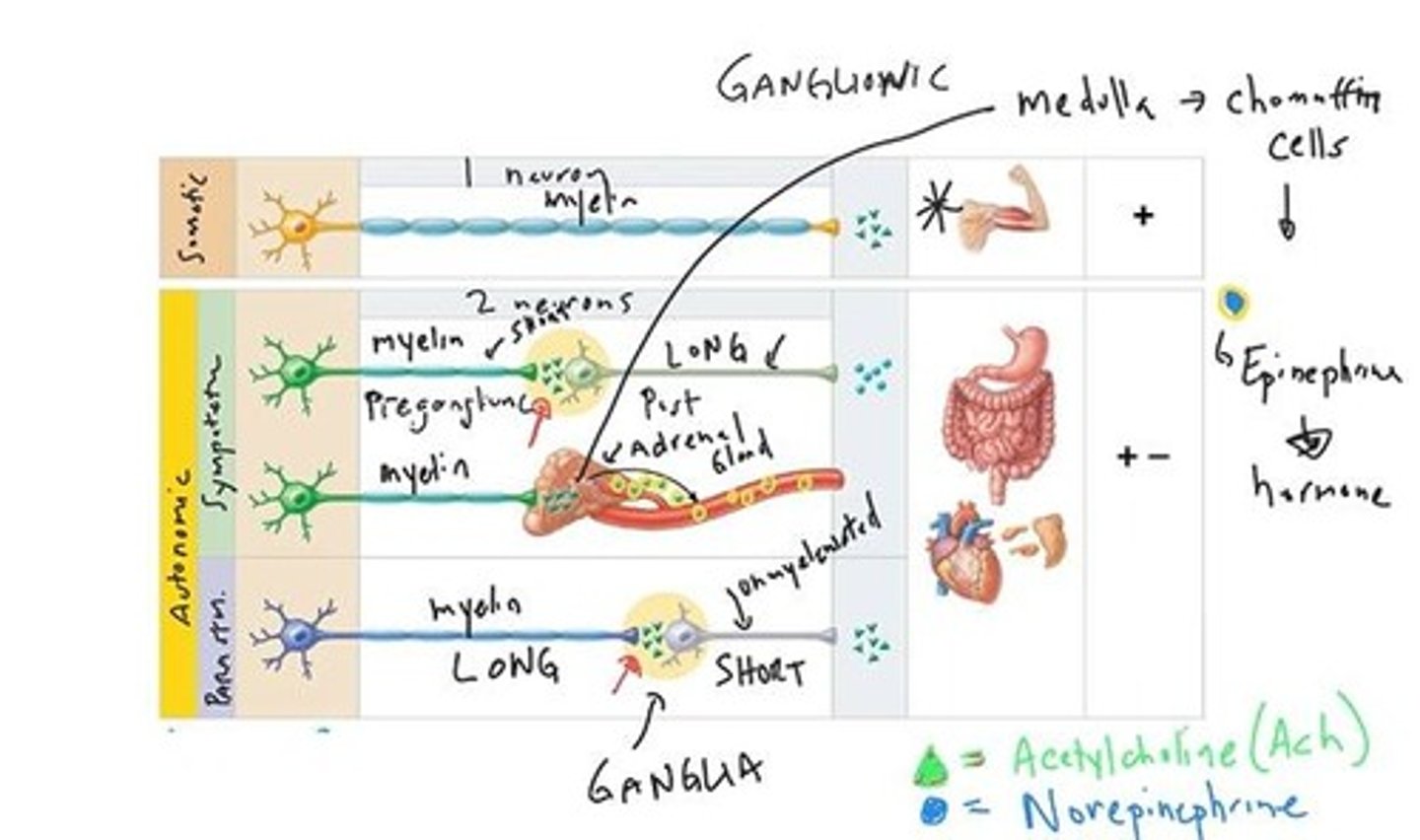
Autonomic Motor
Involves involuntary control of organs and glands.
Preganglionic Neuron
First neuron in autonomic pathways, myelinated.
Postganglionic Neuron
Second neuron in autonomic pathways, unmyelinated.
Autonomic Ganglion
Synapse location between preganglionic and postganglionic neurons.
Acetylcholine (Ach)
Neurotransmitter released by preganglionic neurons.
Norepinephrine
Neurotransmitter released by sympathetic postganglionic neurons.
Epinephrine
Hormone released by adrenal medulla into bloodstream.
Alpha Receptors
Adrenergic receptors, two types: alpha 1 and alpha 2.
Beta Receptors
Adrenergic receptors, three types: beta 1, beta 2, beta 3.
Nicotinic Receptors
Bind acetylcholine at neuromuscular junctions.
Muscarinic Receptors
Bind acetylcholine on target organs.
Parasympathetic Branch
Promotes rest and digest functions.
Sympathetic Branch
Prepares body for fight or flight response.
Craniosacral
Origin of parasympathetic neurons from brain and sacral spinal cord.
Thoracolumbar
Origin of sympathetic neurons from thoracic and lumbar spinal cord.
Hypothalamus
Regulates autonomic nervous system functions.
Limbic System
Influences hypothalamus based on emotional states.
Frontal Lobe
Can influence hypothalamus and autonomic responses.
Chromaffin Cells
Specialized cells in adrenal medulla releasing epinephrine.
Target Tissue
Organs innervated by postganglionic neurons.
Ganglia
Clusters of neuronal cell bodies in autonomic pathways.