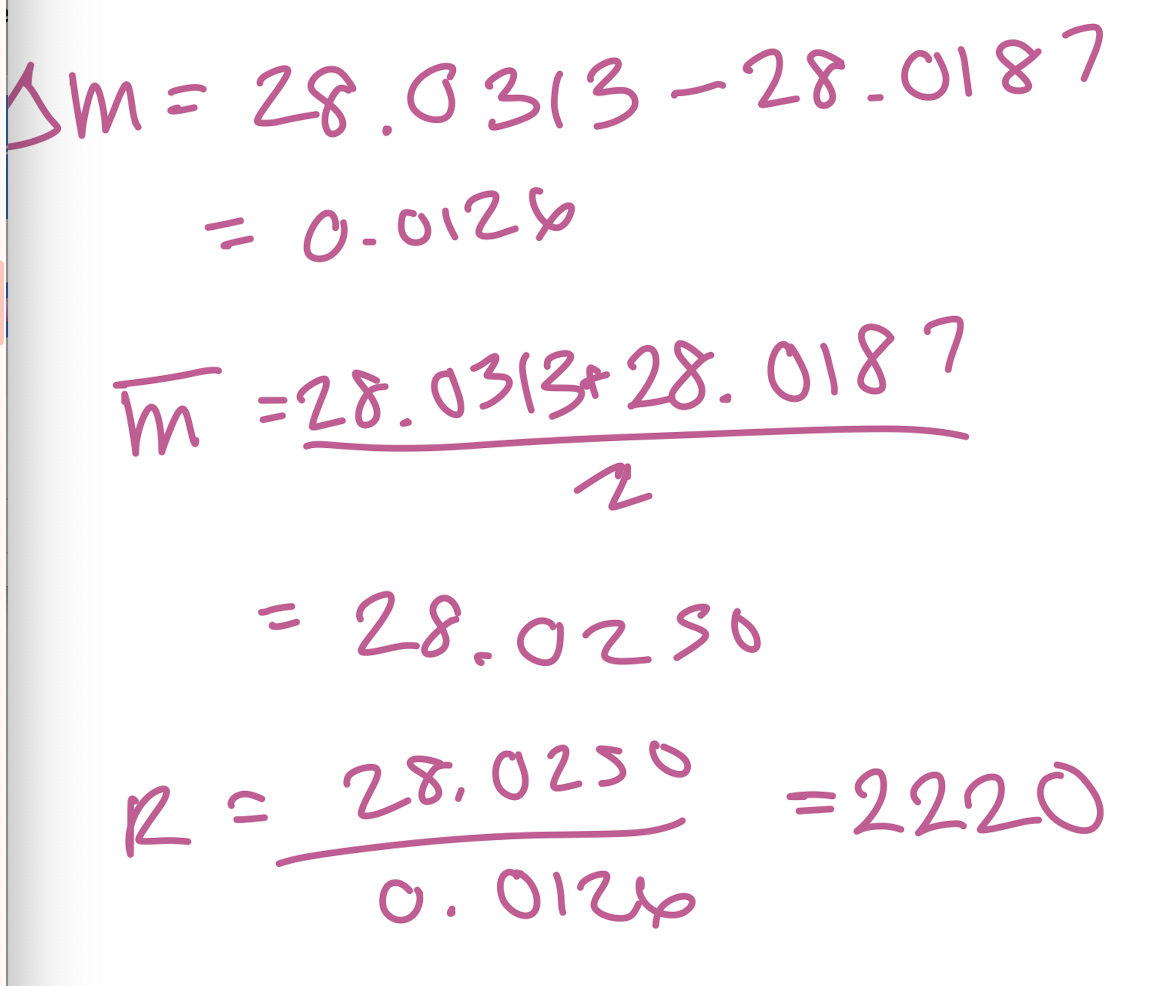Instrumental Chem Exam 3 (Math)
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
At what wavelength in nanometers would the Stokes Raman line for carbon tetrachloride (delta v~ = 218 cm-1) appear if the source were a helium-neon laser (632.8 nm)? (in nm)
641.7 nm
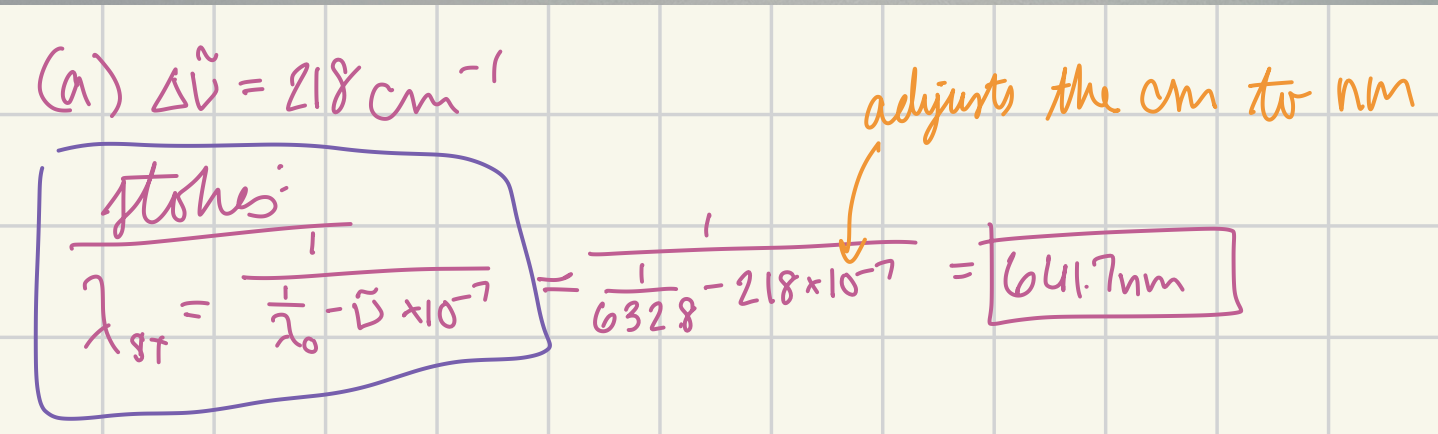
At what wavelength in nanometers would the anti-Stokes Raman line for carbon tetrachloride (delta v~ = 218 cm-1) appear if the source were a helium-neon laser (632.8 nm)? (in nm)
624.2 nm
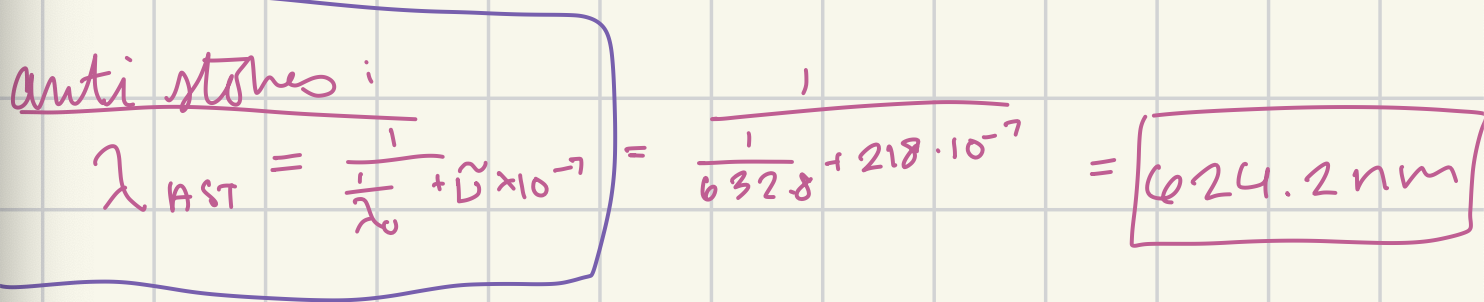
At what wavelength in nanometers would the Stokes Raman line for carbon tetrachloride (delta v~ = 218 cm-1) appear if the source were a argon-ion laser (488.0 nm)? (in nm)
493.9 nm
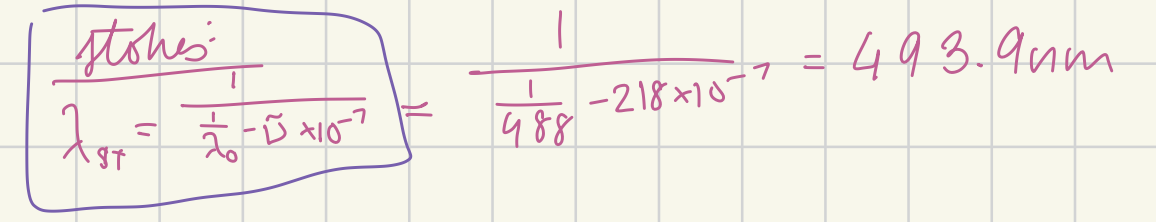
At what wavelength in nanometers would the anti-Stokes Raman line for carbon tetrachloride (delta v~ = 218 cm-1) appear if the source were a argon-ion laser (488.0 nm)? (in nm)
482.9 nm
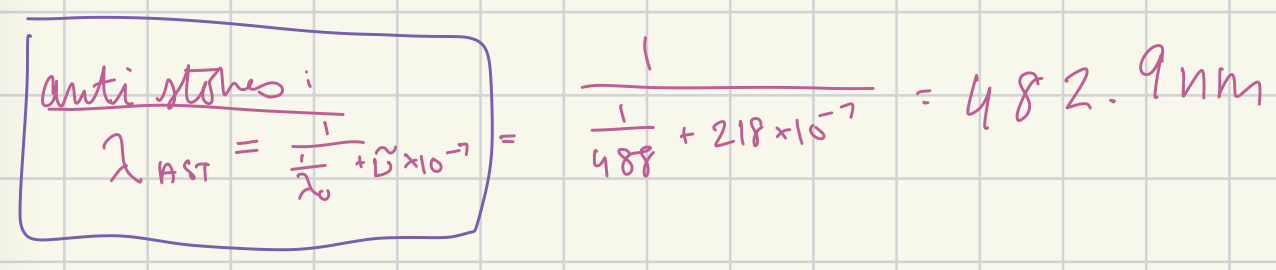

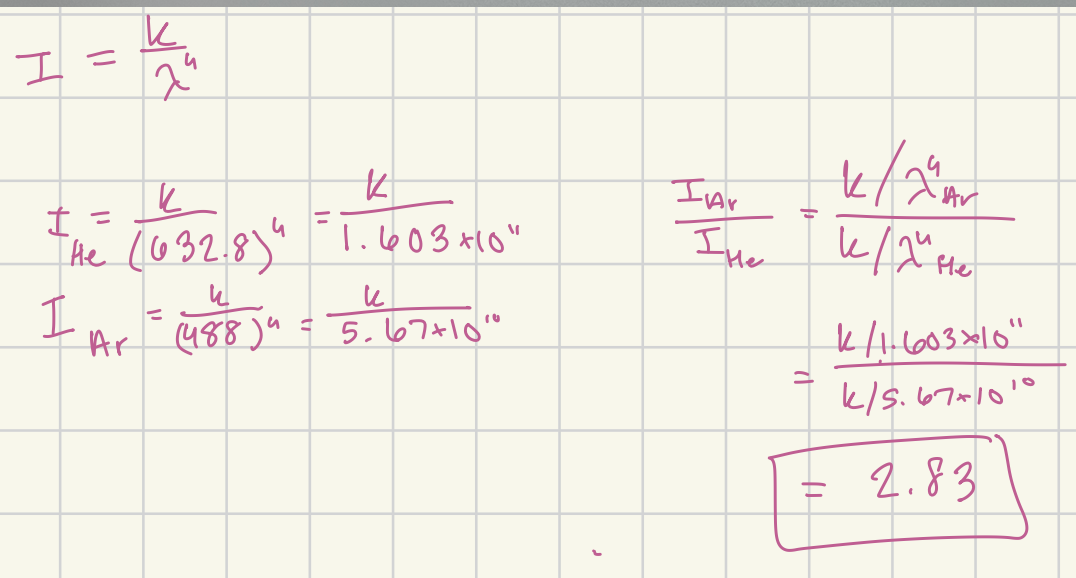
Assume the excitation sources in the attached problem have the same power. Compare the relative intensities of the CCl4 Raman lines when each of the two excitation sources is used.
2.83
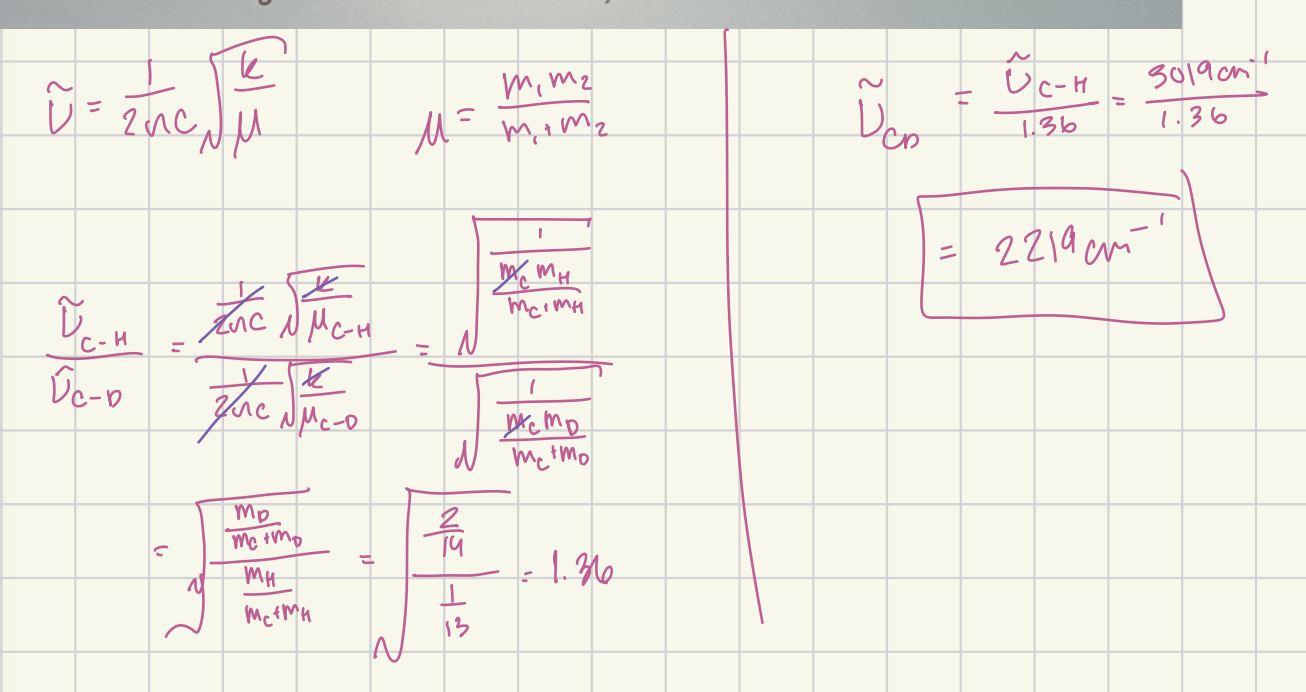
In chloroform, CHCl3, the vibration associated witht he C-H stretch occurs at a Raman shift of 3019 cm-1. In deuterated chloroform, CDCl3, how would you expect the C-D Raman stretch shift to compare to that of C-H? (Deuterated chloroform is used as a NMR solvent)
2219 cm-1
What is the absorption frequency of in a 2.4 T magnetic field of 1H? in MHz
100 MHz
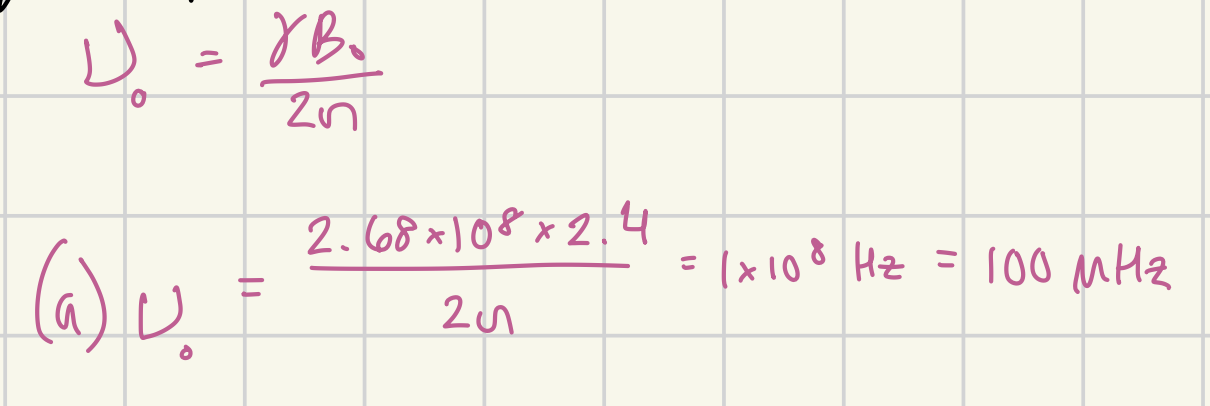
What is the absorption frequency of in a 2.4 T magnetic field of 13C? In MHz
26 MHz
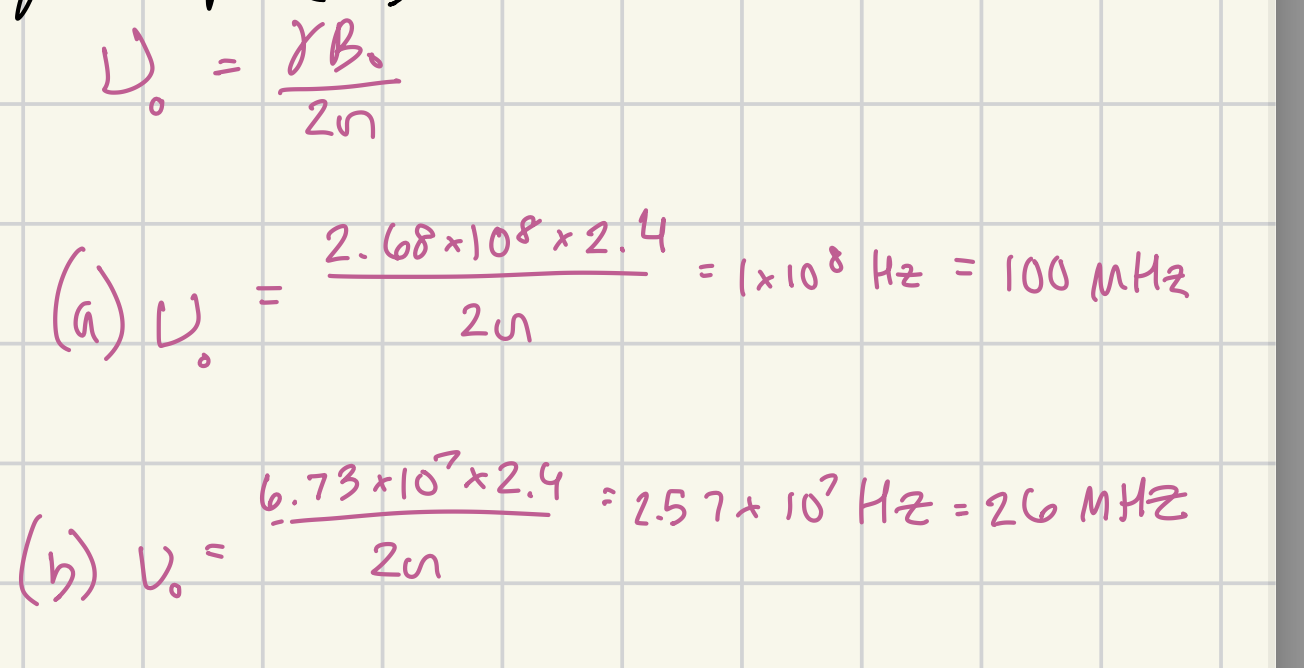
Calculate the relative number of 13C nuclei in the higher and lower magnetic states at 25ºC in 2.4 T magnetic field.
4.1 ppm
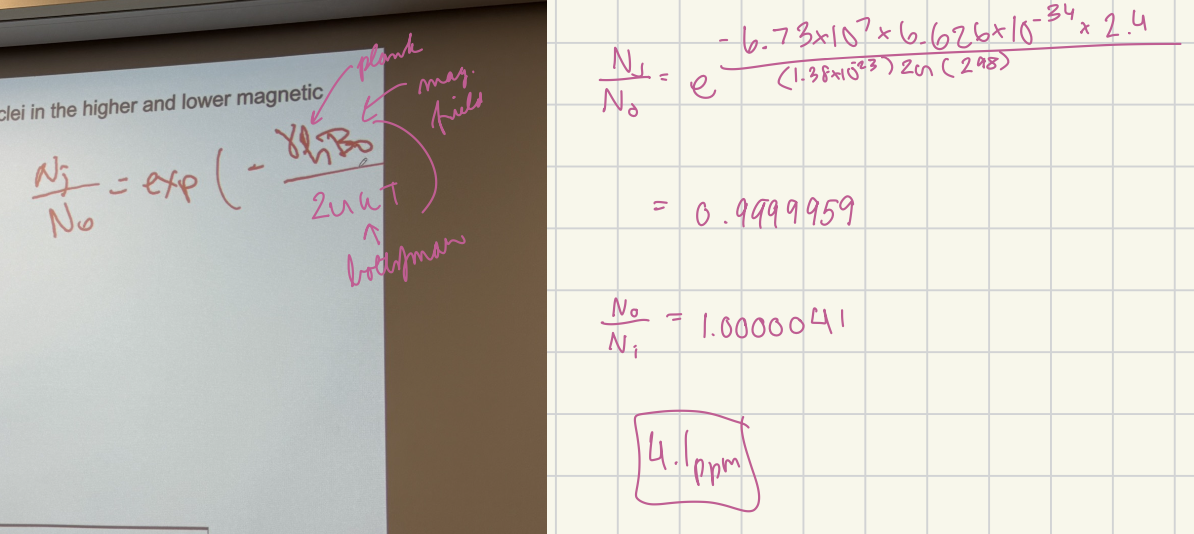
Using ethanol, C2H6O, determine the ratio of spin-active 1H to 13C nuclei for a given sample.
270

Determine the ratio of spin-active 1H to 13C nuclei in chloro(methyl)amine (CH3NHCl)
360


Assuming the noise is the same for 1H and 13C NMR, how many additional experiments (data sets) would you need to perform in a signal averaging experiment in order to obtain the same signal-to-noise (S/N) ratio in your 13C-NMR as you would in your 1H-NMR? Based on part A
129,600 scans
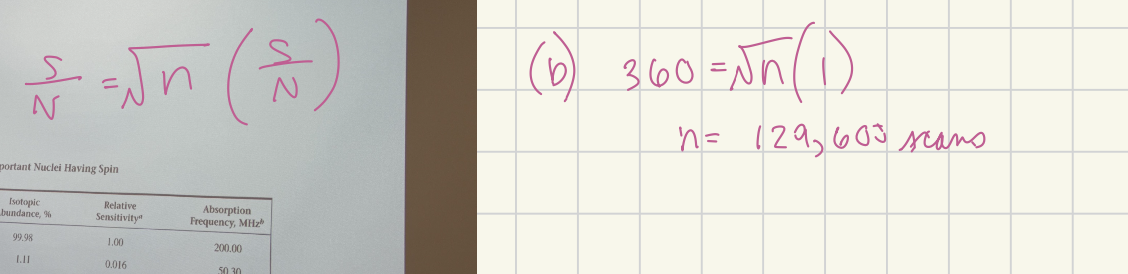
Predict the appearance of the high-resolution proton NMR spectrum of acetone (CH3C(=O)CH3) (shift (multiplicity)…)
2.1 (singlet)
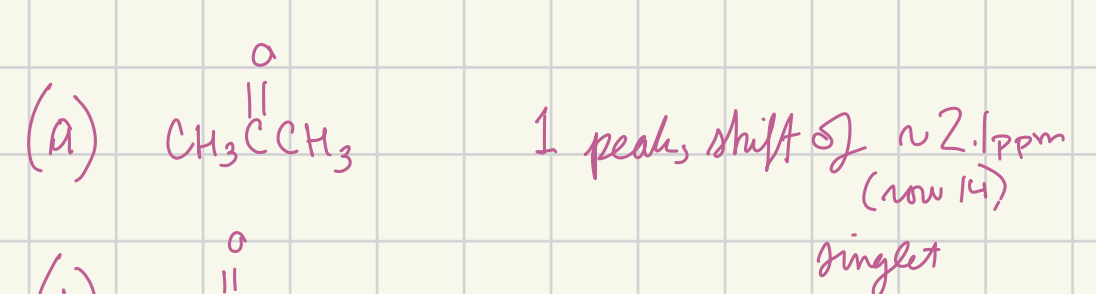
Predict the appearance of the high-resolution proton NMR spectrum of acetaldehyde (CH3C(=O)H) (shift (multiplicity)…)
2.2 (doublet), 9.7 (quartet)

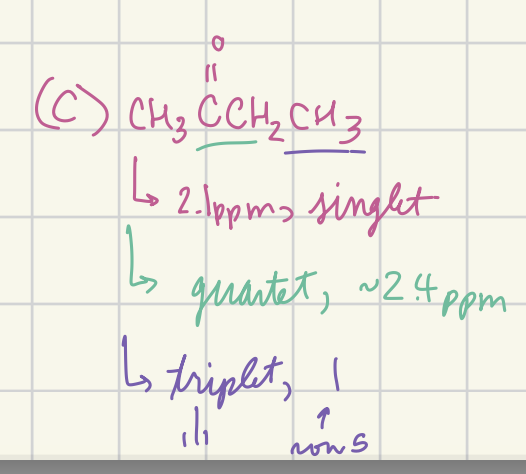
Predict the appearance of the high-resolution proton NMR spectrum of methyl ethyle ketone (CH3C(=O)CH2CH3) (shift (multiplicity)…)
2.1 (singlet), 2.4 (quartet), 1 (triplet)
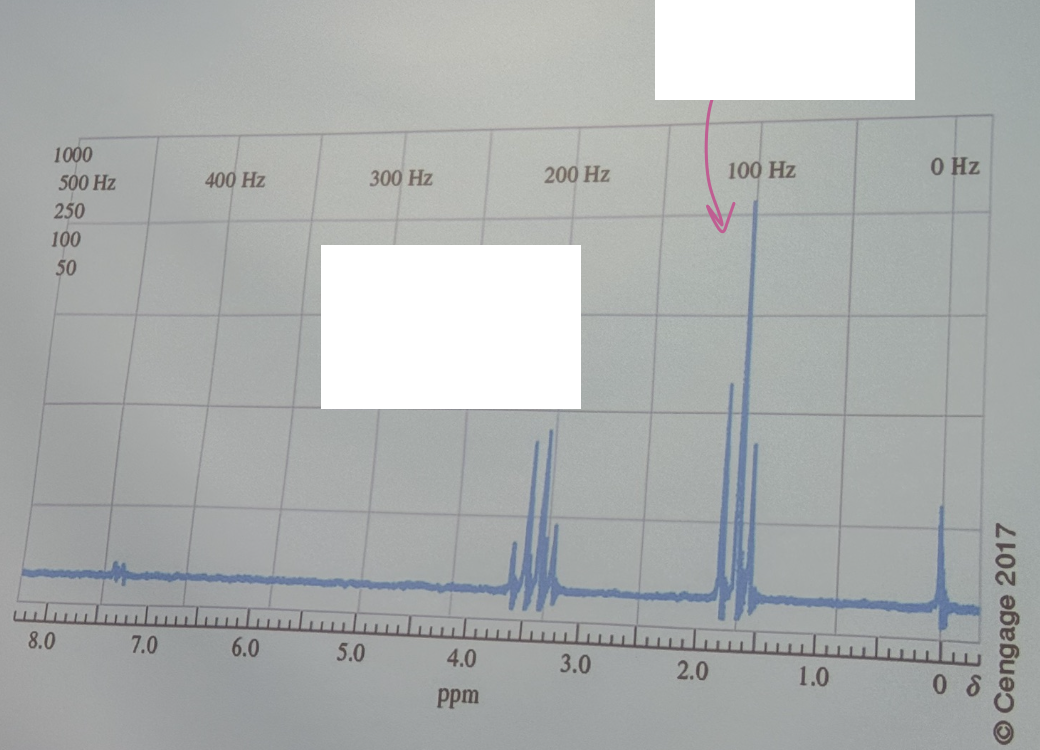
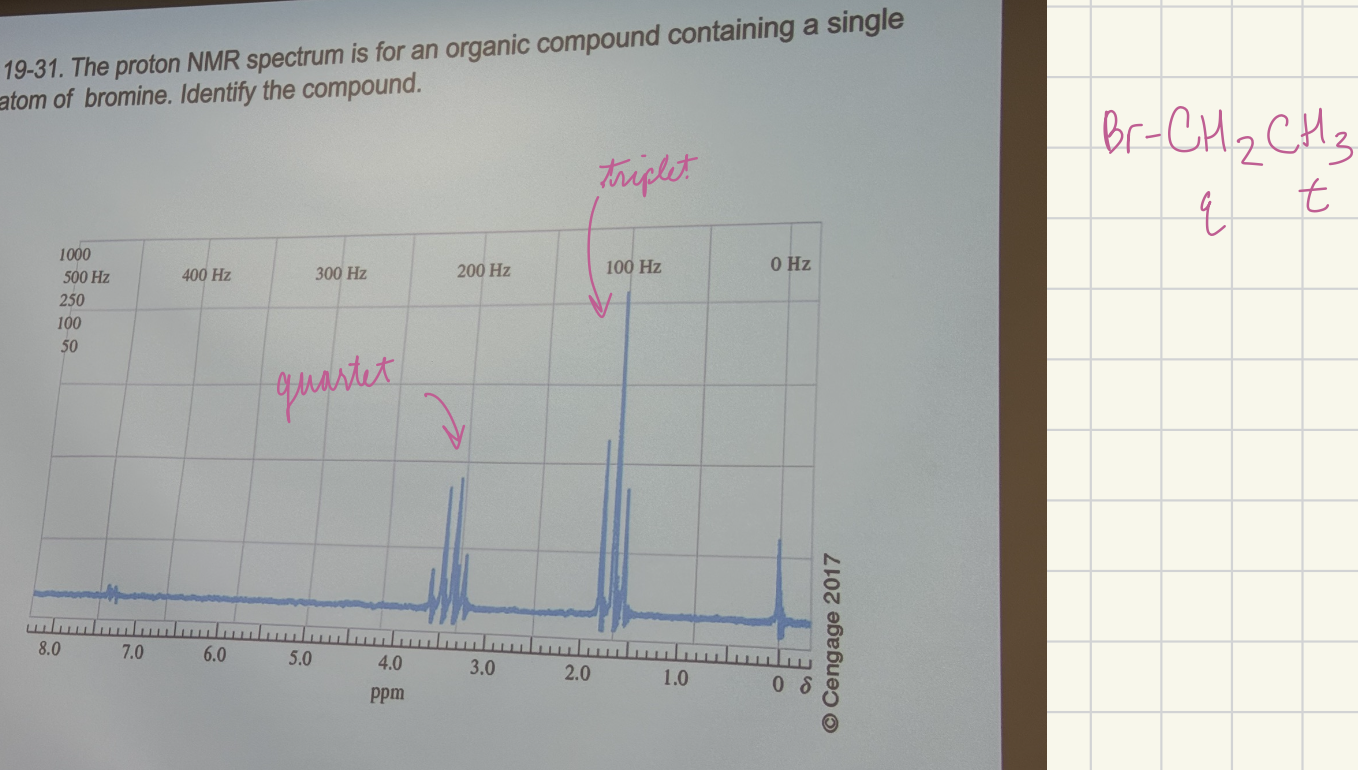
The proton NMR spectrum is for an organic compound containing a single atom of bromine. Identify the compound (begin with Br)
Br-CH2CH3
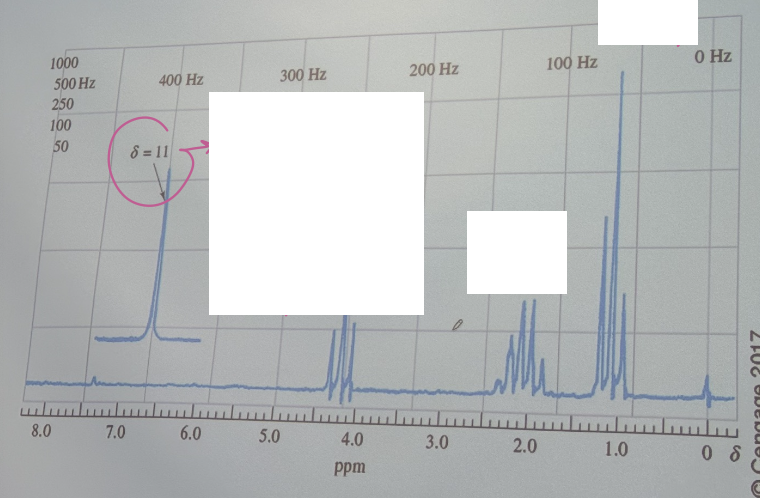
The proton NMR spectrum for a compound having an empirical formula C4H7BrO2. Identify the compound.
CH3CH2C(-Br)HCOOH
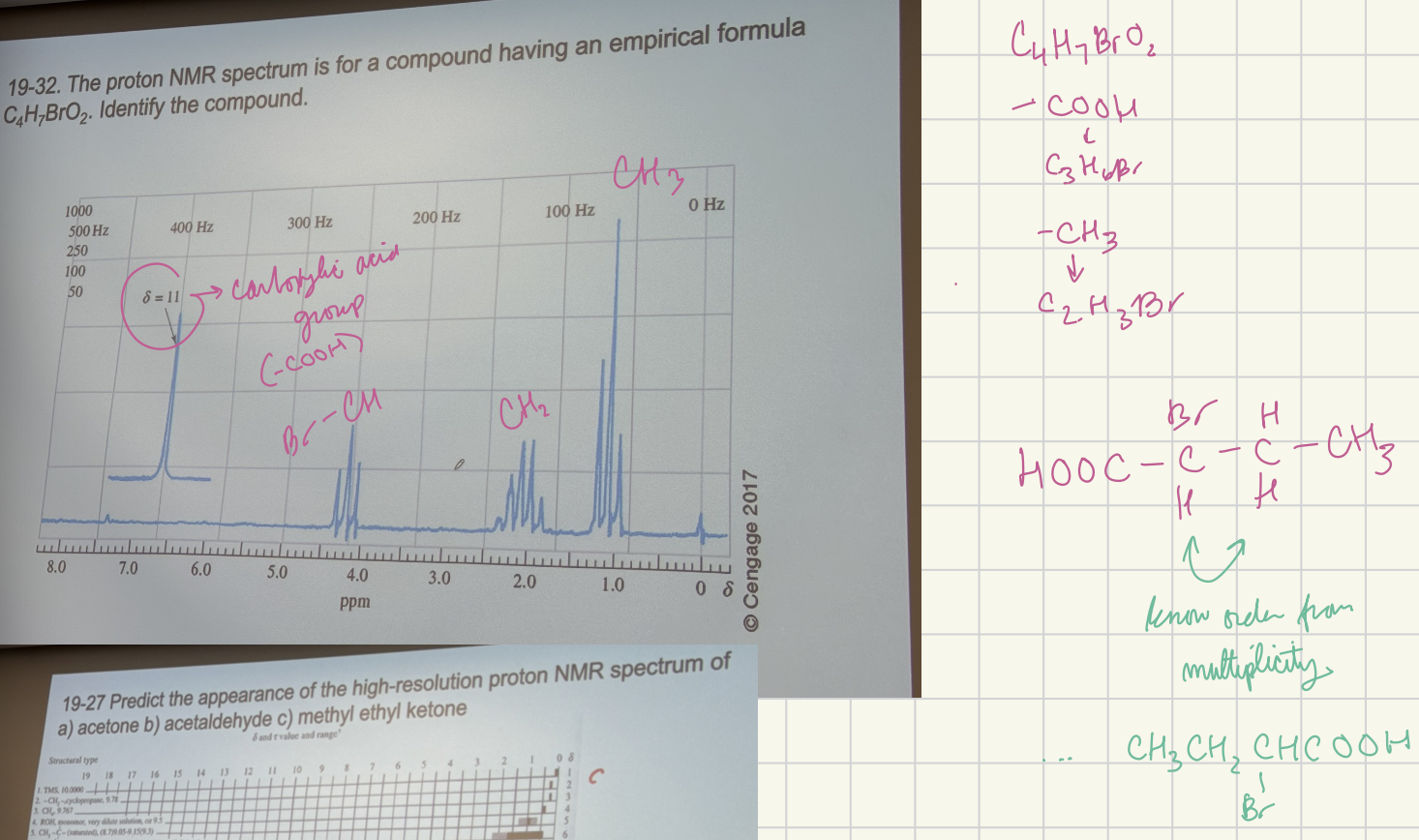
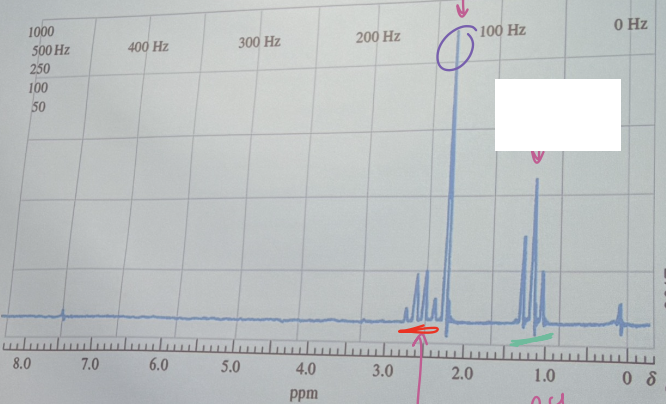
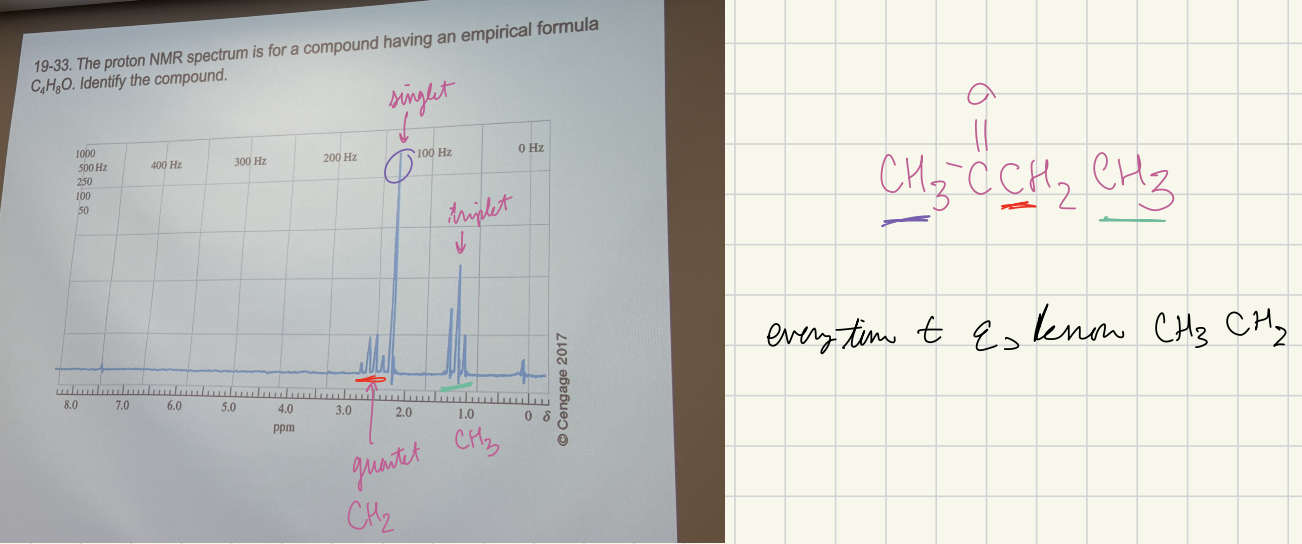
The proton NMR spectrum for a compound having an empirical formula C4H8O. Identify the compound.
CH3C(=O)CH2CH3
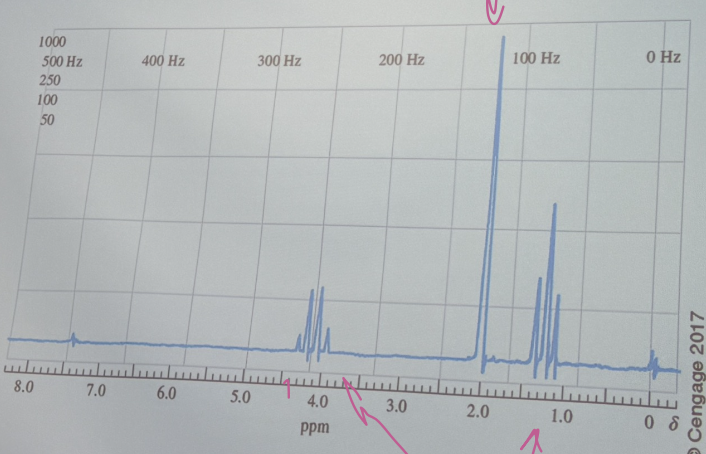
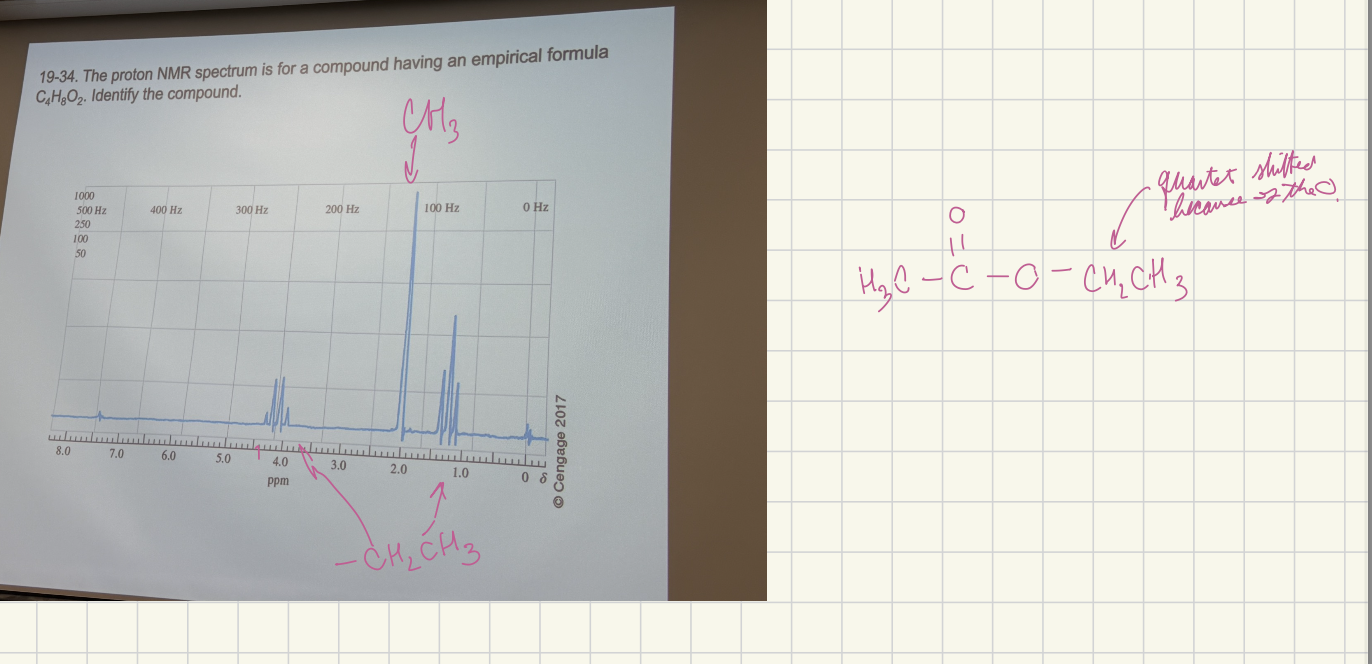
The proton NMR spectrum for a compound having an empirical formula C4H8O2. Identify the compound.
H3CC(=O)OCH2CH3
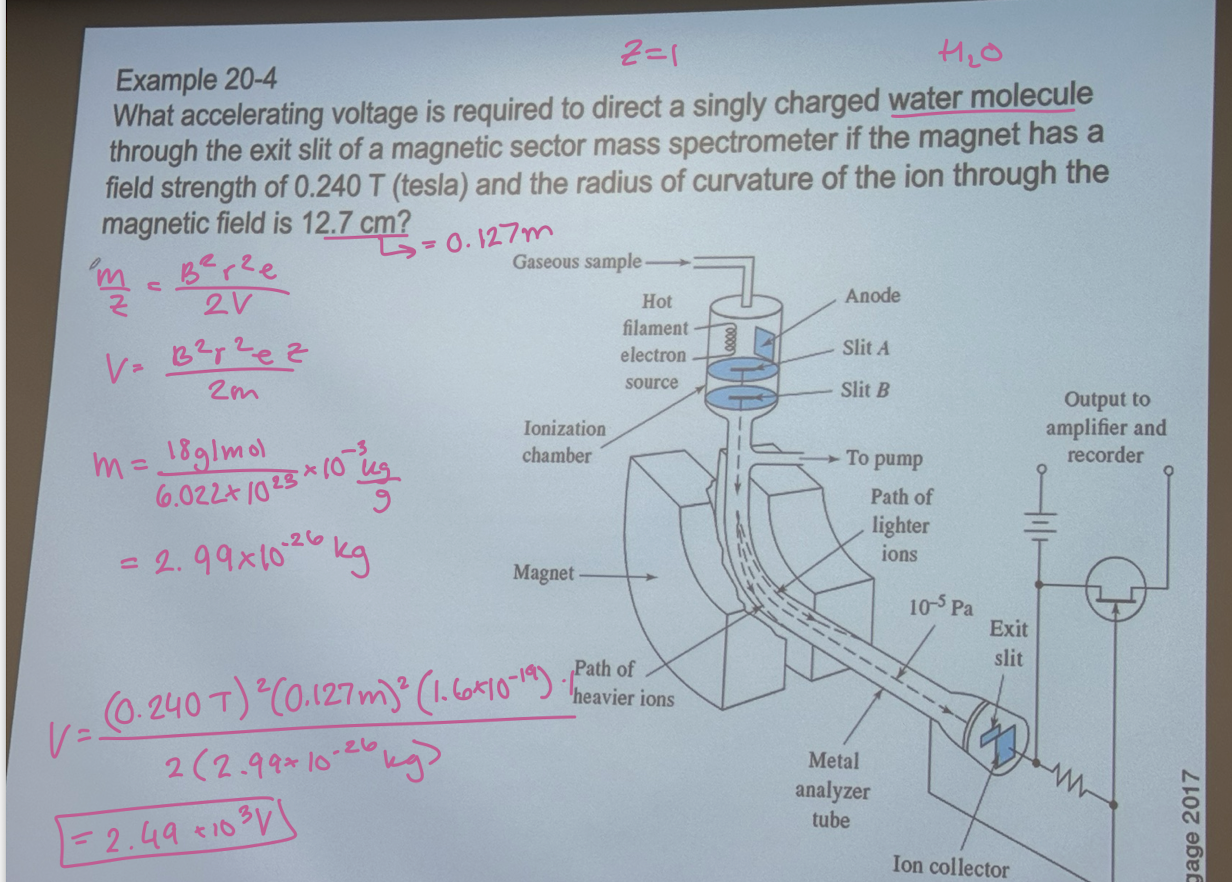
When accelerating voltage is required to direct a singly charged water molecule through the exit slit of a magnetic sector mass spectrometer if the magnet has a field strength of 0.240 T and the radius of curvature of the ion through the magnetic field is 12.7 cm?
2.49 × 10³ V

Calculate the accelerating voltage that would be required to direct singly charged ions of mass 10,000 g/mol through an instrument that is identical to the one described in example 20-4.
4.48 V
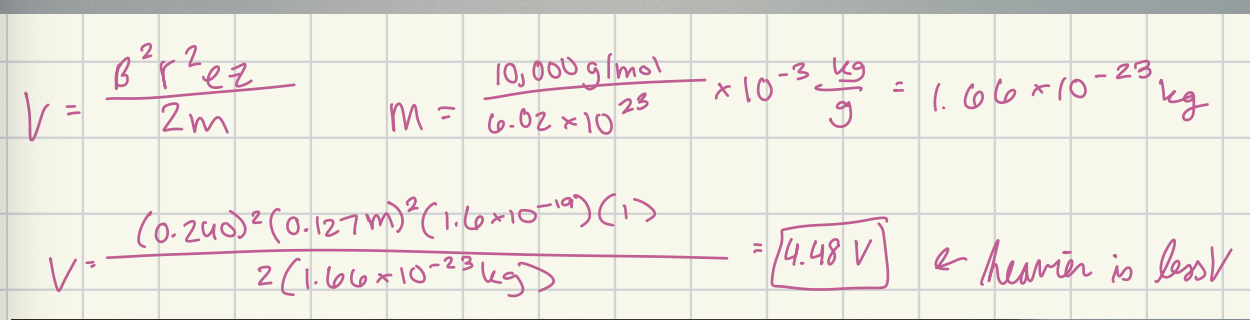
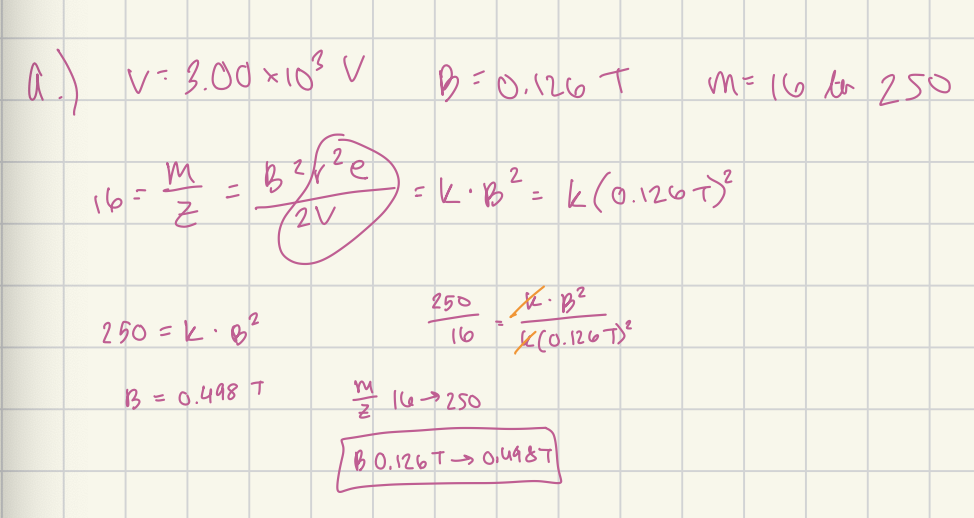
When a magnetic sector instrument was operated with an accelerating voltage of 3.00 × 10³ V, a field of 0.126 T was required to focus the CH4+ on the detector.
(A) What range of field strengths would be required to scan the mass range between 16 and 250, for singly charged ions, if the accelerating voltage is held constant?
0.126 - 0.498 T
When a magnetic sector instrument was operated with an accelerating voltage of 3.00 × 10³ V, a field of 0.126 T was required to focus the CH4+ on the detector.
(B) What range of accelerating voltages would be required to scan the mass range between 16 and 250, for singly charged ions, if the field strength is held constant?
3000 - 192 V

The ion-accelerating voltage in a particular quadrupole mass spectrometer is 5.00 V. How long will it take a singly charged benzene ion to travel the 15.0 cm length of the rod assembly? Assume the initial velocity of the ion in the z direction is zero. Answer in microseconds
42.7 microseconds
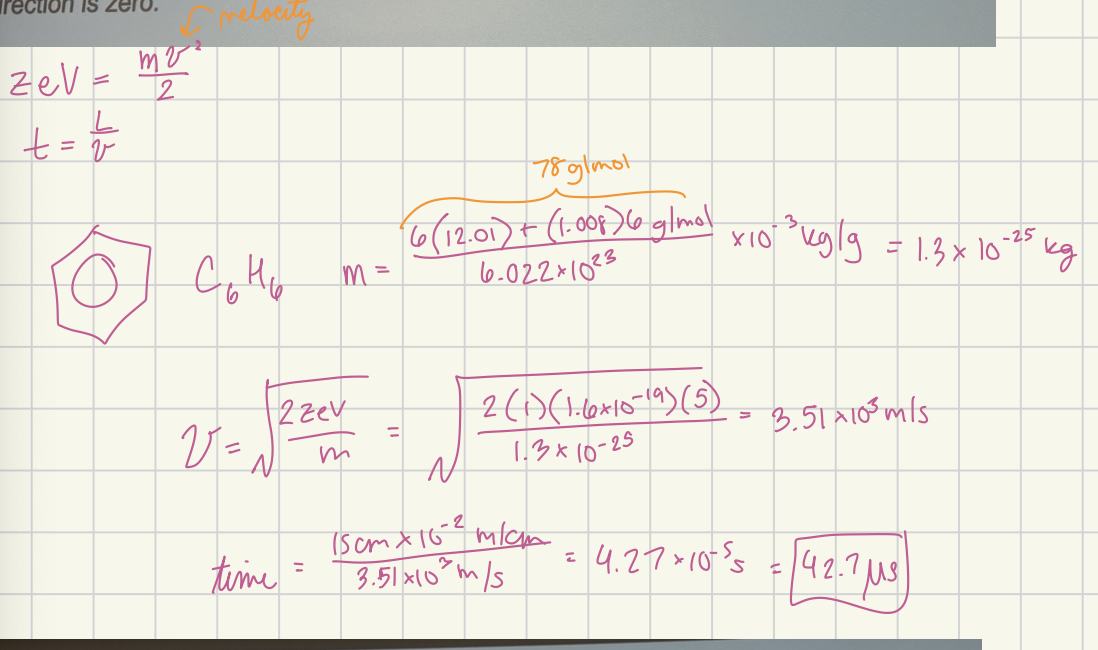

The following igure is a simplified diagram of a commerically available electron-impact source.
(A) What voltage must be applied between the filament and target so that electrons interacting with molecules at the point marked SS (sample source) will have 70 eV of kinetic energy?
140
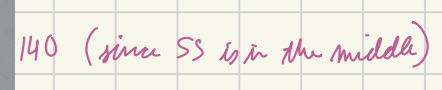

In fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance (FT-ICR) mass spectrometer, a singly charged ion is moving in a magnetic field of strength B = 3.0 T. The detected signal in the frequency domain corresponds to a cyclotron frequency of fc = 500 kHz. Determine the mass of the ion in Daltons.
(A) convert the cyclotron frequency to angular frequency (omegac)
3.14 × 10^6 rad/s

In fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance (FT-ICR) mass spectrometer, a singly charged ion is moving in a magnetic field of strength B = 3.0 T. The detected signal in the frequency domain corresponds to a cyclotron frequency of fc = 500 kHz. Determine the mass of the ion in Daltons.
(B) Relating angular frequency to mass (answer in kg)
1.53 × 10^-25 kg
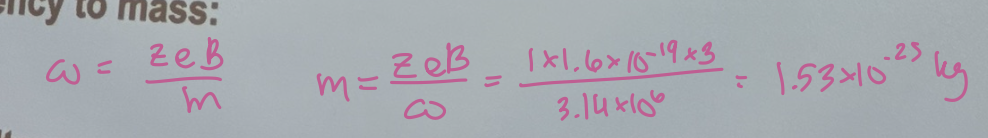

In fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance (FT-ICR) mass spectrometer, a singly charged ion is moving in a magnetic field of strength B = 3.0 T. The detected signal in the frequency domain corresponds to a cyclotron frequency of fc = 500 kHz. Determine the mass of the ion in Daltons.
(C) Convert the mass to Daltons:
92 Daltons
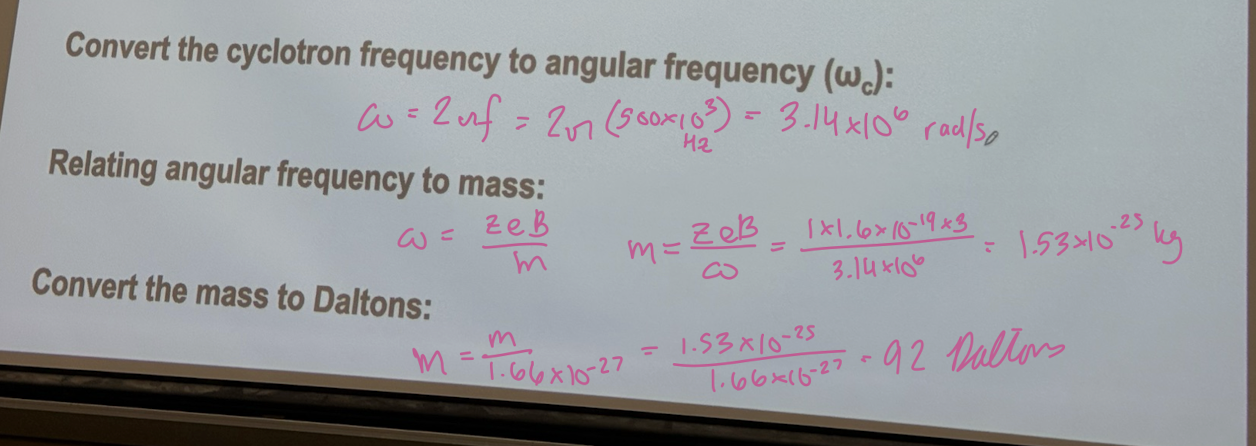
Calculate the resolution required to resolve peaks:
(A) CH2N+ (M=28.0187) and N2+ (M=28.0061)
2.22 × 10³
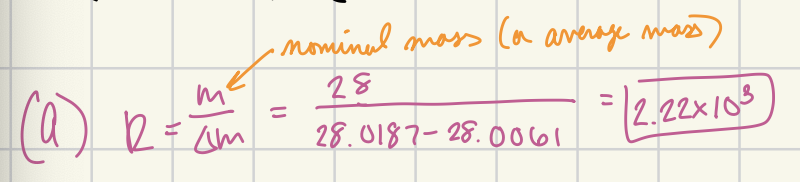
Calculate the resolution required to resolve peaks:
(B) C2H4+ (M=28.0313) and CO+ (M=27.9949)
769
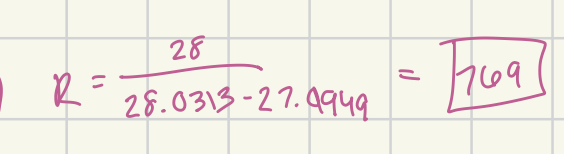
Calculate the ratio of the (M+2)+ to M+ peak heights for C10H6Br2.
1.96
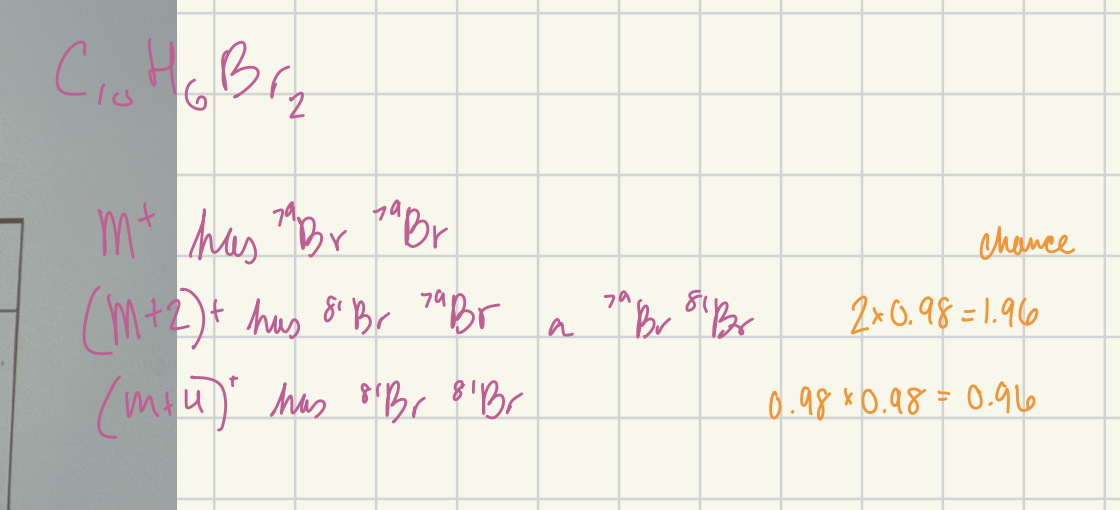
Calculate the ratio of the (M+4)+ to M+ peak heights for C10H6Br2.
0.96
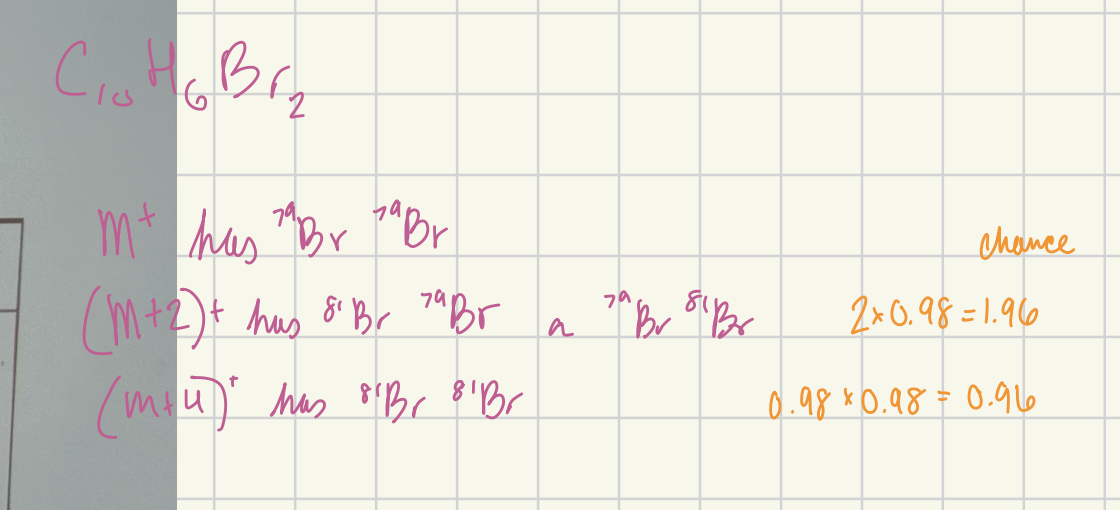
Using a diode laser with emission at 785 nm as a source, you measure a Stokes Raman signal at lambda = 833.5 nm in a sample of gasoline. If you moved to a different laboratory where the source is an argon ion laser (488 nm), at what wavelength would you measure the Stokes Raman signal?
506.3 nm
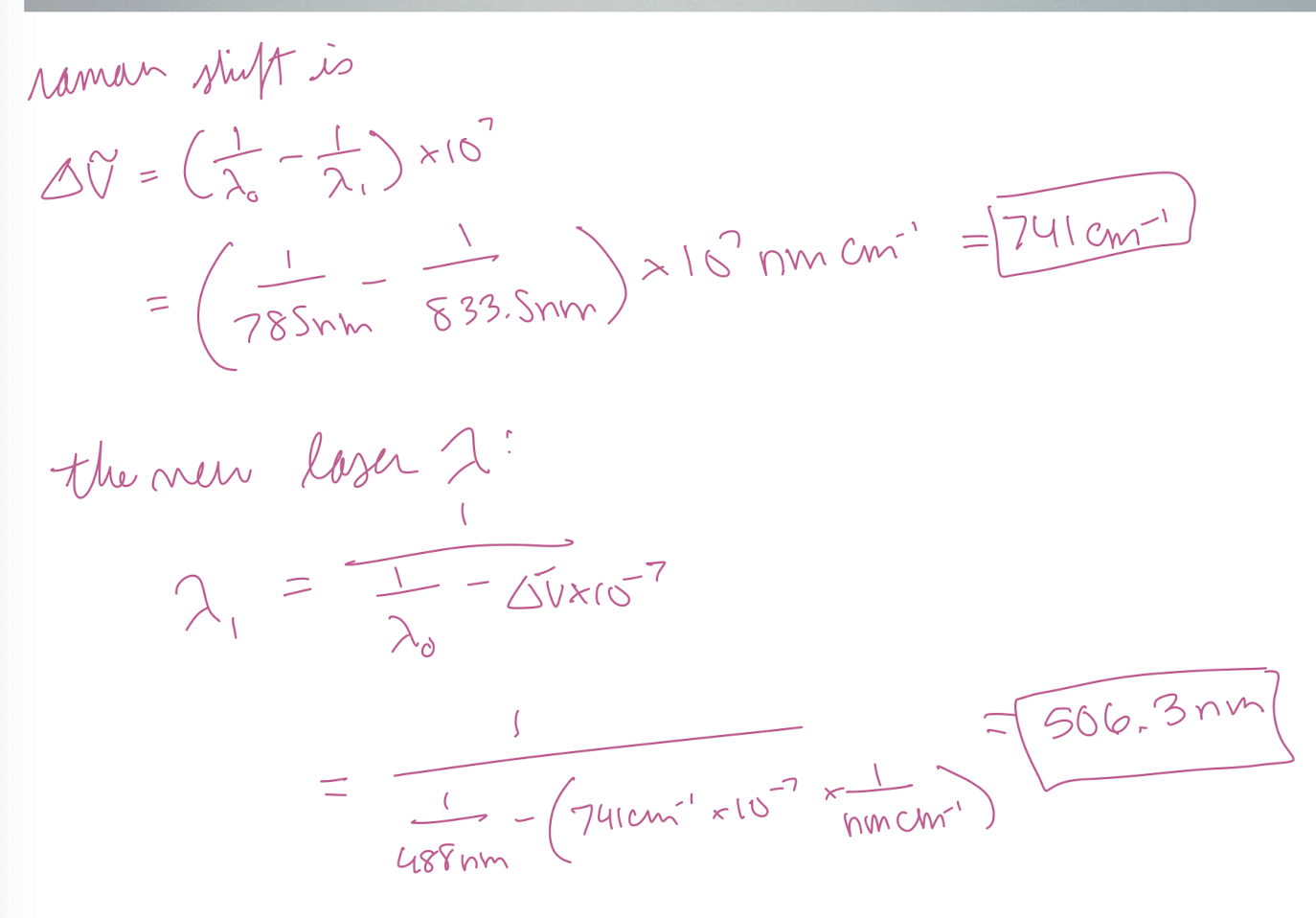
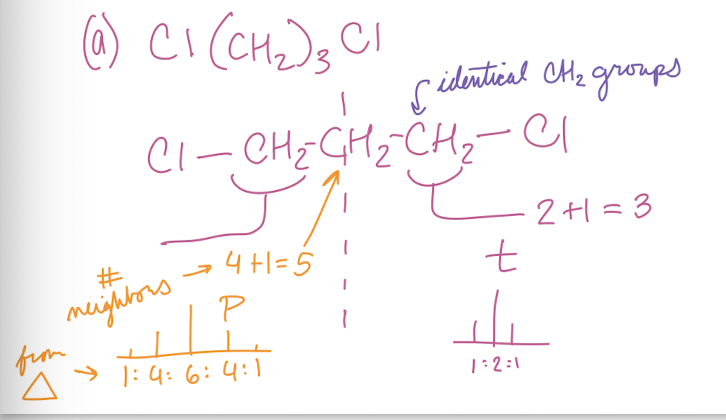
Calculate the number of multiplets for each bond
(A) Cl(CH2)3Cl
Pentet and triplet
Calculate the number of multiplets for each bond
(B) CH3C(-Br)HCH3
7 and doublet
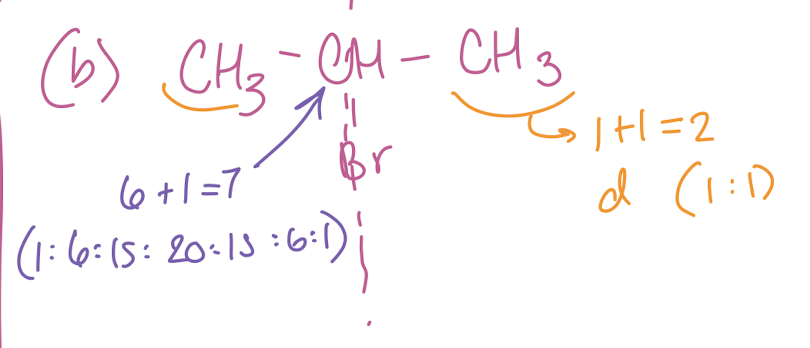
Calculate the number of multiplets for each bond
(C) CH3CH2OCH3
Triplet, quartet, singlet
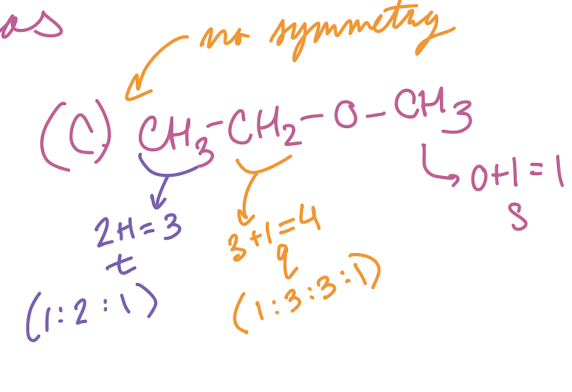
At what wavelength in nanometers would the Stokes Raman lines for carbon tetrachloride (Raman shift of 314 cm-1) appear if the source was a helium/neon laser (632.8 nm) in nm?
645.6 nm
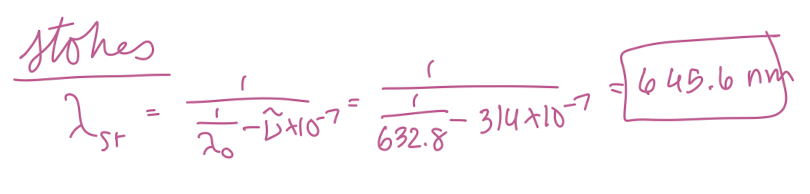
At what wavelength in nanometers would the anti-Stokes Raman lines for carbon tetrachloride (Raman shift of 314 cm-1) appear if the source was a helium/neon laser (632.8 nm) in nm?
620.5 nm
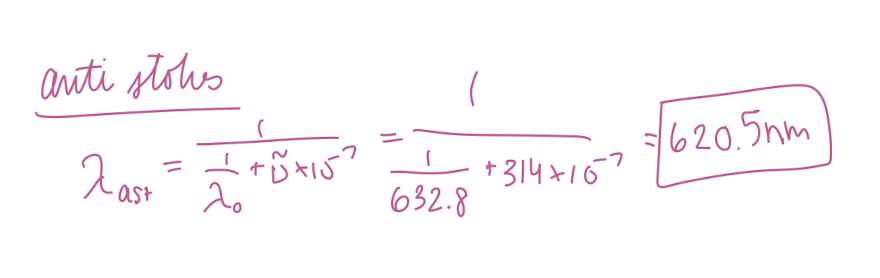
At what wavelength in nanometers would the Stokes Raman lines for carbon tetrachloride (Raman shift of 314 cm-1) appear if the source was an argon ion laser (488 nm) in nm?
495.6 nm
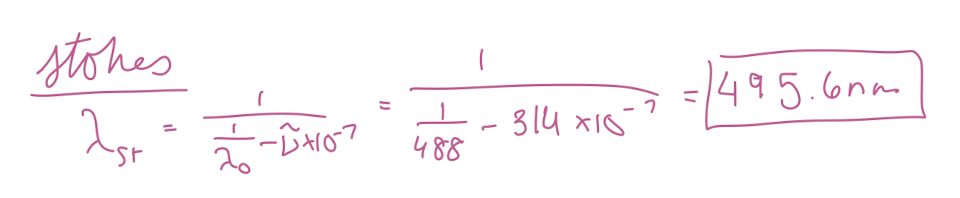
At what wavelength in nanometers would the anti-Stokes Raman lines for carbon tetrachloride (Raman shift of 314 cm-1) appear if the source was an argon ion laser (488 nm) in nm?
480.6 nm
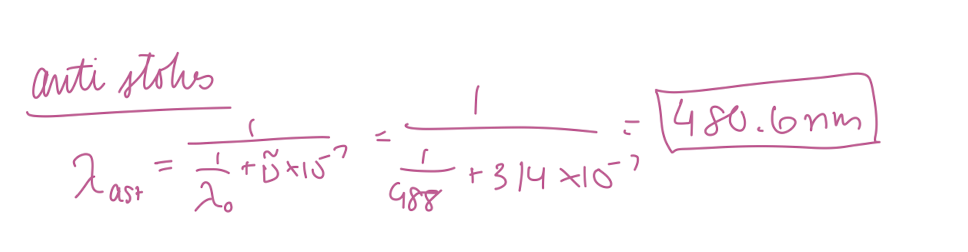
Assume the excitation sources have the same power. (He/Ne 632.8 nm and Ar 488 nm) Compare the relative intensities of the CCL4 Raman lines when each of the two excitation sources is used.
2.83
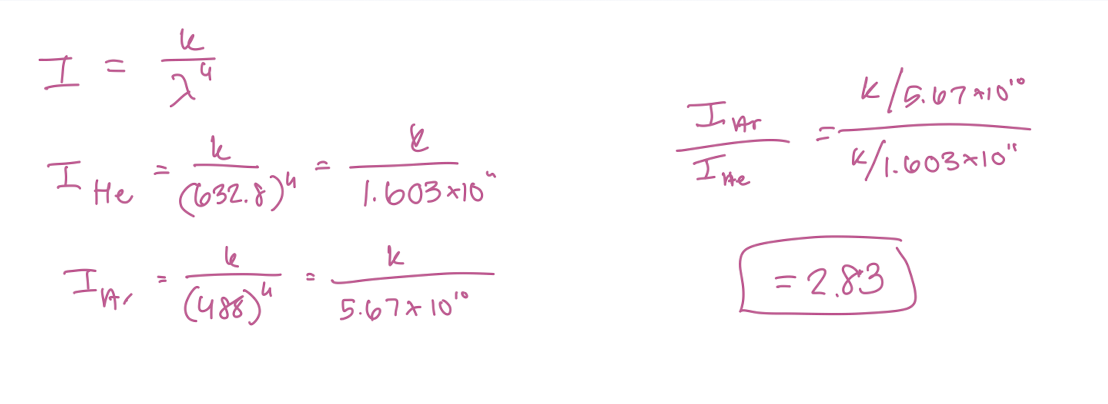
Calculate the kinetic energy that a singly charged (z=1) will acquire if it is accelerated through a potential of 10³ in an EI source in J.
1.6 × 10^-16 J
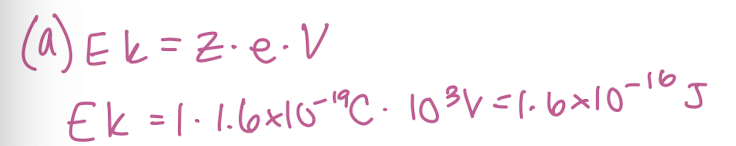
Calculate the energy (in kJ/mol) that electrons acquire as a result of being accelerated through a potential of 70 V.
6.7 × 10³ kJ/mol
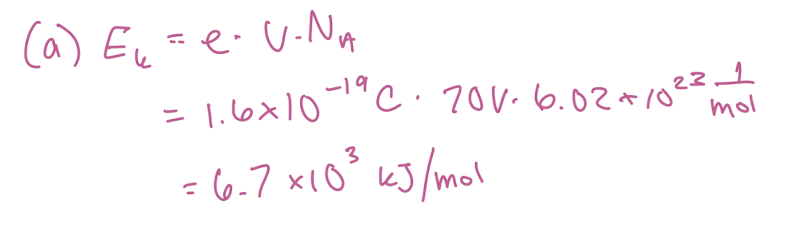
Calculate the ratio of the (M+1)+ to M+ peak heights for the following compound: C6H4N2O4 (M =168) in percent
7.44%

Calculate the ratio of the (M+1)+ to M+ peak heights for the following compound: C12H24 (M =168) in percent
13.32%
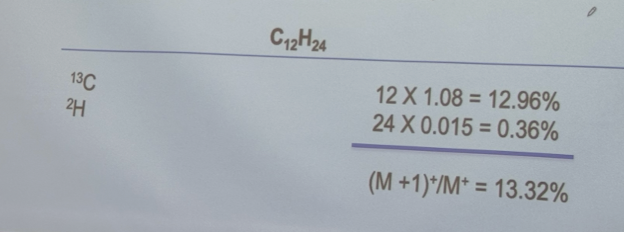
What resolution is needed to separate the ions C2H4+ and CH2N+ with masses of 28.0313 and 28.0187, respectively?
2220