Midterm Study Set Diagram | Quizlet
1/196
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
197 Terms
gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH)
• Produced and released by: Hypothalamus
• Targets: Anterior Pituitary
• Effect: regulates release of FSH & LH
thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH)
• Produced and released by: Hypothalamus
• Targets: Anterior Pituitary
• Effect: stimulates release of TSH
corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH)
• Produced and released by: Hypothalamus
• Targets: Anterior Pituitary
• Effect: stimulates release of ACTH
growth hormone releasing hormone (GHRH)
• Produced and released by: Hypothalamus
• Targets: Anterior Pituitary
• Effect: regulates release of GH
oxytocin (OT)
• Produced in: Hypothalamus
• Stored in and released from: Posterior Pituitary
• Targets: uterus and mammary glands
• Effect: stimulates uterine contractions and milk release
antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
• Produced in: Hypothalamus
• Stored in and released from: Posterior Pituitary
• Targets: Kidneys
• Effect: increases reabsorption of water (decrease urine output)
follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
• Produced and released by: Anterior Pituitary
• Targets: Ovaries & Testes
• Effect: stimulates sex hormone release and development of gametes
luteinizing hormone (LH)
• Produced and released by: Anterior Pituitary
• Targets: Ovaries & Testes
• Effect: stimulates sex hormone release and development of gametes
thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
• Produced and released by: Anterior Pituitary
• Targets: Thyroid gland
• Effect: promotes T3/T4 (thyroid hormone) secretion from follicular cells
prolactin (PRL)
• Produced and released by: Anterior Pituitary
• Targets: mammary glands and testes
• Effect: promotes milk production and release of testosterone
adrenocoricotropic hormone (ACTH)
• Produced and released by: Anterior Pituitary
• Targets: adrenal cortex
• Effect: stimulates release of cortisol from zona fasciculata
growth hormone (GH)
• Produced and released by: Anterior Pituitary
• Targets: widespread (liver and most cells)
• Effect: promotes growth and stimulates liver to release insulin-like growth factors to further promote growth of cells
testosterone
• Produced and released by: Testes
• Targets: reproductive organs and bone
• Effect: aids in development of sex characteristics and helps maintain bone density
estrogen
• Produced and released by: Ovaries
• Targets: reproductive organs and bone
• Effect: aids in development of sex characteristics and helps maintain bone density
progesterone
• Produced and released by: Ovaries
• Targets: uterus
• Effect: prepare and maintain endometrial lining
thyroid hormones (T3 and T4)
• Produced and released by: Thyroid gland
• Targets: all/most cells
• Effect: controls metabolic rates
calcitonin
• Produced and released by: Thyroid
• Targets: Bones
• Effect: regulates blood calcium by depositing excess calcium into the bones; decreases blood calcium levels
epinephrine (EPO)
• Produced in: Adrenal Medulla
• Targets: all/most cells
• Effect: prepares body for heightened level of somatic activity
cortisol
• Produced in: Adrenal Cortex (zona fasciculata)
• Targets: all/most cells
• Effect: triggers release of nutrients (glucose/fatty acids) into the blood
aldosterone
• Produced in: Adrenal cortex (zona glomerulosa)
• Targets: kidneys
• Effect: regulates concentration of sodium and potassium ions
androgens
• Produced in; Adrenal Cortex (zona reticularis)
• Targets: male and female sex organs
• Effect: aid in development of sex characteristics
glucagon
• Produced in: Pancreas (alpha islet cells)
• Targets: Liver and adipocytes
• Effect: increases blood glucose levels
insulin
• Produced in: Pancreas (beta islet cells)
• Targets: all over (not required in brain, liver, kidneys and RBCs)
• Effect: decreases blood glucose levels
parathyroid hormone
• Produced in: Parathyroid
• Targets: bones and kidneys
• Effect: increases blood calcium levels
thyroid gland
endocrine gland that surrounds the trachea in the neck; produces TH and calcitonin
pituitary gland
gland that can be split into anterior and posteior parts; anterior produces TSH, PRL, GH, FSH, LH, and ACTH; posterior stores and releases OT and ADH
parathyroid glands
any one of four endocrine glands on the posterior side of the thyroid gland that produces and secrete PTH
pancreas
organ involved in regulation of glucose levels in the blood and produces digestive enzymes; produces hormones insulin and glucagon
ovaries (singular: ovary)
glands that produce and release estrogen and progesterone
testes (singular: testis)
glands that produce and release testosterone
hypothalamus
gland that produces releasing and inhibiting hormones; controls release of hormones from pituitary glands
adrenal gland
a pair of endocrine glands that sit just above the kidneys that produce aldosterone, cortisol, androgens, and epinephrine
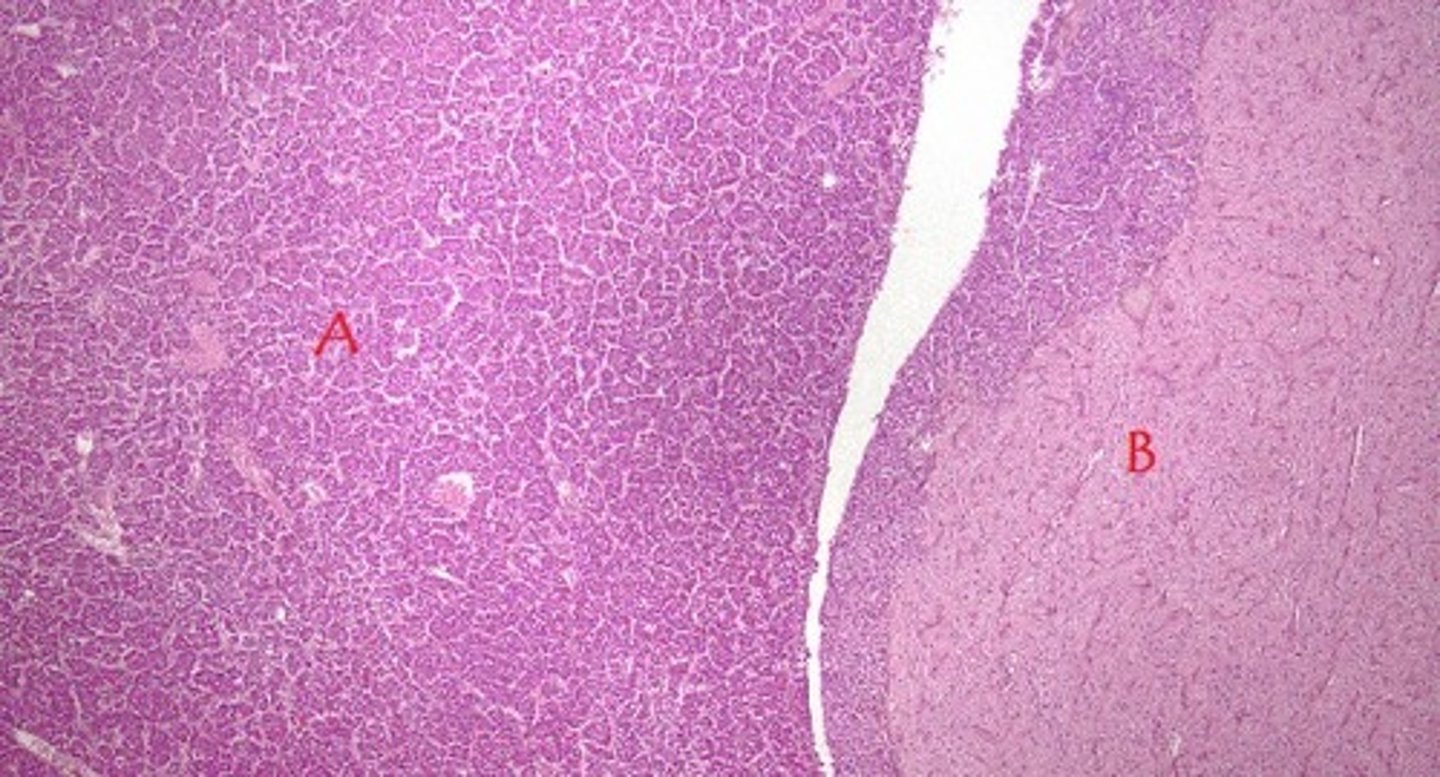
anterior pituitary gland
A in the image
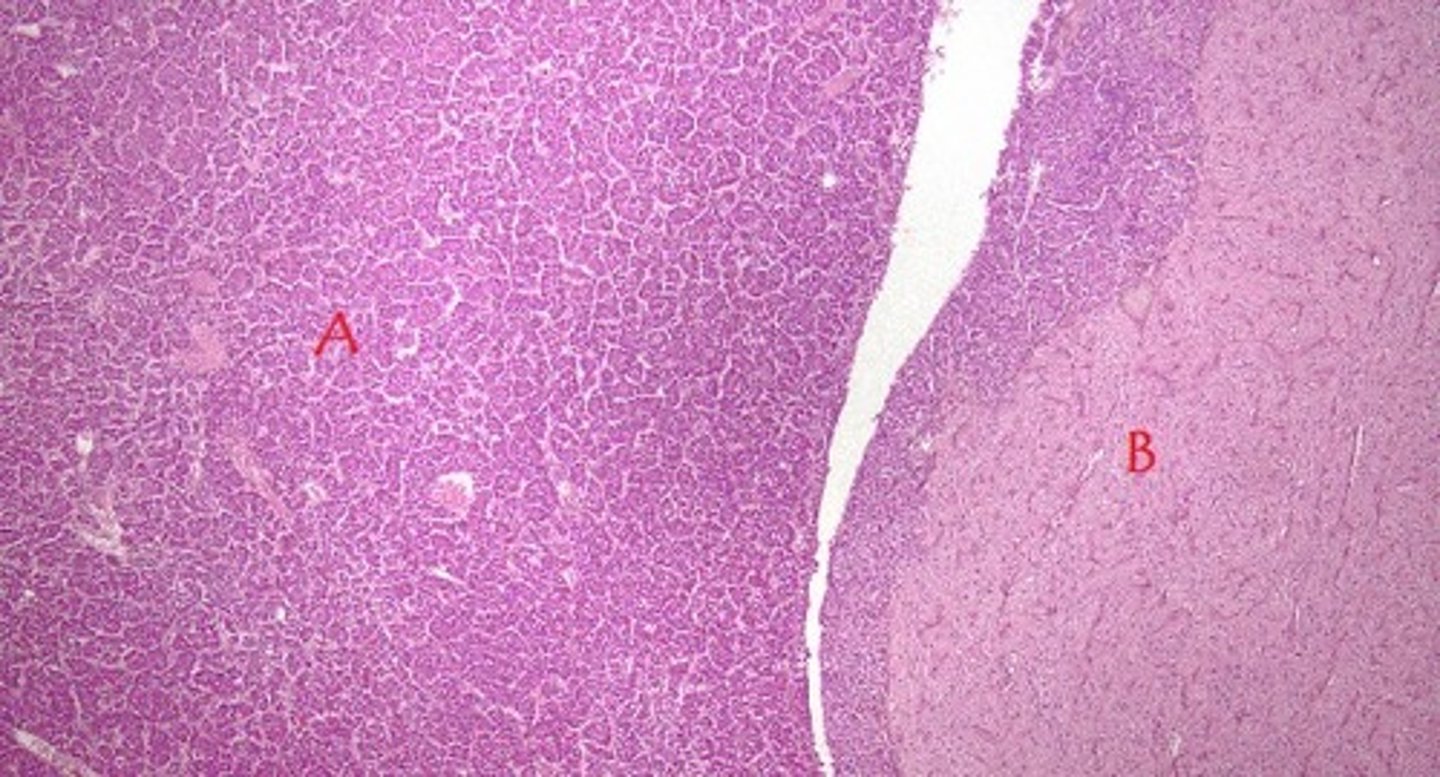
posterior pituitary gland
B in the image
hormones released from the hypothalamus
CRH, TRH, GnRH, GHRH
hormones released from the anterior pituitary gland
GH, FSH, LH, ACTH, TSH, PRL
hormones released from posterior pituitary
ADH and OT
parafollicular cells of thyroid gland
produce and secrete calcitonin
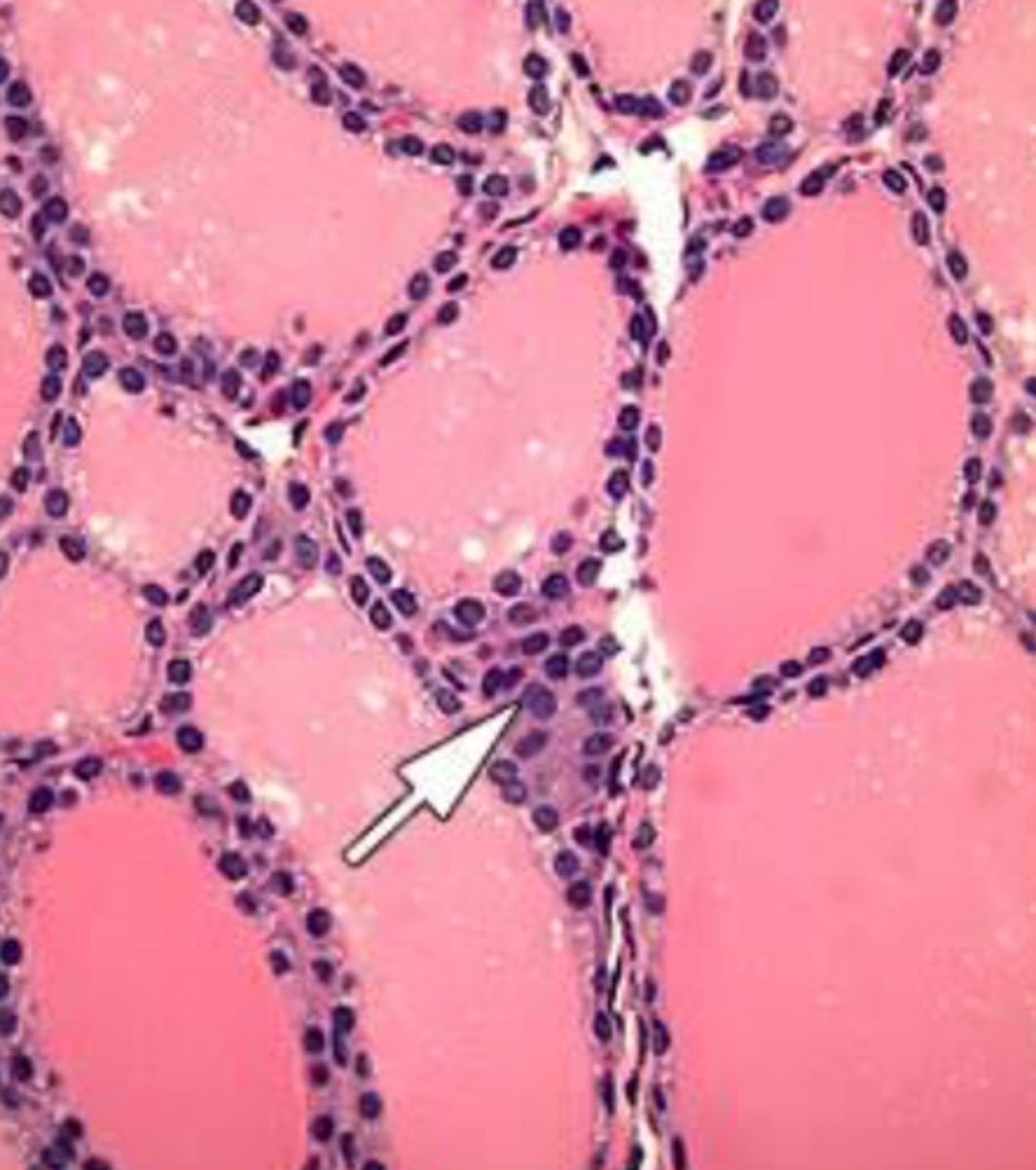
follicular cells of thyroid gland
produce and secrete TH (T3 and T4)
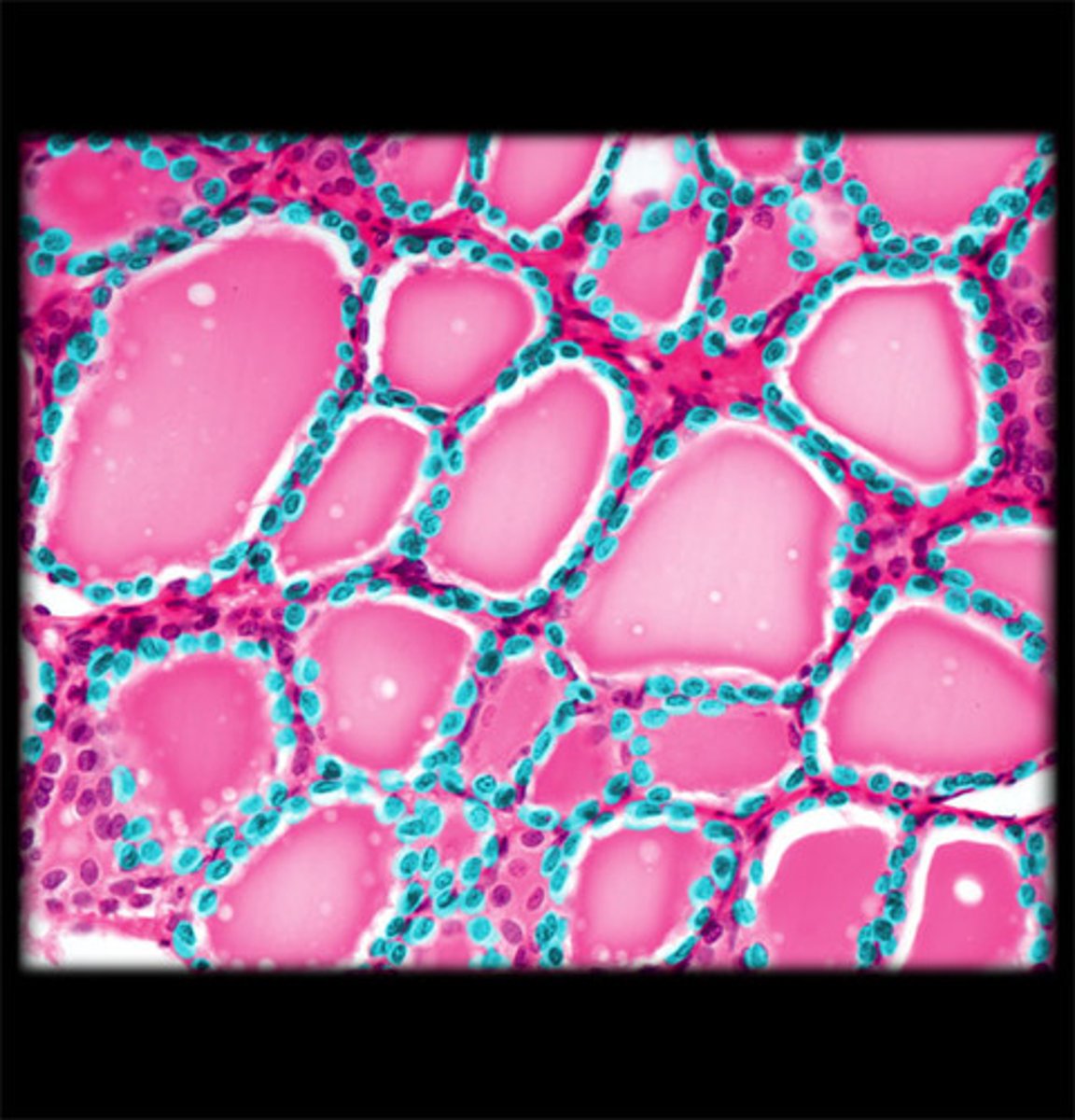
follicle of thyroid gland
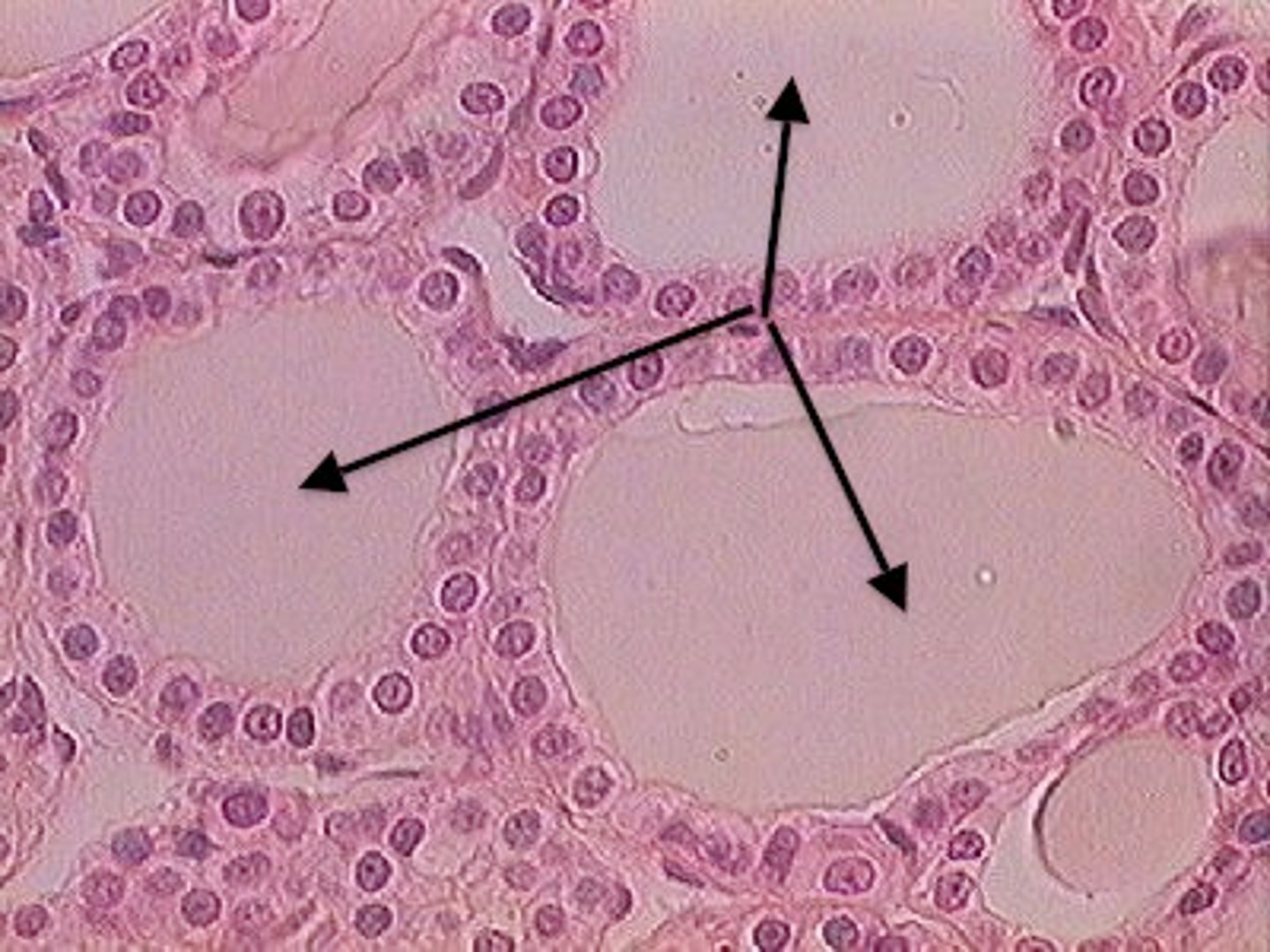
chief cells of parathyroid gland
produce and secrete PTH
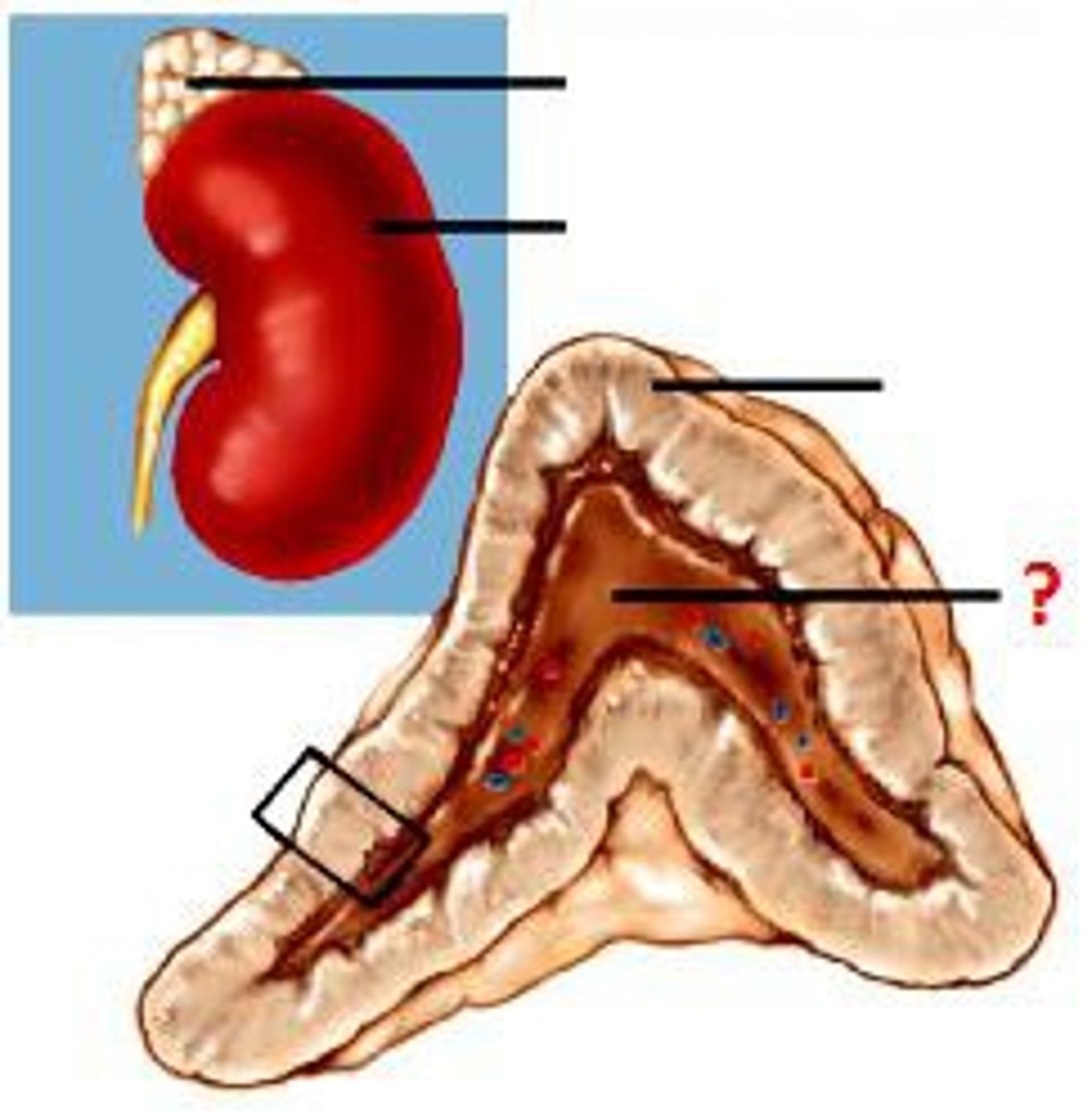
adrenal cortex
outer section of each adrenal gland; produces cortisol, aldosterone, and androgens; split into 3 zones (zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata, and zona reticularis)
zona glomerulosa
produces aldosterone
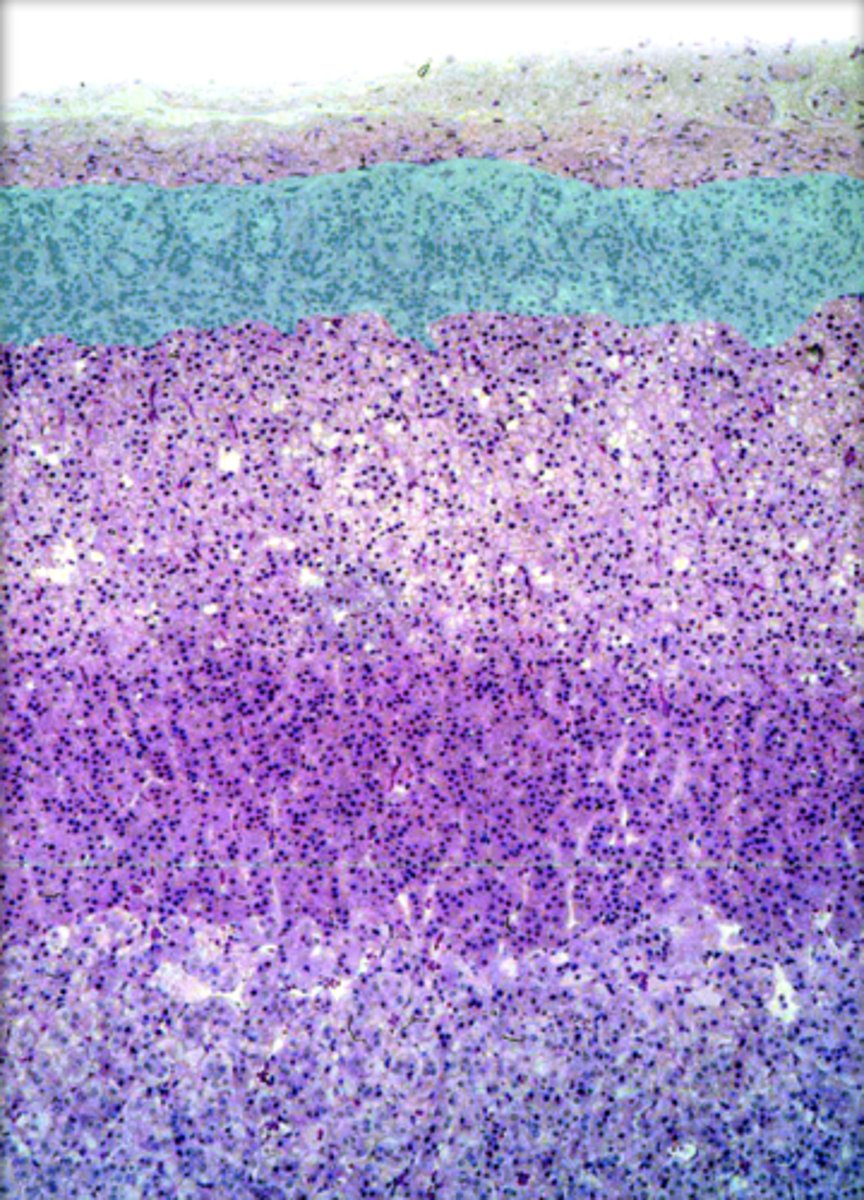
zona fasciculata
produces cortisol
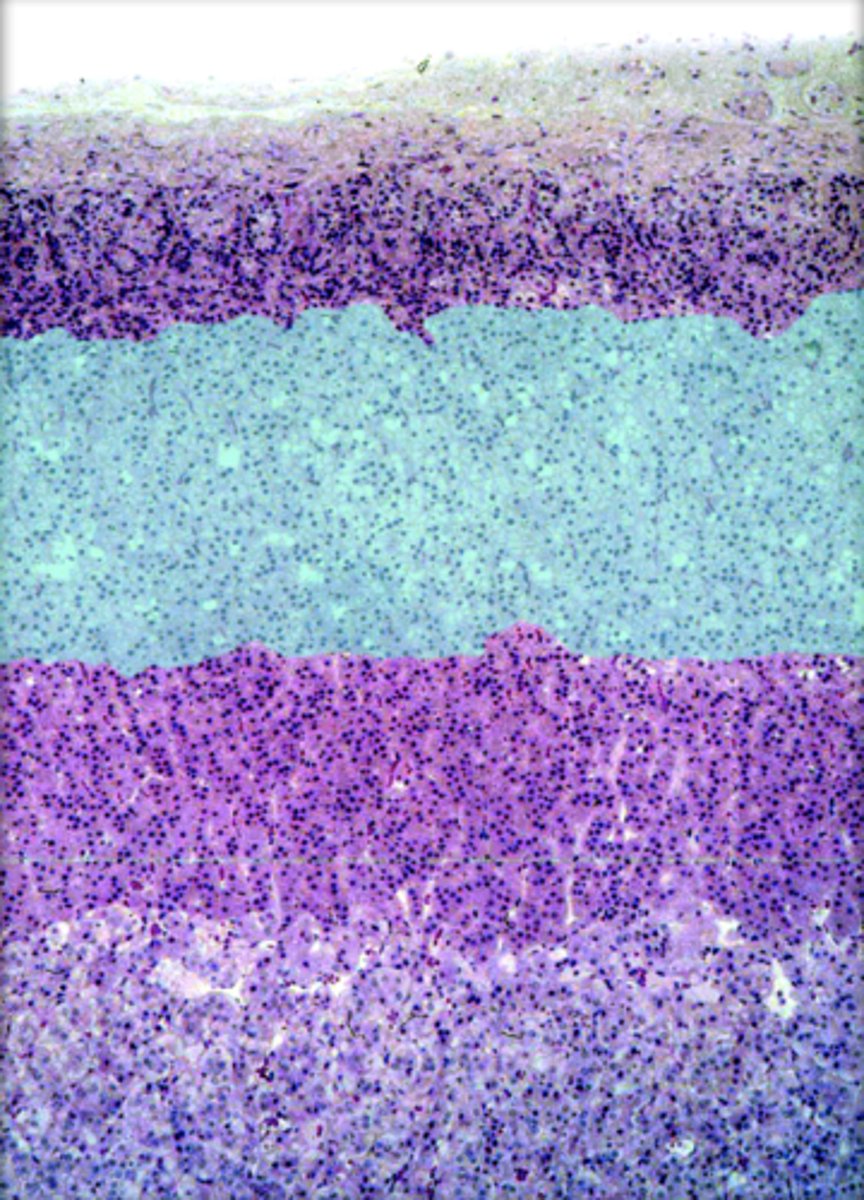
zona reticularis
produces androgens
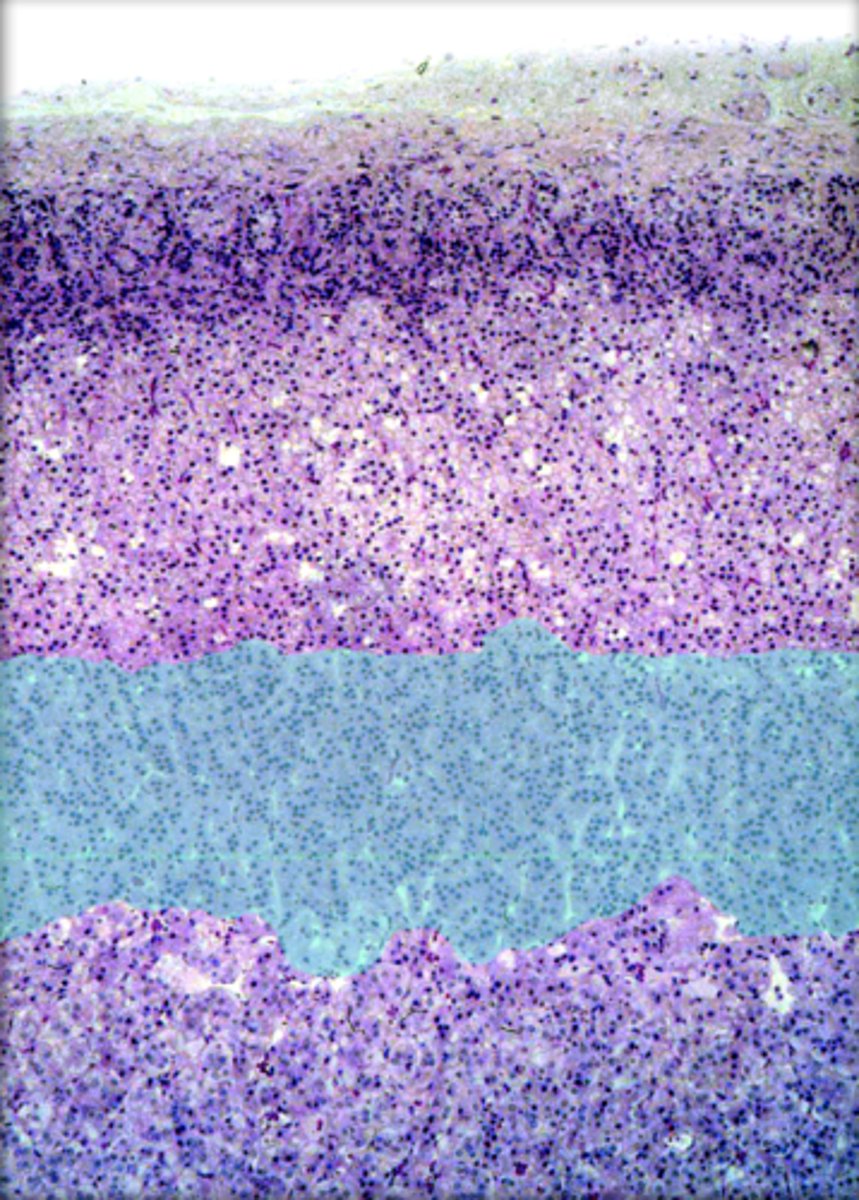
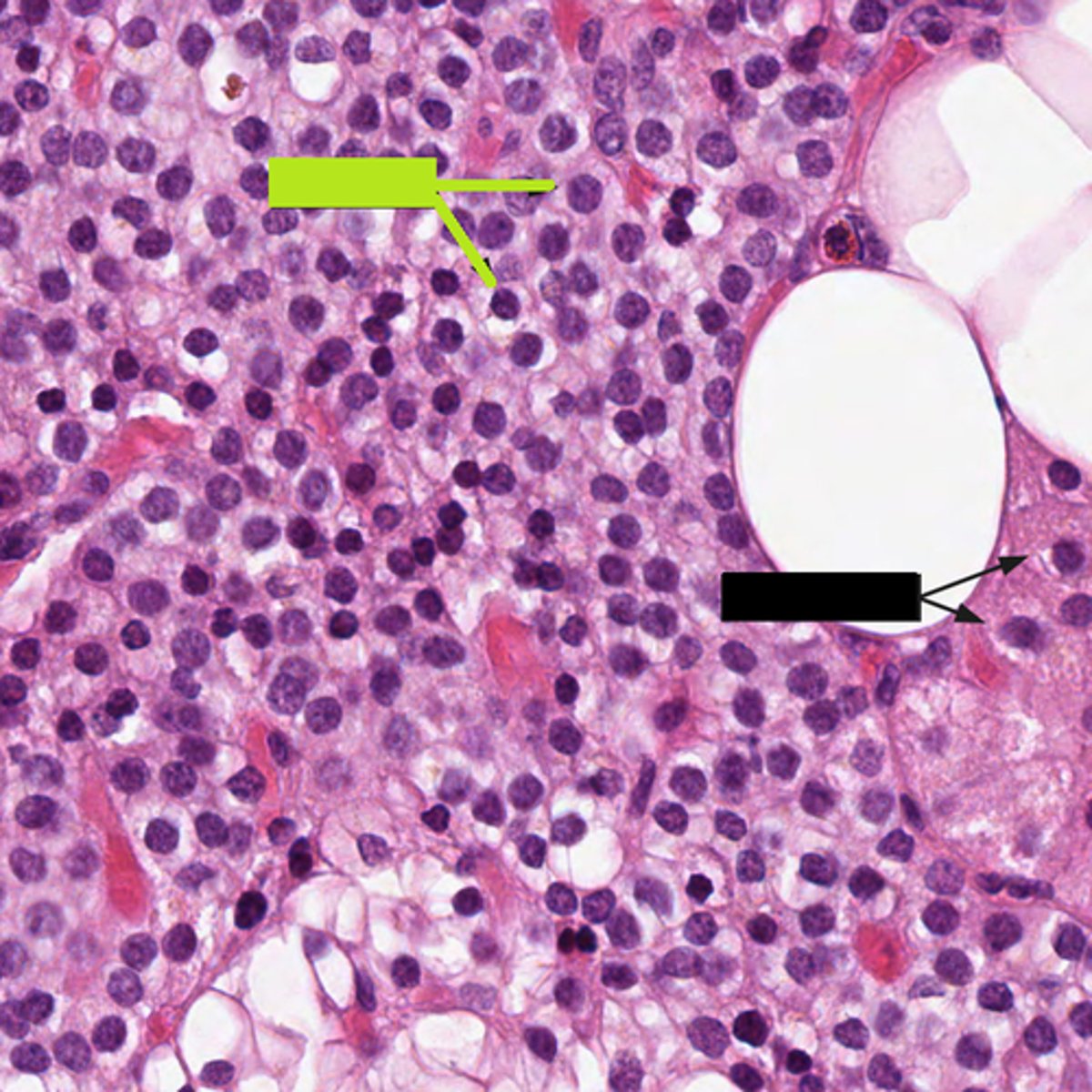
adrenal medulla
inner section of each adrenal gland; produces epinephrine and norepinephrine
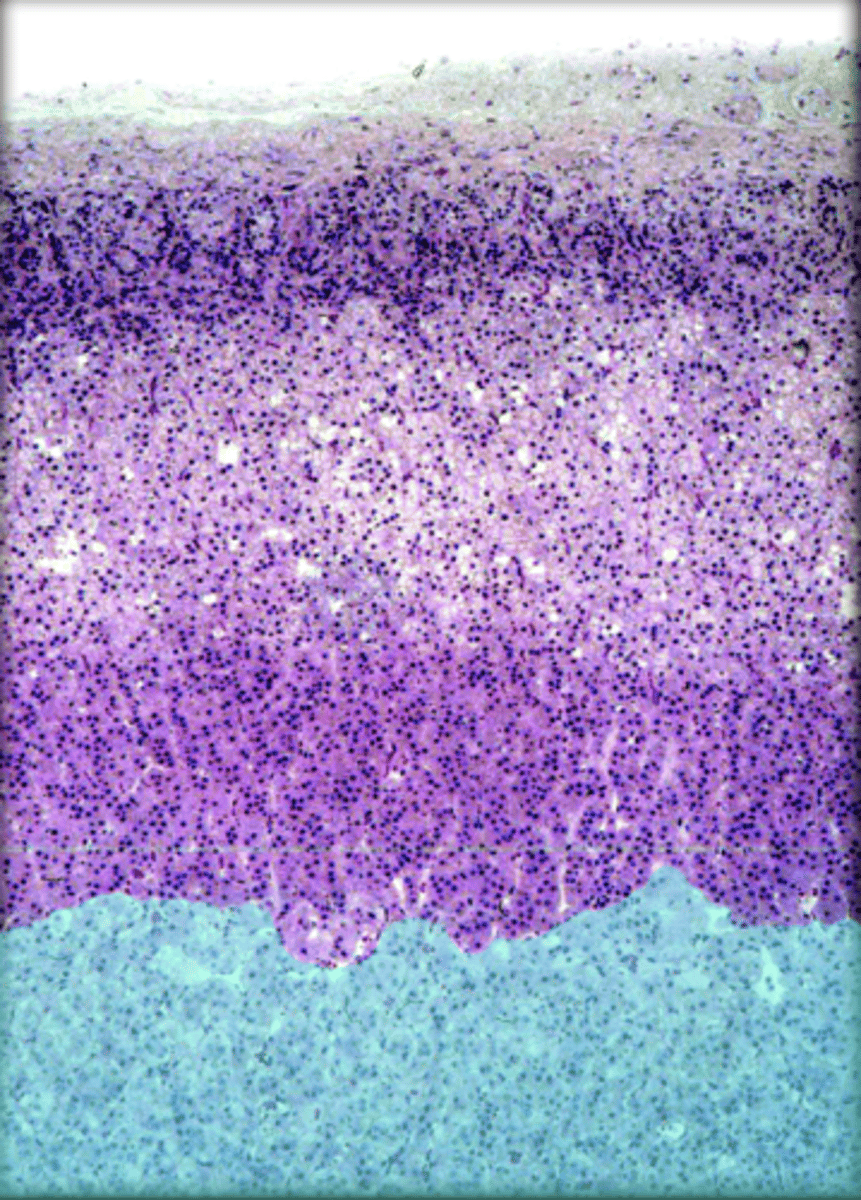
adrenal medulla (histology)
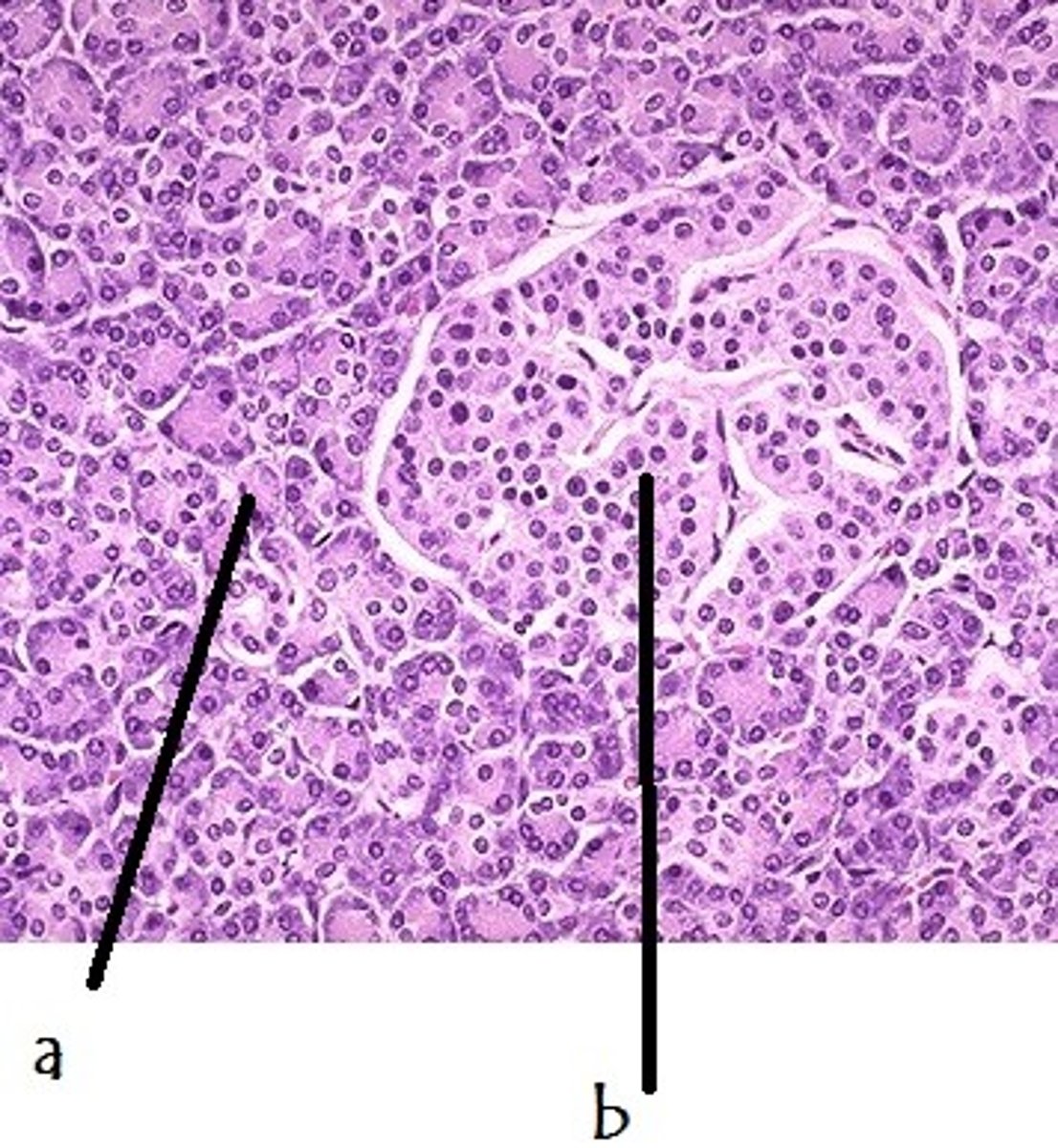
islet cells in pancreas
endocrine cells in the pancreas that control the release of the hormones insulin and glucagon; b in the image
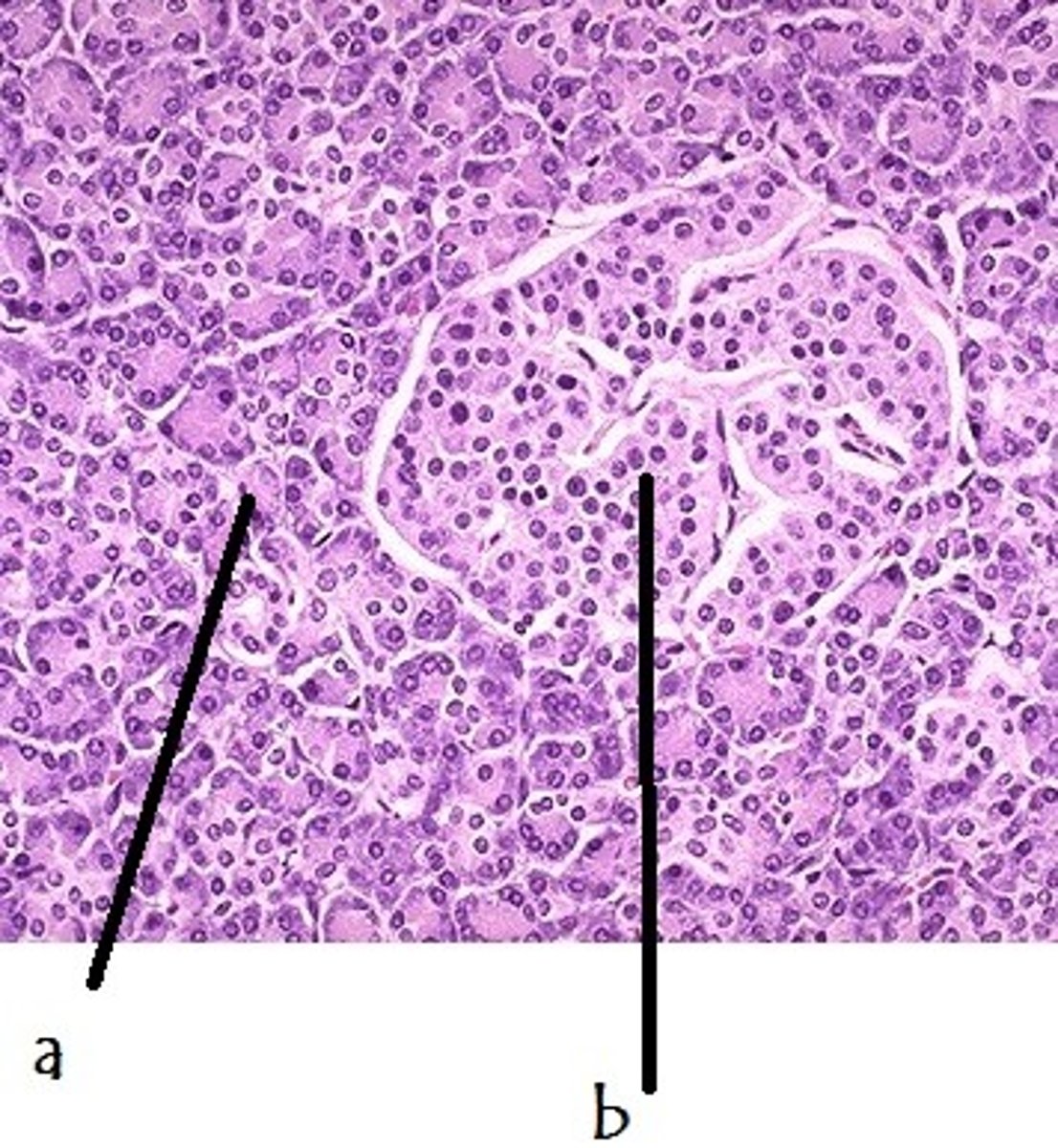
exocrine cells of pancreas
a in the image
thymus gland
lymphoid organ where T cells mature; located in the mediastinal cavity anterior to and superior the heart; produces and secretes thymosin
thymosin
• Produced in: thymus gland
• Targets: thymus gland
• Effect: regulates production and specialization of T lymphocytes
hematocrit
The percent of the volume of whole blood that is composed of red blood cells as determined by separation of red blood cells from the plasma usually by centrifugation.
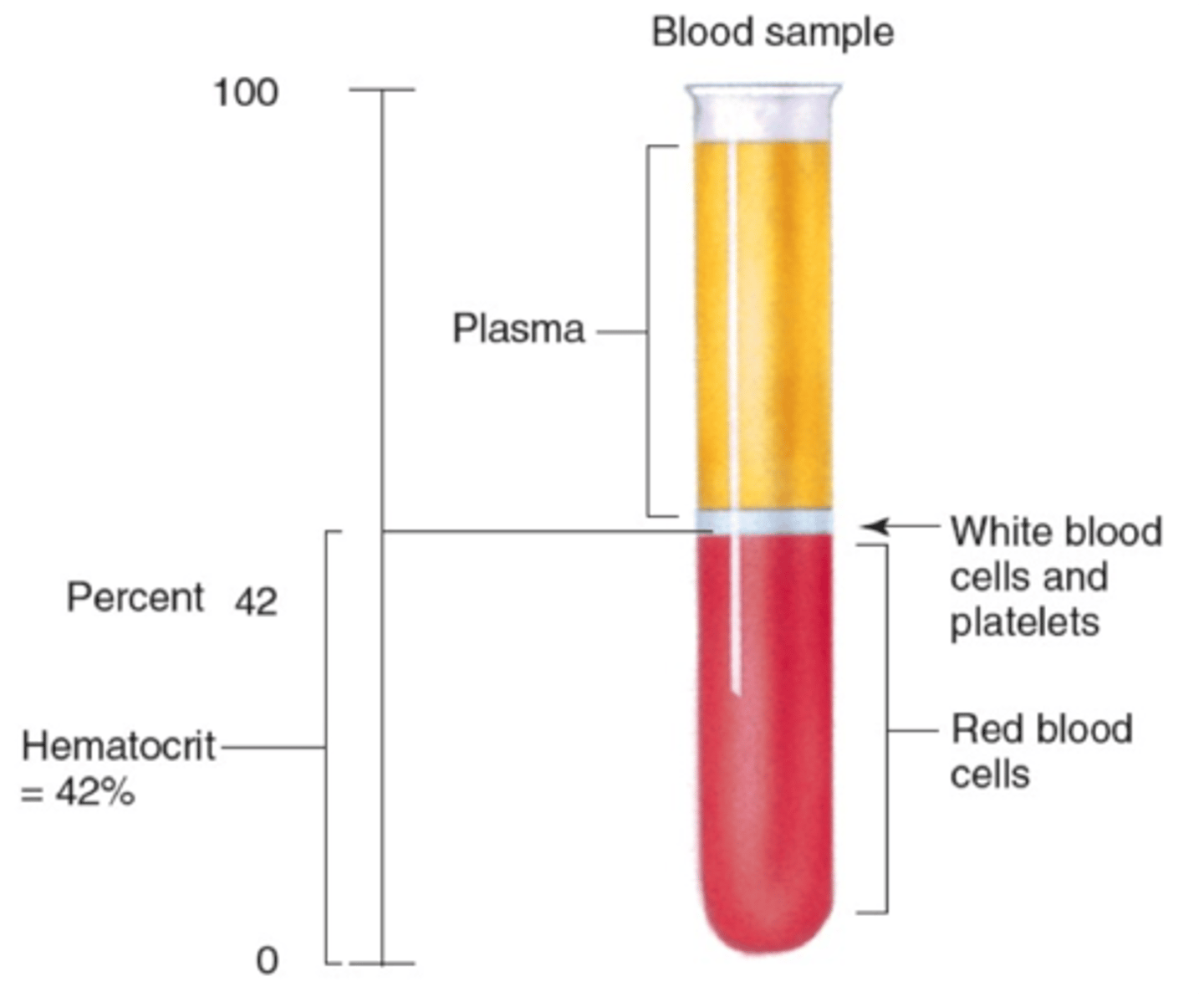
plasma
liquid portion of blood; contains water, proteins, salts, nutrients, lipids, hormones, and vitamins
normal hematocrit range (males)
42-56%; slightly higher than females due to testosterone levels
normal hematocrit range (females)
38-46%
erythrocyte
a mature red blood cell; general function: transport of respiratory gases
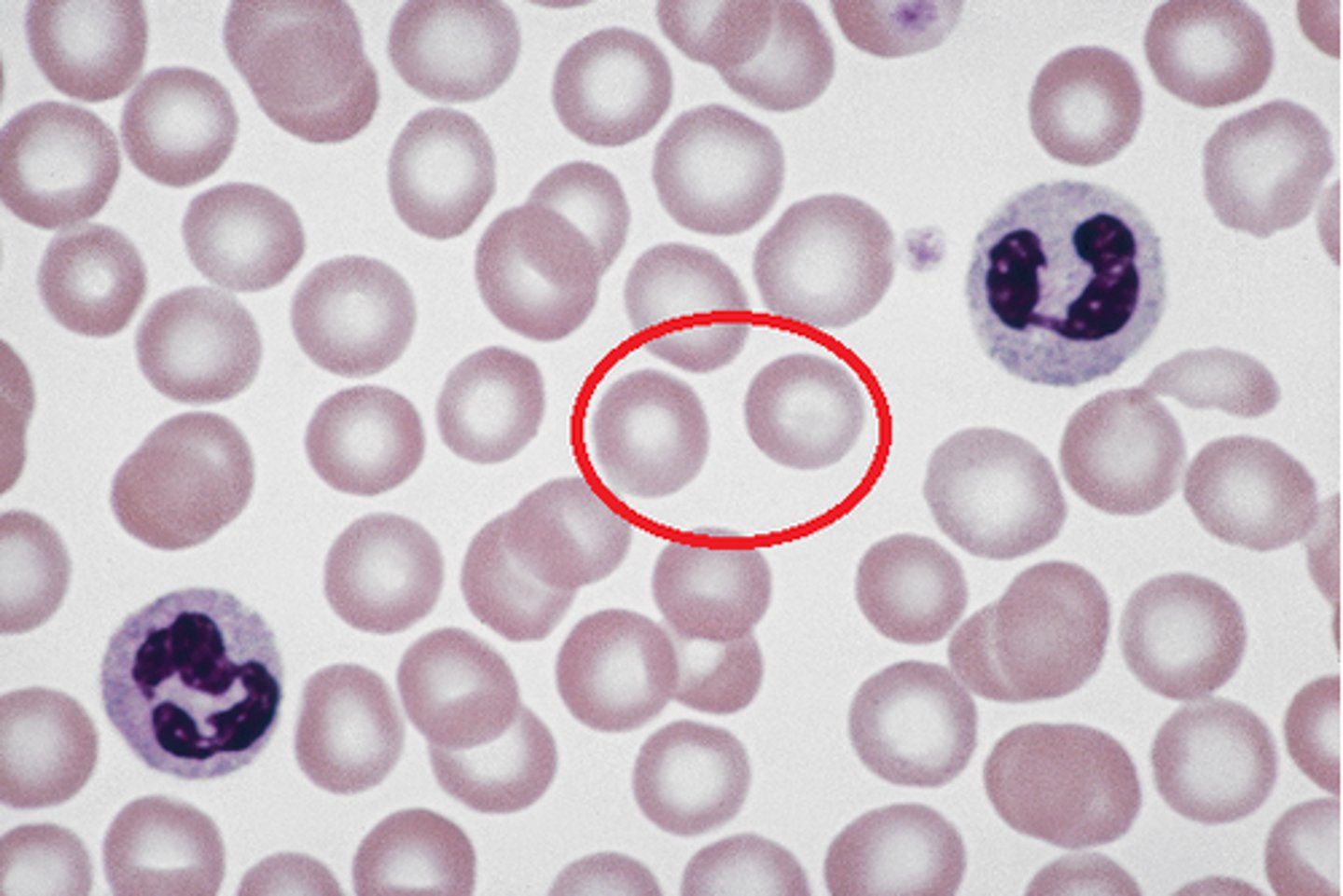
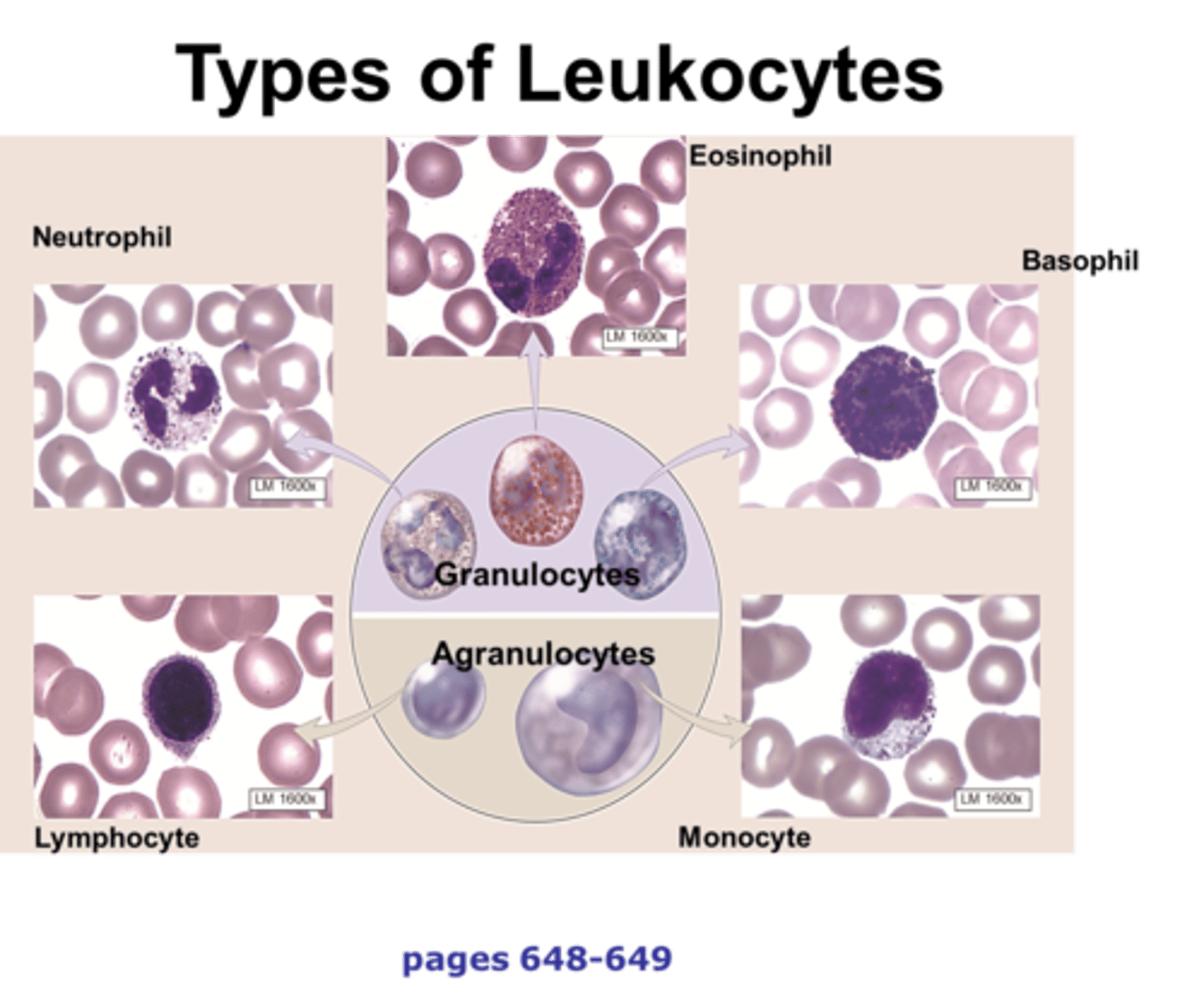
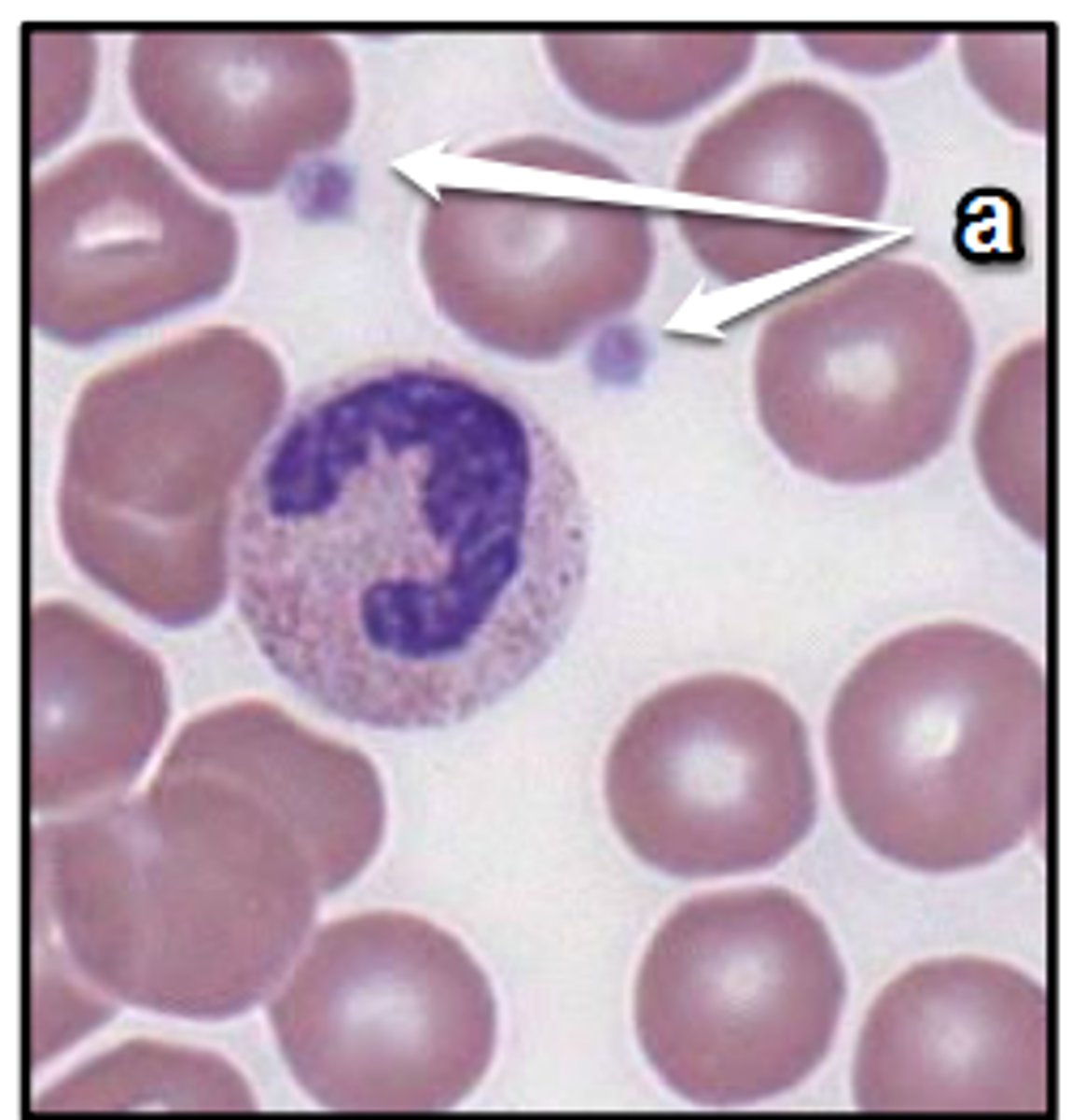
basophil
type of leukocyte containing dark blue to purple staining granules with a large nucleus; general function: immune protection
neutrophil
type of leukocyte containing light purple staining granules with a multi-lobed nucleus; general function: immune protection
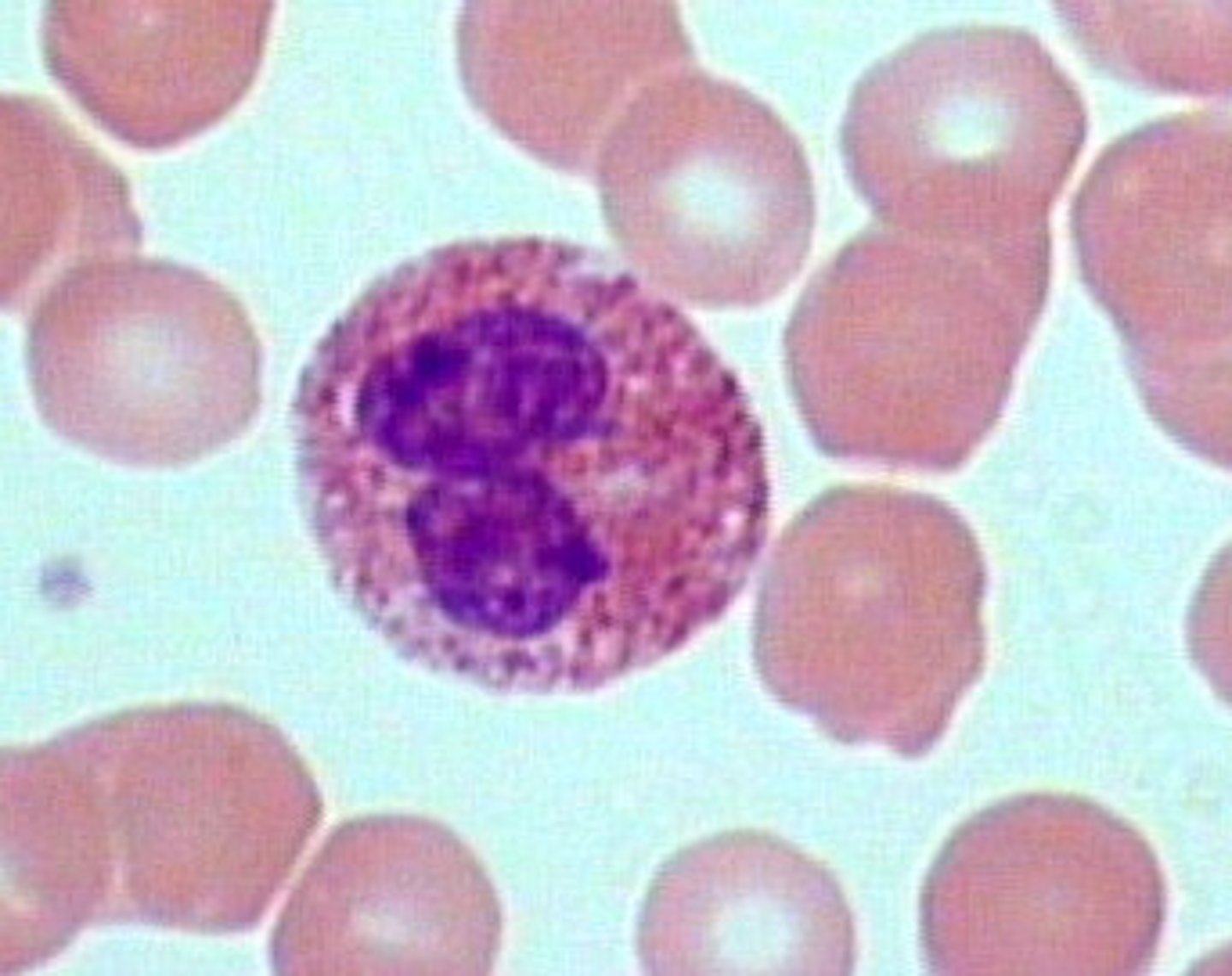
eosinophil
type of leukocyte containing dark orange to red staining granules; general function: immune protection
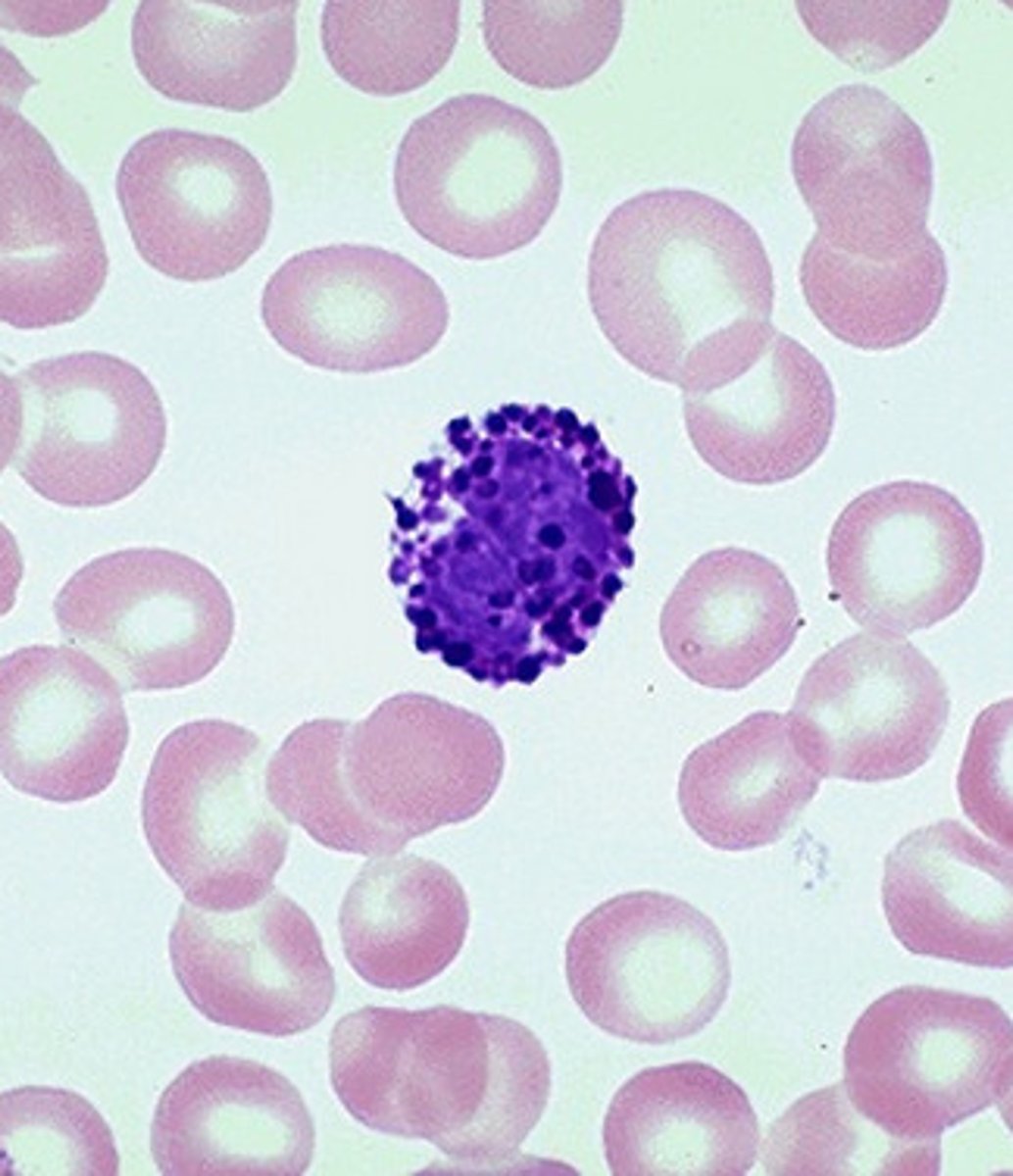
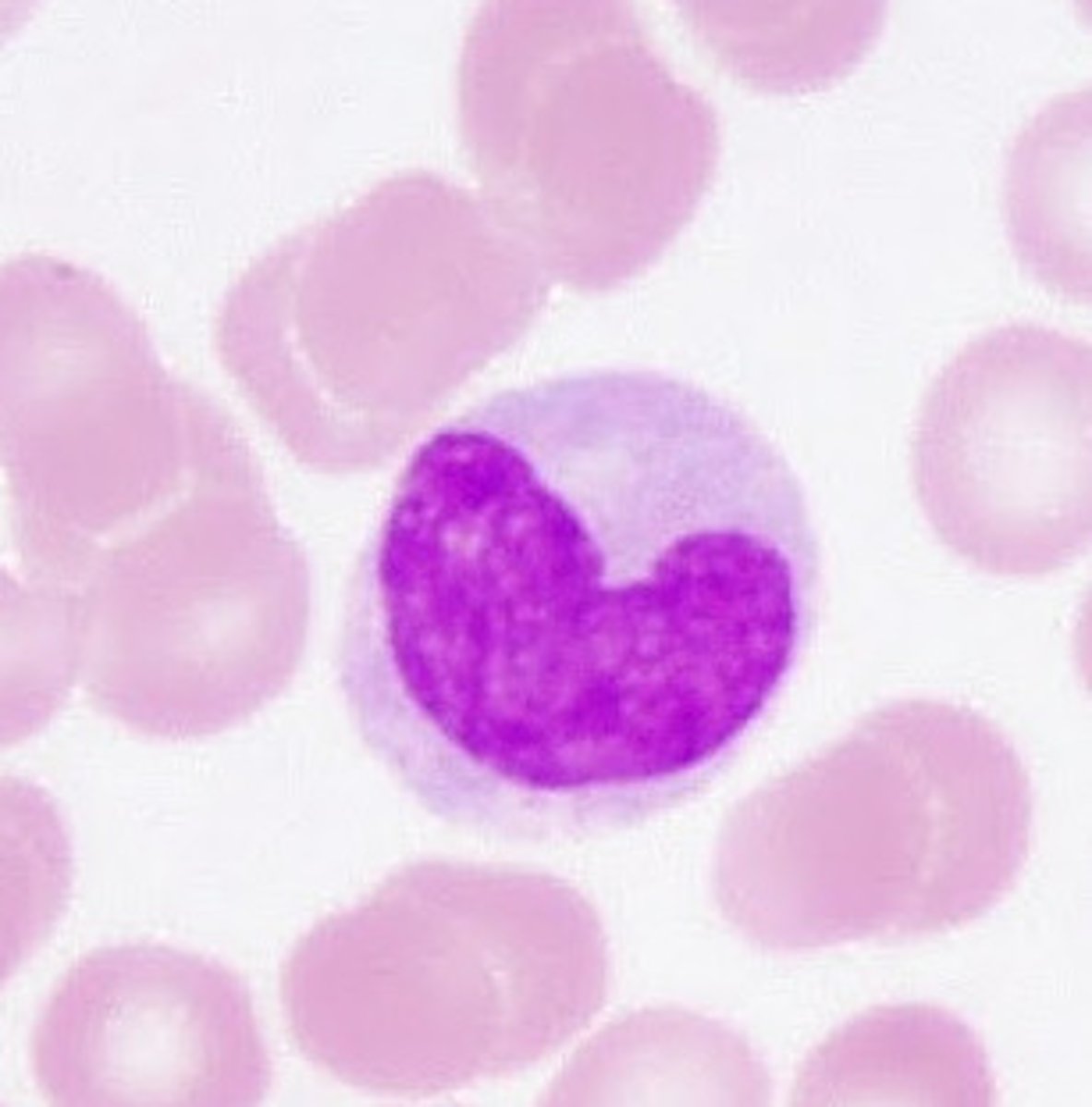
monocyte
type of leukocyte with no granules and a bean shaped nucleus; general function: immune protection
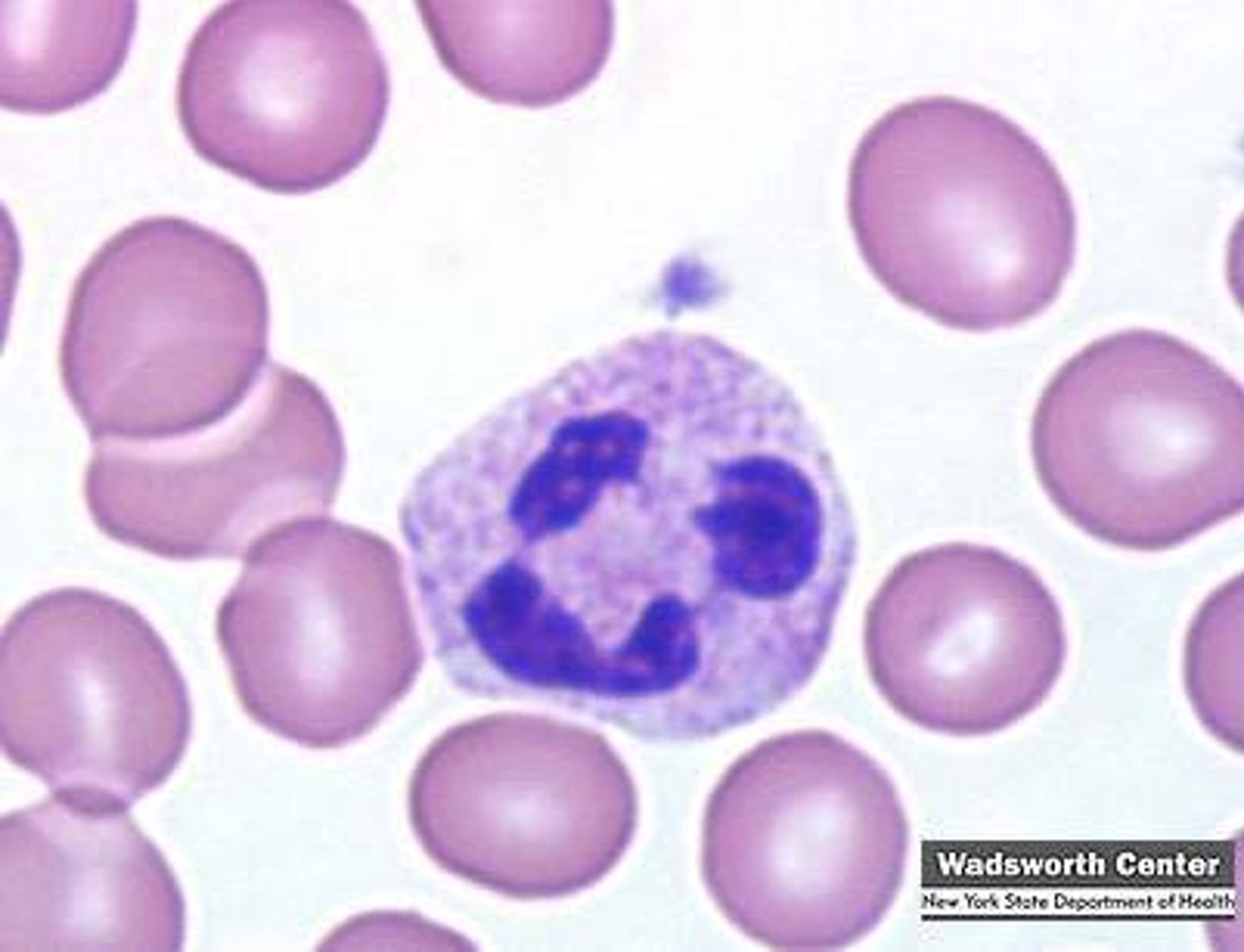
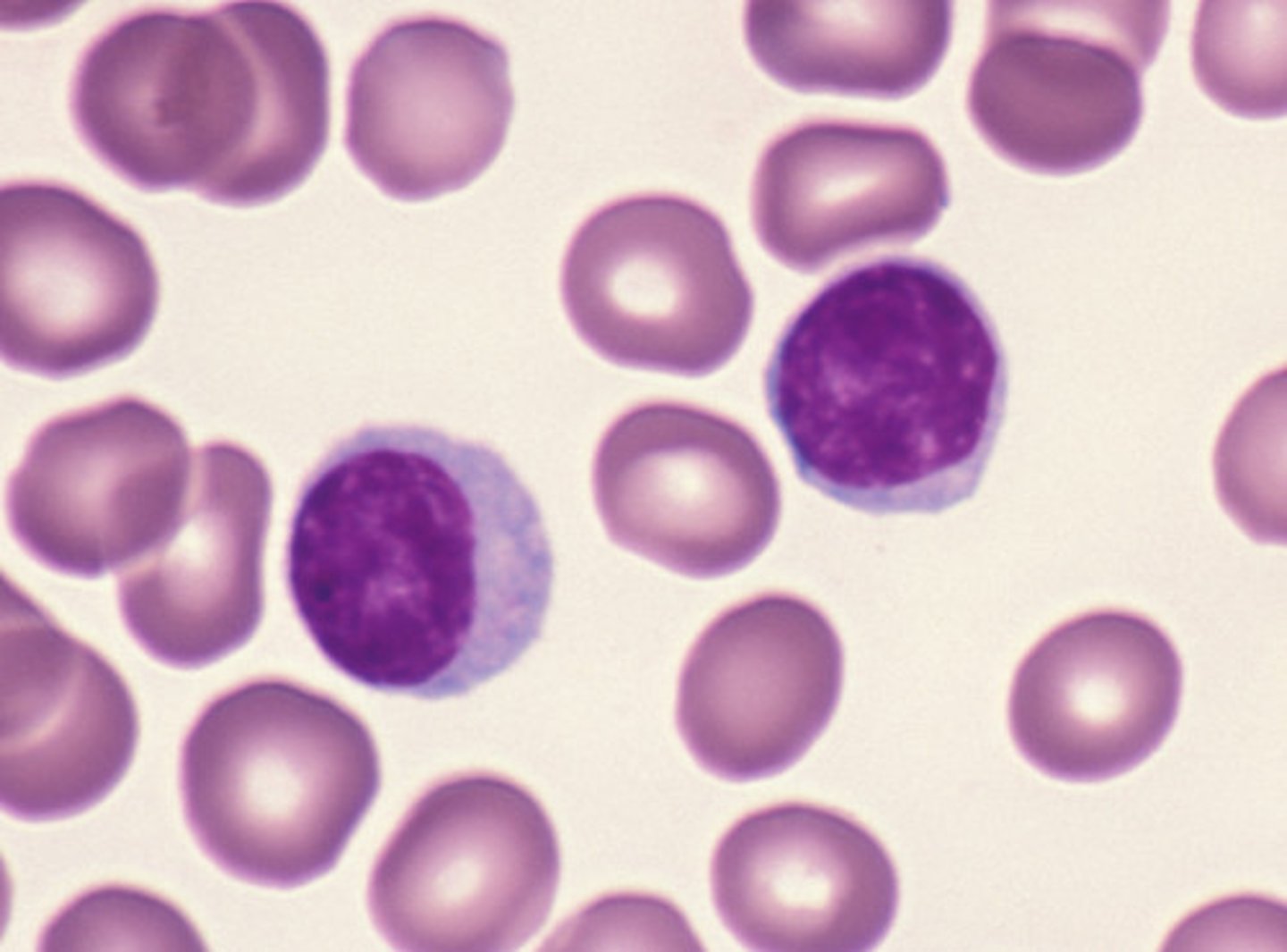
lymphocyte
type of leukocyte with no granules and a large circular nucleus; general function: immune protection
leukocyte
white blood cells; include granulocytes (basophils, neutrophils, eosinophils) and agranulocytes (monocytes and lymphocytes)
megakaryocyte
a large bone marrow cell from which platelets are derived
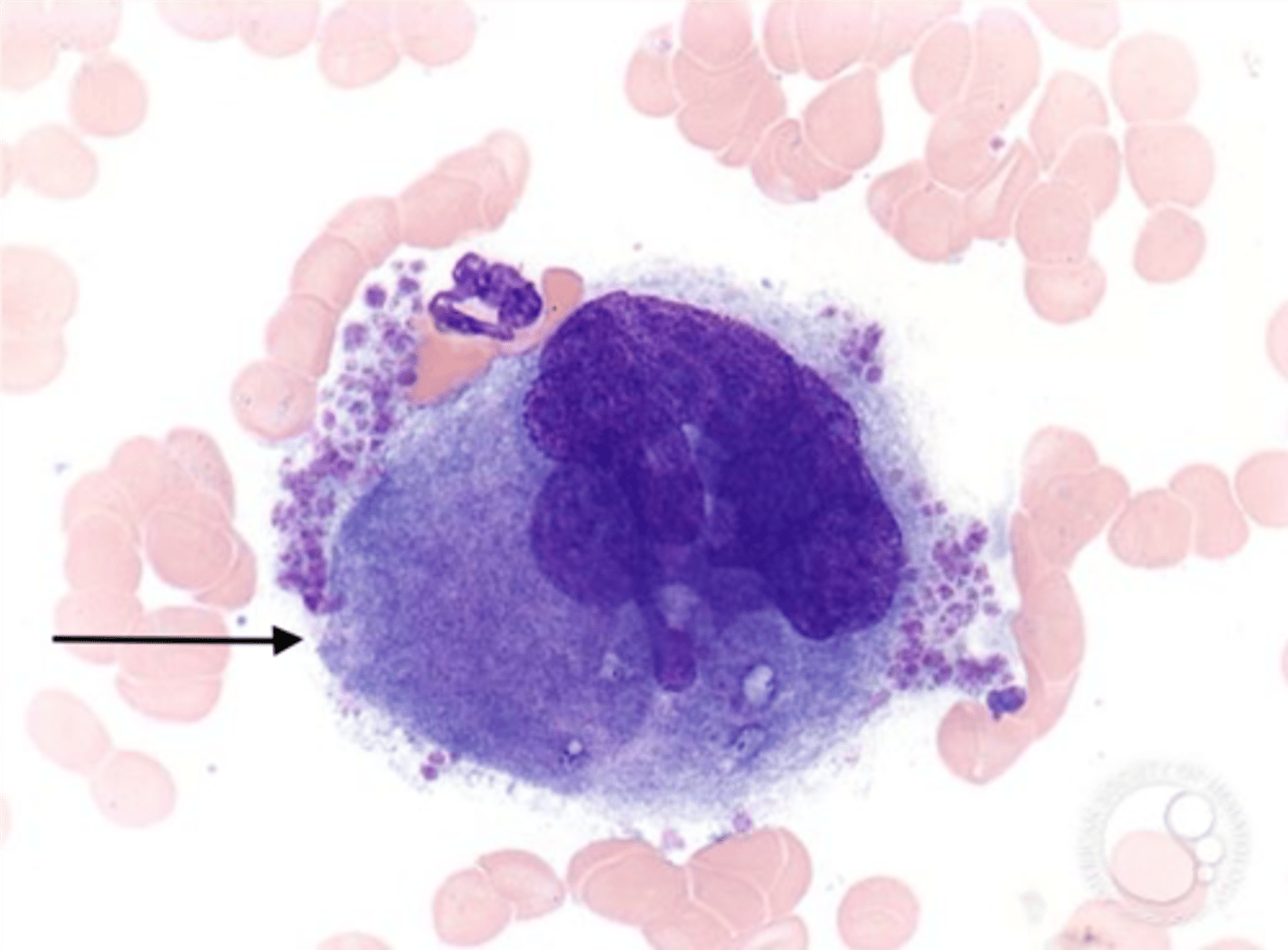
platelet
small blood fragment that collects at sites of injury to begin the clotting process -- forms plug not the actual clot; derived from megakaryocytes
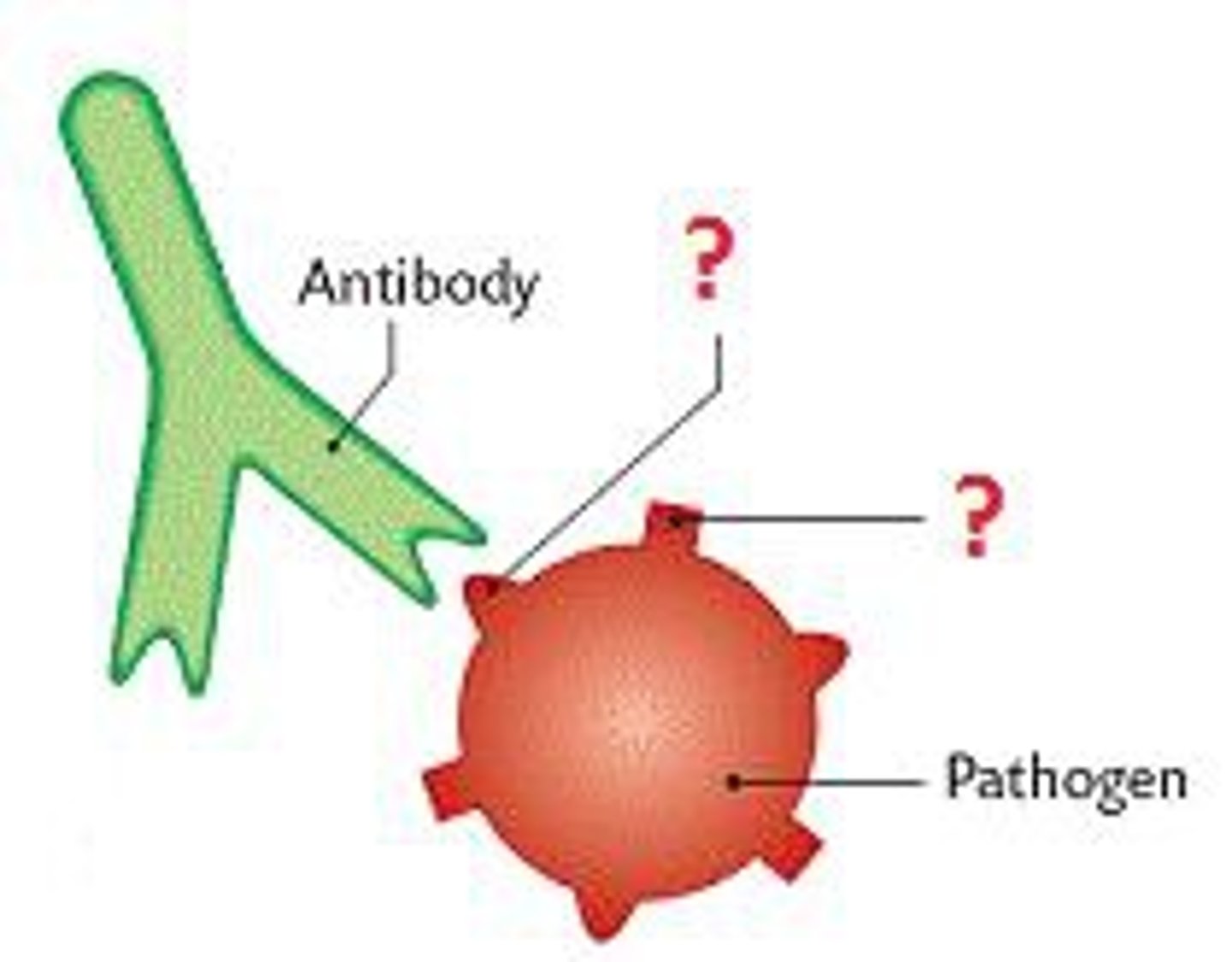
antigen
a protein or carbohydrate that, when introduced in the blood, can trigger the production of an antibody
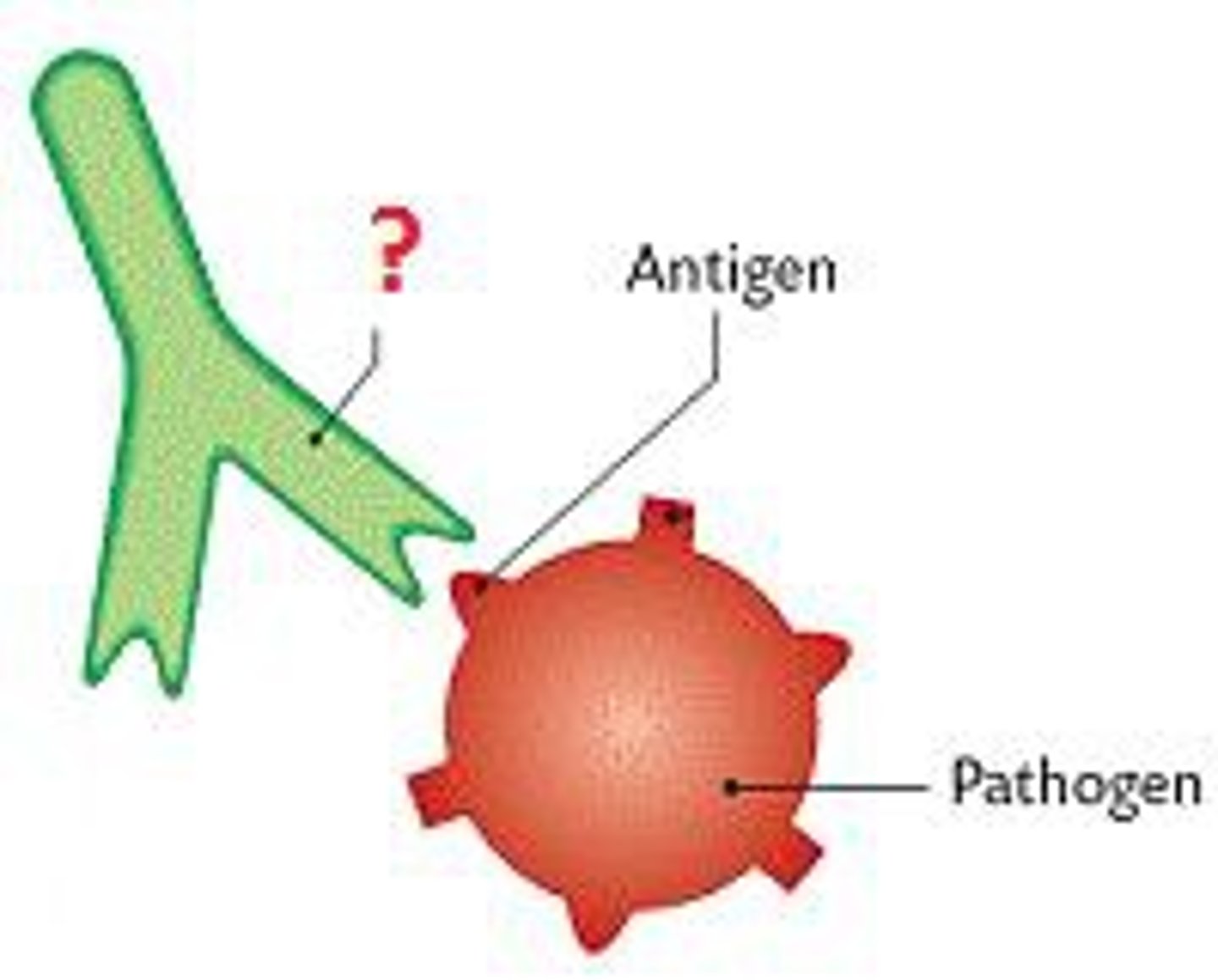
antibody
a protein (immunoglobulin) that acts against a specific antigen
blood type A
A antigens of erythrocytes and anti-B antibodies in plasma; IᴬIᴬ or IᴬIᴼ genotype
blood type B
B antigens of erythrocytes and anti-A antibodies in plasma; IᴮIᴮ or IᴮIᴼ genotype
blood type AB
A and B antigens on erythrocytes; NO anti-A and NO anti-B antibodies; IᴬIᴮ genotype
blood type O
no antigens on erythrocytes; anti-A and anti-B antibodies in plasma; IᴼIᴼ genotype
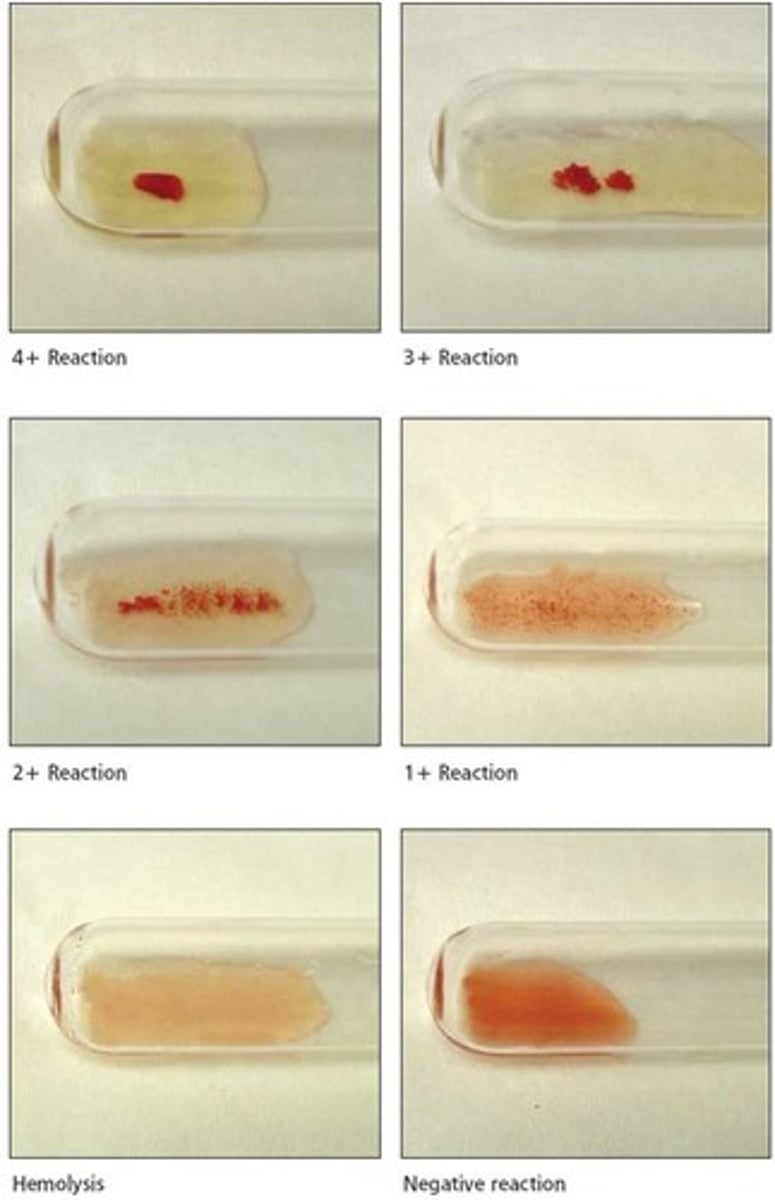
agglutination
clumping of red blood cells; can occur when incompatible blood types are mixed together due to antibodies binding to antigens
Rh factor
Refers to the presence or absence of the D antigen on red blood cells; someone with this factor/antigen would be considered Rh+
Rh+
express Rh factor (D) antigen on erythrocytes
Rh-
do NOT have Rh factor (D) antigen on erythrocytes; have anti-Rh antibodies
aorta
oxygenated blood flows through here from the heart to the rest of the body
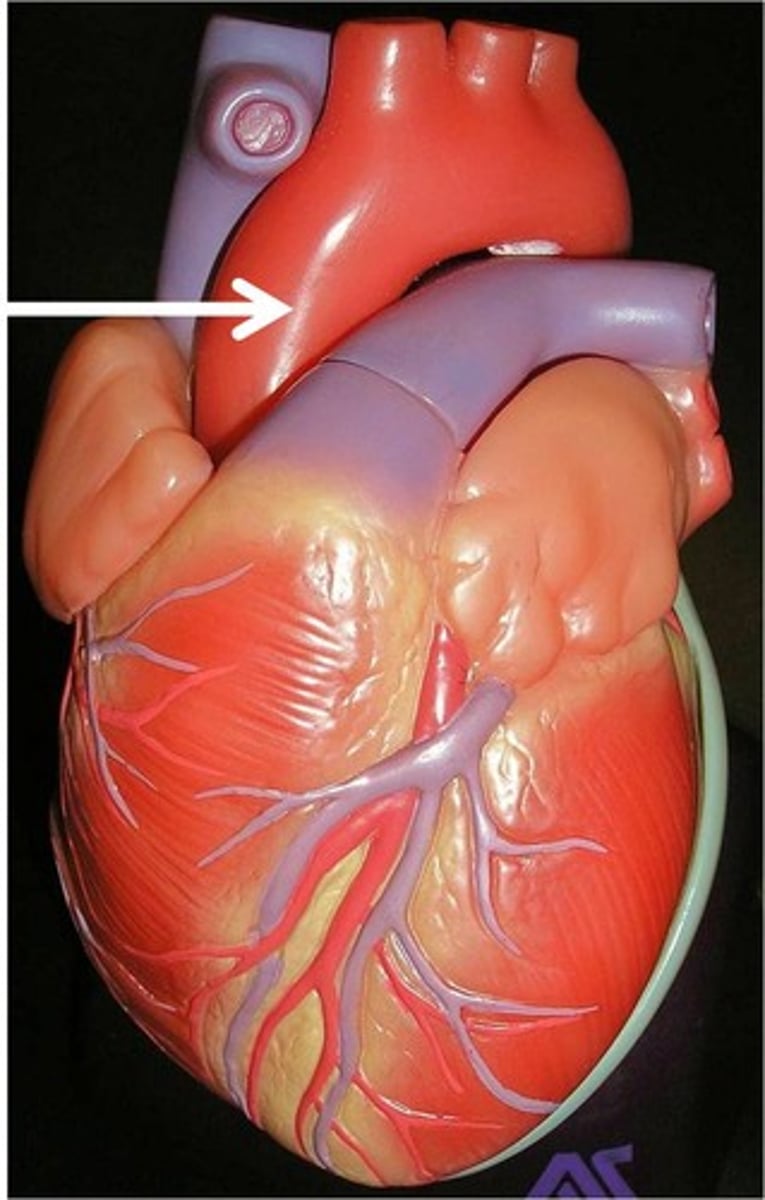
aortic valve
valve located between the left ventricle and the aorta
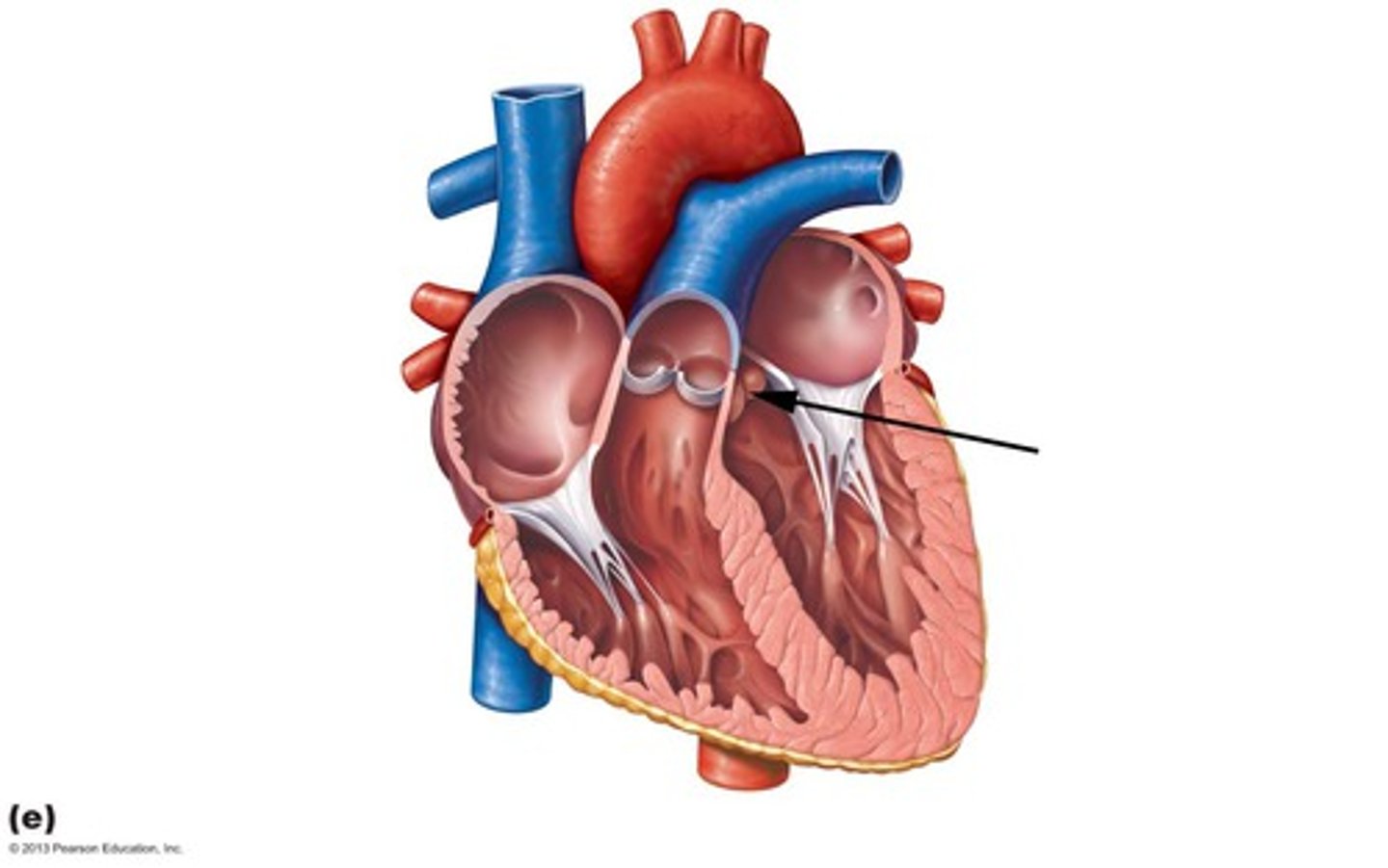
left atrioventricular (bicuspid) valve
valve between left atrium and left ventricle; prevents backflow of blood
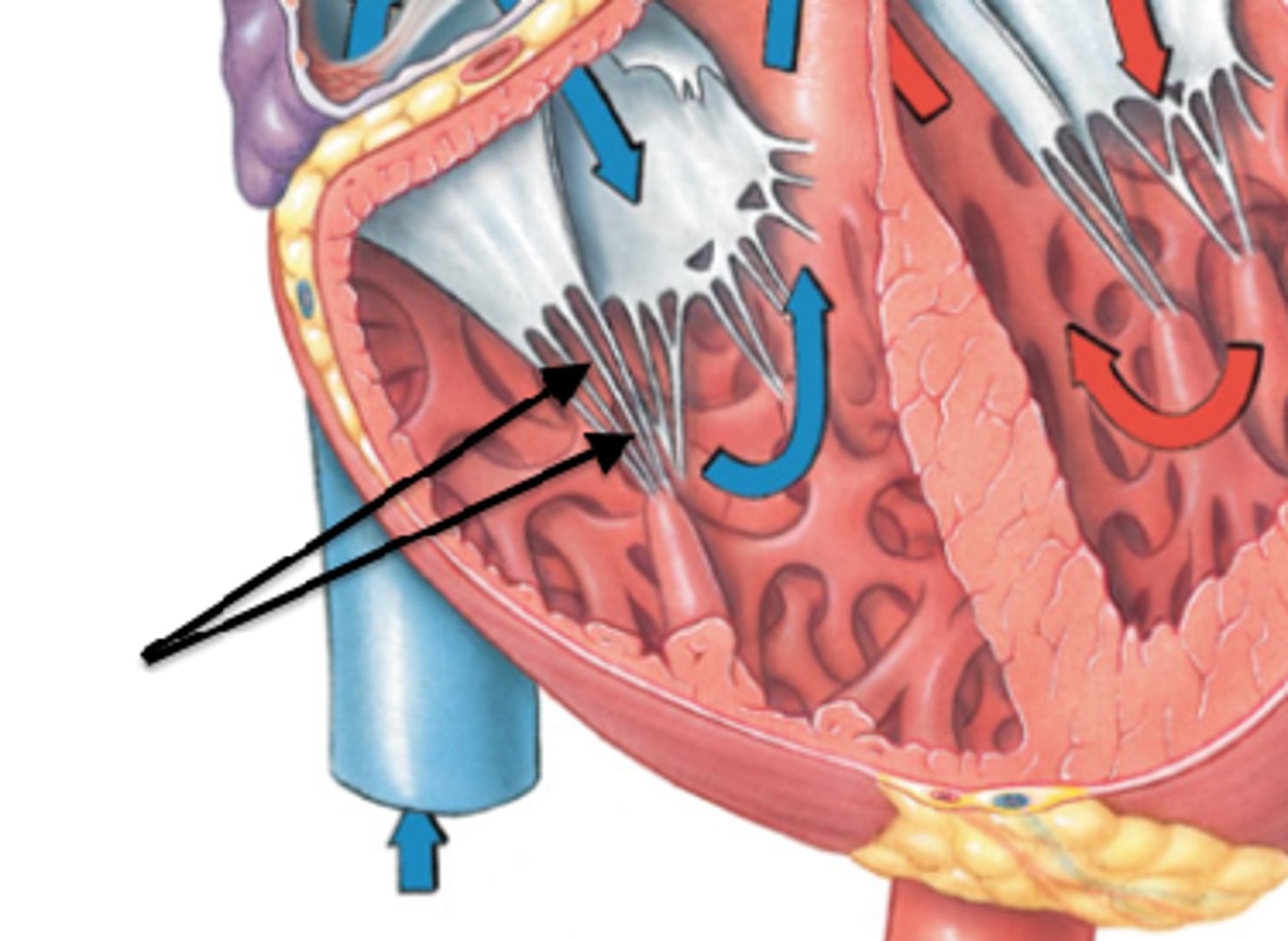
chordae tendineae
thin bands of fibrous tissue that attach to the valves in the heart and prevent them from inverting, also known as heartstrings
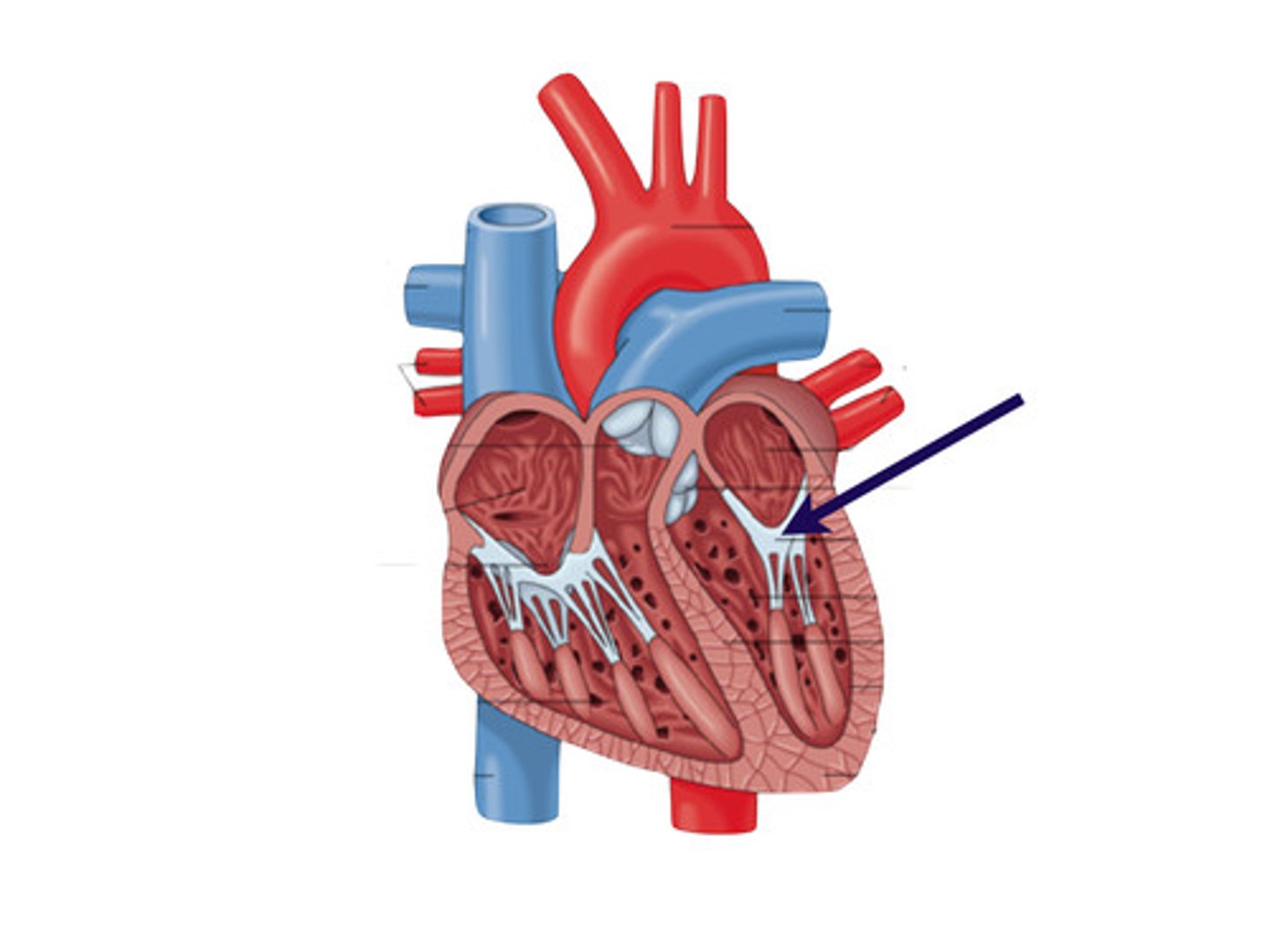
left atrium
chamber that receives oxygenated blood from the lungs
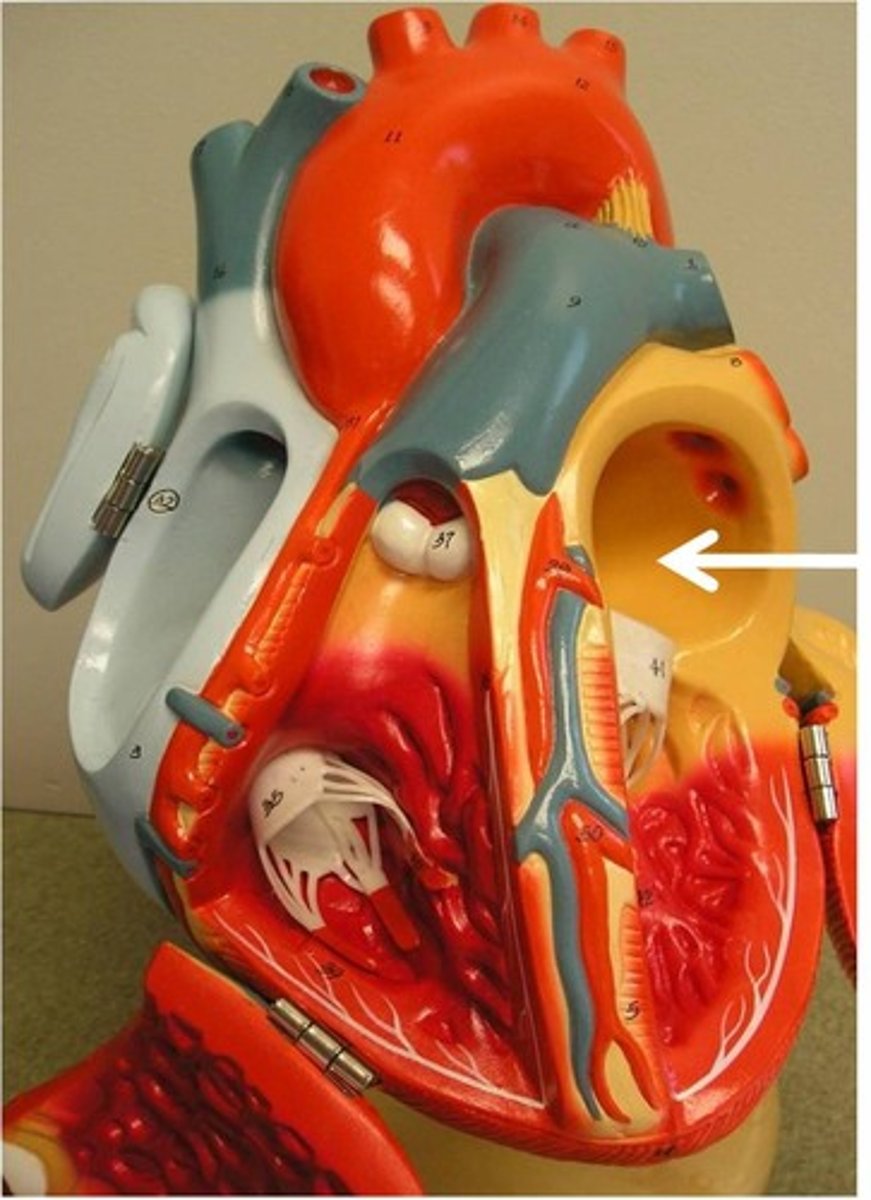
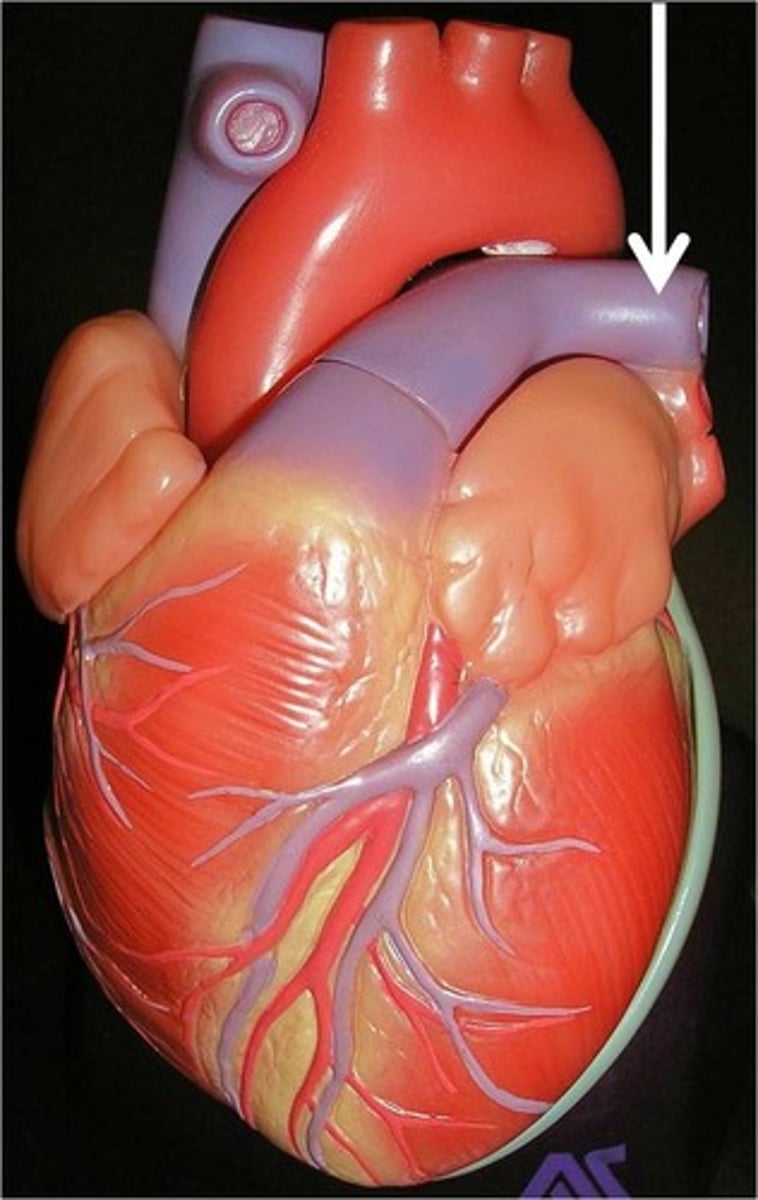
left pulmonary artery
carries blood from the right ventricle to the left lung
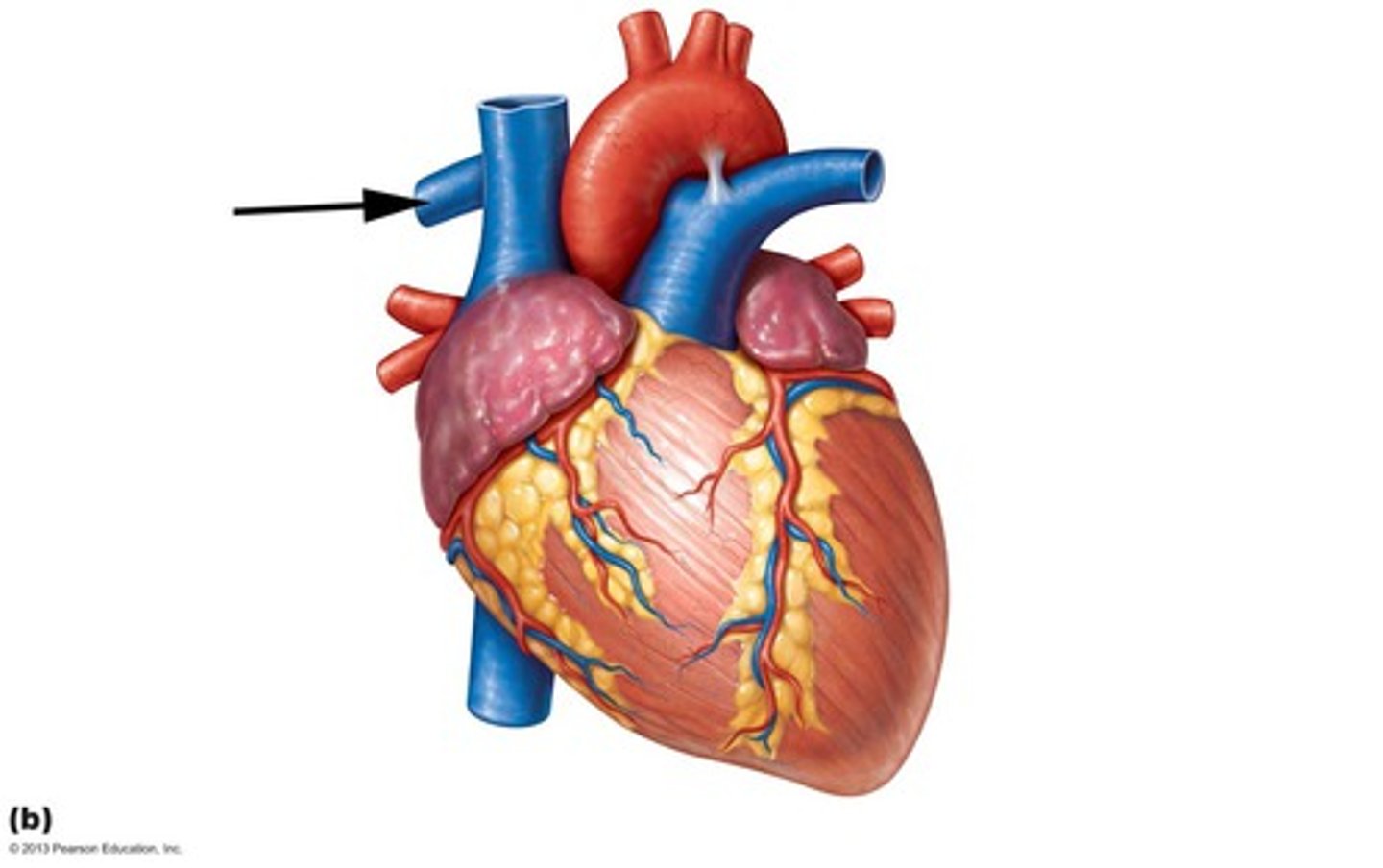
right pulmonary artery
takes blood from the right ventricle to the right lung
left ventricle
chamber that pumps oxygenated blood into the aorta
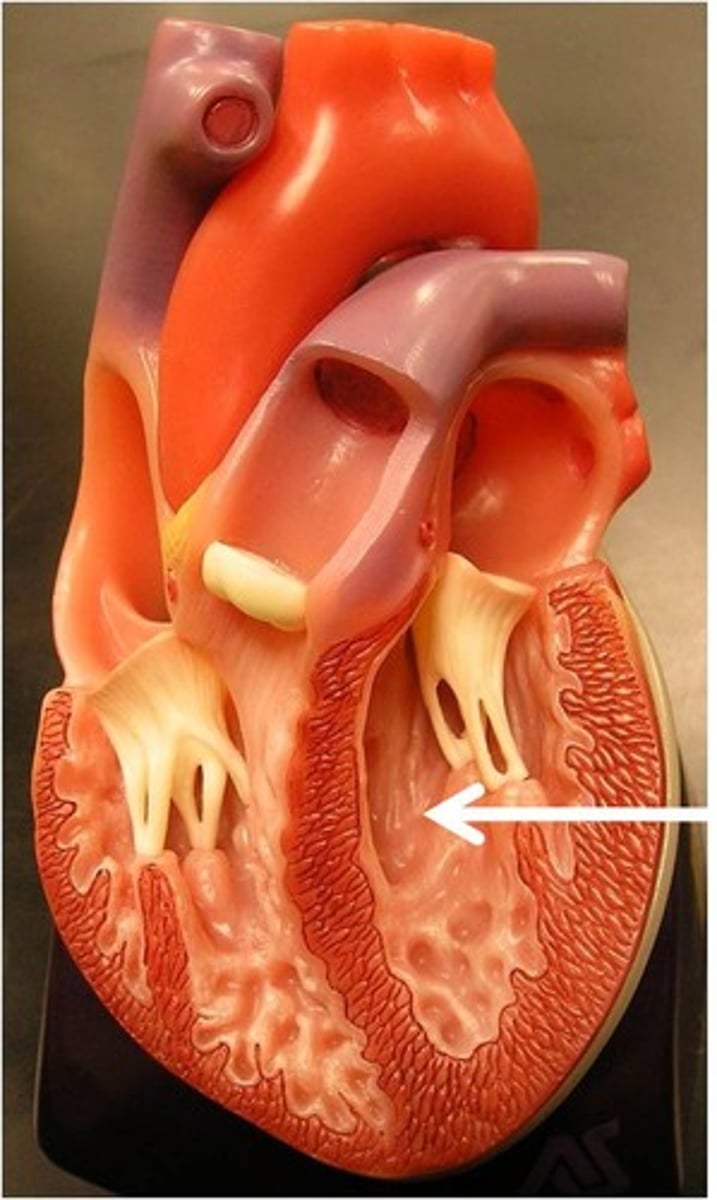
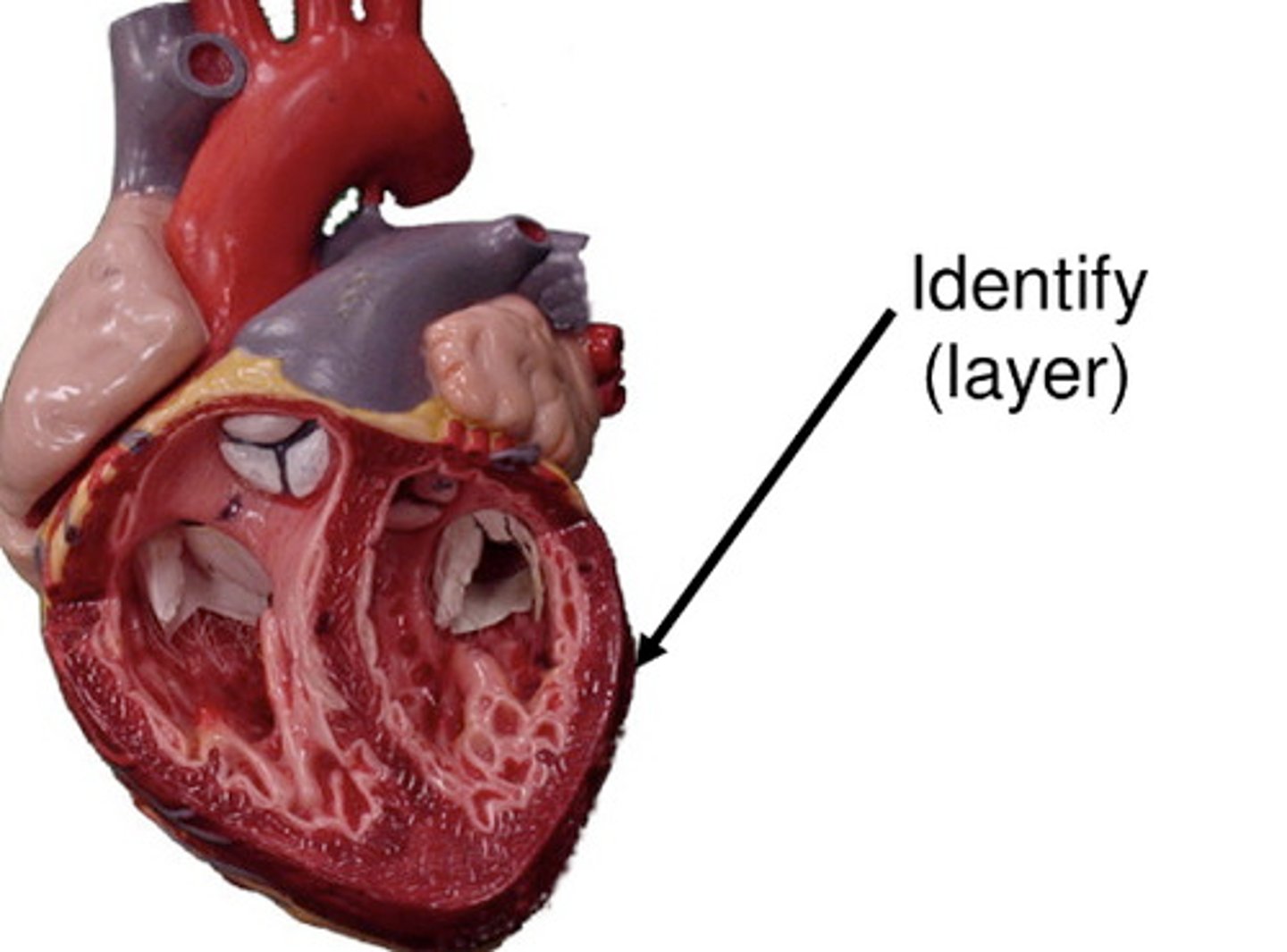
myocardium
muscular, middle layer of the heart
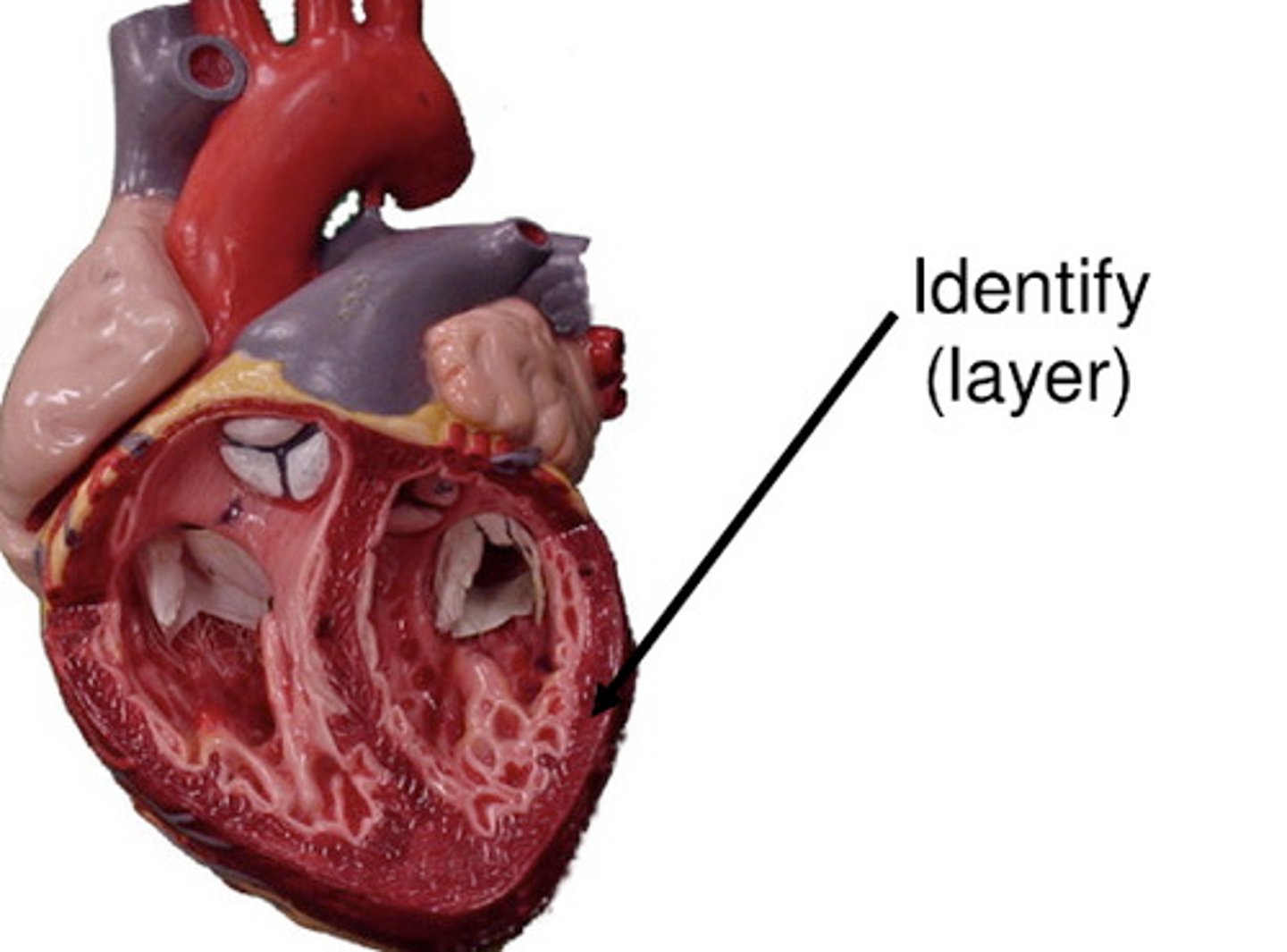
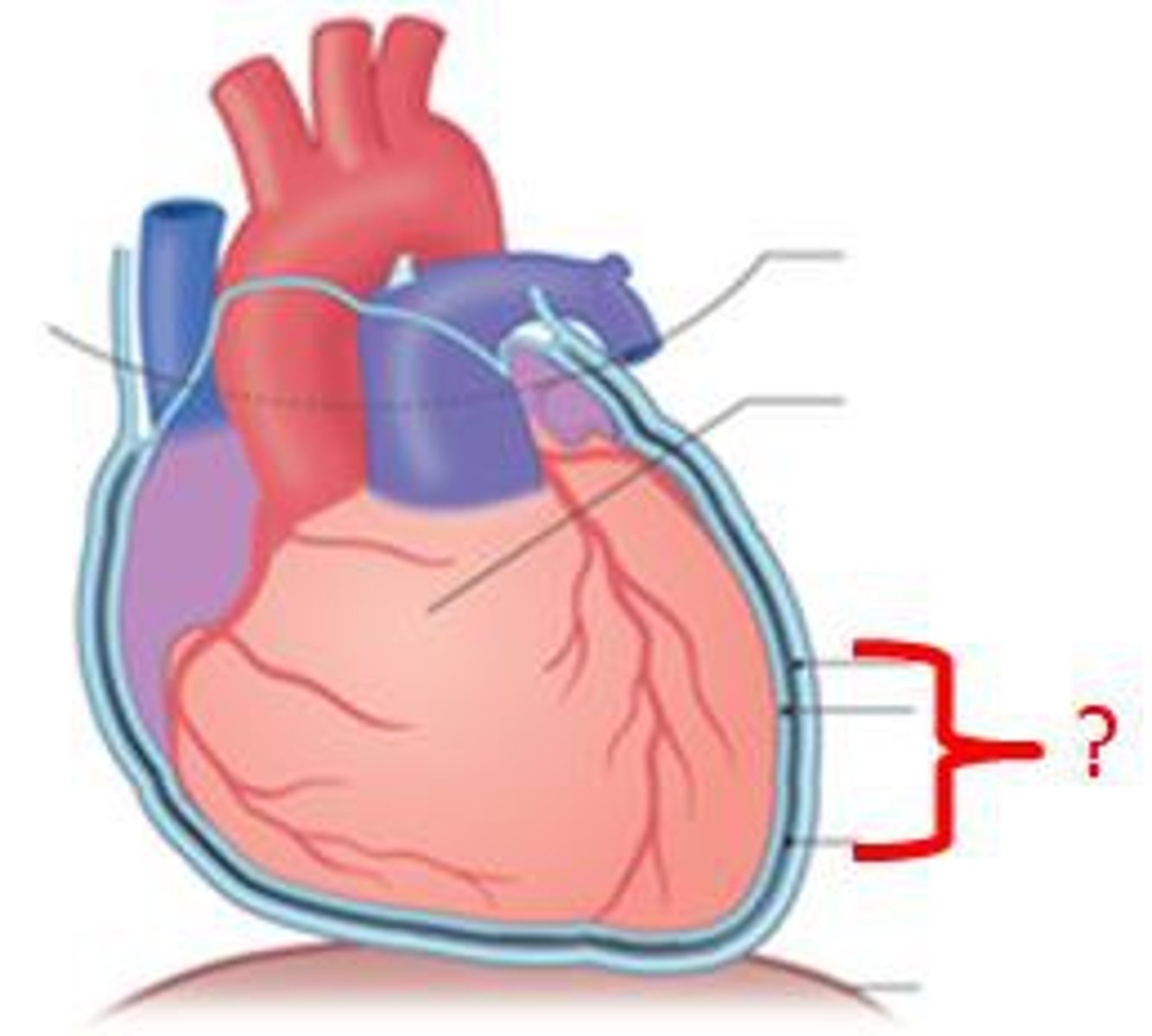
pericardium
Membrane surrounding the heart
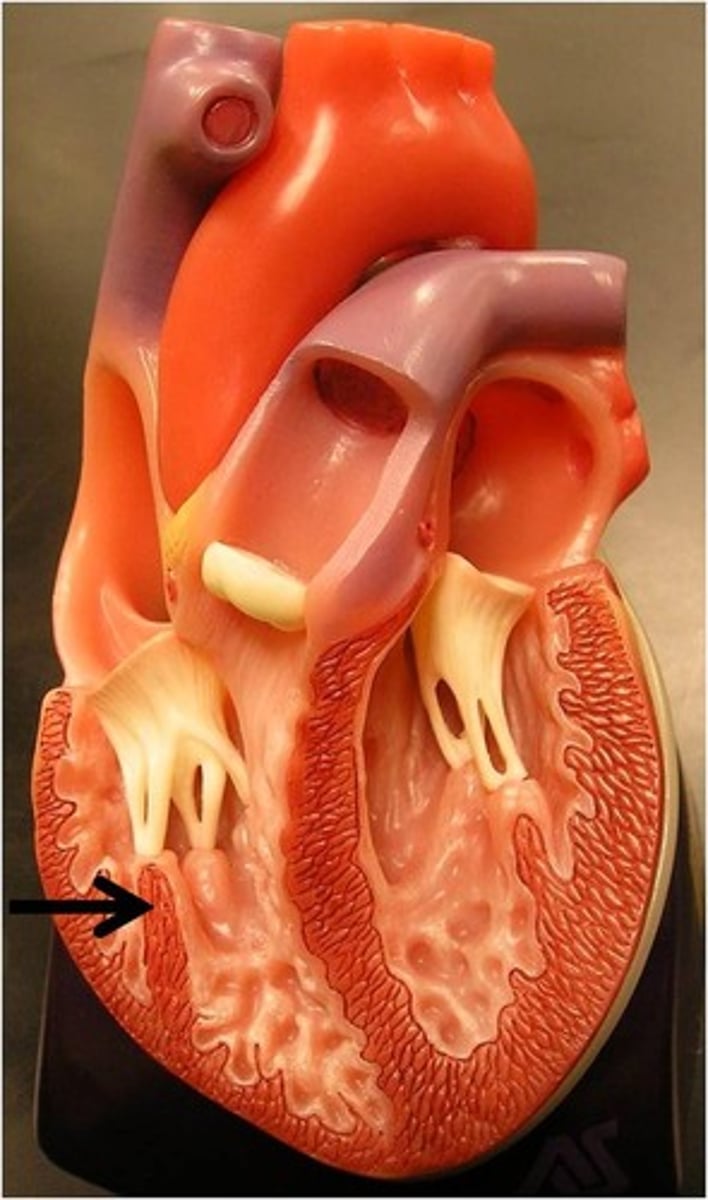
papillary muscles
muscles located in the ventricles of the heart; attach to the atrioventricular valves (bicuspid and tricuspid valves) via the chordae tendineae and contract to prevent inversion or prolapse of these valves on ventricular contraction
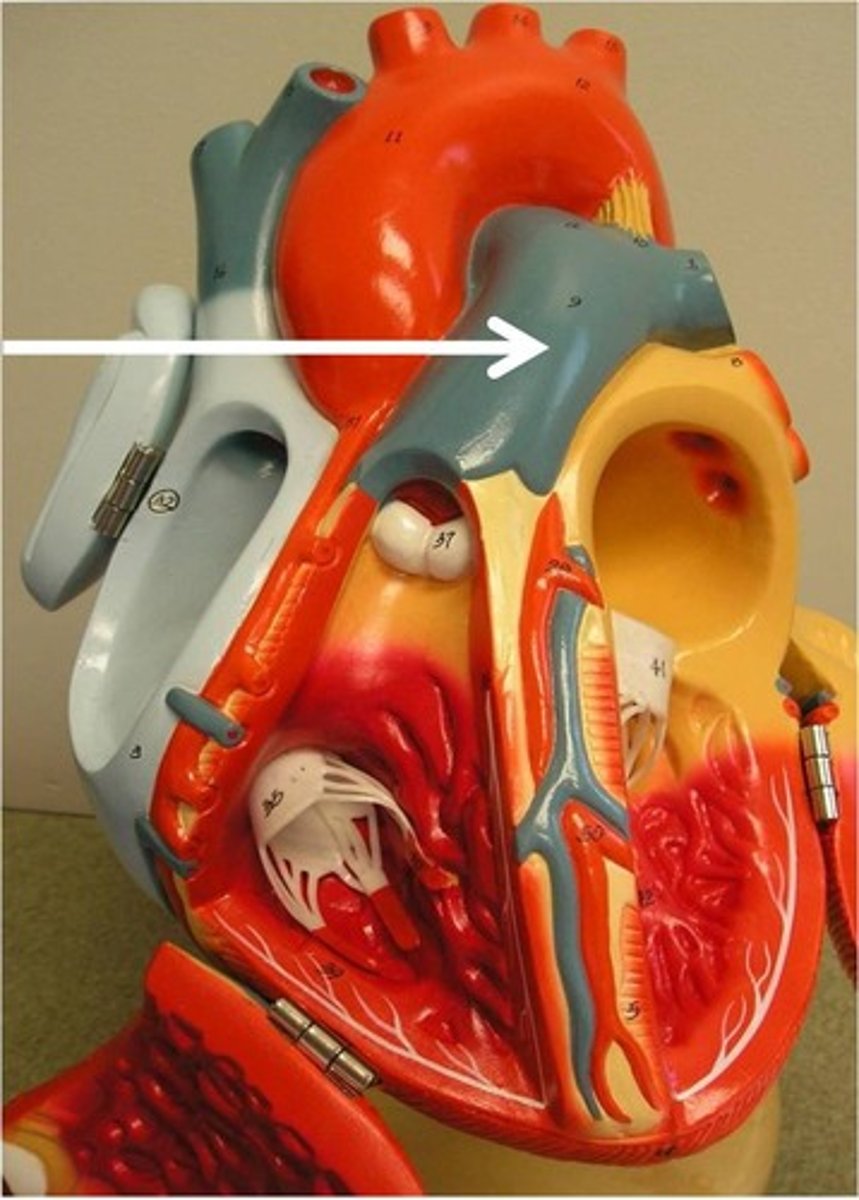
pulmonary trunk
carries blood from right ventricle to pulmonary arteries (which then carry the blood to the lungs)
pulmonary valve
valve opening between the right ventricle and the pulmonary trunk
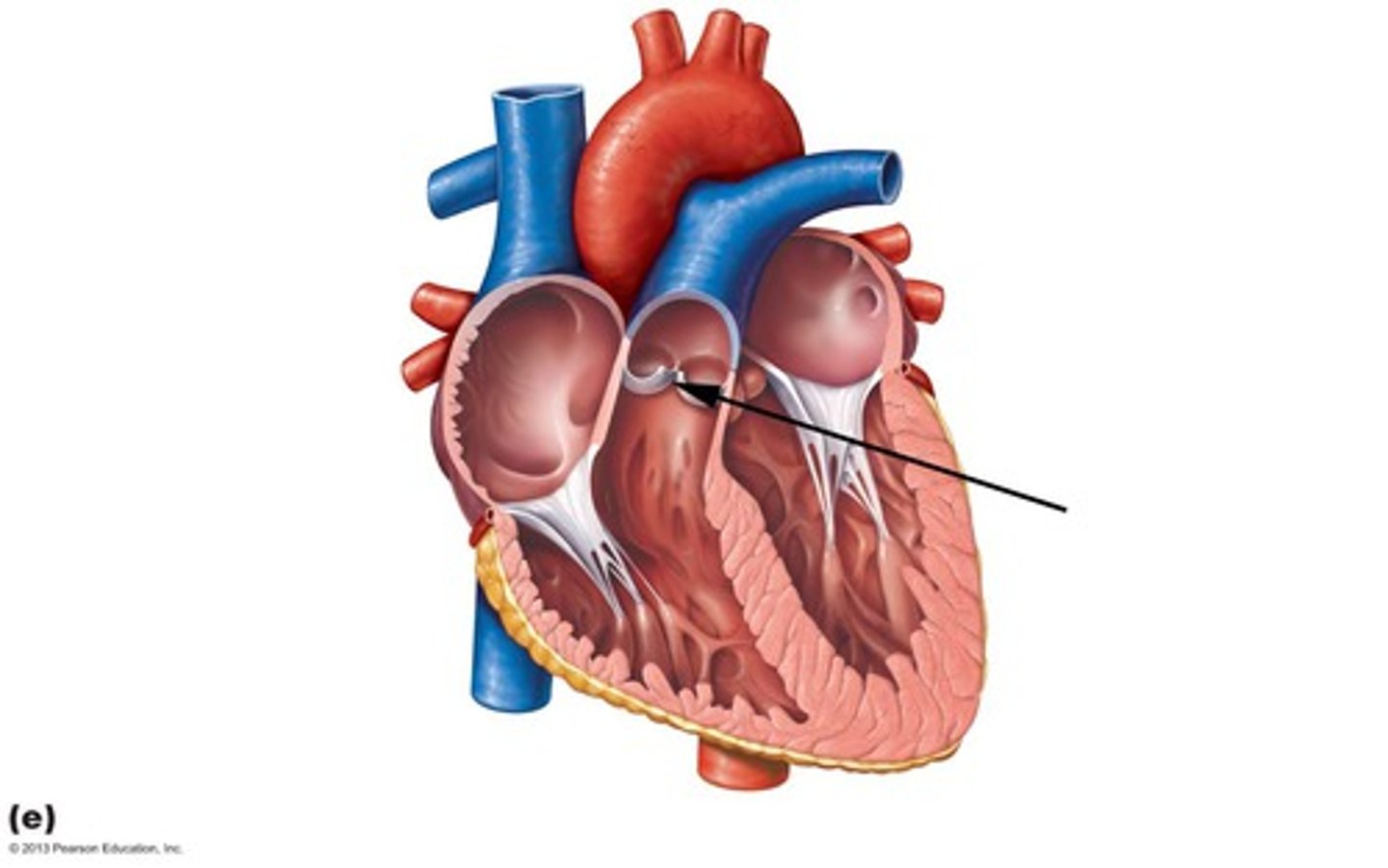
right pulmonary veins
carry the oxygenated blood from the right lung into the left atrium of the heart
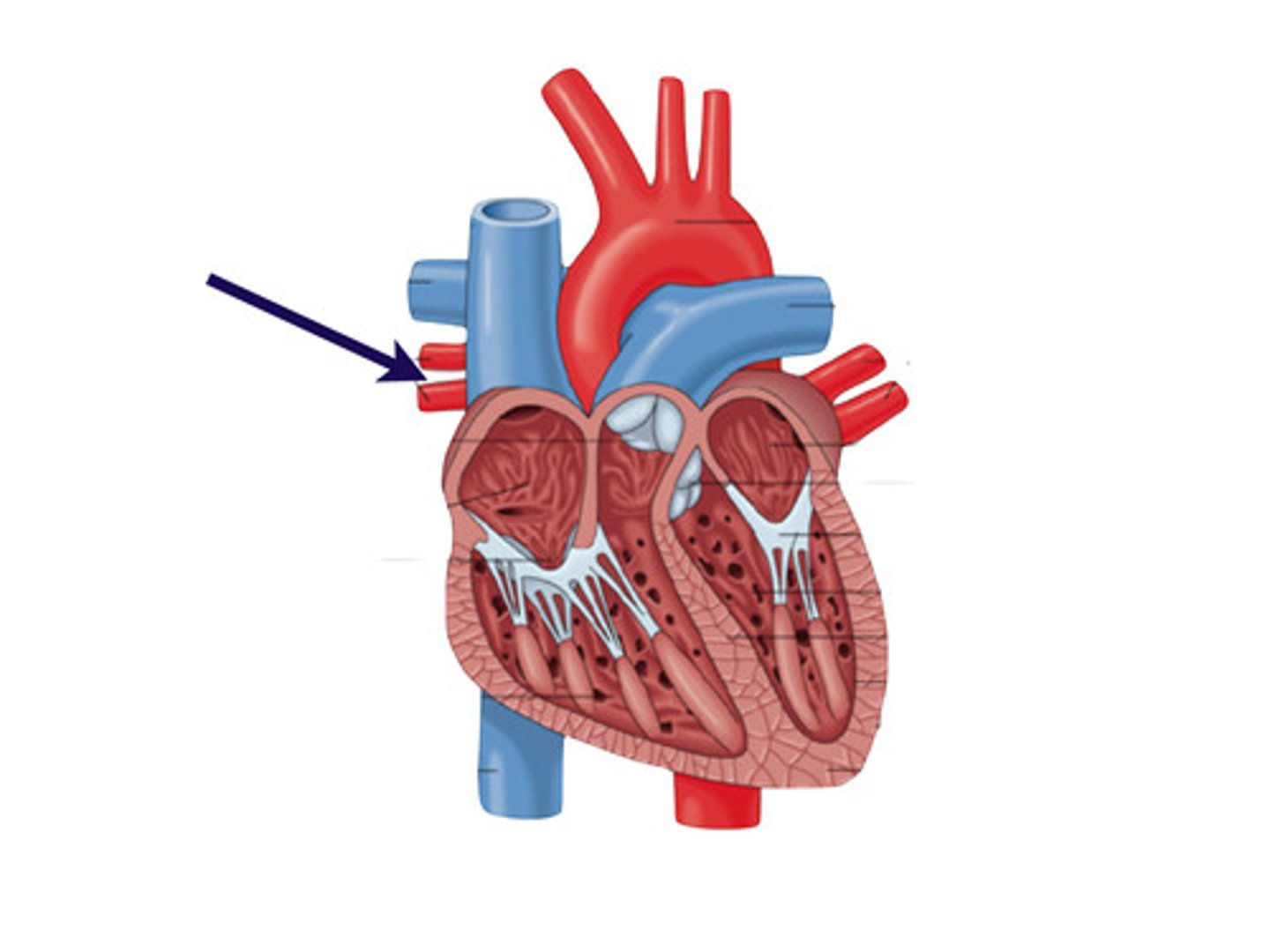
left pulmonary veins
carry the oxygenated blood from the left lung into the left atrium of the heart
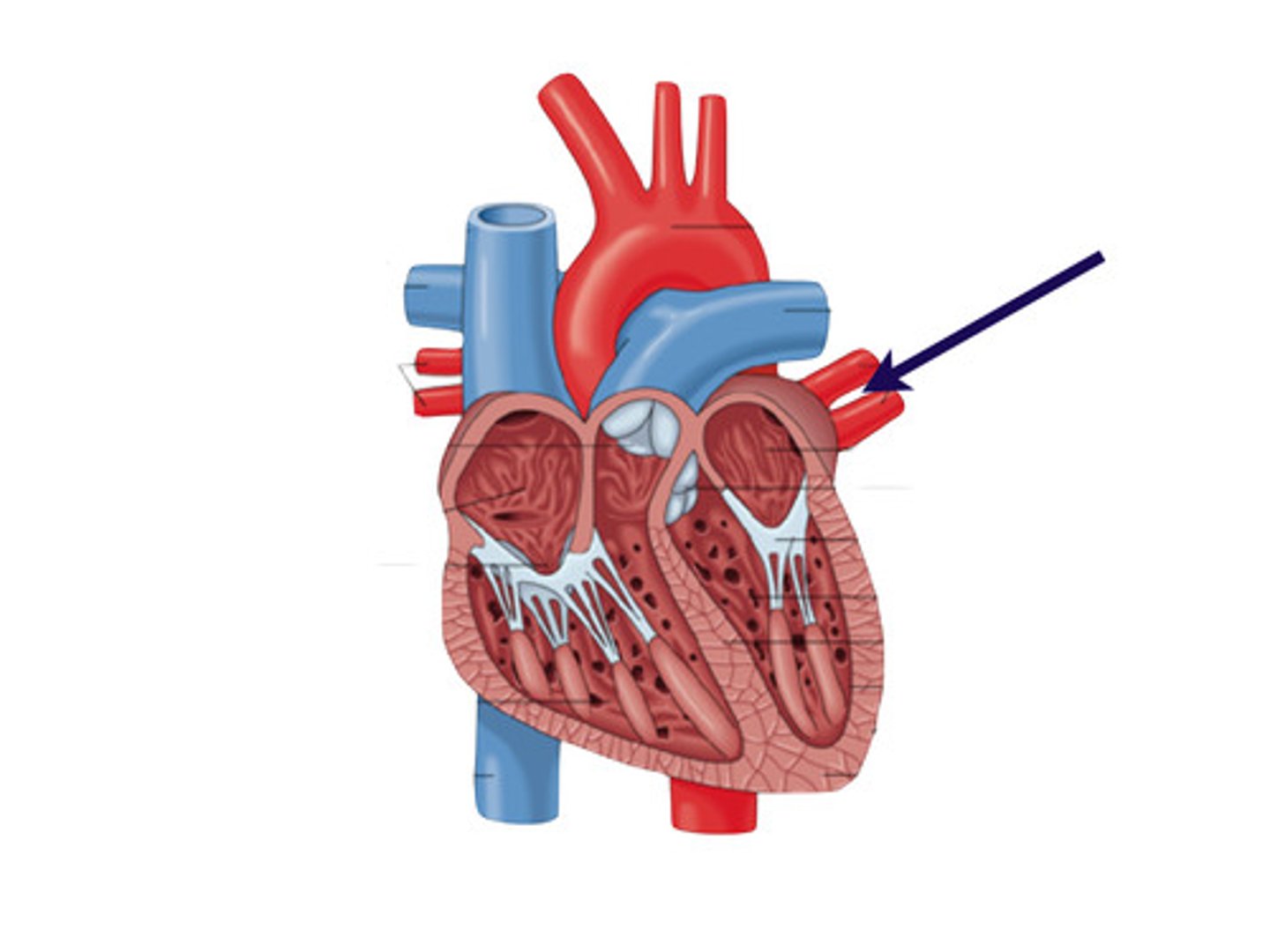
right atrium
chamber that receives deoxygenated blood from the body via the superior and inferior vena cava
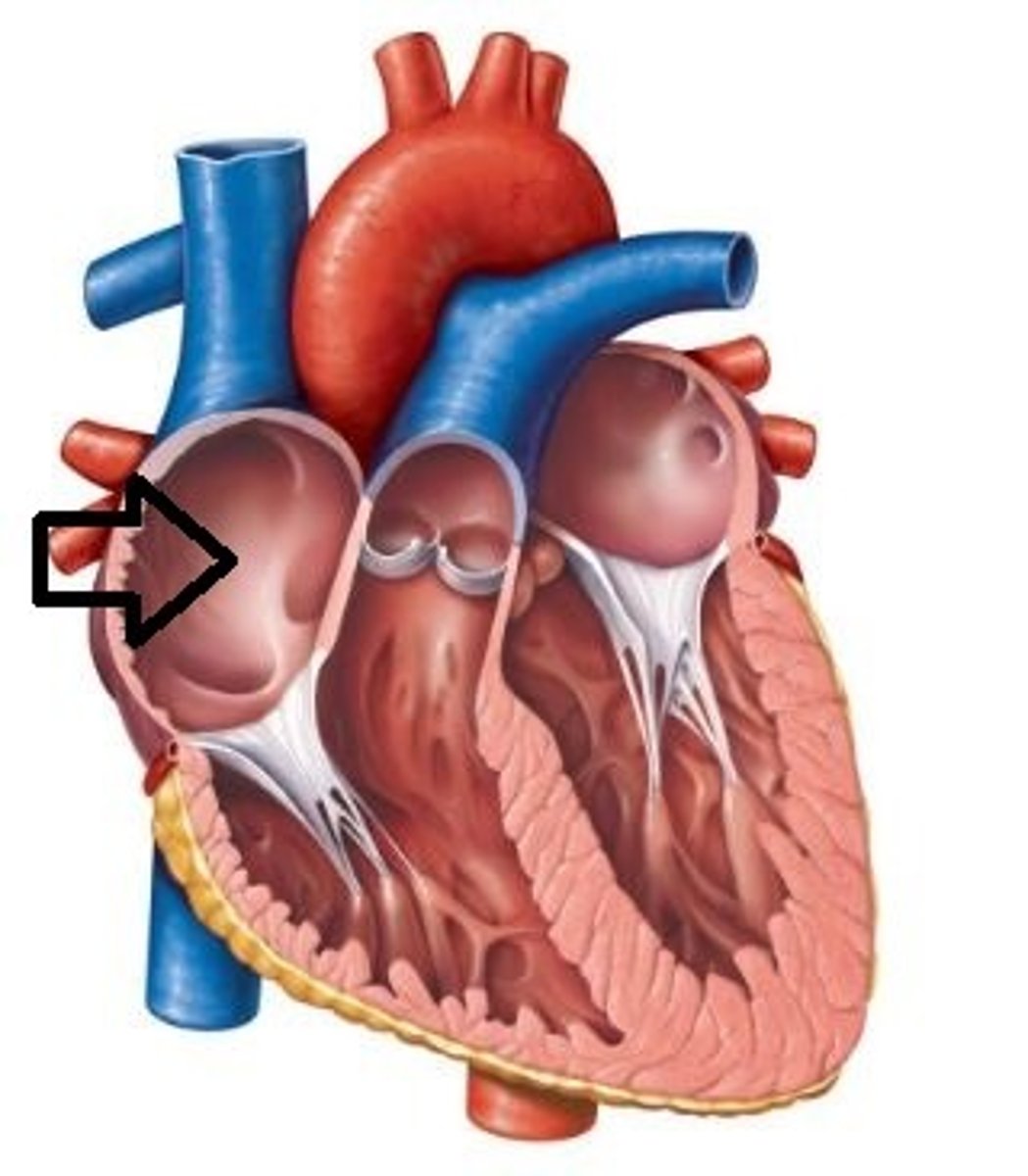
right ventricle
chamber that pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs through the pulmonary trunk (and then pulmonary arteries)
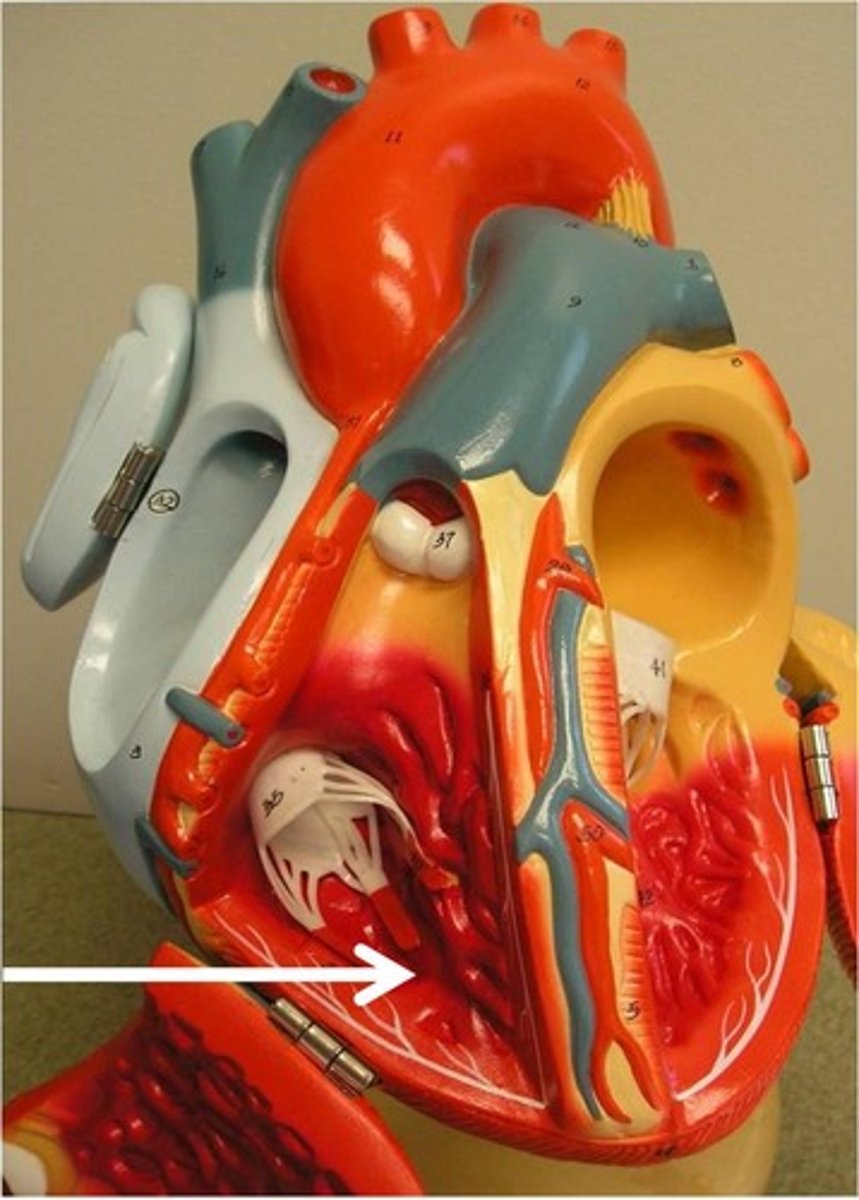
right atrioventricular (tricuspid) valve
valve between the right atrium and the right ventricle; prevents backflow of blood
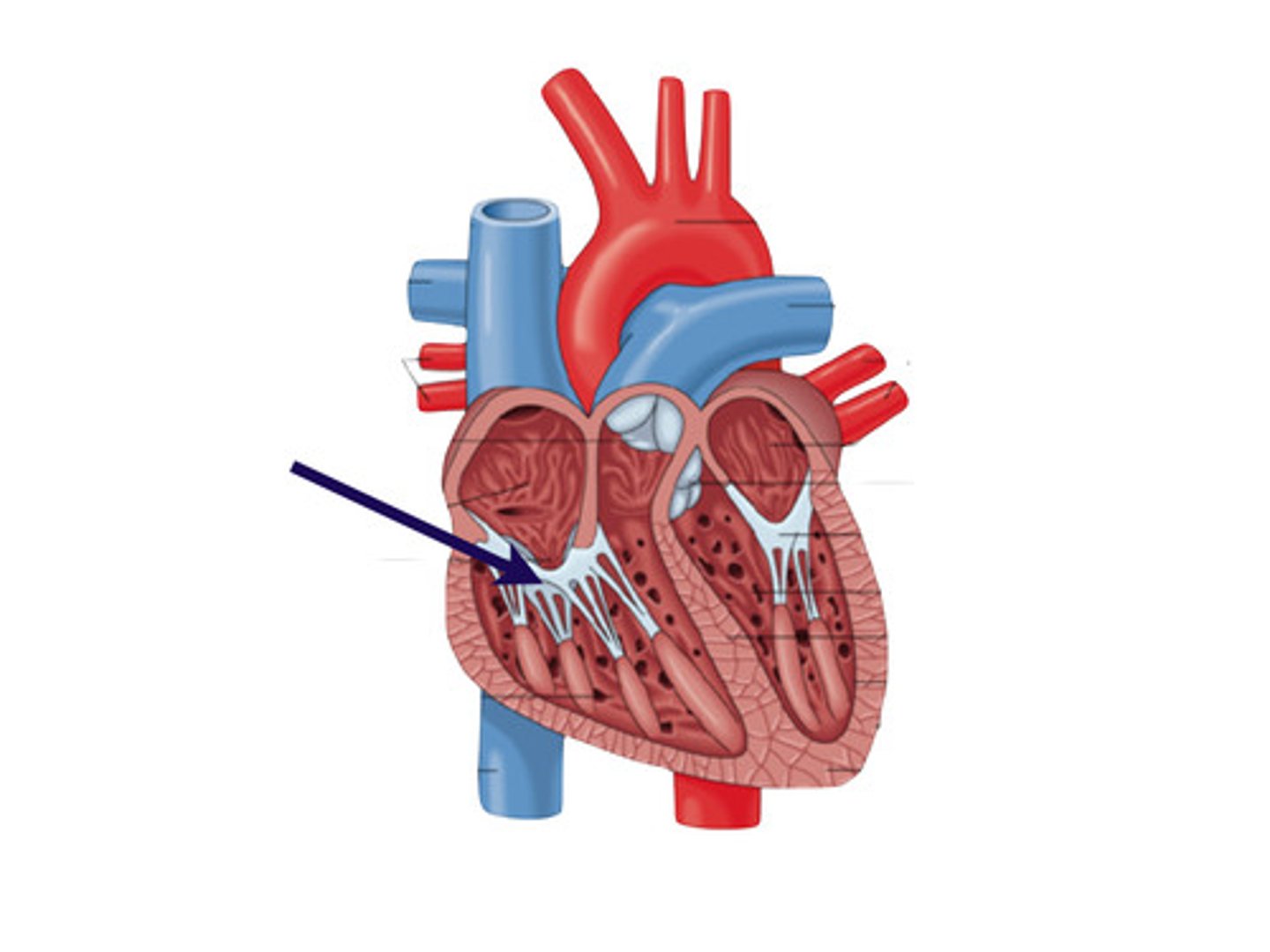
interventricular septum
partition between the right and left ventricles
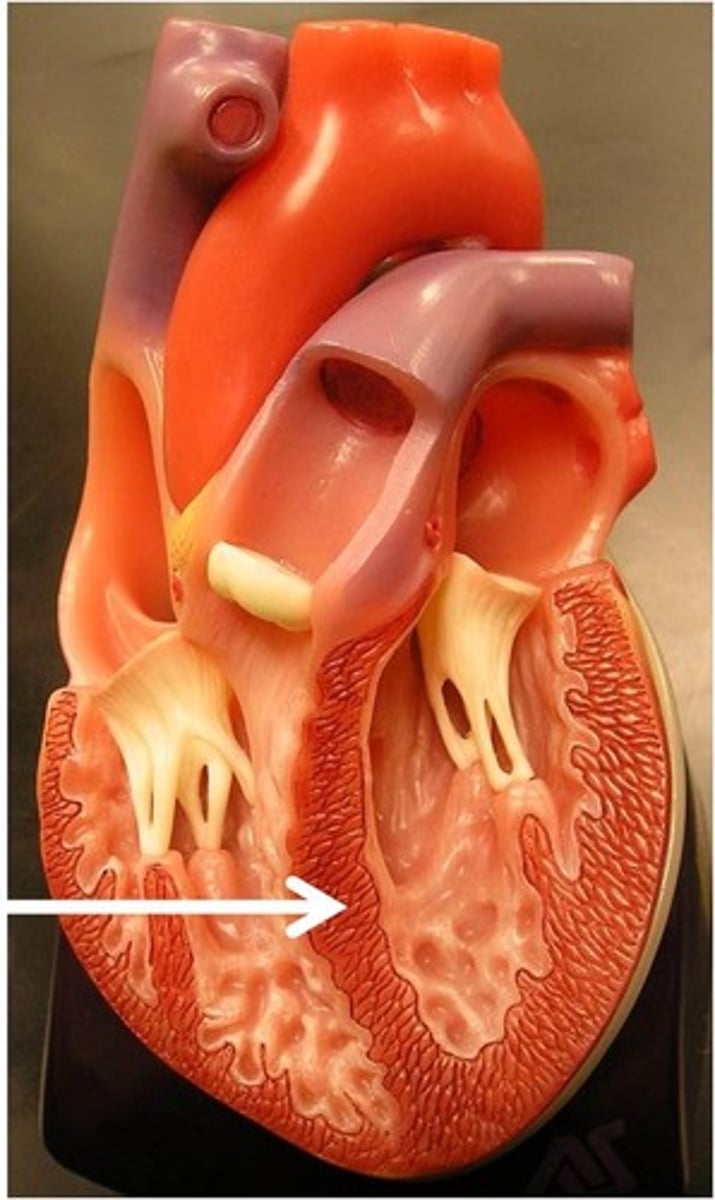
coronary sulcus
groove that marks border between atria and ventricles
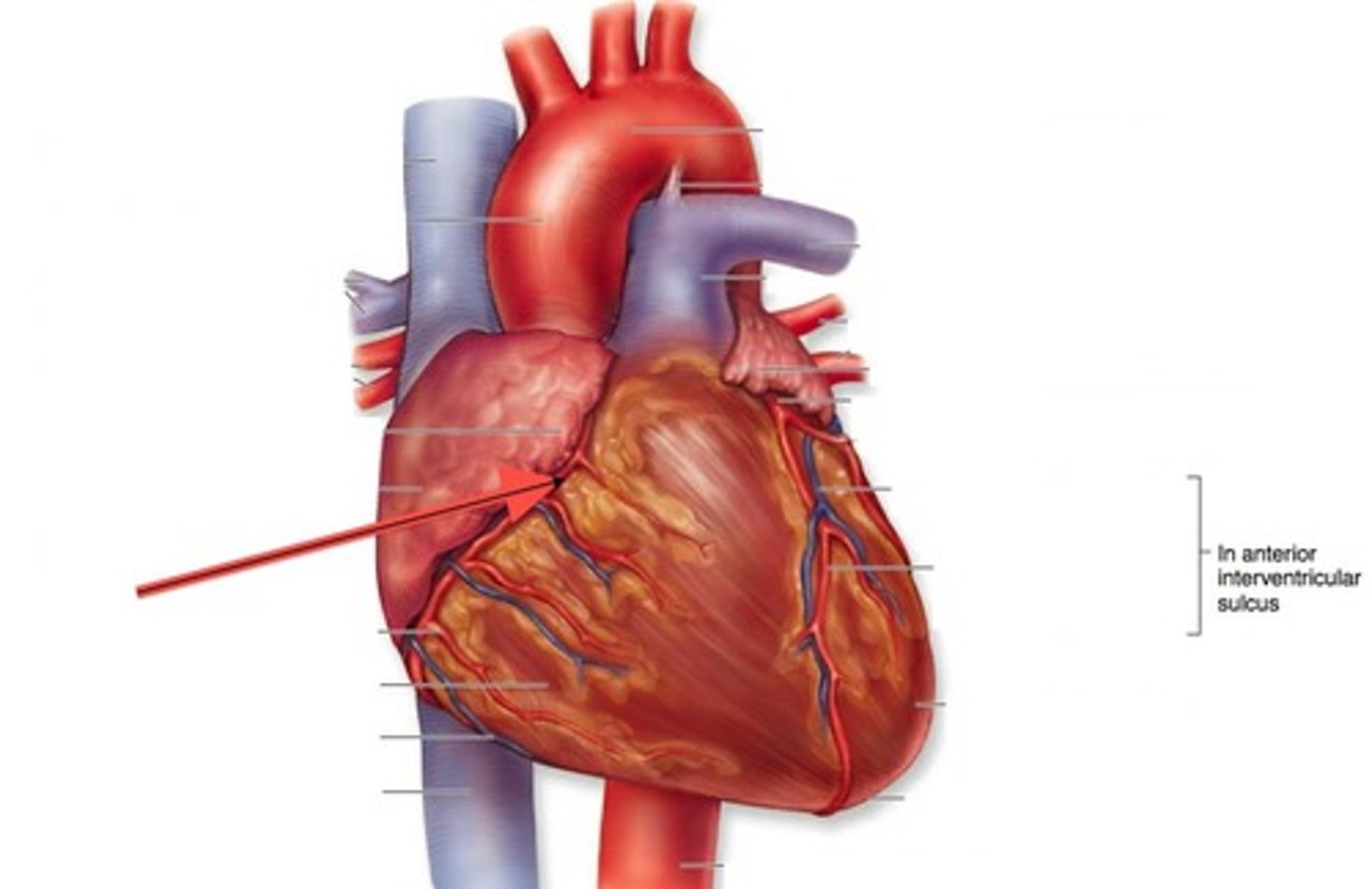
anterior interventricular sulcus
groove between the ventricles anteriorly
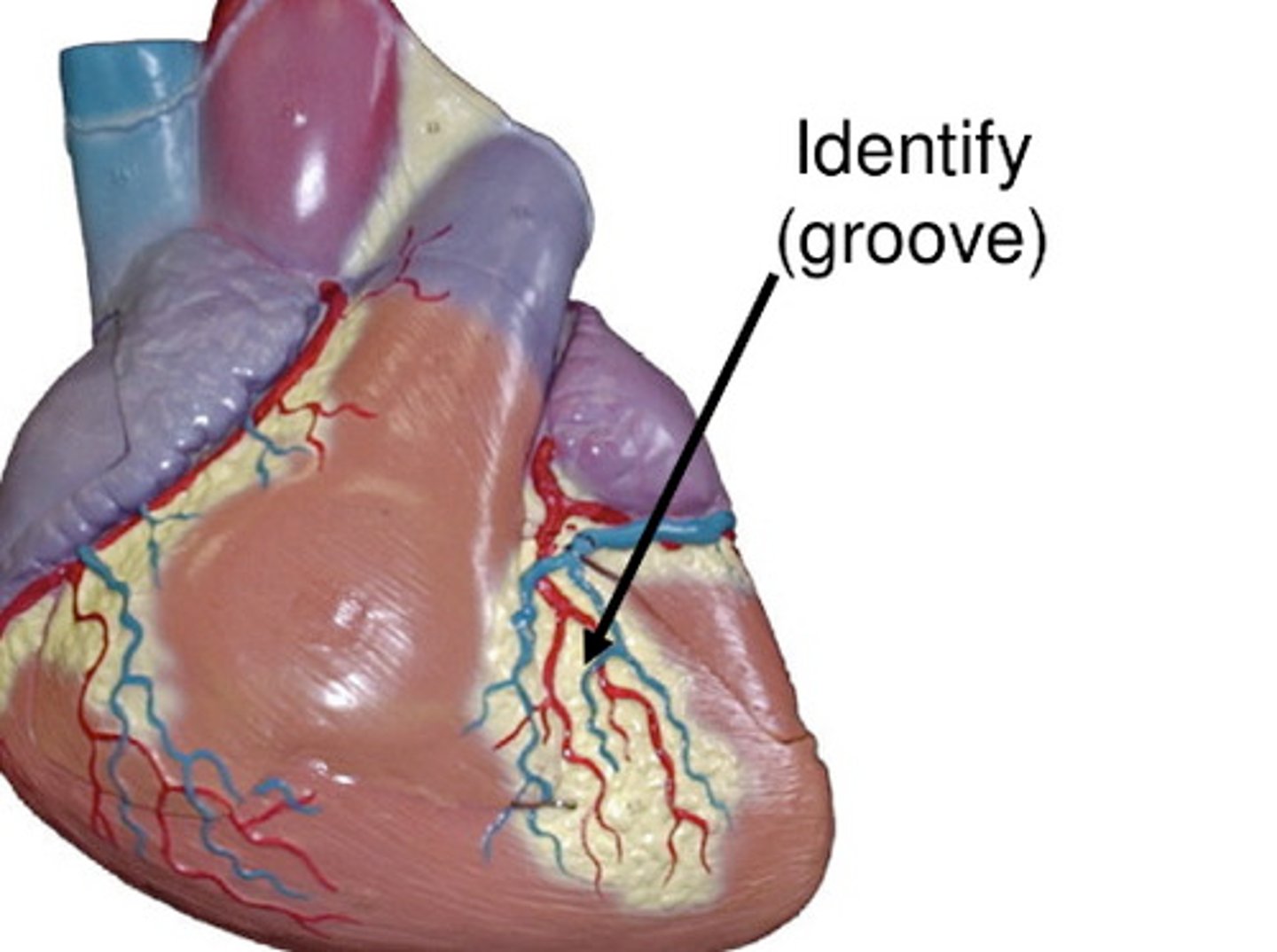
anterior interventricular artery
supplies blood to the interventricular septum and anterior walls of both ventricles
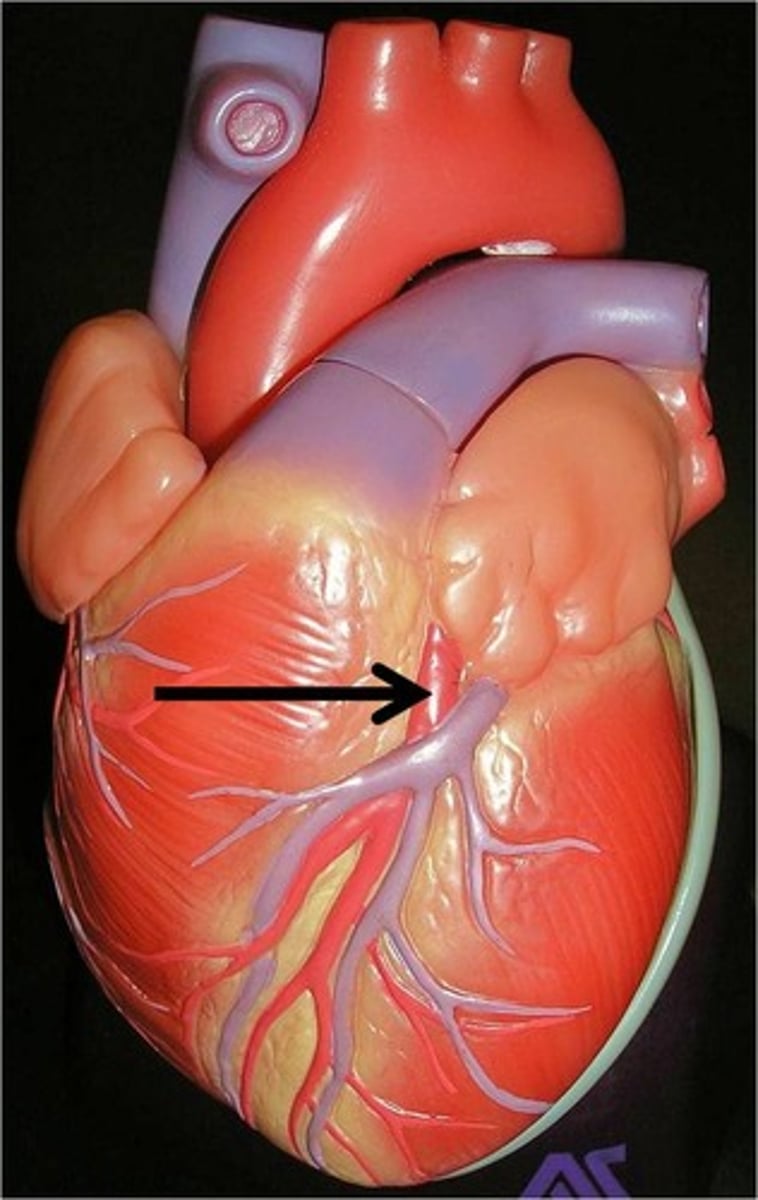
posterior interventricular sulcus
groove between the ventricles posteriorly
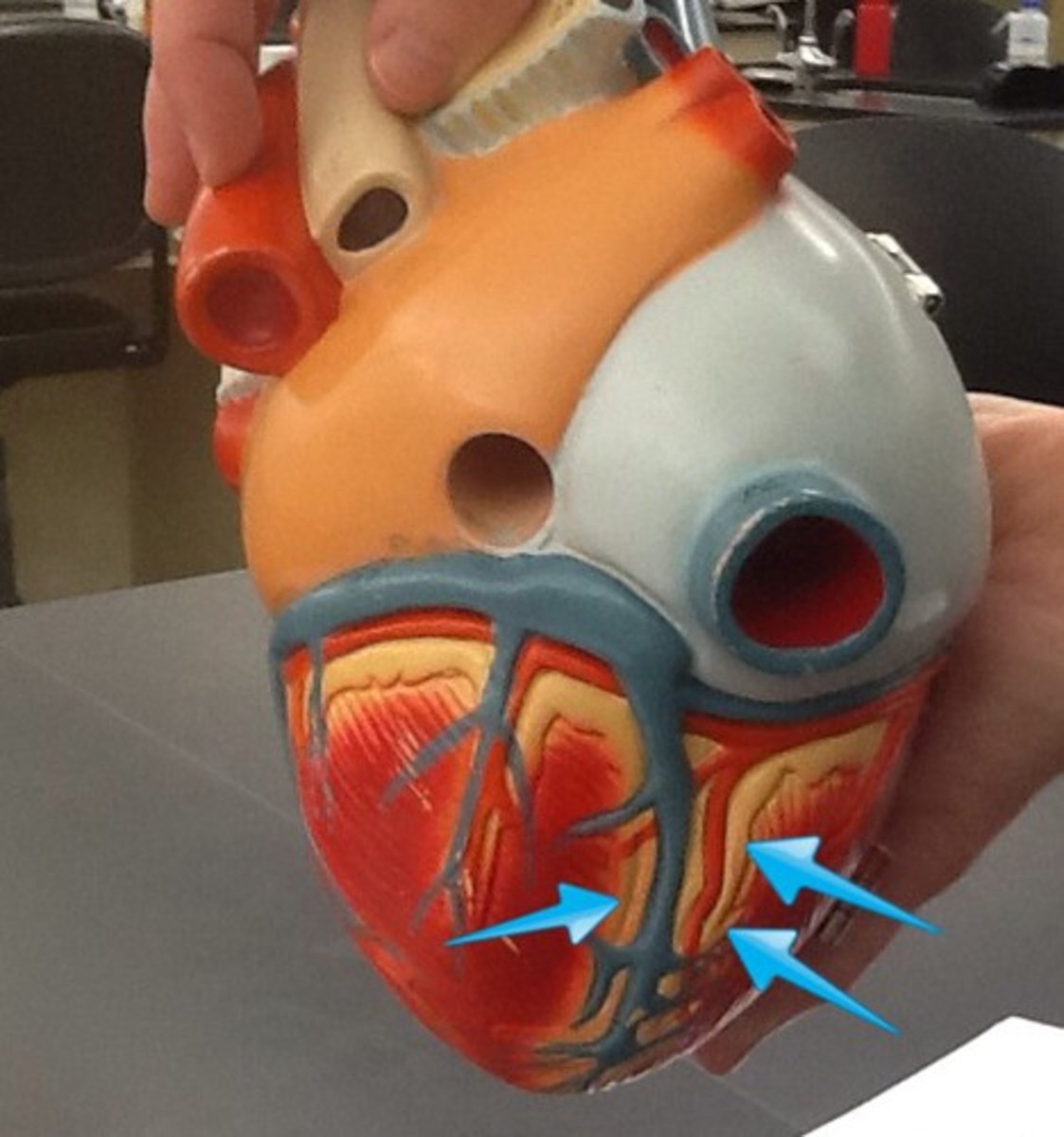
coronary sinus
enlarged vessel on the posterior aspect of the heart that empties blood into the right atrium
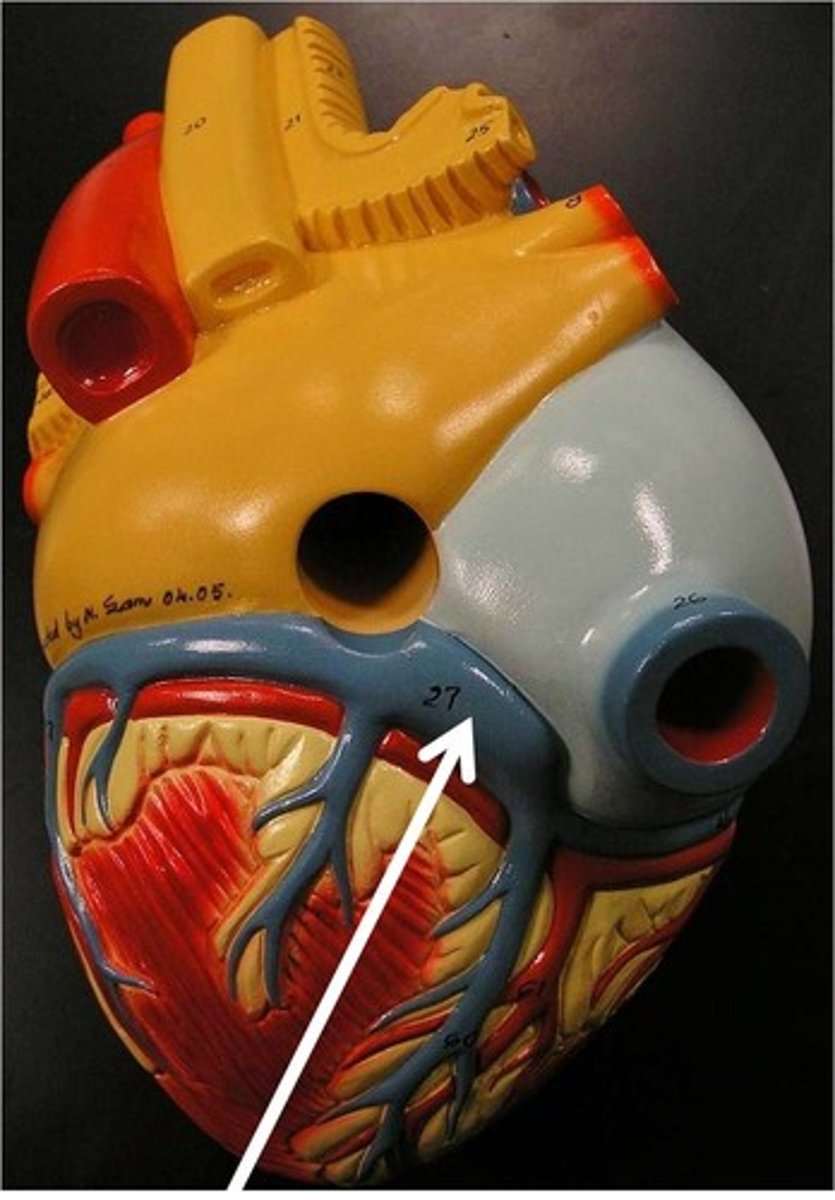
endocardium
membrane lining the cavities of the heart
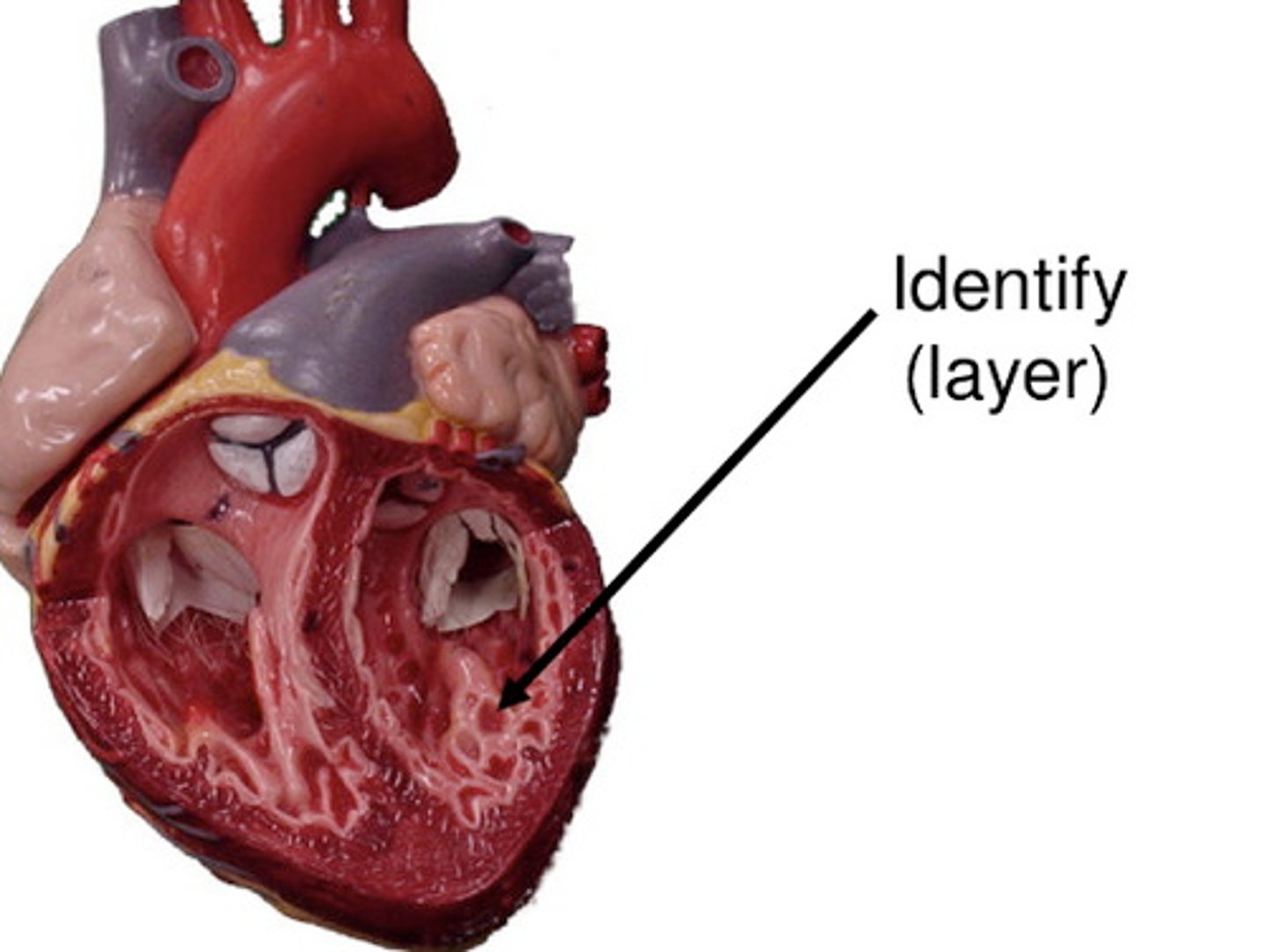
epicardium
visceral pericardium