Plasticity L1,2,3- Mechanical behaviour
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
How to tell if directions lie in plane?
Direction will be perp to plane normal
Dot product of plane normal + direction = 0
How to find angle between 2 planes?
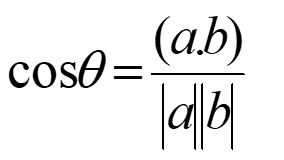
What is the stacking direction in a cubic material?
[111]
What is work hardening?
increasing stress with increasing plastic strain
Toughness
Measure of energy of fracture
Where does necking start?
At strains beyond UTS (ultimate tensile strength)
Stress-strain curve
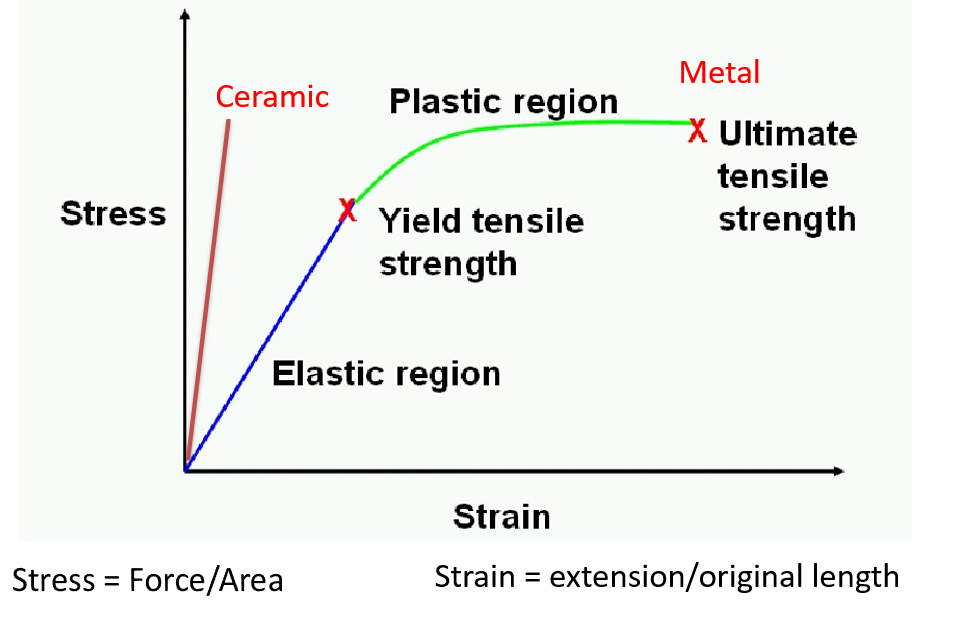
When does necking and uniformity of deformation occur?
occurs when the rate of work hardening is less than
stress increase as the specimen diameter decrease hence area decreases
Why does non-homogenous deformation occur?
microstructural effects (Luders bands, polymer chain straightening)
Equation for true strain
εeng = engineering strain
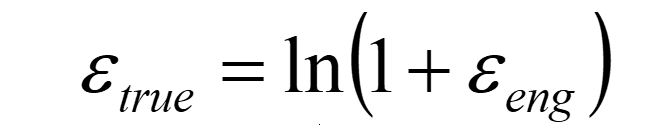
Equation for true stress
P = load (N)
A = Area
σeng = engineering stress
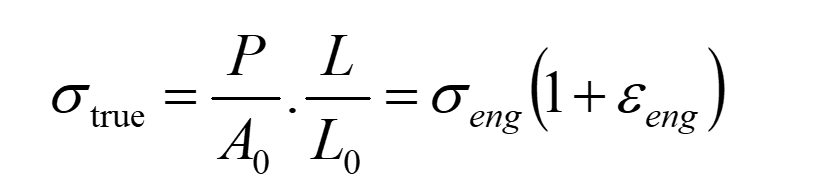
Considere’s Criterion
As vol = constant for plastic deformation
The faster the work hardens, the more stress
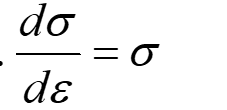
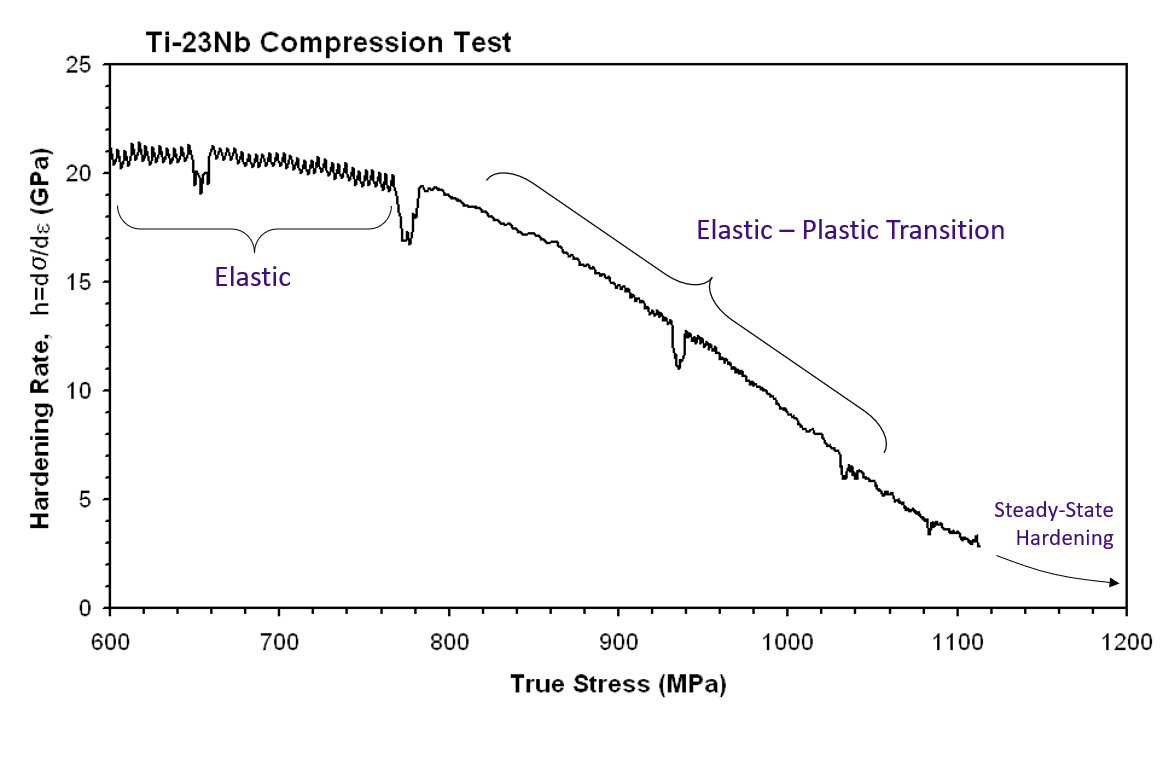
Work hardening curve
During plastic transition, work hardening rate decreases
Condition for neck to develop:
mσ/ε ≤ σ
Condition for necking :
ε≥m
m = work hardening rate
Slip plane
The plane on which deformation occurs- highest atomic density (except dislocations in ionic ceramics must be charge neutral)
slip system = slip plane + slip direction
Slip direction
the direction within slip plane + generally along line of highest atomic density
Slip system
crystal deforms by motion of dislocation on slip plane + in certain direction
Difference between Sessile + Glissile dislocations:
In Glissile dislocations slip plane contains both line + burgers vector ⇒ mobile
Sessile doesn’t
Plane family in FCC that has highest atomic density
{111}
Direction family in FCC that has highest atomic density
<110>
When does yield occur?
When resolved shear stress on 1 of favourable slip systems exceed a critical value i.e. critical resolved sheer stress,τcrss
Equation for CRSS on dislocation:
τcrss = σy cosλcosΦ
λ = angle of force normal to slip direction
Φ = angle to plane
σy= yield stress
cosλcosΦ = m = Schmid factor
During tensile testing, why will crystal lattice rotate ?
interplanar spacing remains constant
no. planes stays constant
hence shear strain from dislocation glide causes material to lengthen ⇒ angle of plane must change
Taylor criterion
In polycrystalline materials, each grain can’t deform freely so must take account of neighbouring grains
must be 5 + independent slip systems to ensure ductility in polycrystalline solid
results from 6 independent components of strain (3 normal + 3 shear)
During plastic def, vol = constant +
Δvol = sum of 3 normal strains
Hexagonal materials don’t have 5 independent slip systems so brittle
Type of schmid factor(m) we want:
Want the absolute largest/ maximum m value
Energy per unit length of dislocation equation
E ≈ αGb²
G = Sheer modulus
b = burgers vector
E = Energy per unit length of a dislocation
Frank’s rule
(b1² + b2²) > b3²
b= burgers vector
Why do we use Frank’s rule?
To decide if it’s energetically favourable for dislocation to combine or separate
Equation for true strain
εtrue = ln(1+εeng)
Equation for true stress
σtrue = σeng(1+εeng)
For plastic deformation
Volume is conserved