Haemolytic Anaemia – Mechanisms, Classification & Autoimmune Causes (Exam-Ready Flashcards)
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
What is haemolysis?
Reduced red cell lifespan due to increased destruction, leading to anaemia that may be compensated or uncompensated.
What are the two mechanisms of haemolysis?
Extravascular – spleen/liver macrophages and Intravascular – destruction within circulation via complement
What characterises extravascular haemolysis?
characterised by macrophage removal of antibody-coated red cells, the presence of spherocytes, increased bilirubin, splenomegaly, and absence of haemoglobinuria.
What characterises intravascular haemolysis?
Complement-mediated lysis, haemoglobinaemia, haemoglobinuria, ↓ haptoglobin, risk of renal damage.
What is Autoimmune Haemolytic Anaemia (AIHA)?
Anaemia caused by autoantibodies directed against the patient’s own red cell antigens.
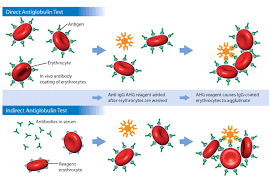
How is AIHA diagnosed?
Positive Direct Antiglobulin Test (DAT / DCT) showing IgG and/or complement on red cells.
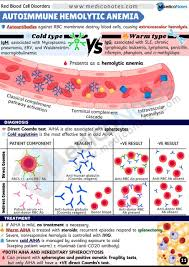
What are the two main types of AIHA?
Warm AIHA(IgG) Cold AIHA(IgM with complement)
Common clinical features of haemolysis?
Pallor, fatigue, jaundice, splenomegaly, dark urine, gallstones.
Key laboratory features of haemolysis?
increase LDH, ↑ unconjugated bilirubin, ↓ haptoglobin, ↑ reticulocytes, polychromasia/NRBCs.
Warm AIHA – mechanism
IgG (± C3d) binds red cells at 37°C → splenic macrophage removal → extravascular haemolysis.
Warm AIHA – diagnosis & blood film
DAT positive for IgG ± C3d, spherocytes on film, anaemia of variable severity.
Warm AIHA – treatment
Steroids (first line), rituximab, splenectomy, immunosuppression, folic acid, transfusion if severe.
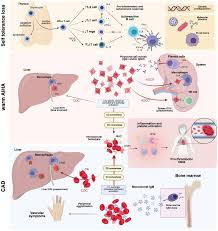
Cold AIHA – mechanism

IgM binds red cells in cold periphery → complement activation → intra ± extravascular haemolysis.
Cold AIHA – diagnosis & lab clues
DAT C3d positive only, red cell agglutination, spurious ↑ MCV/MCHC, mild–moderate anaemia.
Cold AIHA – treatment
Keep warm, rituximab, complement inhibitors (eculizumab), plasmapheresis, cautious transfusion with blood warmer.
what is Paroxysmal Cold Haemoglobinuria (PCH)
Acute severe intravascular haemolysis due to Donath–Landsteiner IgG; DAT complement positive; supportive management.