MCB 3020 L Biochemical Tests and Selective and Differnetial media
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
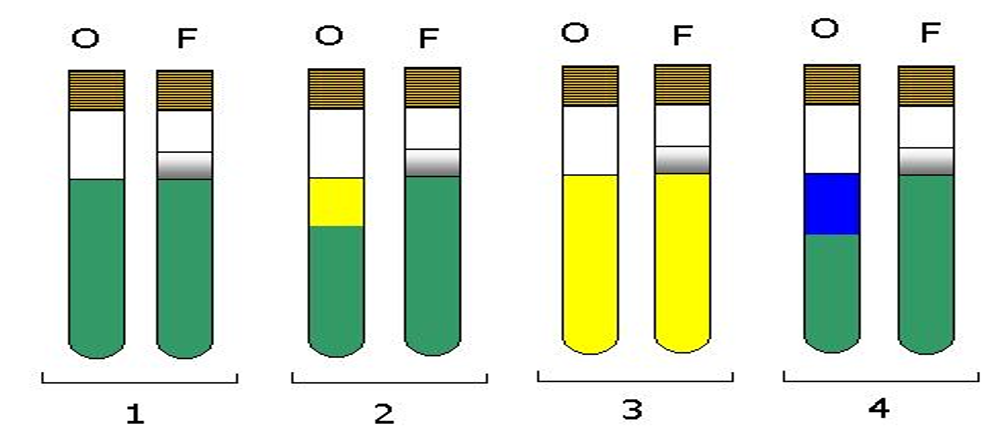
Oxidative Fermentative (OF) Medium Test
•Green(-), yellow(+; acidic), blue (-; alkaline)
•Byproducts: Gas (crack in agar)
•Purpose: To determine if bacteria has the ability to metabolize glucose oxidatively, fermentatively or both
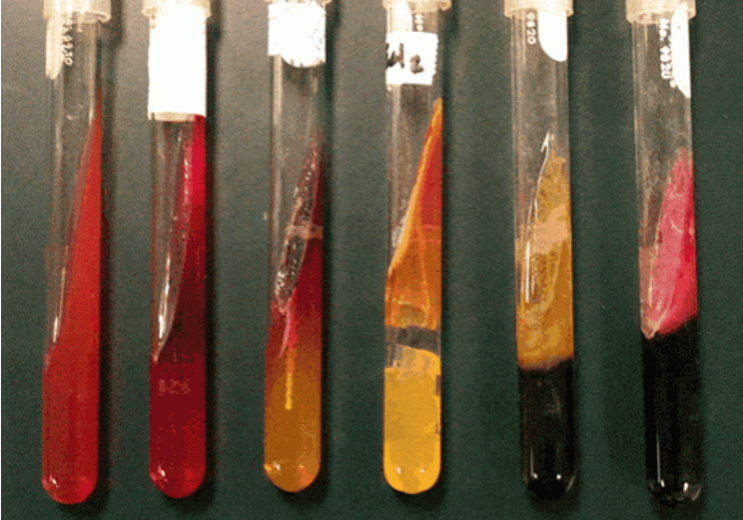

Kligler’s Triple Sugar Iron (TSI) Agar Test
•Reactions: next slide; red (-), yellow (+),
•Byproducts: Gas (crack in agar),
H2S (hydrogen sulfide, black)
•Purpose: To determine if bacteria has the ability to metabolize glucose, lactose or sucrose

Nitrate Reduction Test
•Color change (+): pink/red after reagent A and reagent B
OR (+) brown after Zinc dust
•Color change (-): pink/red after Zinc
•Byproducts: Gas (in Durham tube)
•Purpose: To determine if bacteria has the ability to breakdown nitrates into nitrites via nitrate reductase (enzyme)

Gelatin Hydrolysis
•Reactions:
•After Ice bath: Liquefaction (+); Solid (-)
Proteolysis is the enzymatic process by which gelatinase (enzyme) breakdown gelatin
•Purpose: To determine if bacteria has the ability to breakdown gelatin via enzyme gelatinase
Urease Test
•Purpose: To determine if bacteria has the ability to produce and utilize urease (enzyme)
•Reactions:
•Pink (+); alkaline = urease broken down to urea (basic)
Yellow (-); acidic
Starch Hydrolysis Test
•Purpose: To determine if bacteria has the ability to produce the enzyme alpha-amylase which will breakdown starch).
•Reactions:
•Clear (no color change from orange) zone around bacterial colony after addition of iodine (+); starch NOT present, so what is?
•No zone around colony after addition of iodine (-)
•Must have growth of bacteria for valid result
NOTE: Iodine is an orange color and turns purple in the presence of starch
Methyl Red Test (MR)
•Used to determine if the mixed acid fermentation pathway was used to ferment glucose and produce one or more stable organic acids as a byproduct.
•If the mixture remains red (positive)
•Acidic end products (lactic, acetic, succinic, and formic acids) were produced creating an acidic environment (pH < 4.4) in the tube
•If the mixture turns yellow (negative)
•This pathway was not used (pH > 6)
Voges-Proskauer Test (VP)
•Used to determine if the 2,3 butanediol fermentation pathway was used to ferment glucose
•If mixture is Brownish-red/pink (positive)
•Acetoin is present. Therefore, bacteria produces 2,3 butanediol end product instead of organic acids
•If mixture is Brownish-green/yellow (negative)
•Acetoin is NOT present. Therefore, glucose was not fermented using the 2,3 butanediol pathway
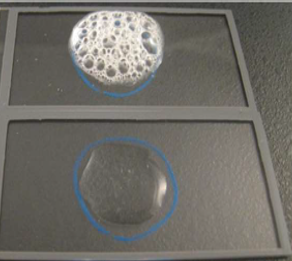
Catalase Test
•Purpose: To determine if bacteria produces and utilizes catalase (enzyme).
•Materials: slide and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)
•Reactions:
•Bubbles (+); why?
•No bubbles (-)
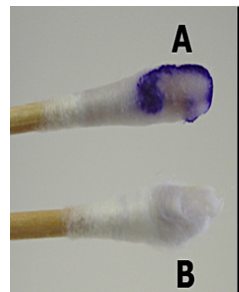
Oxidase Test
•Purpose: To determine if bacteria produces and utilizes Cytochrome-C (enzyme)
•Reactions:
•Blue (+); Cyt-c present
No color (-)
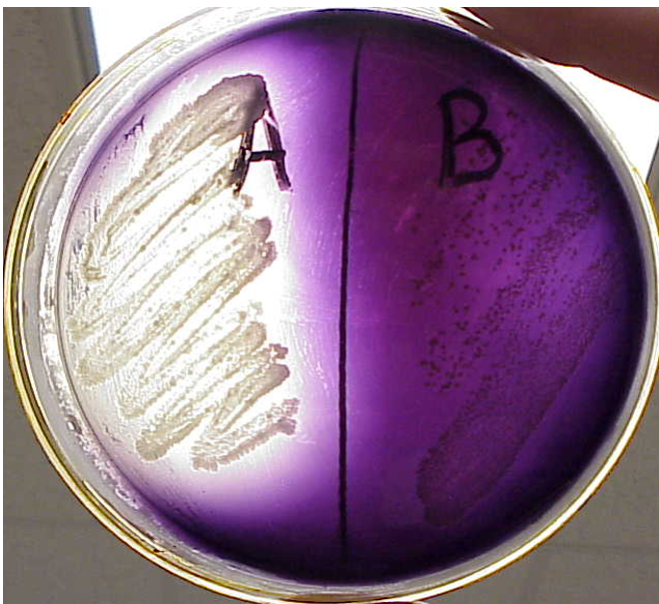
Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA)
•Selective for halophiles
•Differential for mannitol fermenters
•Yellow = acid production from using mannitol
•Red = neutral pH, no fermentation
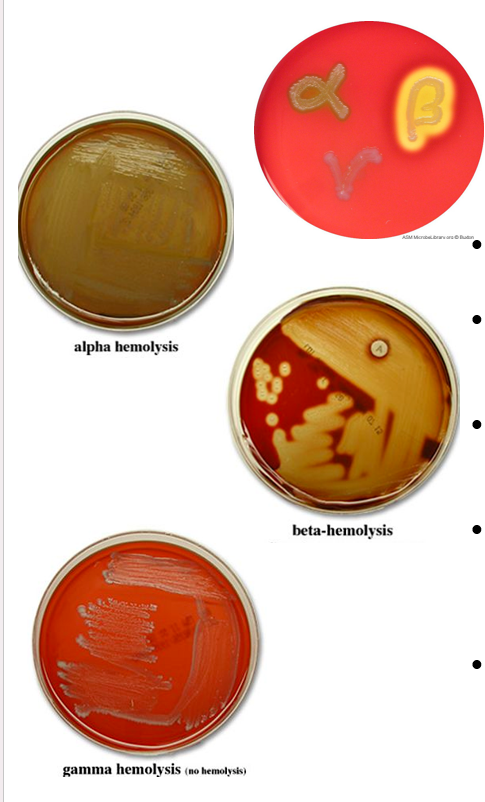
Blood Agar
•NOT selective
•Differential: identifies types of hemolysis of red blood cells
•Beta-hemolysis = zone of clearing complete hemolysis of RBCs
•Alpha-hemolysis = green areas partial hemolysis of RBCs (hemoglobin → met-hemoglobin)
Gamma-hemolysis = whitecolonies (no clearing) no hemolysis
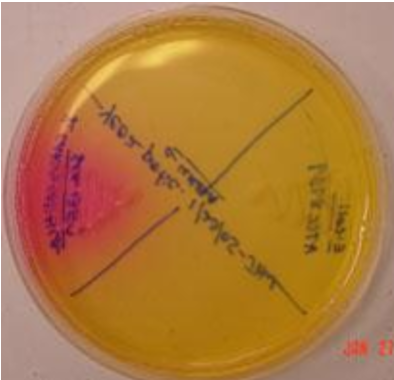
Eosin Methylene Blue Agar (EMB)
•Selective (slightly): Mostly gram-negatives grow on this agar
•Gram positives are inhibited by the dyes (Eosin Y and Methylene Blue)
•Differential: how it utilizes lactose
•Non-lactose fermenter = cream/colorless/light purple/pink colonies
•Lactose fermenter = dark purple colonies
RAPID fermentation + strong acid production = green sheen-like (like E. coli)
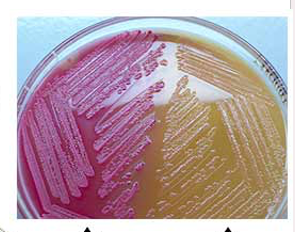
MacConkey Agar
Selective: only Gram negatives grow on this agar
•Gram positive growth is inhibited by bile salts and crystal violet
Differential: utilization of lactose
●Non-lactose fermenter= pale yellow agar; off-white opaque colonies (-)
●Lactose fermenter= bright pink/red, acidic pH (+)

Citrate Test

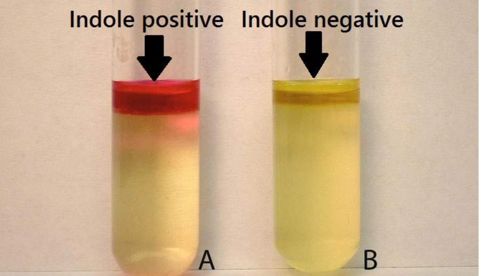
Indole Test
