Chapter 3 Compartmentation: Cells and Tissues単語カード | Quizlet
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
cranial
brain, spinal cord
thoracic
heart, lungs
An incision made between the ribs would be called a ____?
thoracotomy
An incision made through the sternum would be called a _____?
sternotomy
abdominopelvic
abdomen:
- lined with peritoneum which also surrounds the stomach, intestines, liver, pancreas, gallbladder, and spleen.)
Kidneys are retroperitoneal
Pelvis:
reproductive organs, urinary bladder and terminal portion of the large intestine
What is a lumen?
the interior of any hollow organ.
may be wholly or partially filled with air or fluid.
For some organs, the lumen is essentially an extension of the external environment, and material in the lumen is not truly part of the body's internal environment until it crosses the wall of the organ. True or false?
TRUE
Ex.
What are internal lumens?
lined with endothelium
ex. chambers of the heart
ex. blood vessels
What are external lumens?
lined with epithelium (have exit or entrance to body)
ex. air sacs of lungs
ex. digestive system, urinary, reproductive
What percent of the body is water?
60%
How much of body fluid is extracellular?
1/3 or 33%
fluid OUTSIDE of the cells
How much of body fluid is intracellular?
2/3 or 66%
fluid INSIDE of cells
What is the extracellular fluid divided into?
Plasma: (25% of the ECF) & contains more protein than interstitial fluid
Interstitial fluid: (75% of the ECF)
- surrounds cells of tissue, except the blood
each have nearly the same contents, expect for the proteins
How does fluid move among the compartments?
plasma <--> interstitium & extracellular <--> intracellular
What are the functions of the cell membrane (plasma membrane, plasmalemma)?
1. isolates cell (barrier)
2. regulates exchange (phospholipid bilayer, protein channels & transporters)
3. communication (receptors)
4. structure & support (anchor cytoskeleton)
Membrane phospholipids form bilayers, micelles, or liposomes.
How do they arrange themselves?
So that their nonpolar tails are not in contact with aqueous solutions such as ECF.
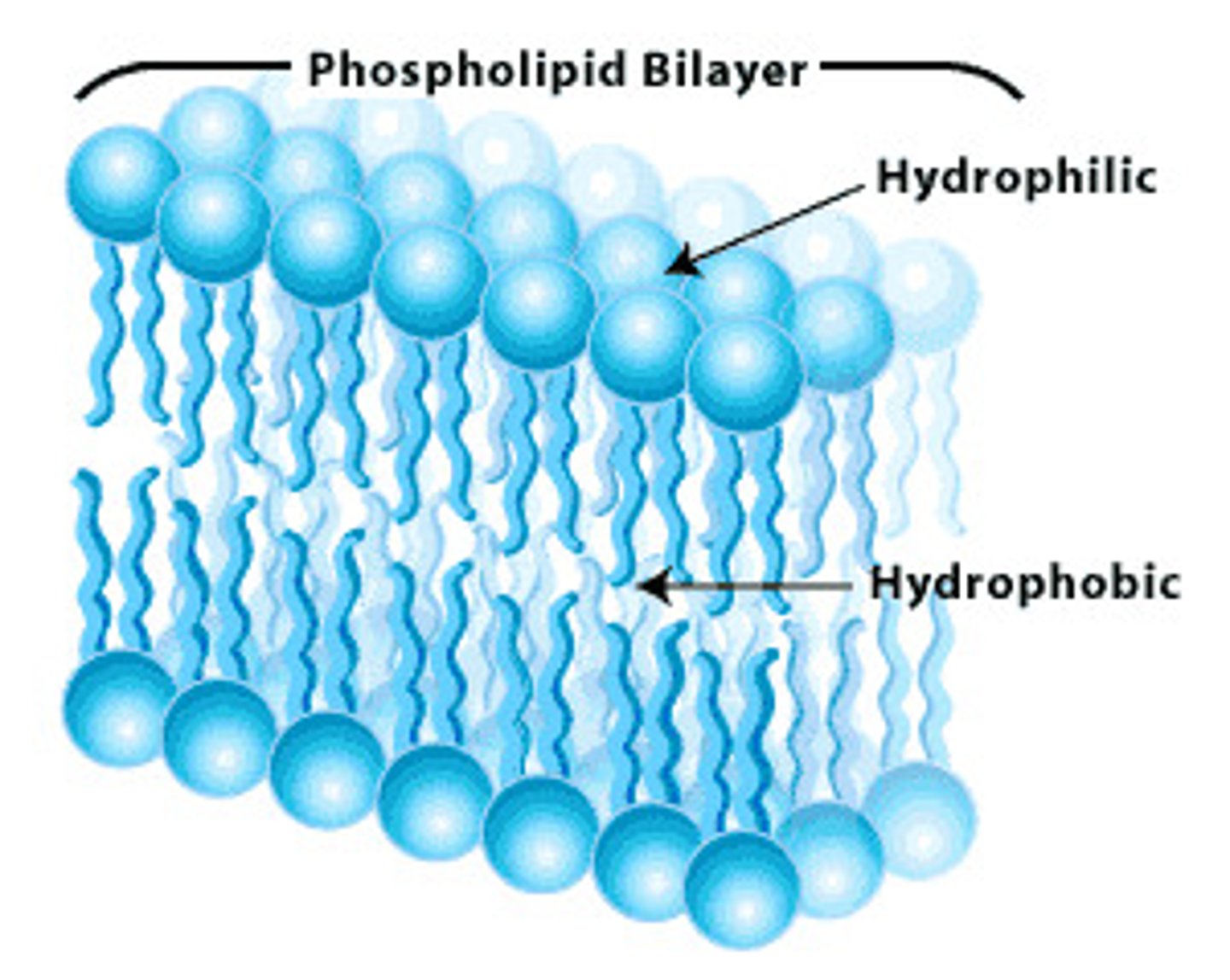
What is a phospholipid bilayer?
amphipathic
forms a sheet - external barriers
they are hydrophobic barriers
have a polar head (phosphate) and non-polar tail (fatty acids)
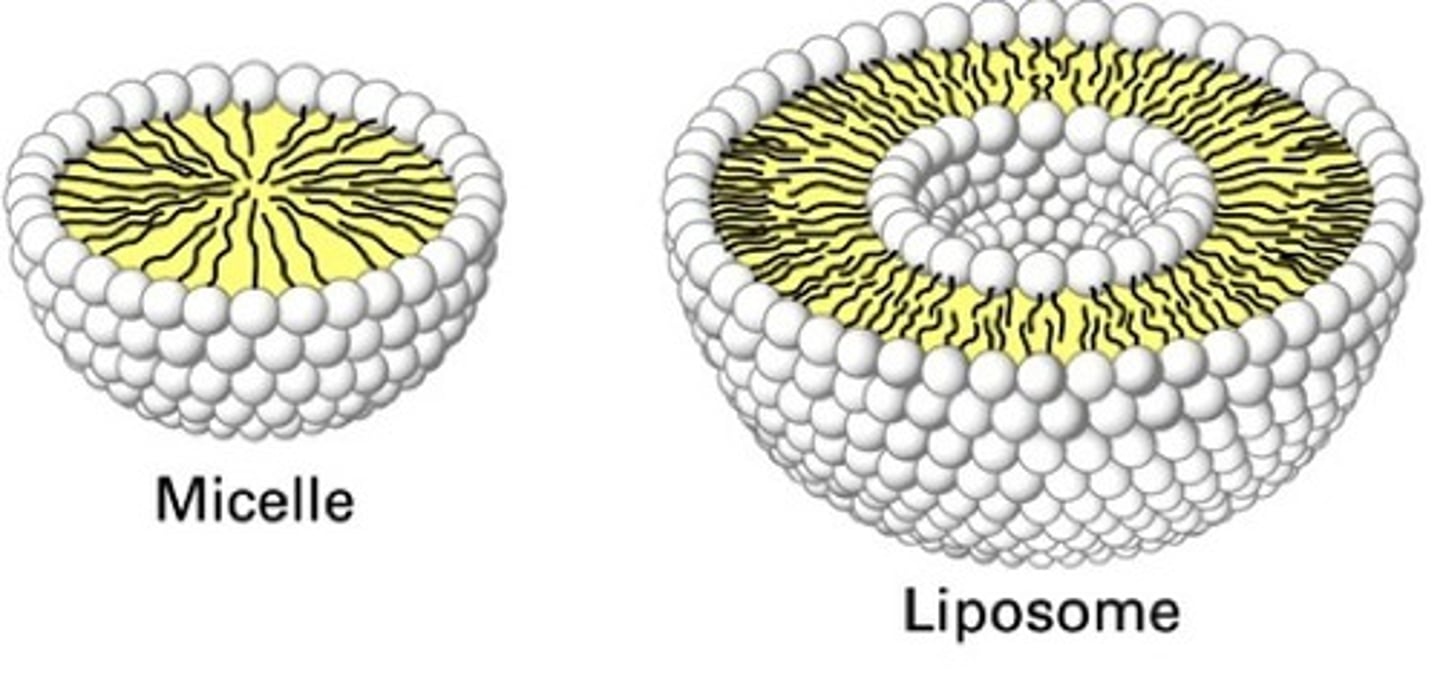
What is a micelle?
droplets of phospholipids.
important in lipid digestion
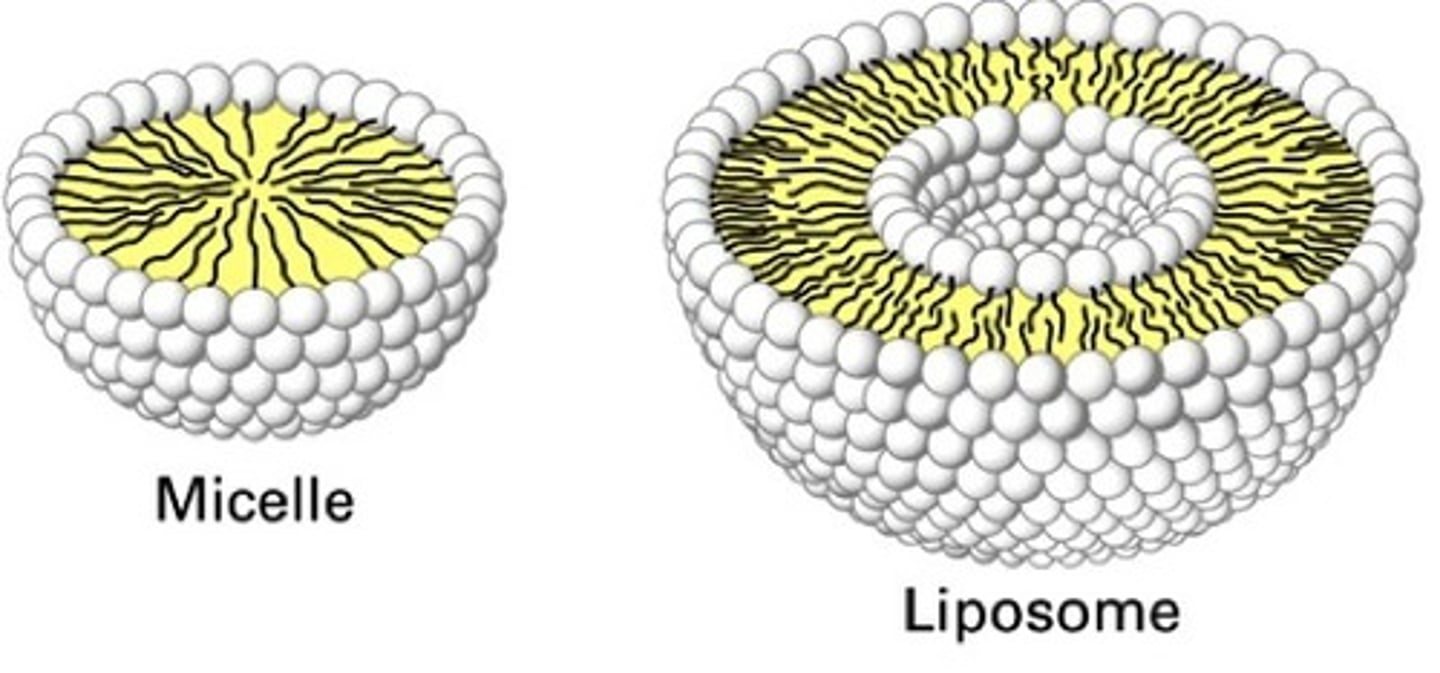
What is a liposome?
has an aqueous center
internal storage (phospholipid bilayer)
potentially the precursor to the first living cell
What does amphipathic mean?
has both hydrophilic and hydrophobic domains
What are the three main types of lipids that make up the cell membrane?
phospholipids
sphingolipids
cholesterol
What are phospholipids made of?
a glycerol backbone with two fatty acid chains extending to one side and a phosphate group extending to the other.
(major lipid of membranes usually)?
What are sphingolipids?
have fatty acid tails, but replaces phosphate with carbohydrate
they are slightly longer than phospholipids
What is cholesterol?
mostly hydrophobic
insert themselves between the hydrophilic heads of phosopholipids
helps make membranes impermeable to small water-soluble molecules and keeps the membrane flexible over a wide range of temperatures
What are integral proteins?
proteins that are embedded in the membrane
transmembrane - span across through the membrane (amphiphatic)
lipid-anchored - anchored into the bilayer on one side or the other (protein bound to fatty acid tail or sphingolipid)
What are peripheral proteins?
proteins on the surface of the membrane that include glycoproteins
can be removed without disrupting the membrane
Most membrane carbohydrates are sugars attached either to membrane proteins (glycoproteins) or to lipids (glycolipids). They are found exclusively where? what do they form there?
Found exclusively on the external surface of the cell, where they form a protective layer (THE GLYCOCALYX)
What does the cytoplasm consist of?
the fluid portion called cytosol;
insoluble particles called inclusions;
insoluble protein fibers; and
membrane bound structures called organelles
1. cytosol
2. inclusions
3. Insoluble protein fibers
4. organelles
Cytosol
intracellular fluid
semi-gelatinous fluid separated from the ECF by the cell membrane.
contains dissolved nutrients and proteins, ions, and waste products.
Inclusions
insoluble materials.
Some are stored nutrients, others are responsible for specific cell functions
i.e. glycogen, lipid droplets, ribosomes & polysomes
tend to clump together in clusters as storage areas of the cell
Cytoskeleton
compartmentalize in the cell
protein fibers and tubules
Organelles
membrane bound compartments that play specific roles in the overall function of the cell.
The inclusions of cells do not have boundary membranes and so are in direct contact with the cytosol. True or False.
TRUE
Does movement of material between inclusions and the cytosol require transport across a membrane?
NO
How are nutrients stored?
as glycogen granules and lipid droplets
What are ribosomes?
small dense granules of RNA and protein that make proteins under the direction of the cell's DNA
fixed and free
What are fixed ribosomes?
attach to the cytosolic surface of organelles, like the Rough ER
What are free ribosomes?
are suspended free in the cytosol...some form groups of 10-20 known as polyribosomes
If a ribosome is fixed, can it later become free and vice versa?
YES.
Where are ribosomes most numerous?
in cells that synthesize proteins for export out of the cell
What are microfilaments/actin fibers?
the thinnest cytoplasmic protein fiber.
function:
cytoskeleton; associates with myosin for muscle contraction
What are microtubules?
the largest protein fibers
hollow
made of tubulin
function; movement of cilia, flagella, and chromosomes; intracellular transport of organelles; cytoskeleton
What do microtubules form?
centrioles, cilia, flagella
What is the centrosome?
microtubule-organizing center
assembles tubulin molecules into microtubules
usually contains two centrioles
Where might you find cilia in the human body?
cells lining the upper airways and part of the female reproductive tract are covered with cilia.
Mitochondria
have an unusual double membrane
mitochondrial matrix is inside the inner membrane; contains enzymes, ribosomes, granules, and its own DNA.
intermembrane space, lies between the outer and inner mitochondrial membranes; plays an important role in ATP production
Endoplasmic Reticulum
a network of interconnected membrane tubes with three major functions
1. synthesis
2. storage
3. transport of biomolecules
rough and smooth
Rough ER
main site of protein synthesis
proteins are assembled on ribosomes attached to cytoplasmic surface of the RER, then inserted into the RER lumen, where they undergo chemical modification
Smooth ER
lacks attached ribosomes and is the main site for the synthesis of fatty acids, steroids, lipids
phospholipids for the cell membrane are produced here
can also detoxify in liver and kidney
stores calcium ions in skeletal muscles
Golgi Apparatus
consists of a series of hollow curved sacs (cisternae) stacked atop one another.
receives proteins made on the RER, modifies them and packages them into the vesicles
Nucleus
contains the DNA
has a nuclear envelope which is a two membrane structure that separates the nucleus from the cytoplasmic compartment.
has pores in which communication between the nucleus and cytosol takes place.
Protein synthesis
1. mRNA is transcribed from the genes in DNA
2. mRNA leaves the nucleus and attaches to cytosolic ribosomes, intiating protein synthesis
3. some proteins are released by free ribosomes into the cytosol or are targeted to specific organelles
4. ribosomes attached to the RER direct proteins destined for packaging into the lumen of the RER
5. Proteins are modified as they pass through the lumen of the ER
6. transport vesicles move the proteins from the ER to the golgi
7. golgi cisternae migrate toward the cell membrane
8. some vesicles bud off the cisternae and move in a retrograde
9. some vesicle bud off to form lysosomes or storage vesicles
10. other vesicles become secretory vesicles that release their contents outside of the cell.

How are cells in tissues held together?
cell junctions and other support structures
What is the extracellular matrix?
extracellular material that is synthesized and secreted by the cells of a tissue.
structures outside of cells or structures that allow cells to connect
always has two basic components: proteoglycans and insoluble protein fibers
What are proteoglycans?
glycoproteins which are covalently bound to polysaccharide chains
What insoluble protein fibers are included in the matrix?
like collagen, fibronectin, laminin
they provide strength and anchor cells to the matrix.
During growth and development, cells form cell-cell adhesions that may be transient or that may develop into more permanent cell junctions. True or false
true
What are cell adhesion molecules?
CAMs are membrane-spanning proteins responsible for both cell junctions and for transient cell adhesions.
mediate cell-cell or cell-matrix adhesions necessary for normal growth/development
What are the 3 major cell-cell junctions?
1. gap junctions
2. tight junctions
3. anchoring junctions
Gap junctions
simplest cell-cell junctions
all direct and rapid cell-cell communication through cytoplasmic bridges between adjoining cells.
connexins interlock to create passageways that are able to open or close
allow chemical and electrical signals to pass rapidly from cell-cell
Tight junctions
occluding junctions that restrict the movement of material between the cells they link.
cell membranes of adjacent cells partly fuse together with the help of claudins and occludins to make a barrier.
these create the blood-brain barrier
Desmosomes
attach to intermediate filaments of the cytoskeleton.
strongest cell-cell anchoring
important in the heart; keeps the cardiac cells together as they work together to pump
Epithelial tissue
lines all free body surfaces
- entering or exiting the body proper requires crossing epithelium
What are the functions of epithelial tissue?
protection, regulation, movement, secretion
Exchange epithelium
usually simple squamous
one layer of cells
flattened cell shape
features: pores between cells permit easy passage of molecules
permit rapid exchange of materials, like gases
found: in lungs, lining of blood vessels
Transporting epithelium
usually cuboidal or columnar
- apical membrane (against cavity) faces lumen
has microvilli that increase SA
-basolateral membrane (anchored) faces ECF, has folds to increase SA
one layer of cells
tight junctions prevent movement between cells; surface area increased by folding of cell membrane into fingerlike microvilli
found in intestine, kidney, some exocrine glands
selective about what can cross them
regulate the exchange of nongaseous materials like ions and nutrients between internal and external environments
Ciliated Epithelium
external movement: trachea moves mucus away from lungs from trachea up to larynx
columnar or cuboidal
one layer of cells
one side covered with cilia to move fluid across surface
found in: nose, trachea, upper airways; female reproductive tract
Protective Epithelium
many layers of cells; keratinized
flattened (squamous) in surface layers; polygonal in deeper layers
cells tightly connected by desmosomes
found in: skin and lining of cavities (like mouth) that open to the environment
Secretory epithelium
exocrine & endocrine
produces a lot of mucus, sometimes enzymes, hormones
one to many layers
columnar or polygonal
protein secreting cells filled with membrane bound secretory granules and extensive RER; steroid secreting cells contain lipid droplets and extensive SER
found in: exocrine glands (pancreas, sweat glands, salivary glands); endocrine glands (gonads, thyroid)
Structure of epithelia: basal lamina/basement membrane
thin layer of extracellular matrix lying between the epithelial cells and underlying tissues
composed of collagen and laminin filaments embedded in proteoglycans.
Leaky epithelia
anchoring junctions allow molecules to cross epithelium by passing through the gap between two adjacent epithelial cells. i.e. wall of capillaries
Tight epithelia
(in kidney)
adjacent cells are bound to each other by tight junctions that create a barrier, preventing substances from traveling cell-cell.
Types of epithelia
simple or stratified
squamous (flat)
cuboidal
columnar