Eutrophication, P Loading, and Trophic States
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Slide Deck 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
effects of cultural eutrophication
algal blooms
hypoxia
taste and odor problems
loss of economic vitality
changes in community structure
loss fish production
loss of biodiversity
facilitation of invasive species
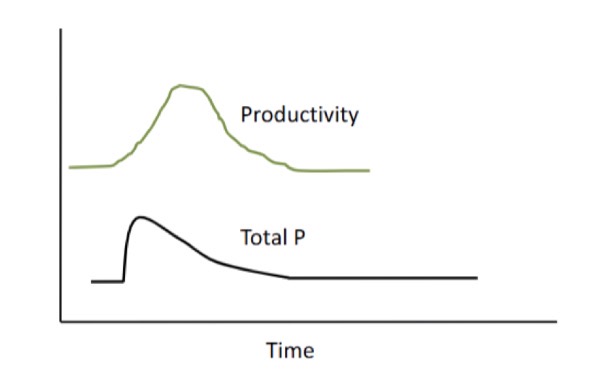
what happens when P is added to a P-limited lake as a one-time pulse
short-lived productivity boom
productivity increases right when total P starts to decrease
vollenweider’s P loading model equation
[P]λ = [P]i / (1 + √Tw)
total P concentration in the lake predicted as a function of inflow total P concentration and water resistance time
key idea of vollenweider’s
predicts lake phosphorus concentration based on external P loading and lake physical characteristics
residence time
long residence time - phosphorus accumulates - higher eutrophication risk
(more vulnerable to nutrient enrichment)
short residence time - nutrient flushed quickly - lower accumulation
when vollenweider’s model is valid
phosphorus is the primary limiting nutrient
the lake is well-mixed
the system is near steady state
external P loading dominates over internal loading
benefits to vollenweider’s
predictive
links watershed inputs to lake response
useful for management decisions
helps set nutrient loading targets
key idea of carlson’s trophic state index (TSI)
an empirical classification tool that assigns a numeric value to lake trophic states using
secchi depth
chlorophyll-a
total phosphorus
how carlson’s TSI
compares trophic state among lakes
tracks changes in lake over time
communicates lake conditions to managers and the public
benefits of carlson’s TSI
requires minimal data
ideal for monitoring and comparison
simple
differences between carlson’s TSI and vollenweider model
carlson’s TSI: describes current condition
vollenweider model: predicts response to P-loading