OS: Computer System Architecture
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Computer Hardware
it refers to the physical components that make up
a computer system. these components work
together to process, store and communicate data.
Computer Software
It is a collection of programs, instructions, and
data that enable a computer to perform specific
tasks.
Input, Output, Processing, and Storage Devices
Types of Hardware Devices
Operating System
a SOFTWARE that MANAGES and
CONTROLS the hardware, allowing programs and users to interact with the machine.
Central Processing Unit
It acts as the active brain of the computer system that is responsible for executing and managing sequence of instructions called programs directed by the operating system. Just like our brain, it simultaneously regulates all of the internal function inside the computer system.
Parts of the CPU: Control Unit
It directs the operation of the CPU and coordinates the activities of other components, such as memory and input/output devices.
Parts of the CPU: Arithmetic Logic Unit
The component of the CPU that performs arithmetic and logical operations, allowing the execution of mathematical calculations and decision-making processes.
Parts of the CPU: Registers
It is a small and fast storage within the CPU that temporarily holds data, instructions, or addresses being used by the processor
Parts of the CPU: Cache Memory
It is a high-speed memory within the CPU that stores frequently used data and instructions to reduce access time.
Parts of the CPU: Clock
It synchronizes the operations of the CPU by generating a steady pulse of electrical signals.
Parts of the CPU: I/O Interface
It manages communication between the CPU and external devices.
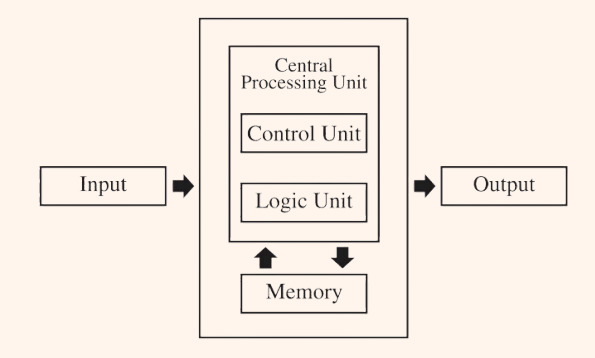
Vonn Neumann Model
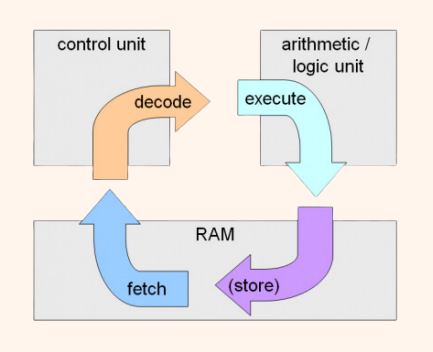
Fetch - Decode - Execute Cycle
Memory
is the faculty of the brain (CPU) in which data and information is encoded, stored, and retrieved when needed.
Primary Memory
is the main storage area in a computer system, where data is stored temporarily for quick access by the CPU during processing.
Volatile, Temporarily stores data and instructions, Much Faster, Accessed by CPU
Secondary Memory
Non-volatile
Long Term Storage
Much Slower
Accessed thru I/O Operations
Random Access Memory (RAM)
Is the main working memory of a computer. It temporarily stores data and instructions that the CPU is currently processing.
Dynamic Random Access Memory (DRAM)
Must be continuously refreshed
Consume more power
Requires less space
Cost less
Hold more data
Typically uses for main memory
Static Random Access Memory (SRAM)
does not required
refreshing.
consume less power
requires more space
expensive
hold less data
typically uses for
cache memory.
L1 Cache
Located directly on the CPU, the fastest
and smallest cache.
L2 Cache
Slightly slower than L1 but larger and typically located on or near the CPU.
L3 Cache
Larger and slower than L1 and L2,
often shared between CPU cores.
Types of Registers: Program Counter
Holds the memory address of the next instruction to be executed.
Types of Registers: Accumulator
The accumulator typically holds the result of a calculation performed by the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU).
Instruction Register
After the instruction is fetched from memory, it is loaded into the IR for decoding and execution.
Memory Address Register
Holds the memory address of the location being accessed for reading or writing.
Memory Buffer Register
Holds the data to be transferred to/from memory.
Status Registers/ Flag Registers
Used by the control unit to make decisions based on the results of previous operations.
HARD DISK DRIVE
it is a magnetic storage devices that use spinning disks (platters) to read and write data. It can stored several hundreds of gigabytes to multiple terabytes.
SOLID STATE DRIVE
It uses flash memory to store data, which provides faster access speeds than HDDs. It is more durable than HDD’s because it has no moving parts.
OPTICAL DISC
It uses lasers to read and write data to disks like CDs, DVDs, or Blu-ray discs. It is commonly used in media distribution.
USB FLASH DRIVE
It is a portable, solid-state storage devices that use flash memory. they uses USB ports for transferring and receiving files between devices.
NETWORKED ATTACHED STORAGE
it is a file-level data storage device connected to a network, allowing multiple users and devices to access and share data over the network.
VIRTUAL MEMORY
It is considered a part of secondary memory. It is a memory management technique that uses secondary storage, such as a hard drive or SSD, to extend the capabilities of primary memory (RAM).