PY 211 Midterm 1 Practice
1/34
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
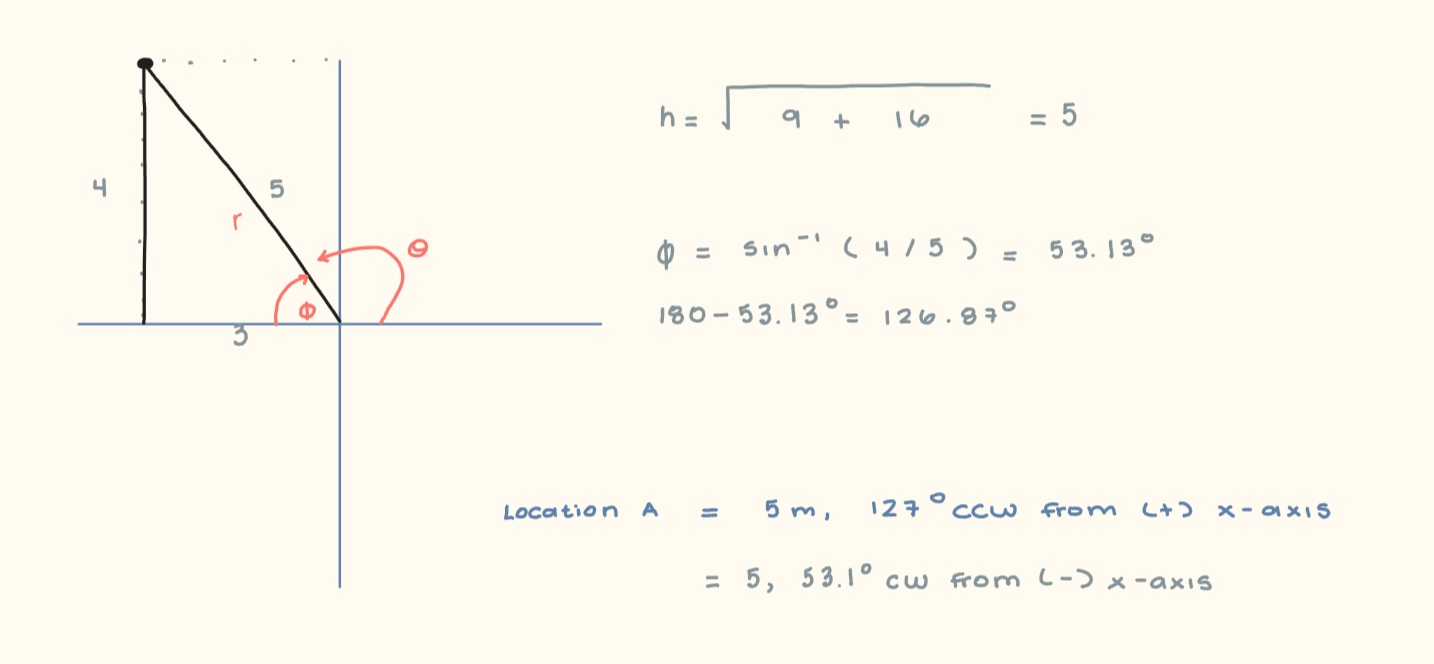
In Cartesian Coordinates, point ‘A’ is located at (-3 , 4) m. What is its location in Polar Coordinates (describe the angle CCW from the +x axis)?
5m, 127° CCW from +x-axis
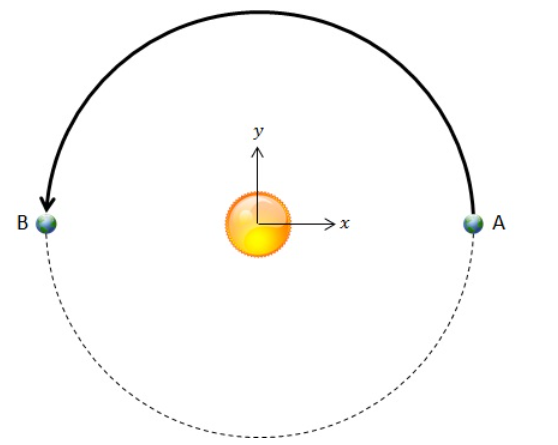
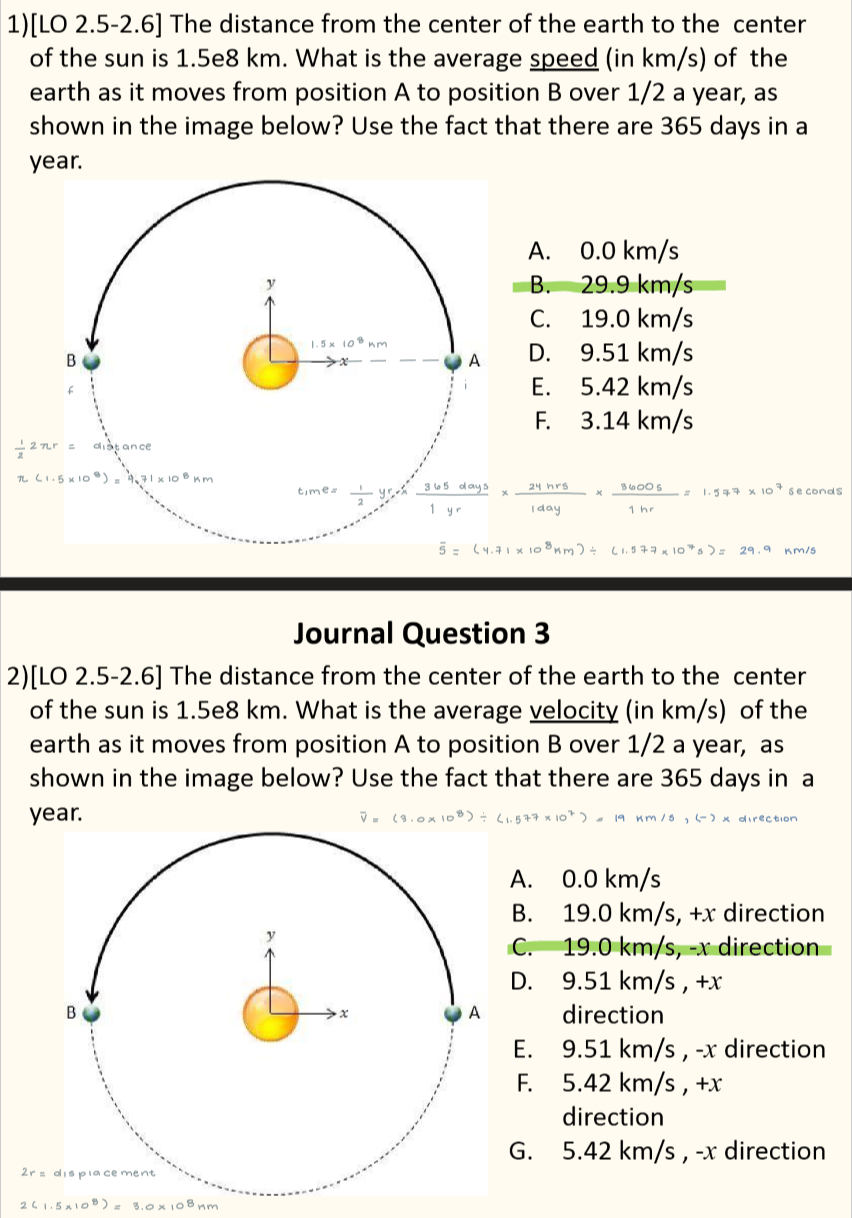
The distance from the center of the earth to the center of the sun is 1.5e8 km. What are the average speed and the average velocity of the earth as it moves from position A to position B over 1/2 a year in the image below? In your calculations, use the fact that there are 365 days in a year. When entering the velocity, use the sign of the value to indicate its direction.
Speed = 29.9 km/s
Velocity = -19.0 km/s
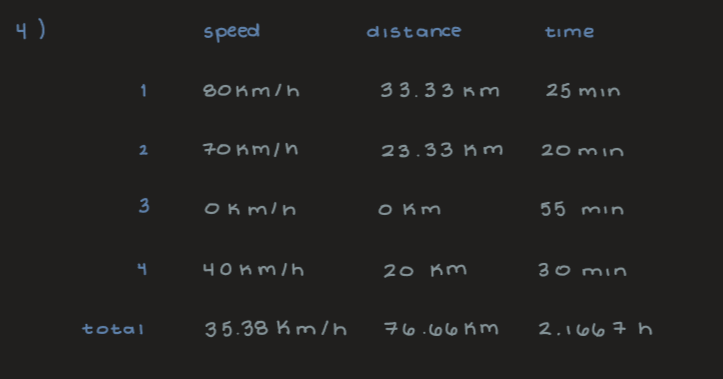
A woman drives a car from one city to another with different constant speeds along the trip. She drives at a speed of 80.0 km/h for 25.0 min, 70.0 km/h for 20.0 min, makes a stop for 55.0 min, then continues at 40.0 km/h for 30.0 min, at which point she reaches her destination.
What is the total distance between her starting point and destination (in km)?
What is the average speed for the entire trip (in units of km/h)?
76.66 km
35.38 km/h
Deceleration
slowing down; acceleration is in the opposite direction of the velocity
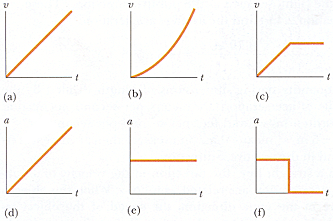
Plots (a), (b), and (c) in the figure below represent the velocities as a function of time of three different objects moving in straight-line paths. The possible accelerations of each object as functions of time are shown in plots (d), (e), and (f). Match each velocity plot with the acceleration plot that best describes the motion.
Velocity plot (a) goes with acceleration plot e
Velocity plot (b) goes with acceleration plot d
Velocity plot (c) goes with acceleration plot f
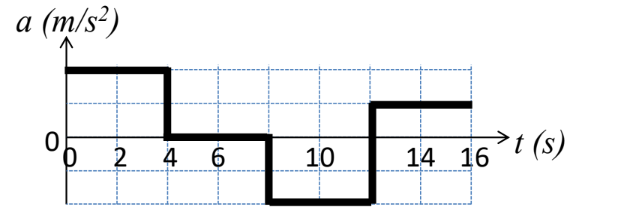
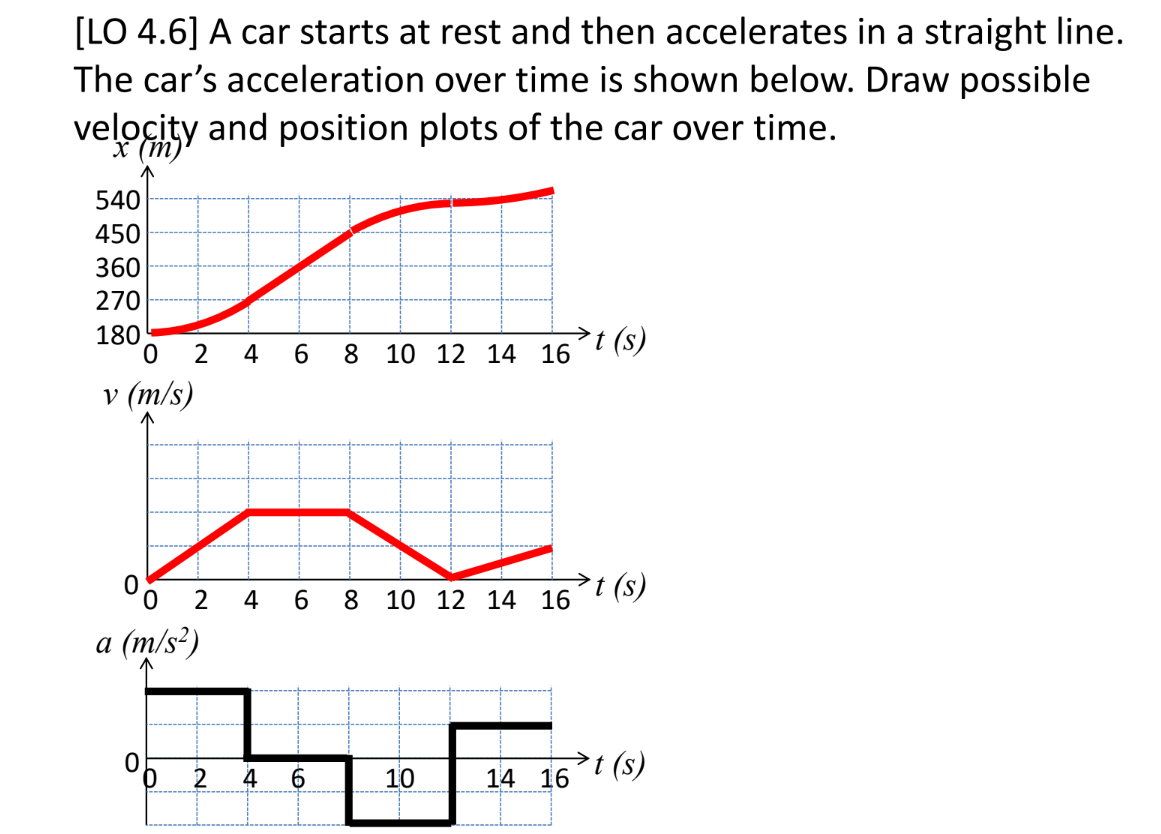
A car starts at rest and then accelerates in a straight line. The car’s acceleration over time is shown below. Draw possible velocity and position plots of the car over time.
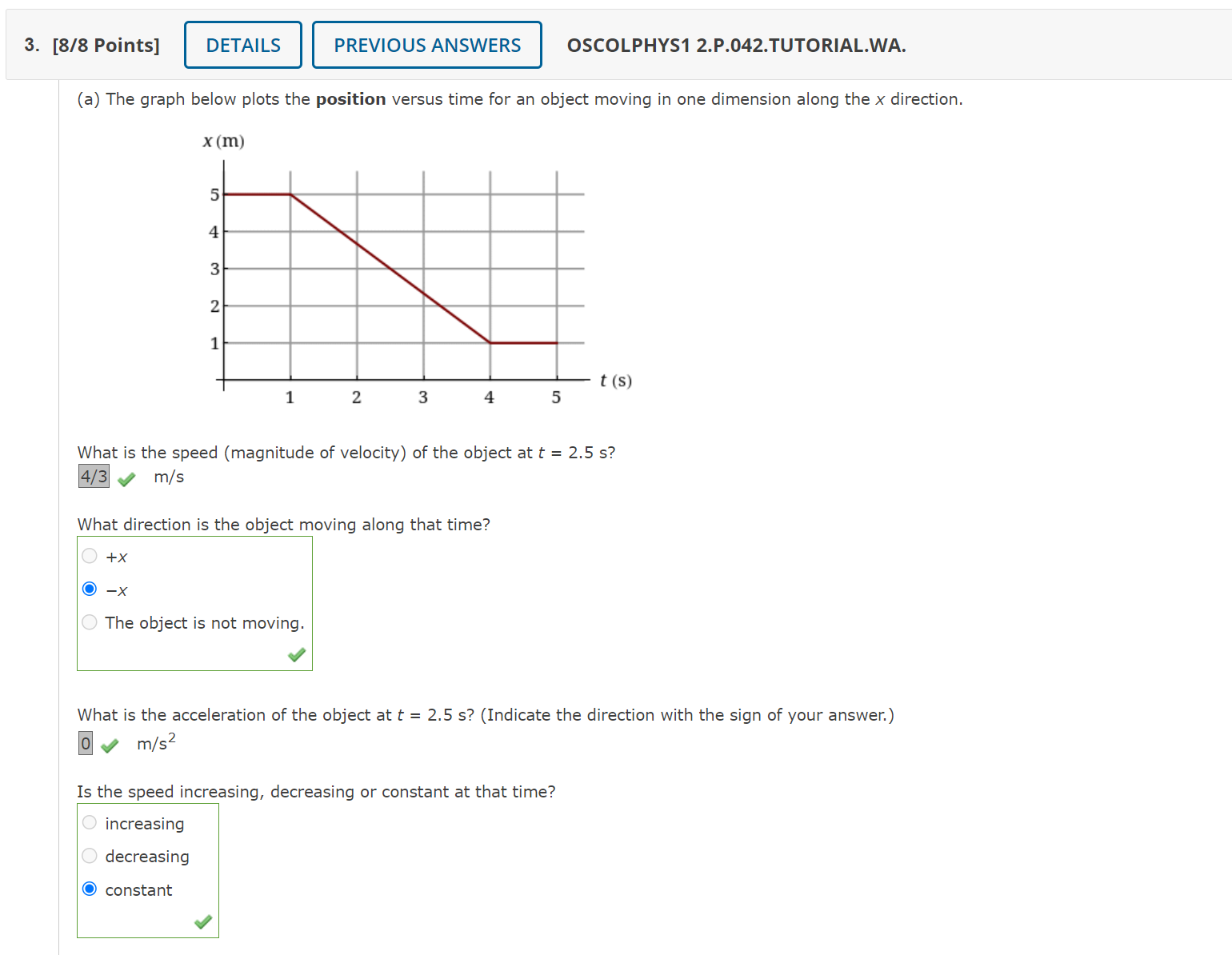
If a 1 kg ball and a 2 kg ball are dropped at the same time and from the same height, and air resistance is negligible, which ball will hit the ground first?
They will hit the ground at the same time.


A swimmer bounces straight up from a diving board and falls feet first into a pool. She starts with a velocity of 3.00 m/s, and her takeoff point is 1.40 m above the pool.
(a) How long are her feet in the air?
(b) What is her highest point above the board?
(c) What is her velocity when her feet hit the water?
(a) 0.922 s
(b) 0.459 m
(c) -6.037 m/s
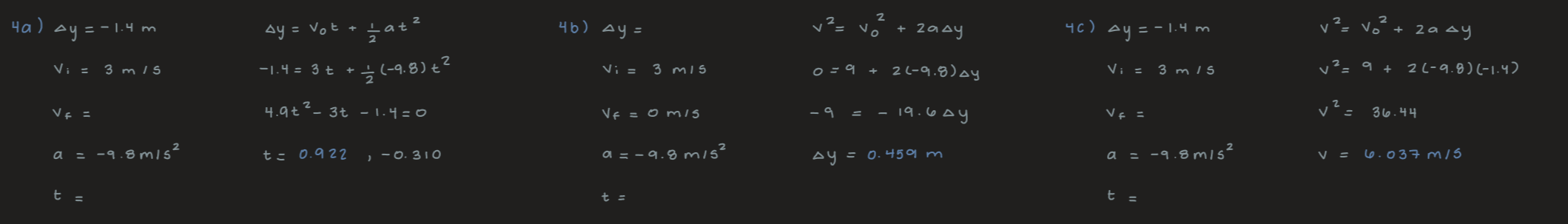
An inflatable raft (unoccupied) floats down a river at an approximately constant speed of 4.5 m/s. A child on a bridge, 84 m above the river, sees the raft in the river below and attempts to drop a small stone onto the raft. The child releases the stone from rest. In order for the stone to hit the raft, what must be the horizontal distance between the raft and the bridge when the child releases the stone?
18.63 m

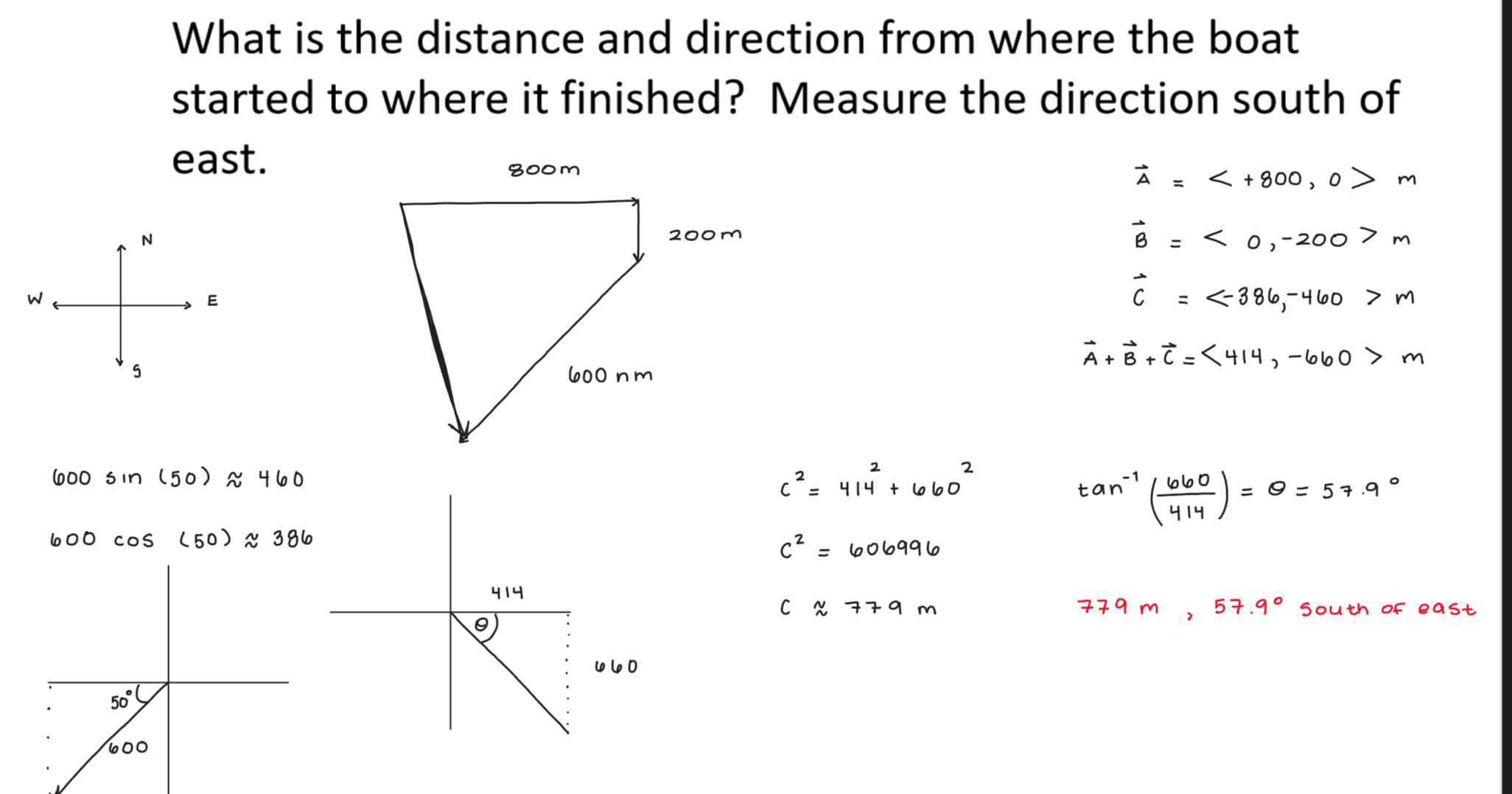
A boat travels 800m east, then 200m south, then 600m at a direction of 50° south of west. What is the distance and direction from where the boat started to where it finished? Measure the direction south of east.
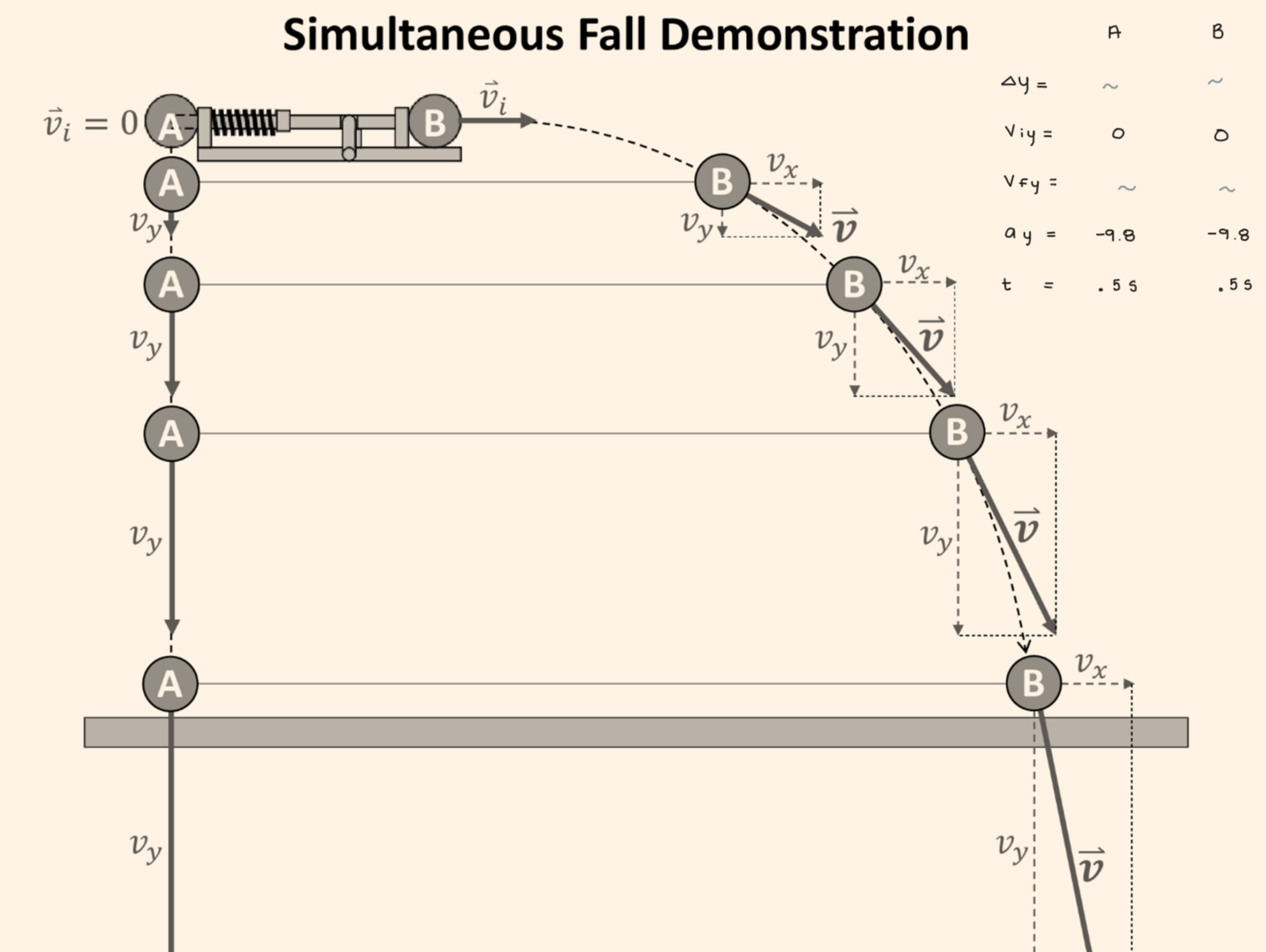
In the “simultaneous fall” demonstration, one ball is released from rest, and a second ball is shot out horizontally at the same time. If air resistance is neglected, which ball will hit the ground first?
The two balls will hit the ground at the same time.
Only the y-component matters
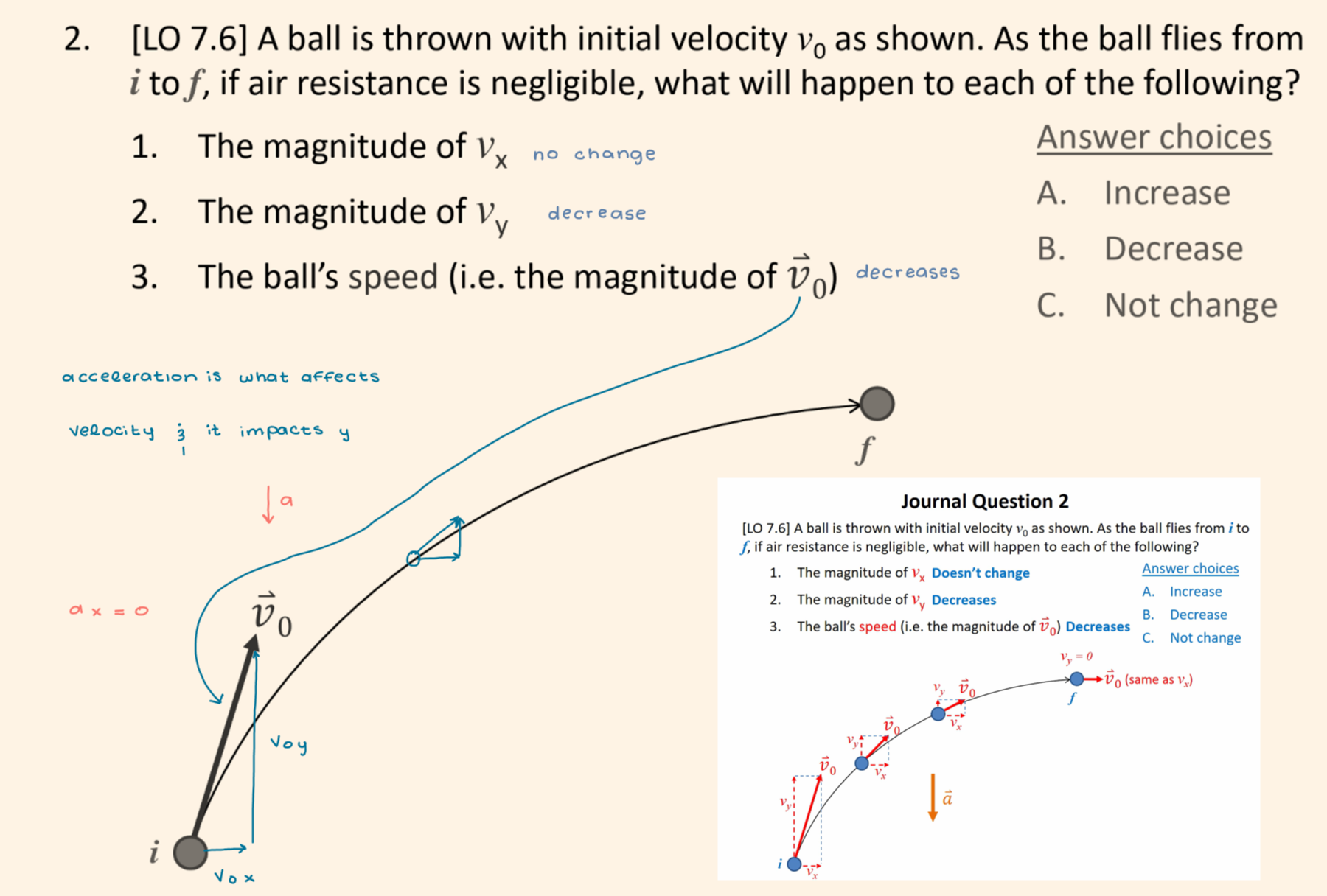
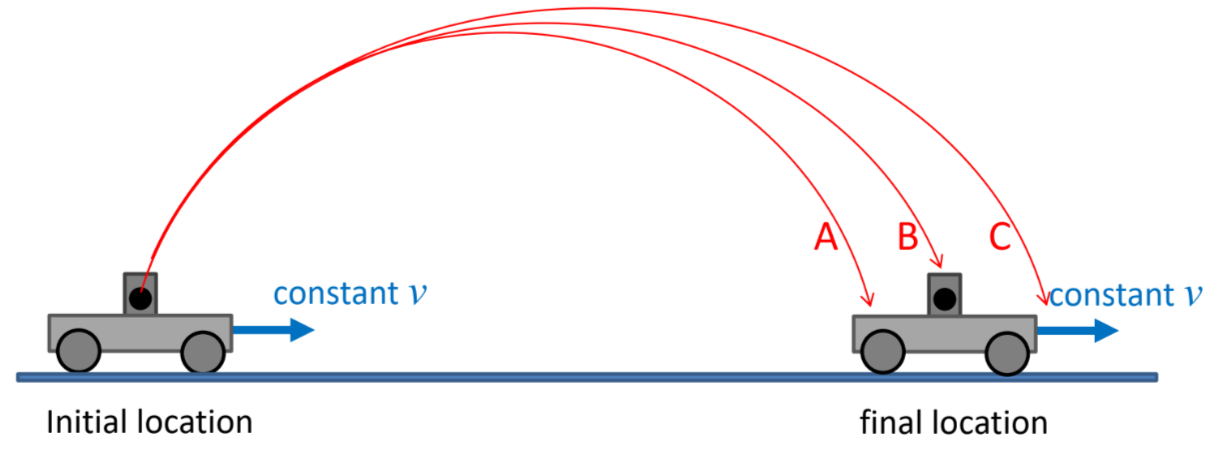
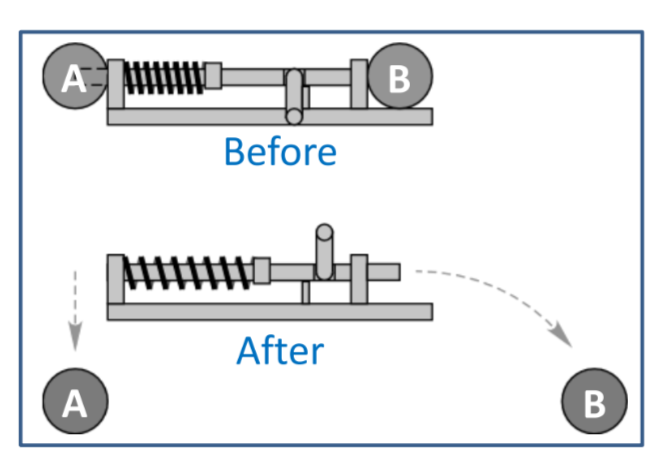
In the “howitzer” demonstration, a cart is traveling at a constant velocity and then a ball is shot straight up into the air from the moving cart (with respect to the cart). If air resistance is neglected, where does the ball land?
The ball lands back in the launcher.
The velocity in the x-direction is the same for the ball & the cart, acceleration doesn’t change in x-direction
In a tee-ball game, a baseball is placed on the “tee”, 1 meter above the ground and is hit with an initial velocity of 15m/s horizontally. If air resistance is negligible, how far does the ball go in the air before hitting the ground?

A field goal kicker is 50 m (about 55 yds) from the field goal posts and kicks the ball from the ground at 23 m/s at 40° above the horizontal. The cross bar that the ball needs to clear is 3.05 m (10 ft) high. If air resistance is neglected, will the kick be successful, i.e. will the ball clear the crossbar?
no

In a football game, the quarterback is preparing to throw a long pass to his receiver who is 30 m away. If the quarterback throws the ball at an angle of 35°, what speed should he throw the ball so that it reaches the receiver? Neglect air resistance, and assume that the receiver catches the ball at the same height the quarterback throws the ball.
17.7 m/s



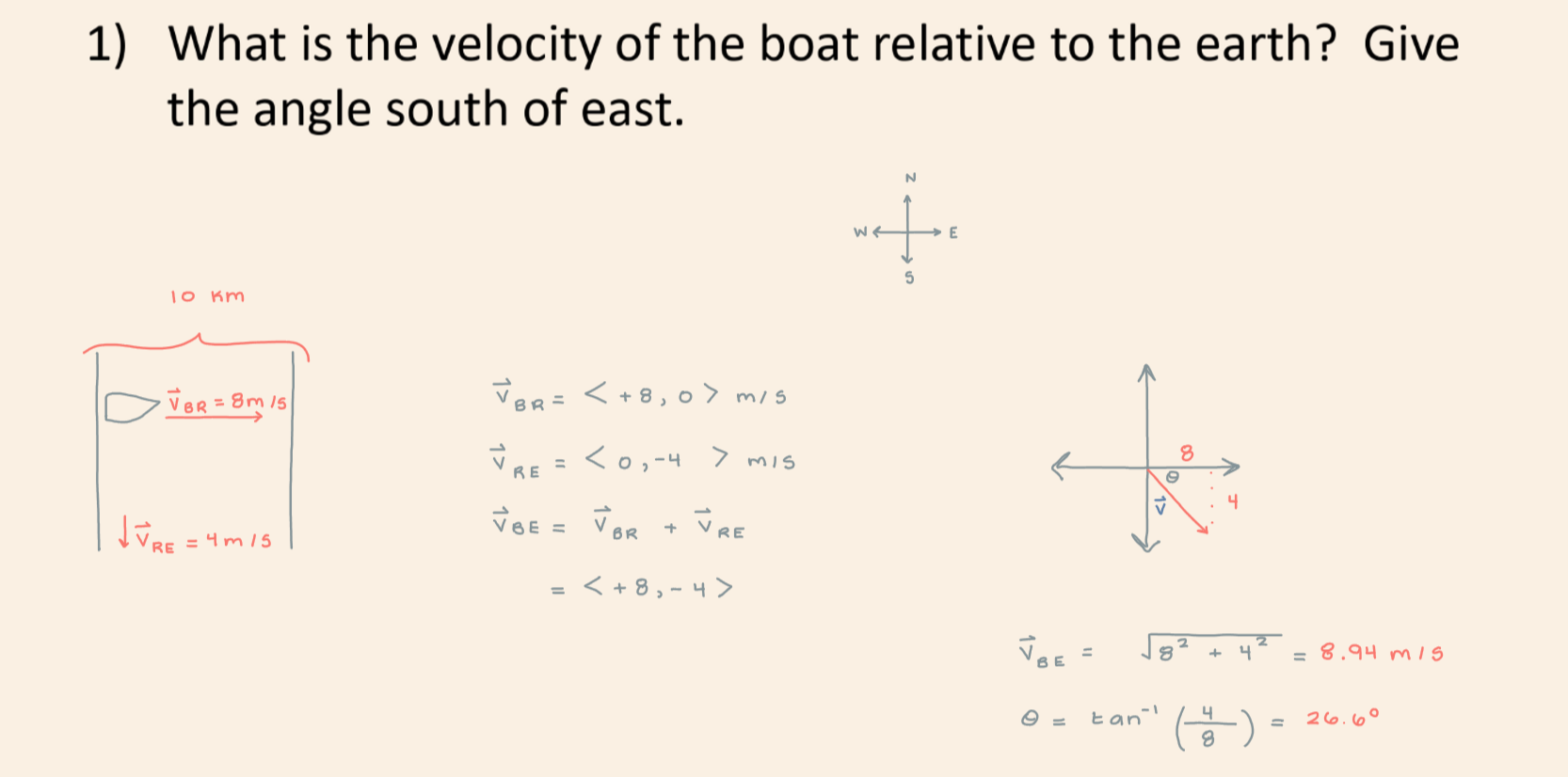
A river is 10 km wide and flows south at a constant 4.0 m/s relative to the earth. A boat starts on the west bank of the river and travels east at a constant 8.0 m/s relative to the river. What is the velocity of the boat relative to the earth? Give the angle south of east.
An antelope is running at 55 mph toward the east relative to the earth. Suddenly, a cheetah runs toward the antelope. If the cheetah is running at 70 mph at a direction of 30° west of south with respect to the earth, what is the velocity of the antelope from the cheetah’s perspective, i.e. what is the velocity of the antelope relative to the cheetah?
108.5 mph, 34° N of E
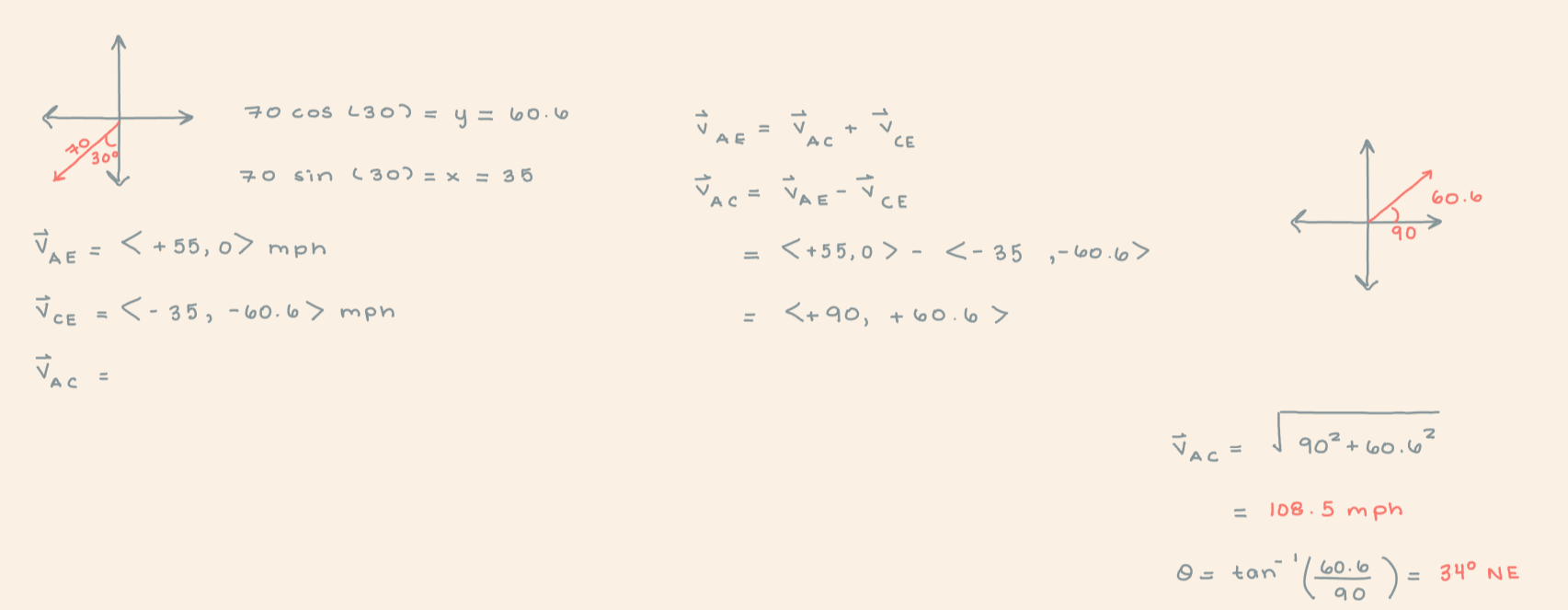
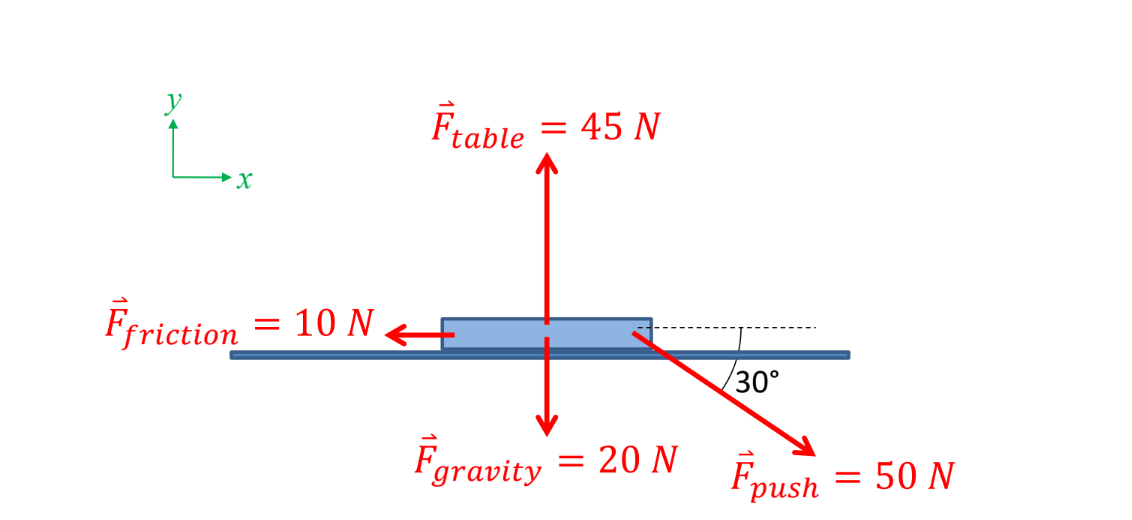
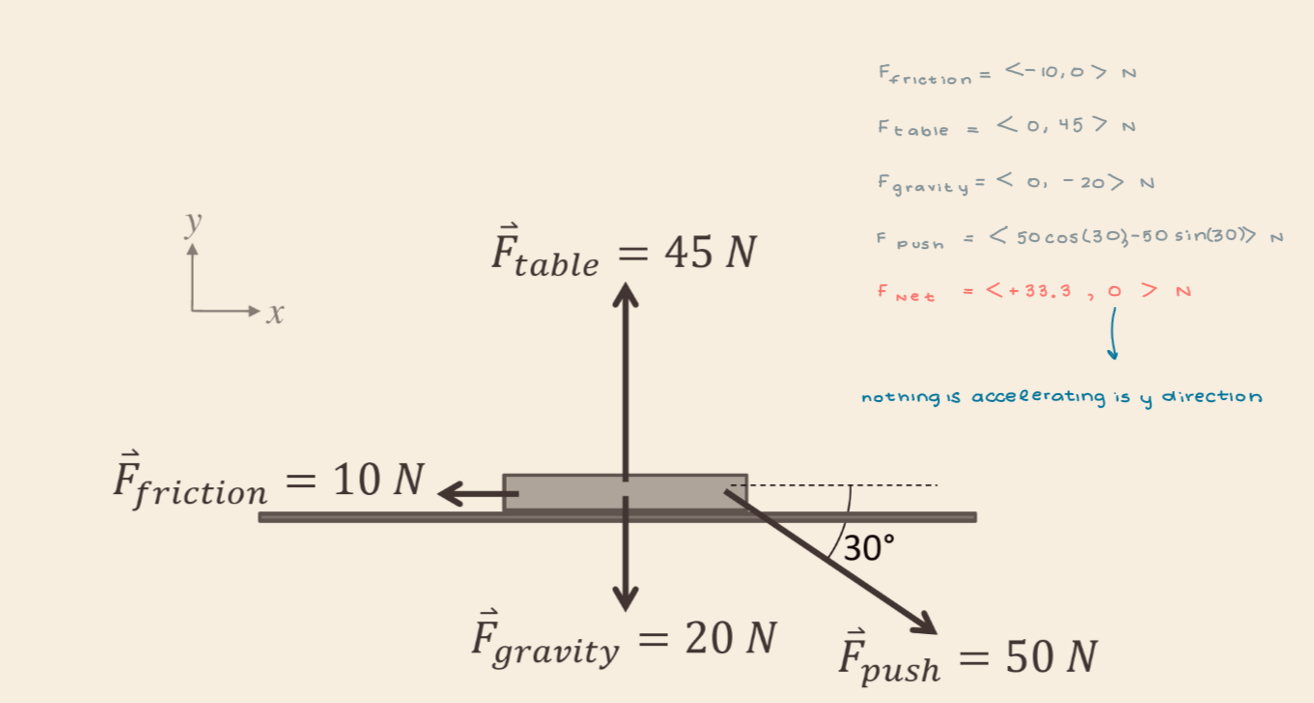
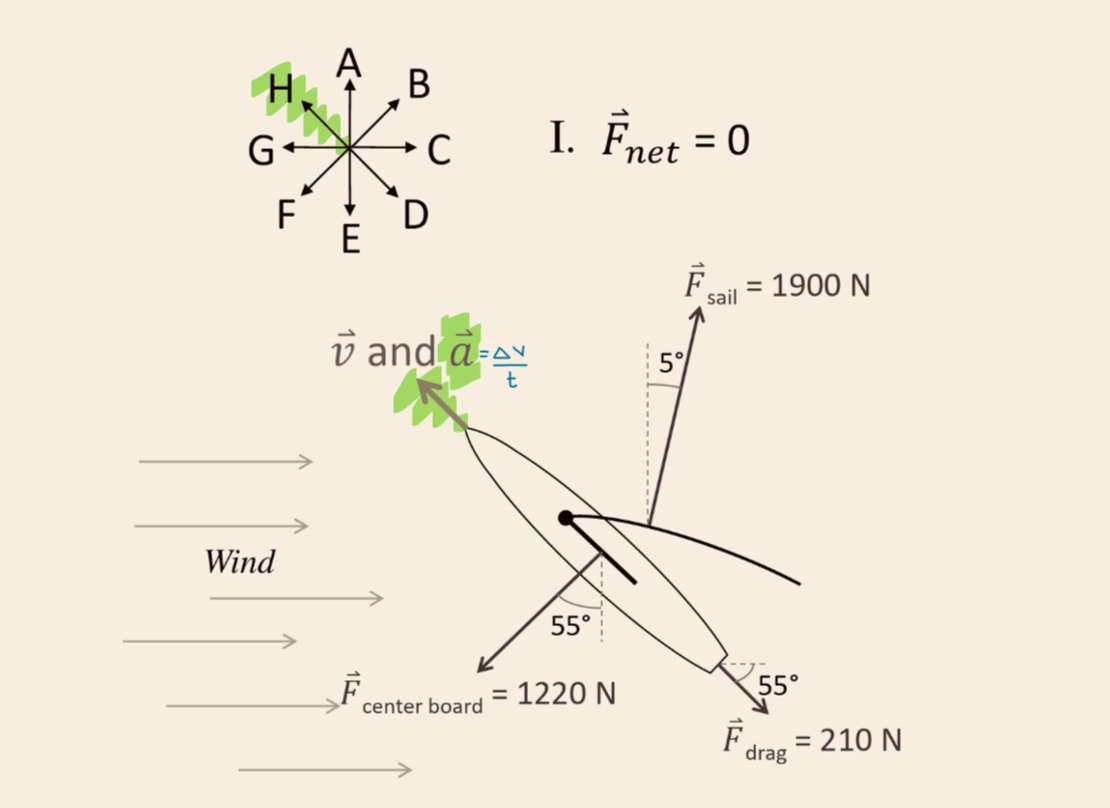
When a 2.04 kg book is being pushed across a table, the forces shown in the figure act on the book. What is the net force on the book?
33.3 N, in the +x direction
A 75 gram bird flies with a constant velocity of 10 mph, south. What is the direction of the net force on the bird?
Net force = 0 because acceleration = 0
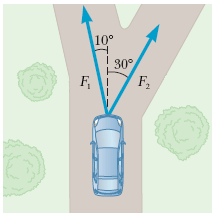
Two forces are applied to a car in an effort to move it, as shown in the following figure, where F1 = 442 N and F2 = 391 N. (Assume up and to the right as positive directions.) What is the sum of these two forces acting on the car?
magnitude | 782.96 N |
direction | 8.7234° to the right of the forward direction |
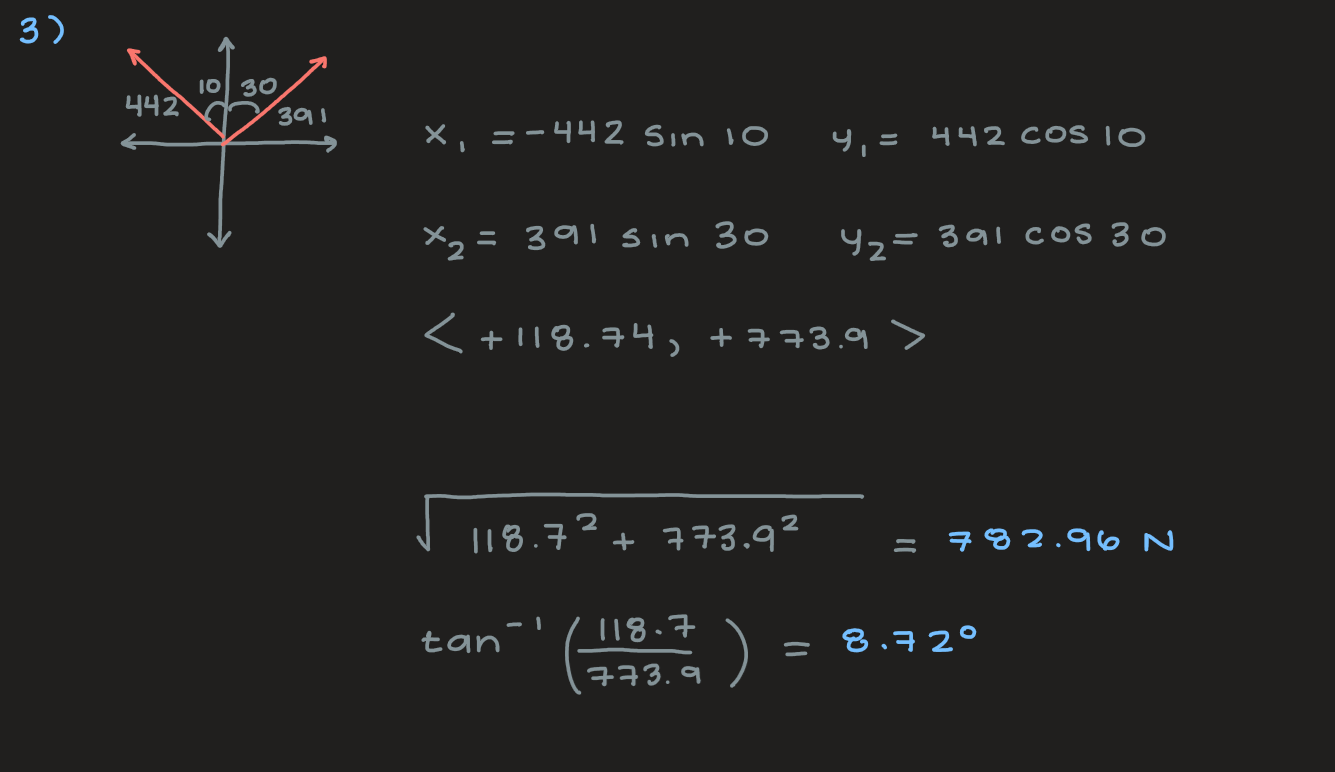
A truck loaded with sand accelerates along a highway. The driving force on the truck remains constant. What happens to the acceleration of the truck as its trailer leaks sand at a constant rate through a hole in its bottom?
It decreases at a steady rate.
It increases and then decreases.
It remains constant.
It decreases and then increases.
It increases at a steady rate.
It increases at a steady rate.
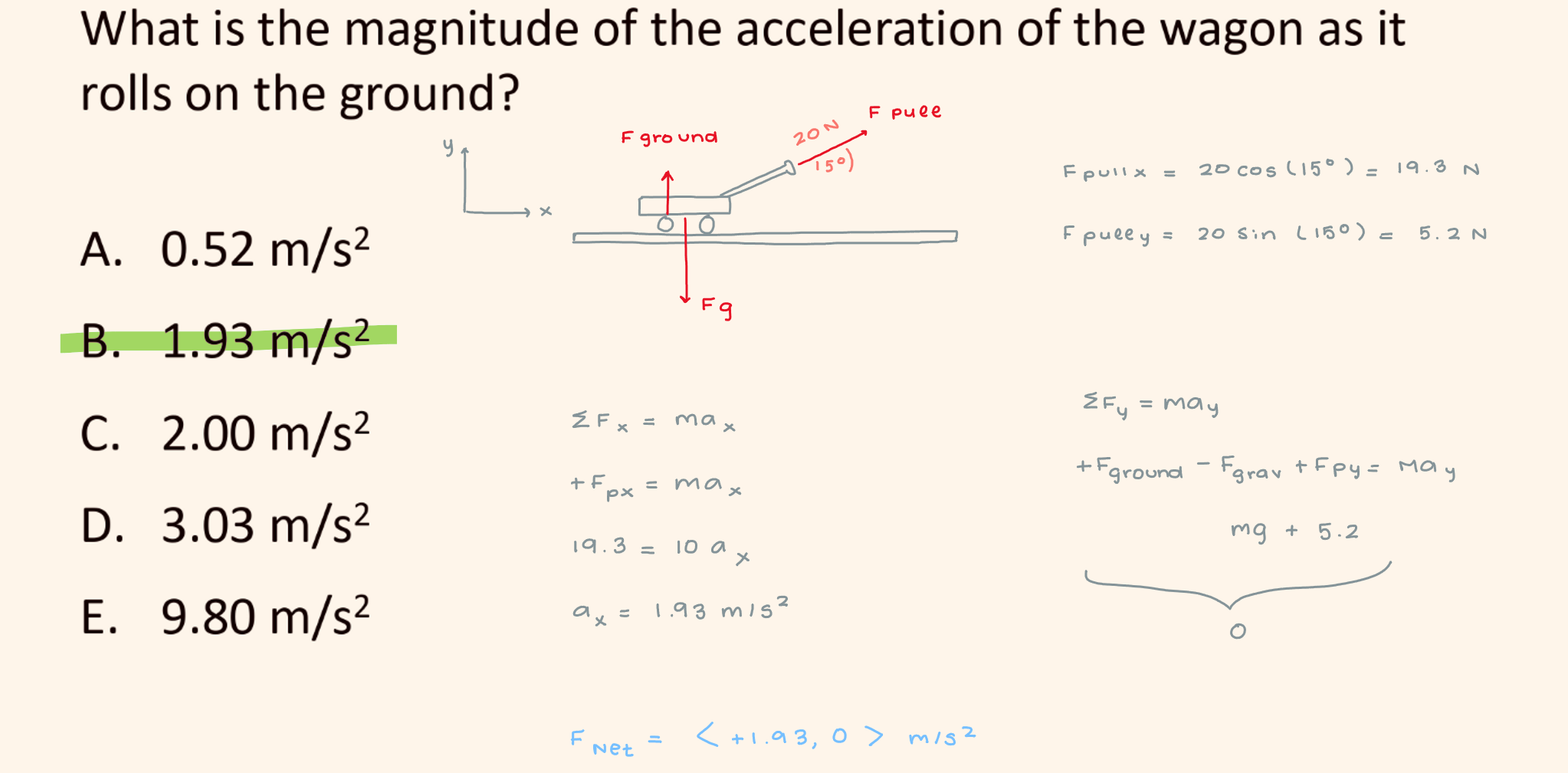
A child pulls a 10 kg wagon with a force of 20 N, 15° above the horizontal. There are no friction or air resistance forces opposing the wagon’s motion. What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the wagon as it rolls on the ground?
1.93 m/s²
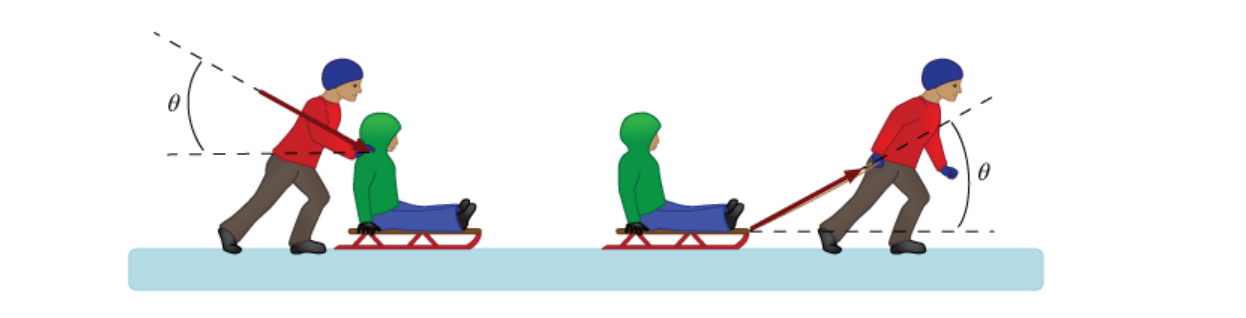
You promised your younger brother that you would give him a ride on his sled. You first push him from behind with a force of magnitude F1 directed downward at an angle of 25° below the horizontal. After a while you decide to pull him with a force of magnitude F2 directed upward at the same angle above the horizontal. In both cases the sled moves with the same acceleration and friction is negligible. Which of the following statements is true regarding the two forces you used?
F1 = F2
As the acceleration is the same in both cases, the horizontal component of the pulling or pushing force will be the same in both cases.
Therefore F1 = F2 since the angle is the same in both cases.

a) What is the magnitudeand direction of
Q (in N) when the block moves with constant velocity? (Indicate the direction with the sign of your answer.)
b) What is the magnitude and direction of
Q (in N) when the acceleration of the block is +7.1 m/s2. (Indicate the direction with the sign of your answer.)
c) What is the magnitude and direction of
Q (in N) when the acceleration of the block is -7.1 m/s2. (Indicate the direction with the sign of your answer.)
a) 9.1 N
b) 44.6 N
c) -26.4 N

Two forces P and Q act on an object of mass 10.0 kg with Q being the larger of the two forces. When both forces are directed to the left, the magnitude of the acceleration of the object is 1.20 m/s². However, when the force P is directed to the left and the force Q is directed to the right, the object has an acceleration of 0.600 m/s² to the right. Find the magnitudes of the two forces P and Q in newtons.
P = 3 N
Q = 9 N

A 0.4 kg football is punted through the air. At one instant, as the ball flies through air, the force due to air resistance on the ball is 2.0 N, 25° below the negative x-axis. What is the acceleration of the football (magnitude and direction)?

A mother and her daughter are on roller skates. At one point, they face each other and push off from each other. The mass of the daughter is 40 kg, and the mass of the mother is 60 kg.
The pushing force causes the mother to accelerate at 1.5 m/s². What is the magnitude of the daughter’s acceleration? (Neglect air resistance and friction).
2.25m/s²

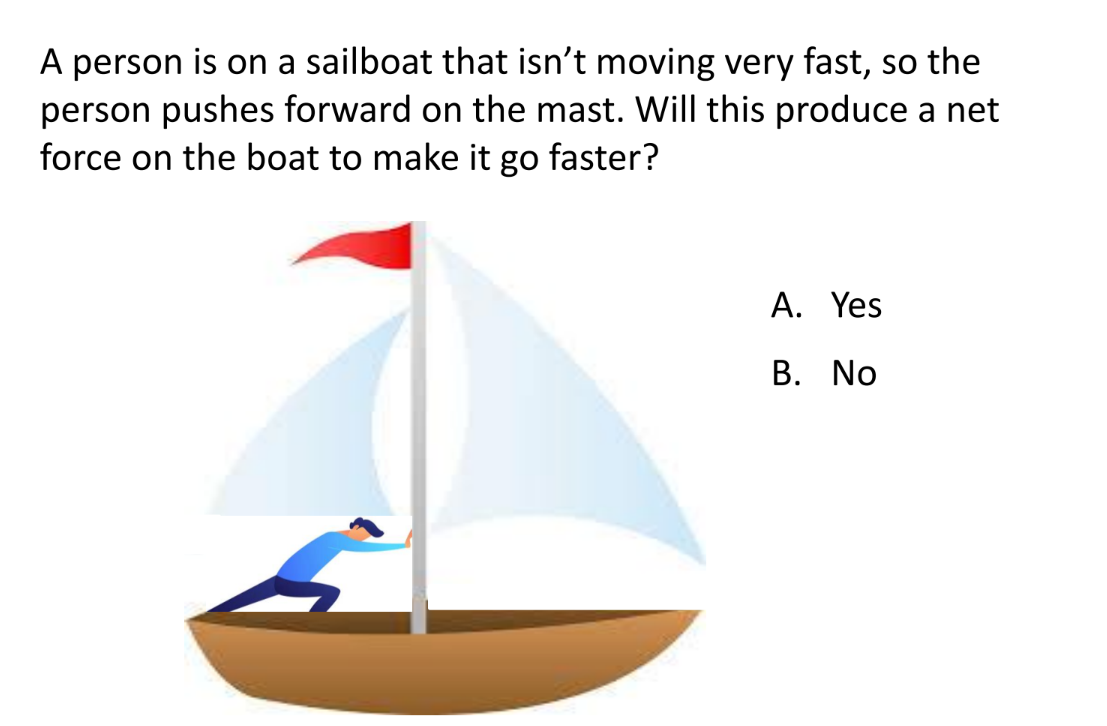
A flea jumps by exerting a force of 1.02e-5 N straight down on the ground. A breeze blowing on the flea parallel to the ground exerts a force of 1.20e-6 N on the flea. Find the direction and magnitude (in m/s2) of the acceleration of the flea if its mass is 6.0e-7 (Let us assume that Fwind points to the right. We will consider this to be the +x direction and vertical to be the +y direction.)
magnitude 7.473 m/s²
15.5° (measured clockwise from the vertical)
