Biology MCAS Study Guide + Practice Questions
3.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/112
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
113 Terms
1
New cards
An ________ compound is any compound that contains a combination of carbon atoms, while an ________ compound contains no combination of carbon atoms.
organic, inorganic
2
New cards
The molecule ATP is composed of elements commonly found in organic molecules. Which of the following is one of these elements?
A. aluminum
B. calcium
C. phosphorus
D. tin
A. aluminum
B. calcium
C. phosphorus
D. tin
C. phosphorus
3
New cards
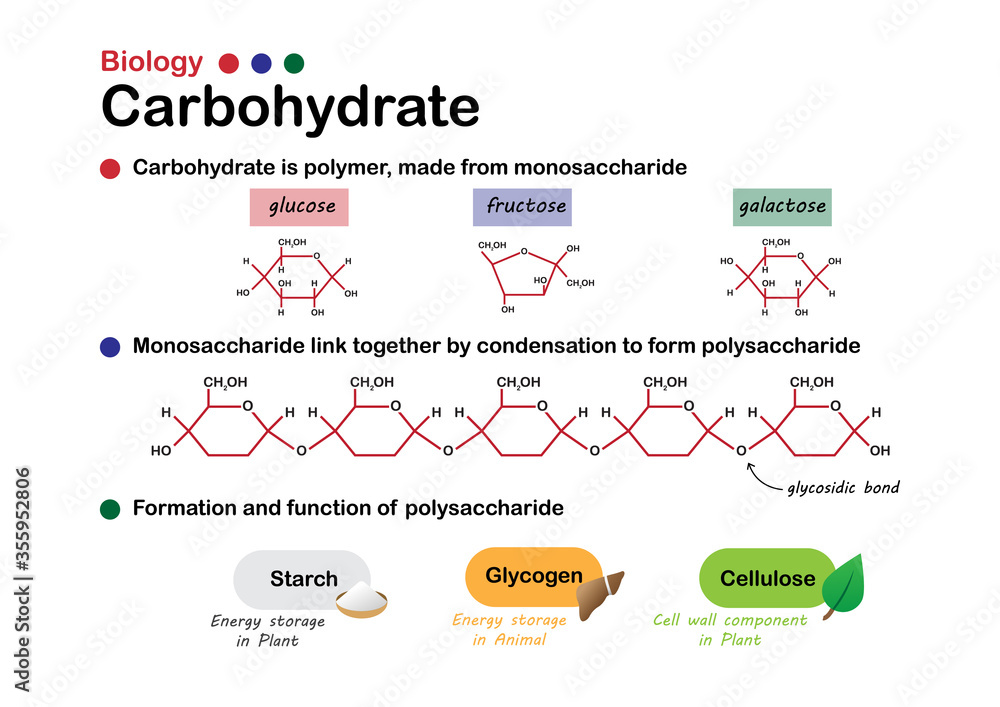
What is the monomer of a carbohydrate, and what is a carbohydrate's function?
Monomer of a carbohydrate: Monosaccharide
Carbohydrates serve as a primary source of energy for the body and play a crucial role in cell structure and communication.
Carbohydrates serve as a primary source of energy for the body and play a crucial role in cell structure and communication.
4
New cards
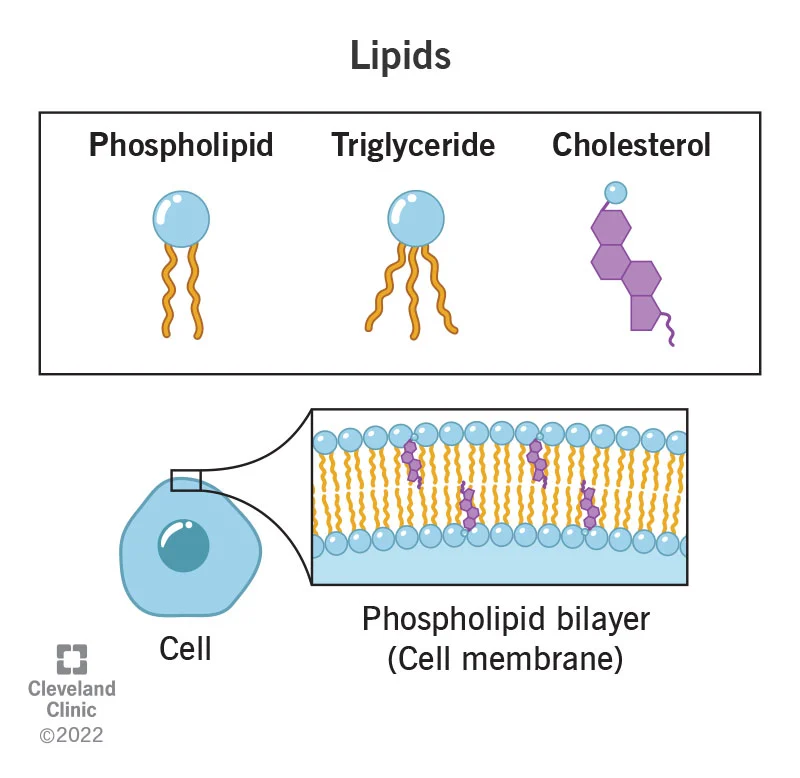
What is the monomer of a lipid, and what is a lipid's function?
Monomer of a lipid: Fatty Acid.
Function of Lipid: Energy storage, insulation, protection, cell membrane structure.
Function of Lipid: Energy storage, insulation, protection, cell membrane structure.
5
New cards
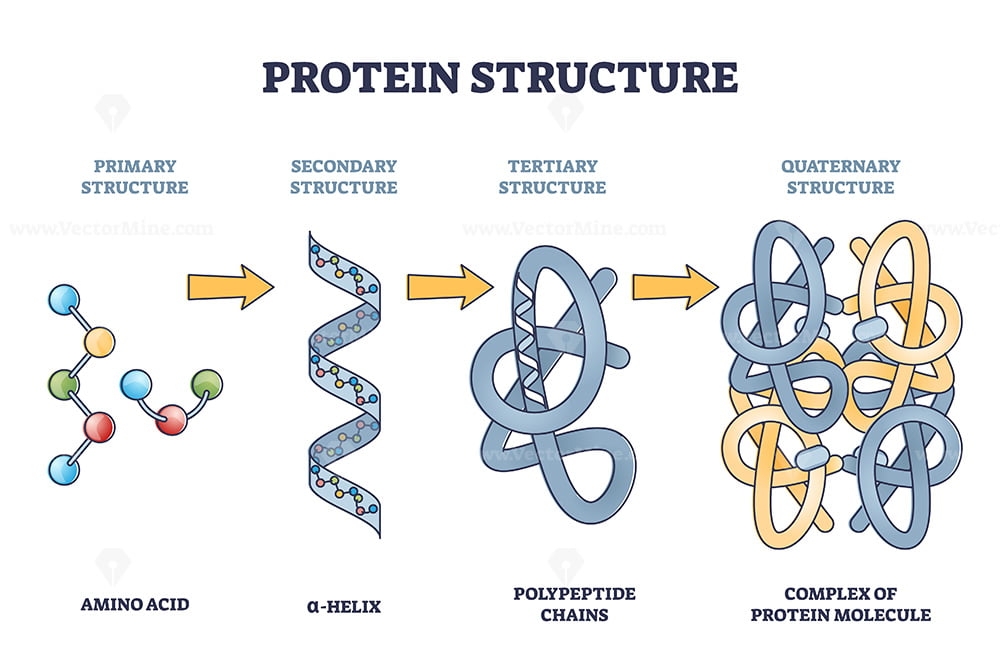
What is the monomer of a protein, and what is a protein’s function?
Monomer of protein: Amino Acid.
Proteins function as enzymes, hormones, structural components, transporters, and antibodies.
Proteins function as enzymes, hormones, structural components, transporters, and antibodies.
6
New cards
Collagen is found in connective tissue throughout the human body. Collagen is made of three amino acid chains that are twisted around each other. What **best** explains why collagen is classified as a protein?
A. It is found in the human body
B. It consists of amino acids
C. It is found in tissue
D. It has a twisted shape
A. It is found in the human body
B. It consists of amino acids
C. It is found in tissue
D. It has a twisted shape
B. It consists of amino acids.
7
New cards
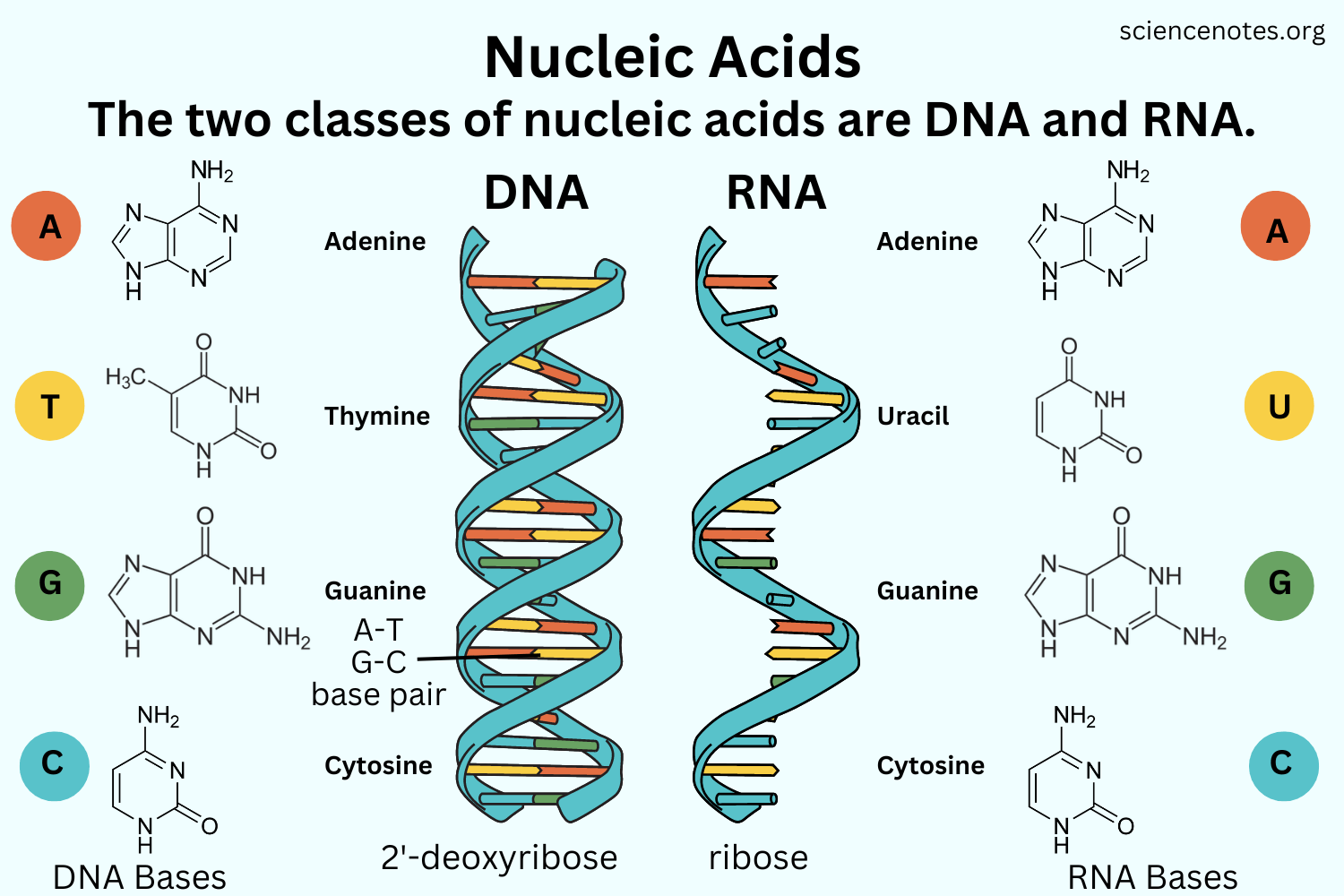
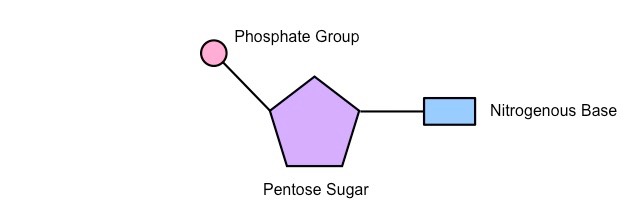
What is the monomer of nucleic acid, and what is nucleic acid's function?
Monomer of nucleic acid: Nucleotide - made up of a sugar, phosphate, and nitrogenous base.
Function: Store and transmit genetic information, control cellular activities.
Function: Store and transmit genetic information, control cellular activities.
8
New cards
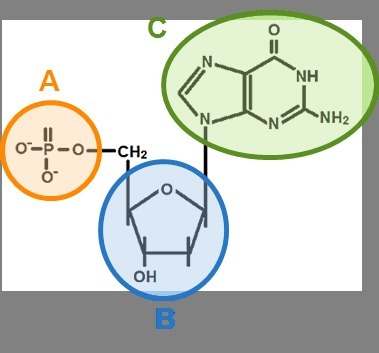
In the diagram is a model of a nucleotide. Label A, B, and C
A: Phosphate
B: Sugar
C: Nitrogenous Base
B: Sugar
C: Nitrogenous Base
9
New cards
Human tears contain the enzyme lysozyme, which damages the cell walls of bacteria. Which of the following statements about lysozyme is most accurate?
A. Lysozyme causes mutations in bacterial cell wall molecules.
B. Lysozyme is destroyed as it digests bacterial cell wall molecules.
C. Lysozyme breaks a specific type of bond in a bacterial cell wall molecule.
D. Lysozyme is converted to another chemical by a bacterial cell wall molecule
A. Lysozyme causes mutations in bacterial cell wall molecules.
B. Lysozyme is destroyed as it digests bacterial cell wall molecules.
C. Lysozyme breaks a specific type of bond in a bacterial cell wall molecule.
D. Lysozyme is converted to another chemical by a bacterial cell wall molecule
C. Lysozyme breaks a specific type of bond in a bacterial cell wall molecule.
10
New cards
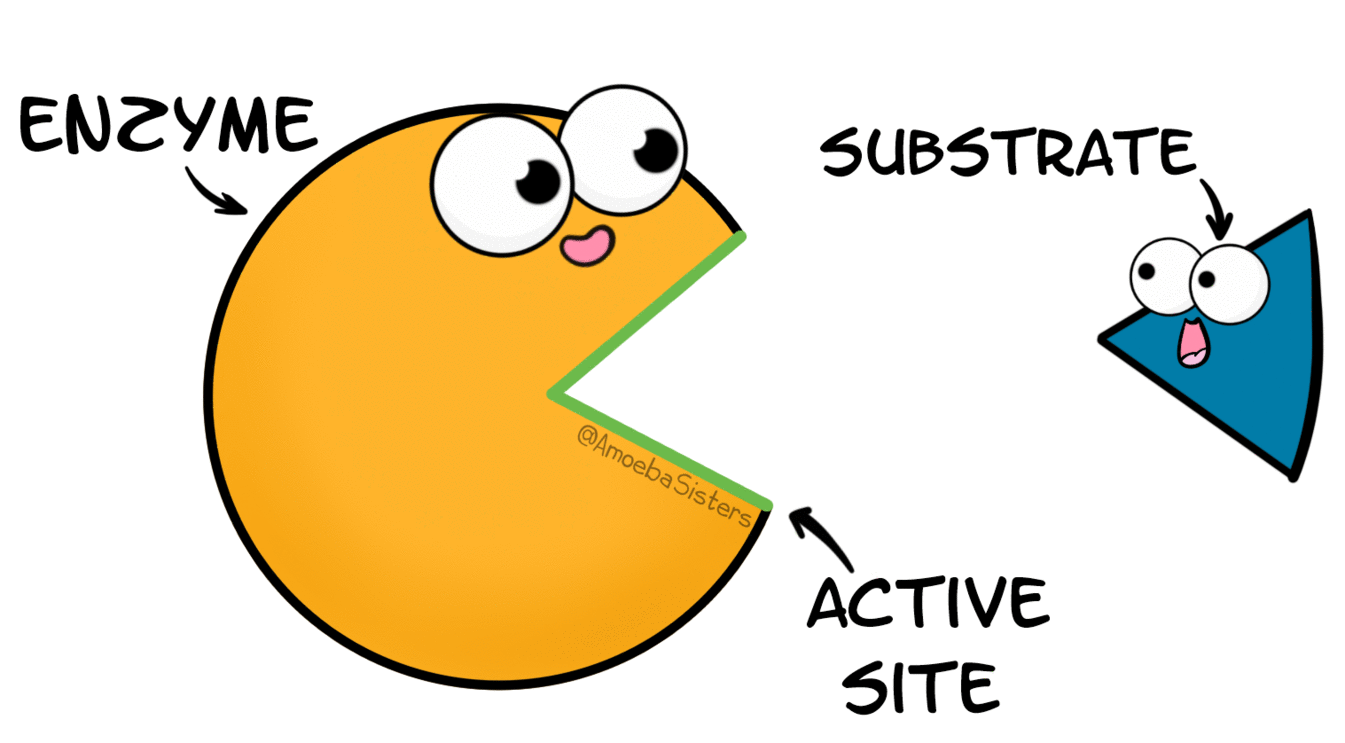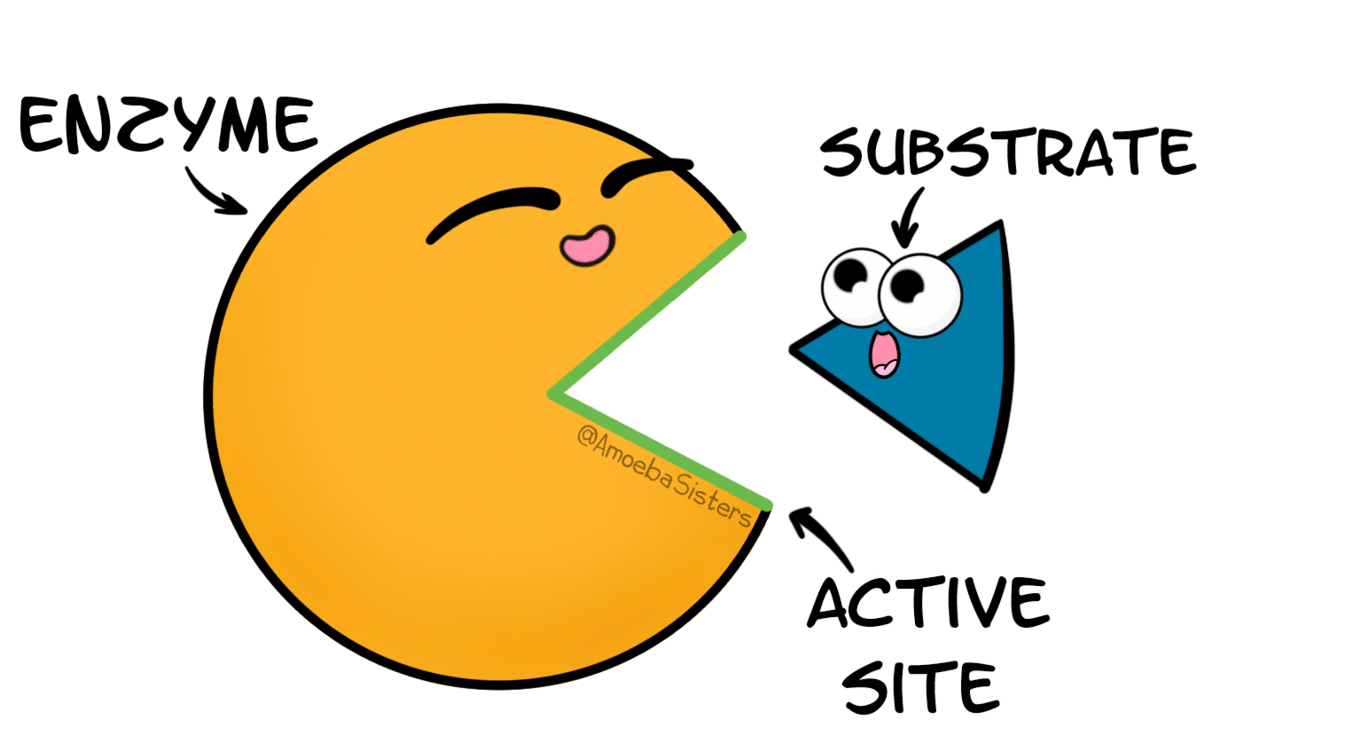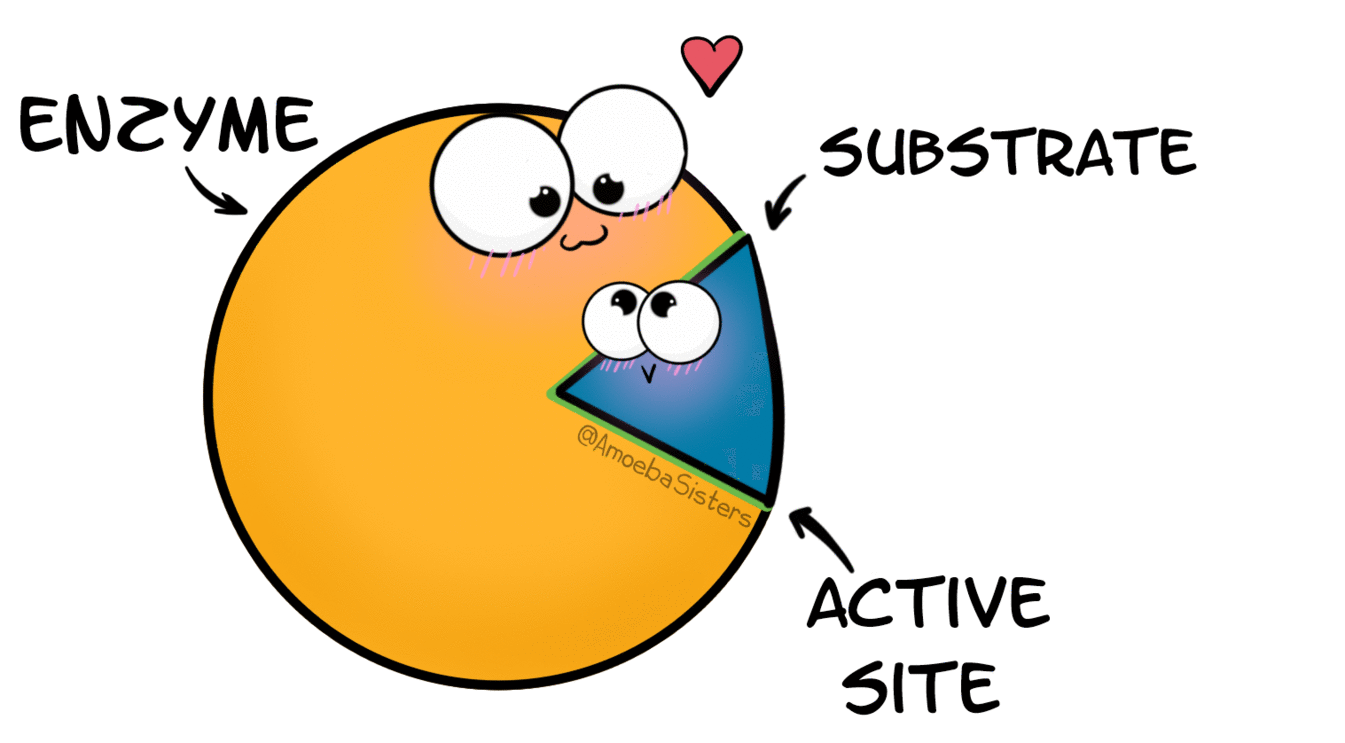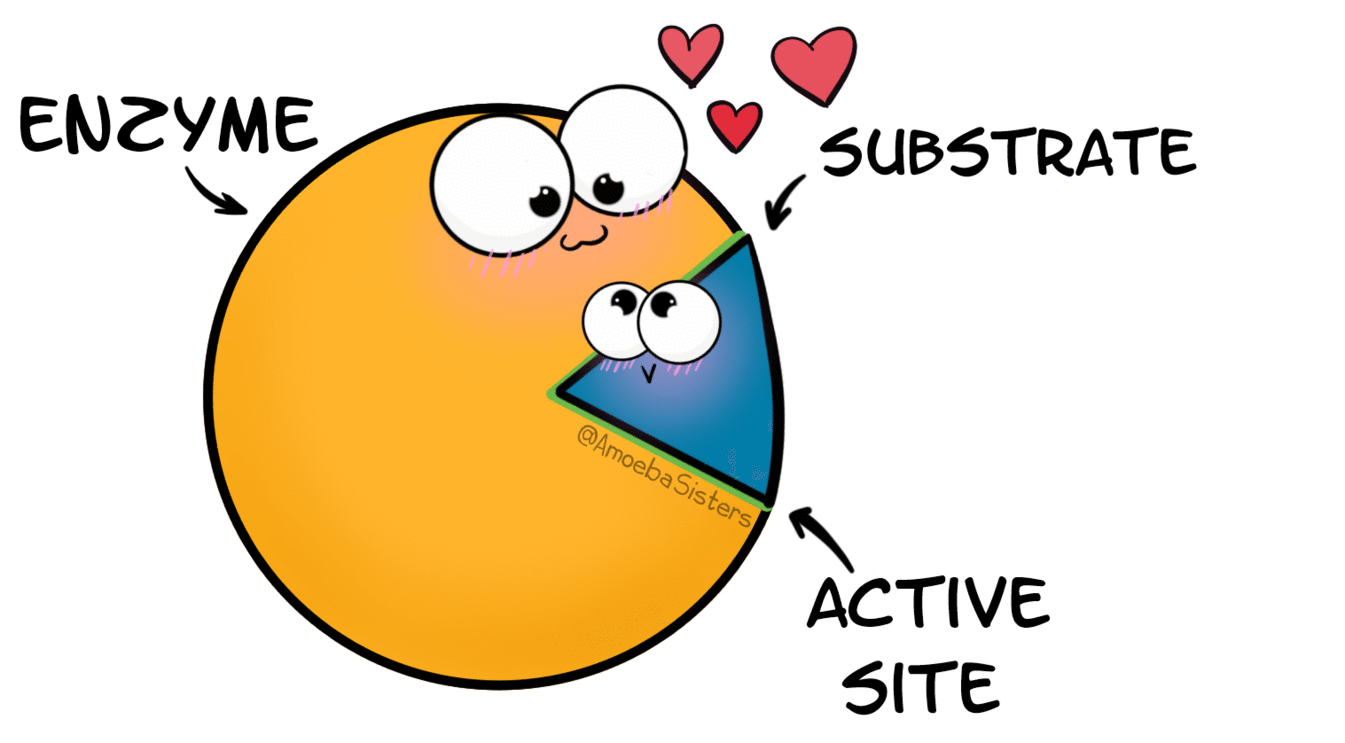
What are enzymes?
Special types of proteins that speed up chemical reactions in the body but are not changed by the reactions.
11
New cards
Describe the effect of temperature on an enzyme’s activity.
Warmer temperatures SPEED UP enzymes, cooler temperatures SLOW them down. Temperatures that are TOO HOT can kill an enzyme and slow it down! (Denaturation)
12
New cards
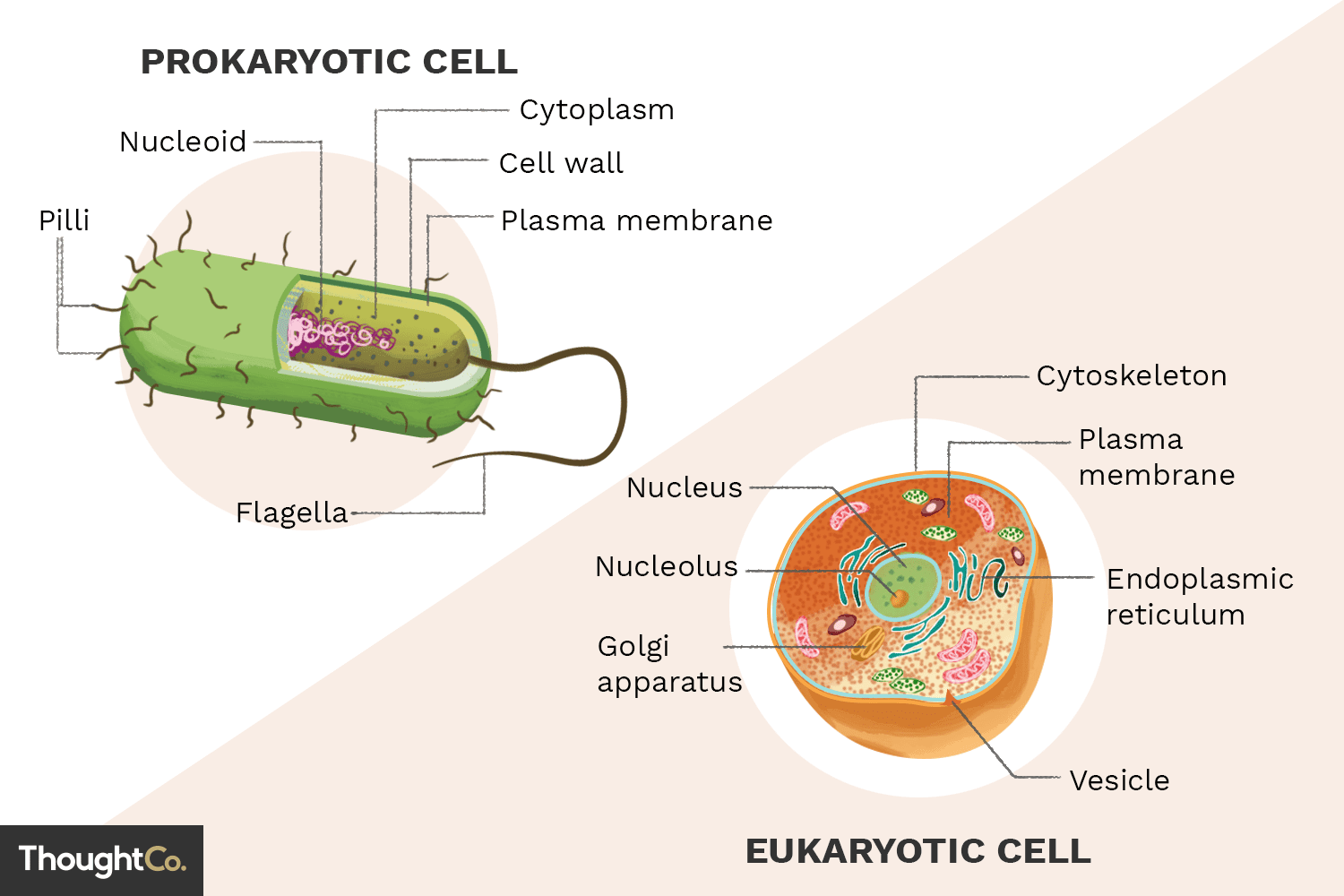
What are the main differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells?
Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, while prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotic cells are generally larger and more complex than prokaryotic cells.
13
New cards
A single prokaryotic cell can divide several times in an hour. Few eukaryotic cells can divide as quickly. Which of the following statements best explains this difference?
A. Eukaryotic cells are smaller than prokaryotic cells.
B. Eukaryotic cells have less DNA than prokaryotic cells.
C. Eukaryotic cells have more cell walls than prokaryotic cells.
D. Eukaryotic cells are more structurally complex than prokaryotic cells.
A. Eukaryotic cells are smaller than prokaryotic cells.
B. Eukaryotic cells have less DNA than prokaryotic cells.
C. Eukaryotic cells have more cell walls than prokaryotic cells.
D. Eukaryotic cells are more structurally complex than prokaryotic cells.
D. Eukaryotic cells are more structurally complex than prokaryotic cells.
14
New cards
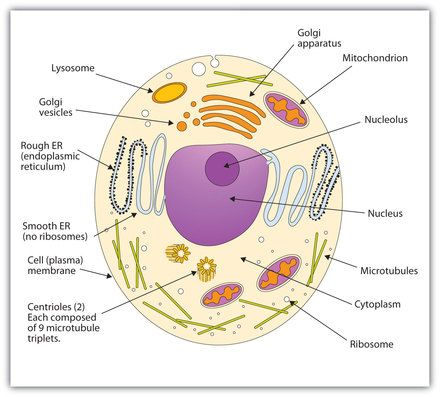
Describe the functions of the following organelles of an an animal cell: Nucleus, Cell Membrane, Cytoplasm, Endoplasmic Reticulum, Golgi Body, Ribosomes, Mitochondria, Lysosomes, Centrioles.
Nucleus: Controls cell activities and stores genetic material.
Cell Membrane: Regulates what enters and exits the cell.
Cytoplasm: Holds organelles and facilitates cell processes.
Endoplasmic Reticulum: Transports proteins and lipids.
Golgi Body: Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins.
Ribosomes: Synthesize proteins.
Mitochondria: Produces ATP for energy.
Lysosomes: Digests waste and foreign material.
Centrioles: Aids in cell division and organization of cytoskeleton.
Cell Membrane: Regulates what enters and exits the cell.
Cytoplasm: Holds organelles and facilitates cell processes.
Endoplasmic Reticulum: Transports proteins and lipids.
Golgi Body: Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins.
Ribosomes: Synthesize proteins.
Mitochondria: Produces ATP for energy.
Lysosomes: Digests waste and foreign material.
Centrioles: Aids in cell division and organization of cytoskeleton.
15
New cards
Which of the following matches a cell organelle with its function?
A. chloroplast-movement
B. nucleus-cell regulation
C. vacuole-energy production
D. mitochondrion-photosynthesis
A. chloroplast-movement
B. nucleus-cell regulation
C. vacuole-energy production
D. mitochondrion-photosynthesis
B. nucleus-cell regulation
16
New cards
List the three organelles that are found exclusively in plant cells and describe their functions.
The three organelles that are found exclusively in plant cells are chloroplasts, cell walls, and central vacuoles. Chloroplasts are responsible for photosynthesis, cell walls provide structural support and protection, and central vacuoles store water, food, and waste.
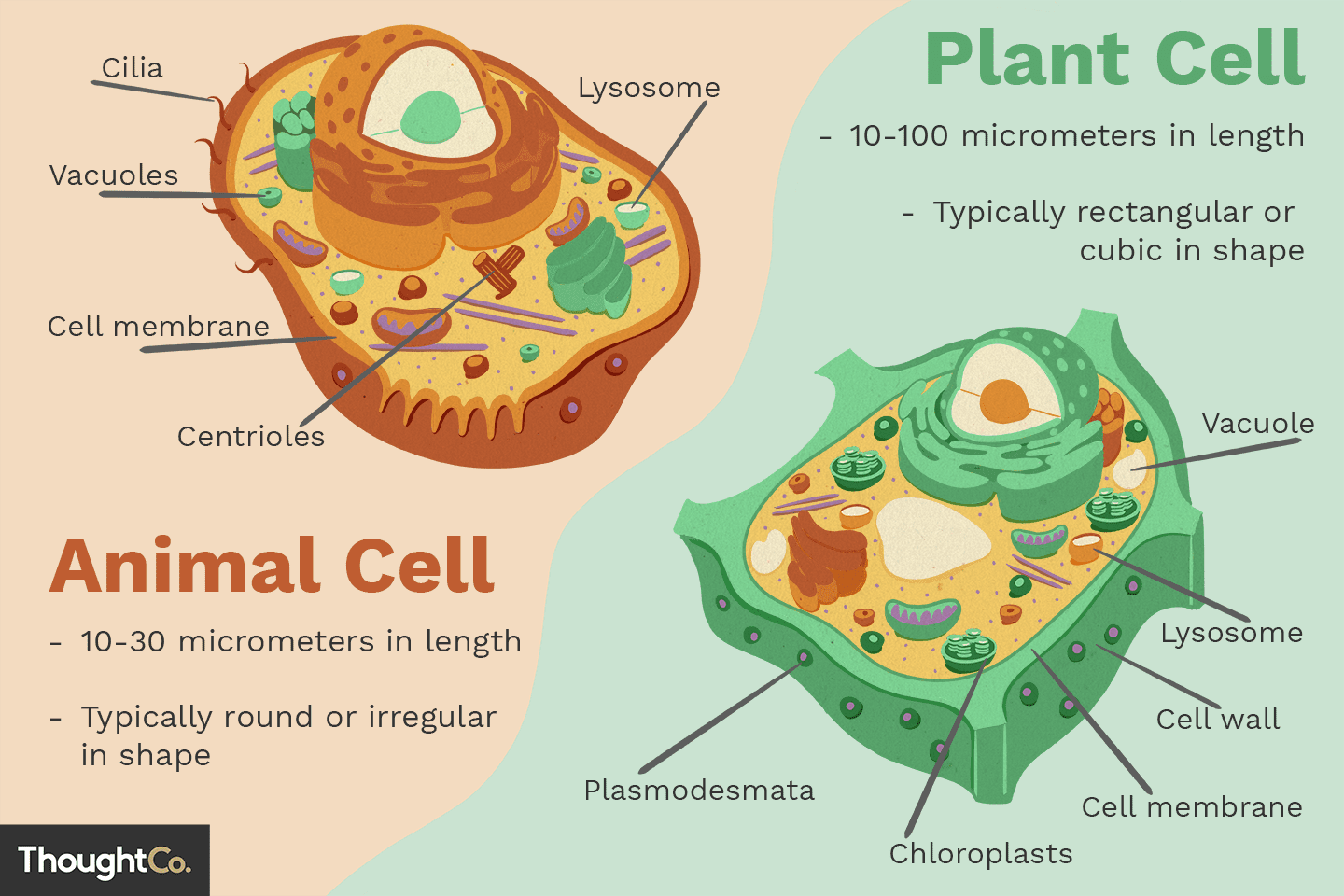
17
New cards
Which of the following is more likely to occur in a plant cell than in an animal cell?
A. synthesis of enzymes
B. formation of cellulose
C. breakdown of glucose
D. active transport of ions
A. synthesis of enzymes
B. formation of cellulose
C. breakdown of glucose
D. active transport of ions
B. formation of cellulose
18
New cards
Describe the basic structure of a bacterial cell. (Hint: Bacteria are prokaryotic)
No nucleus, no membrane-bound organelles, have a single closed loop of DNA, cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm and ribosomes.
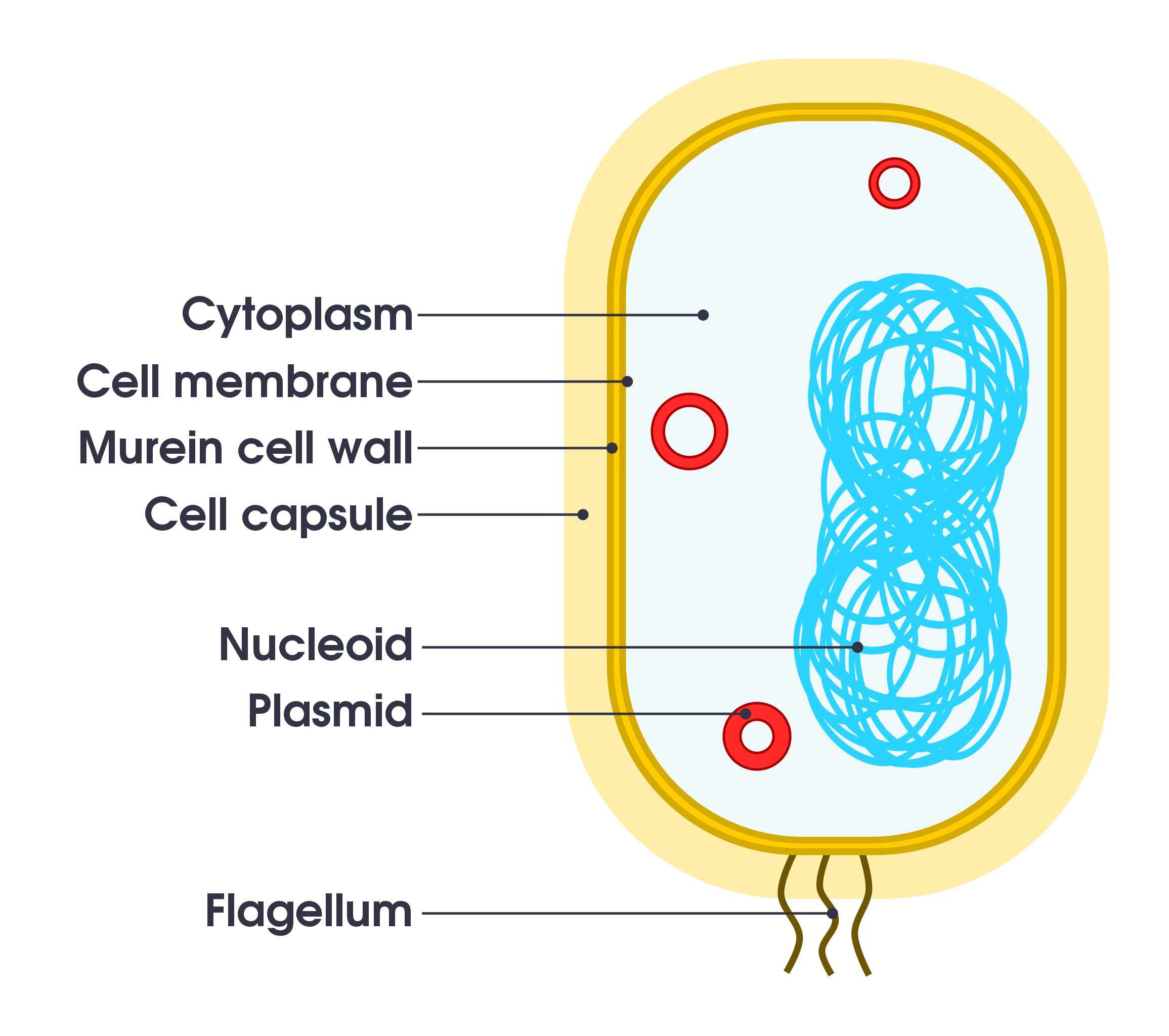
19
New cards
Fill in the blanks:
The cell membrane is ___ __,__ which means that it allows _______ compounds, but not ___ ones, to pass right through
The cell membrane is ___ __,__ which means that it allows _______ compounds, but not ___ ones, to pass right through
selectively permeable, small, large
20
New cards
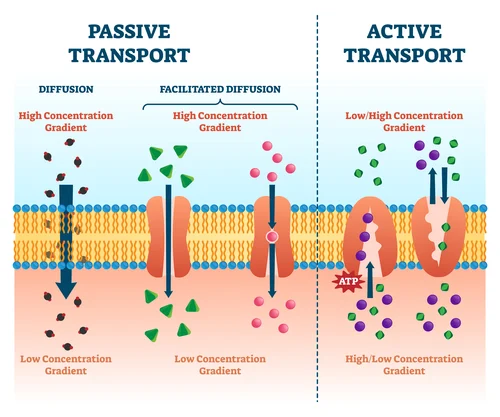
List the two types of passive transport and describe them.
Diffusion- movement of molecules from high to low concentration.
Osmosis- movement of water from low to high solute concentration.
Osmosis- movement of water from low to high solute concentration.
21
New cards
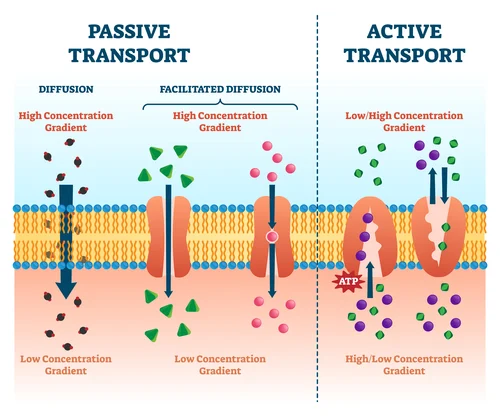
List the two types of active transport and describe them.
Endocytosis- large compounds are brought into the cell
Exocytosis- large compounds are exported out of the cell
(Hint: Endo=in, Exo=out)
Exocytosis- large compounds are exported out of the cell
(Hint: Endo=in, Exo=out)
22
New cards
Match up the following types of solutions and descriptions:
\
1\. Hypotonic solutions
2\. Hypertonic solutions
3\. Isotonic solutions
\
A. cause water to move out of the cell so the cell shrivels up
B. cause no movement of water into or out of the cell
C. cause water to move into the cell so the cell swells up
\
1\. Hypotonic solutions
2\. Hypertonic solutions
3\. Isotonic solutions
\
A. cause water to move out of the cell so the cell shrivels up
B. cause no movement of water into or out of the cell
C. cause water to move into the cell so the cell swells up
1. C
2. A
3. B
23
New cards
What is the chemical equation for photosynthesis?
6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy → C6H12O6 (Glucose) + O2
24
New cards
Chloroplasts have a green pigment called ___.
chlorophyll
25
New cards
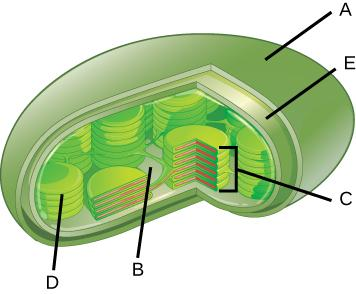
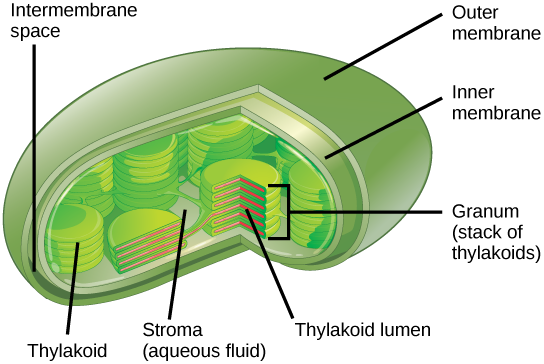
Label the following parts of a chloroplast.
A. outer membrane
B. stroma
C. granum
D. thylakoid
E. inner membrane
B. stroma
C. granum
D. thylakoid
E. inner membrane
26
New cards
What is the chemical equation for cellular respiration? (Hint: It’s the “reverse” of photosynthesis)
C6H12O6 (Glucose) + O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP energy
27
New cards
What are the differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration?
Aerobic Respiration:
* Requires oxygen
* Highly efficient, produces more ATP (36-38)
* End products: CO2 and H2O
* Sustains energy for longer durations
Anaerobic Respiration/Fermentation:
* No oxygen required or limited supply
* Less efficient, produces less ATP
* End products vary (lactic acid, ethanol, CO2)
* Short-term energy
* Requires oxygen
* Highly efficient, produces more ATP (36-38)
* End products: CO2 and H2O
* Sustains energy for longer durations
Anaerobic Respiration/Fermentation:
* No oxygen required or limited supply
* Less efficient, produces less ATP
* End products vary (lactic acid, ethanol, CO2)
* Short-term energy
28
New cards
Scientists are studying a drug to see how effective it is at reducing the production of usable energy in cells. What should the scientists measure to determine whether the drug is effective?
A. the amount of ATP in cells
B. the amount of RNA in cells
C. the number of new cells produced by old cells
D. the number of nerve signals produced by cells
A. the amount of ATP in cells
B. the amount of RNA in cells
C. the number of new cells produced by old cells
D. the number of nerve signals produced by cells
A. the amount of ATP in the cells
29
New cards
Some cells, such as human nerve and muscle cells, contain many more mitochondria than do other cells, such as skin cells. Why do some cells have more mitochondria than others?
A. The cells use more energy.
B. The cells store more nutrients.
C. The cells degrade more proteins.
D. The cells divide more frequently.
A. The cells use more energy.
B. The cells store more nutrients.
C. The cells degrade more proteins.
D. The cells divide more frequently.
A. The cells use more energy.
30
New cards
What are chromosomes?
Chromosomes are DNA strands in the nucleus that contain the instructions for making and sustaining an organism.
31
New cards
How many SETS of chromosomes do humans have? (Hint: Each set contains 23 chromosomes)
Humans have two sets of chromosomes, one from each parent, in their diploid cells.
32
New cards
What are homologous chromosomes?
Homologous chromosomes are two chromosomes coding for the same trait.
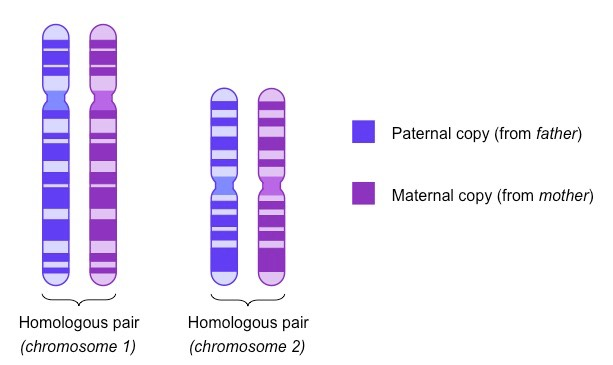
33
New cards
What type of cells do humans have mostly?
Humans have mostly diploid cells in their body, such as skin cells and muscle cells.
34
New cards
What is the difference between haploid and diploid cells?
Haploid cells, like human gametes (sperm and egg cells), have only one set of chromosomes, while diploid cells have two sets of chromosomes.
35
New cards
What is the difference between autosomes and sex chromosomes?
Autosomes are chromosomes that do **not** determine an individual's sex. Sex chromosomes are chromosomes that determine an individual's sex.
*In humans, girls have two X chromosomes (XX), and boys have one X and one Y chromosome (XY).*
*In humans, girls have two X chromosomes (XX), and boys have one X and one Y chromosome (XY).*
36
New cards
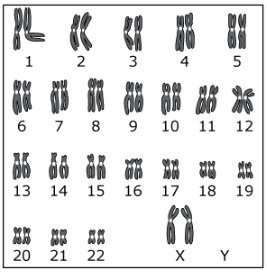
The karyotype diagram shows the *(diploid/haploid)* number of chromosomes that would be found in *(gametes/body cells)* of a human female.
diploid, body cells
37
New cards
List the four stages of the cell cycle and what occurs in each.
1. G1 phase: Cell grows
2. S phase: DNA synthesis (chromosomes are copied)
3. G2 phase: Cell grows
4. M phase: Mitosis (cell division) occurs
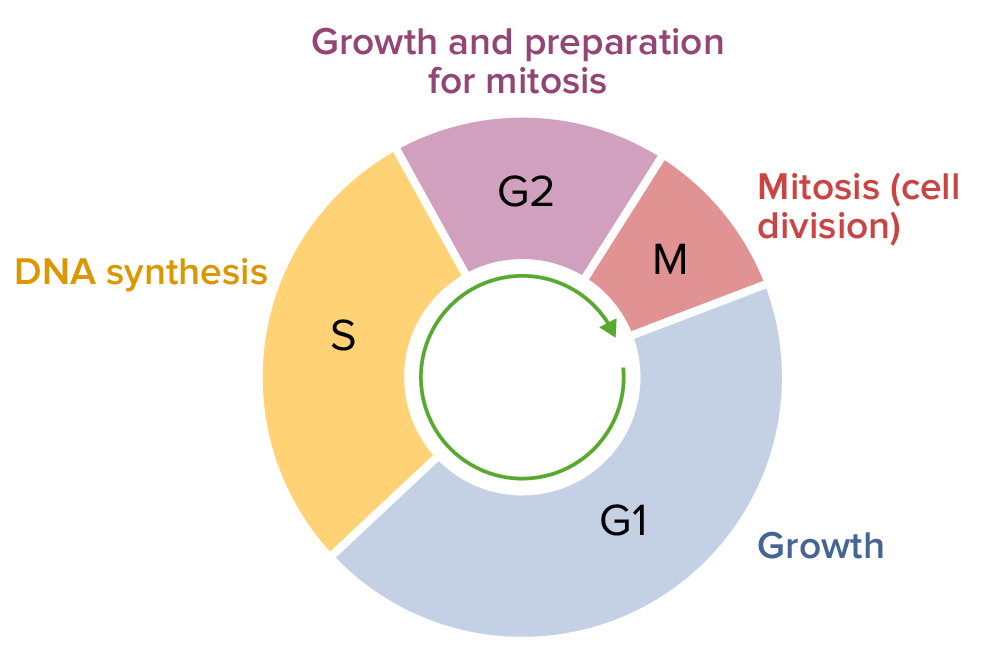
38
New cards
___ must be copied before mitosis so that new cells receive the same ones found in old cells
Chromosomes
39
New cards
List and describe the 5 phases of mitosis, including cytokinesis.
Prophase: Nuclear membrane falls apart and spindle fibers start to form
Metaphase: Sister chromatids line up along the middle of the spindle fibers
Anaphase: Sister chromatids separate and move to opposite ends of the cell
Telophase: Spindle fibers break down and new nuclear membrane forms around each set of chromosomes
Cytokinesis occurs when the cytoplasm actually divides, forming two new cells
Metaphase: Sister chromatids line up along the middle of the spindle fibers
Anaphase: Sister chromatids separate and move to opposite ends of the cell
Telophase: Spindle fibers break down and new nuclear membrane forms around each set of chromosomes
Cytokinesis occurs when the cytoplasm actually divides, forming two new cells
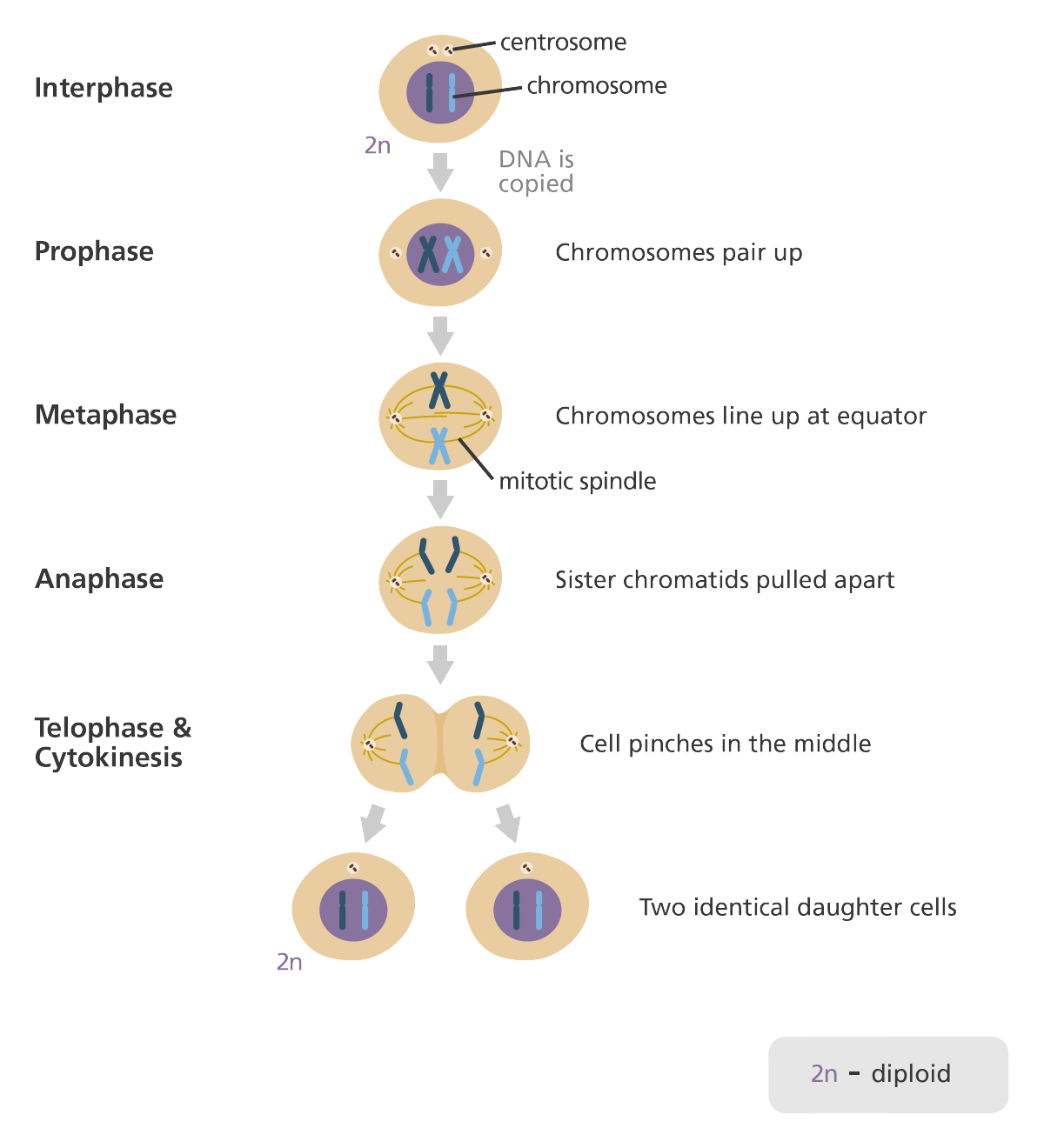
40
New cards
What is the product of fertilization?
Zygote
41
New cards
List and describe the two steps of meiosis.
Meiosis I: Chromosome pairs separate into two new cells
Meiosis II: Each chromosome separates from its copy into 4 new cells... each with HALF THE AMOUNT of DNA as the parent cell!
Meiosis II: Each chromosome separates from its copy into 4 new cells... each with HALF THE AMOUNT of DNA as the parent cell!
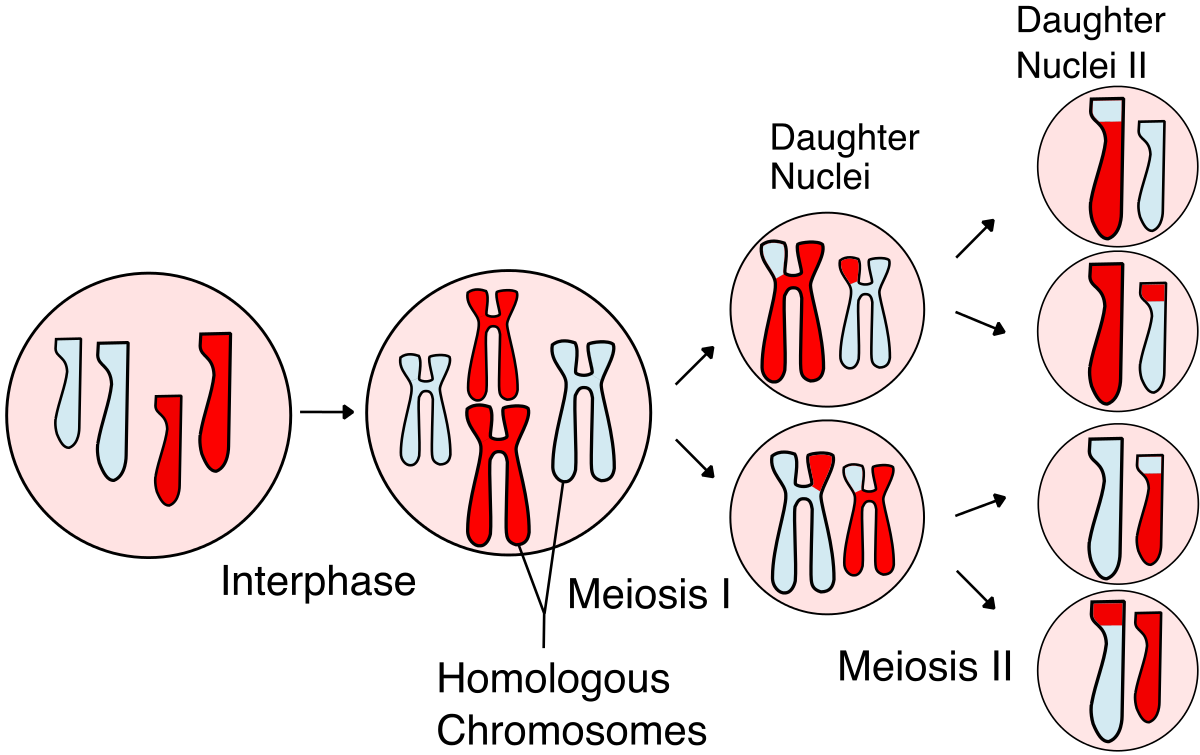
42
New cards
Match up the following strand to a complementary strand of DNA:
Strand 1: ATG CCT GAC
Strand 1: ATG CCT GAC
Strand 2: TAC GGA CTG
43
New cards
DNA replication is the process by which DNA copies itself and each new piece of DNA is made up of 1 old strand and 1 new strand. What is this also known as?
Semiconservative replication

44
New cards
RNA is ___*-stranded and has* ___ rather than thymine (T).
single, uracil (U)
45
New cards
Transcribe the following DNA strand:
DNA: ATG CCA AAG
DNA: ATG CCA AAG
RNA: UAC GGU UUC
46
New cards
Describe the process of using DNA to make a protein.
1\. Transcription: DNA in the nucleus is used to make messenger RNA (mRNA)
2\. RNA moves out into the cytoplasm to meet the ribosome
* RNA carries the directions to other parts of the cell
3\. Translation: The RNA attaches to a ribosome and is used to make a protein
* Proteins do all the work in the cell
* Every 3 bases in RNA is called a codon and codes for 1 amino acid
2\. RNA moves out into the cytoplasm to meet the ribosome
* RNA carries the directions to other parts of the cell
3\. Translation: The RNA attaches to a ribosome and is used to make a protein
* Proteins do all the work in the cell
* Every 3 bases in RNA is called a codon and codes for 1 amino acid
47
New cards
Why is the particular sequence of bases in a segment of DNA important to cells?
A. Some base sequences code for protein production.
B. Some base sequences cause the release of lipids from the nucleus.
C. Some base sequences contain the order of sugars in polysaccharides.
D. Some base sequences produce electrical signals sent to the cytoplasm.
A. Some base sequences code for protein production.
B. Some base sequences cause the release of lipids from the nucleus.
C. Some base sequences contain the order of sugars in polysaccharides.
D. Some base sequences produce electrical signals sent to the cytoplasm.
A. Some base sequences code for protein production
48
New cards
True/False: If a mutation happens in a body cell, it can be passed to offspring.
False. If the mutation happens in a body cell, it only affects the organism that carries it.
49
New cards
Describe the types of effects mutations can have on an organism.
Mutations can be
* harmful if they reduce an organism’s chances for reproduction or survival
* helpful if they improve an organism’s chances for survival
* neutral if they do not produce an obvious changes in an organism
* lethal if they result in the immediate death of an organism
* harmful if they reduce an organism’s chances for reproduction or survival
* helpful if they improve an organism’s chances for survival
* neutral if they do not produce an obvious changes in an organism
* lethal if they result in the immediate death of an organism
50
New cards
Mutagen
A factor in the environment like UV and chemicals that causes a mutation.
51
New cards
Describe key differences between heterozygous and homozygous traits.
* Homozygous traits have two identical alleles, while heterozygous traits have two different alleles.
* Homozygous traits can be either dominant or recessive, whereas heterozygous traits express the dominant allele.
* Homozygous individuals always produce offspring with the same trait, while heterozygous individuals can produce offspring with either dominant or recessive traits.
* Homozygous traits can be either dominant or recessive, whereas heterozygous traits express the dominant allele.
* Homozygous individuals always produce offspring with the same trait, while heterozygous individuals can produce offspring with either dominant or recessive traits.
52
New cards
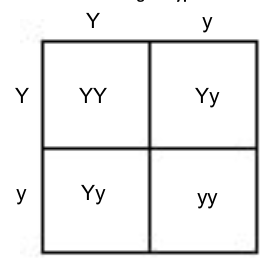
What is the genotype ratio of this Punnett Square? Phenotype ratio?
(Y=yellow, y=green)
(Y=yellow, y=green)
Genotype ratio: 1YY:2Yy:1yy
Phenotype ratio: 3 Yellow:1 Green
Phenotype ratio: 3 Yellow:1 Green
53
New cards
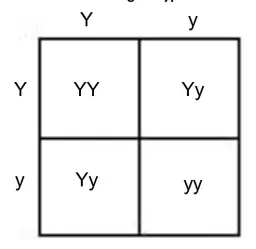
What are the chances of the offspring being **yellow**?
75%
54
New cards
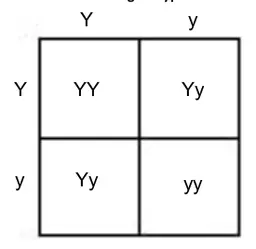
What are the chances of the offspring being green?
25%
55
New cards
In tigers, the allele for orange fur is dominant to the allele for white fur. If two heterozygous tigers mate and produce offspring, what is the probability of an individual offspring having white fur?
25%
56
New cards
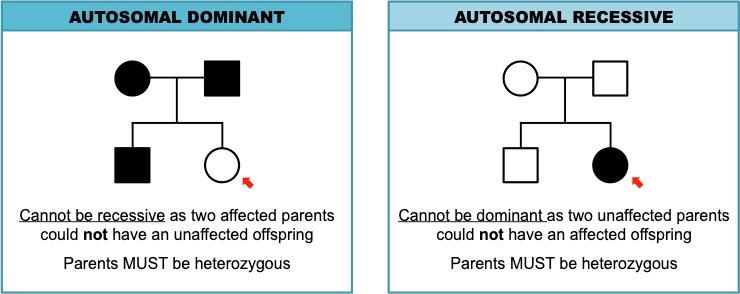
What are key differences between dominant vs. recessive traits when shown on a pedigree?
Recessive
* If both parents do not have the disorder, but some of the children do
* The disease can skip generations
Dominant
* If both parents have the disorder, and one of the offspring does not have it
* The disease is present in every generation, because if a child has the disease, one of the parents must have it also
* If both parents do not have the disorder, but some of the children do
* The disease can skip generations
Dominant
* If both parents have the disorder, and one of the offspring does not have it
* The disease is present in every generation, because if a child has the disease, one of the parents must have it also
57
New cards
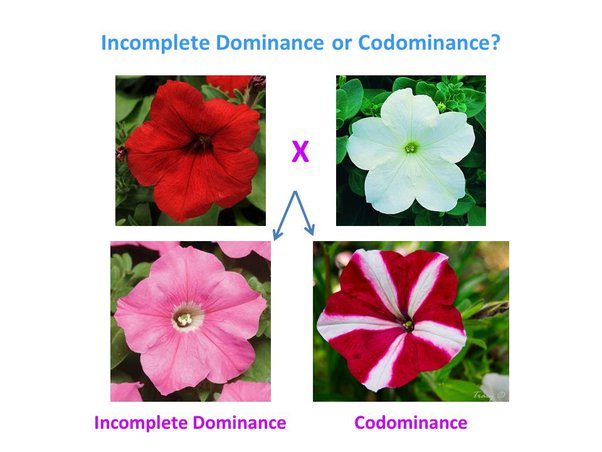
What are the key differences between codominance and incomplete dominance?
* Codominance involves the **full** expression of both alleles, whereas incomplete dominance results in an **intermediate** phenotype.
* In codominance, the traits associated with each allele are visible and **distinct**, while in incomplete dominance, the traits **blend** together.
* Codominance shows a clear presence of **both** alleles, while incomplete dominance demonstrates an intermediate or **blended** effect.
* In codominance, the traits associated with each allele are visible and **distinct**, while in incomplete dominance, the traits **blend** together.
* Codominance shows a clear presence of **both** alleles, while incomplete dominance demonstrates an intermediate or **blended** effect.
58
New cards
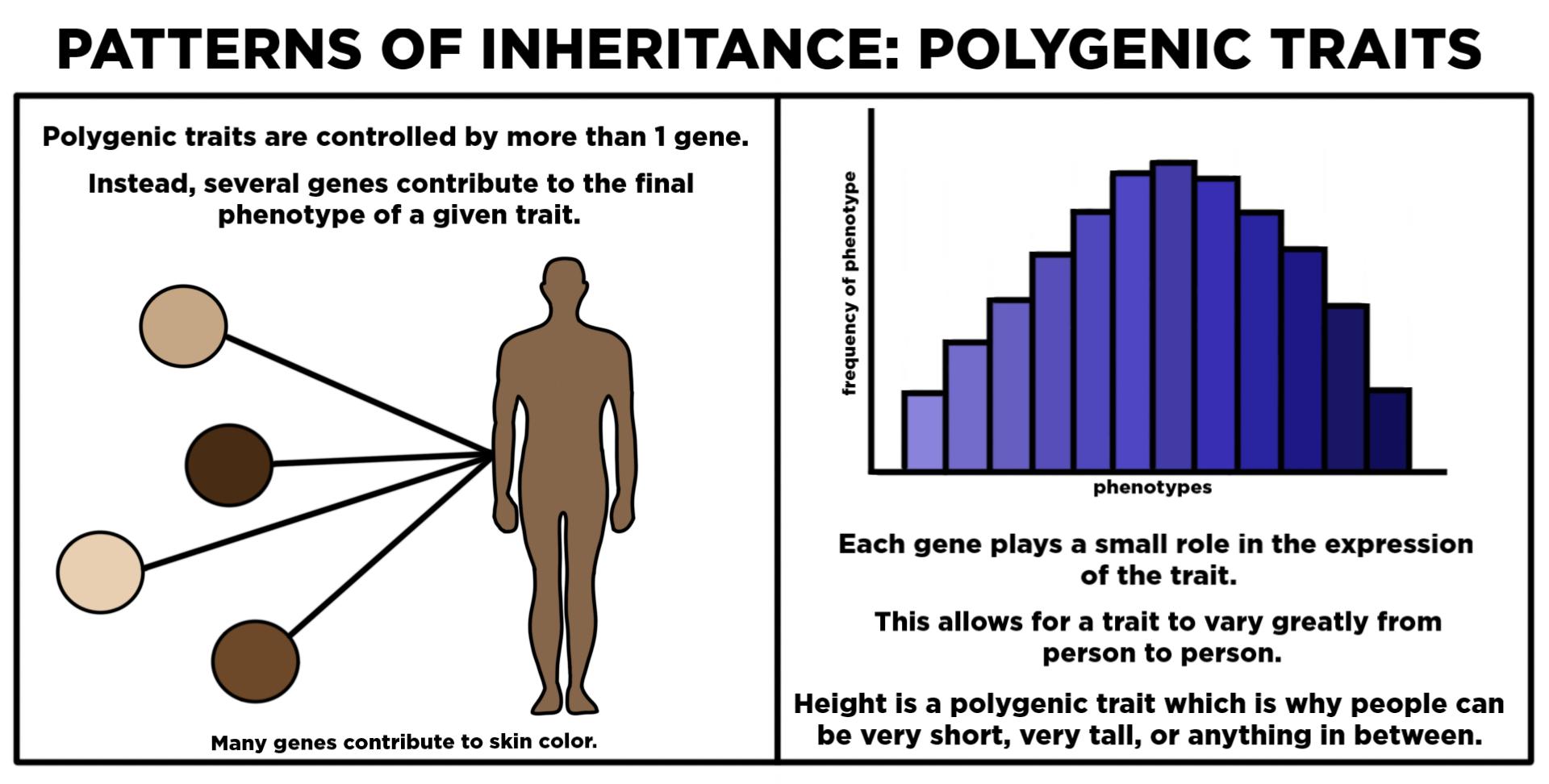
Traits that are controlled by more than one gene are called polygenic traits. What are some examples of polygenic traits?
Examples of polygenic traits include skin color, hair color, eye color, and height.
59
New cards

A Siamese cat has both dark and light fur on its body, as shown. The production of the protein that determines fur color is dependent upon temperature. The fur on the body of the cat is lighter colored because its body is warmer than its head, feet, and tail.
Which of the following **best** describes how fur color is determined in a Siamese cat?
A. Fur color is determined only by genes and RNA sequences that code for temperature.
B. Fur color is determined by proteins from the environment and the temperature of the genes.
C. Fur color is determined by a gene that codes for a protein and by the temperature of the environment.
D. Fur color is determined only by environmental factors that include genes and the temperature of the cat.
Which of the following **best** describes how fur color is determined in a Siamese cat?
A. Fur color is determined only by genes and RNA sequences that code for temperature.
B. Fur color is determined by proteins from the environment and the temperature of the genes.
C. Fur color is determined by a gene that codes for a protein and by the temperature of the environment.
D. Fur color is determined only by environmental factors that include genes and the temperature of the cat.
C. Fur color is determined by a gene that codes for a protein and by the temperature of the environment.
60
New cards
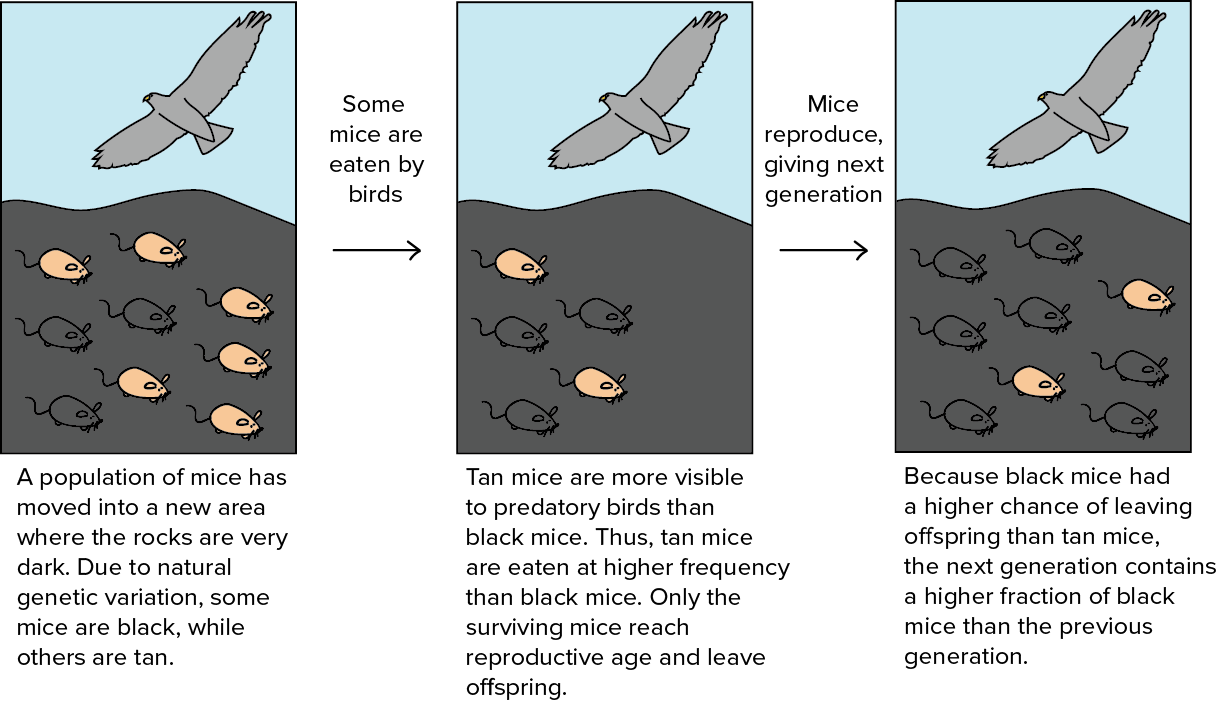
Natural selection says that organisms with ___ traits that fit an environment are more likely to __________ than organisms without these favorable traits
good, survive and reproduce
61
New cards
During the fall reproductive season, the belly of a male brook trout becomes bright orange. The orange belly provides some camouflage and helps attract females. This trait evolved in brook trout because, compared to males with pale bellies, males with bright orange bellies are more likely to
A. live in good habitats.
B. be eaten by predators.
C. mate with other species of fish.
D. fertilize eggs to produce offspring.
A. live in good habitats.
B. be eaten by predators.
C. mate with other species of fish.
D. fertilize eggs to produce offspring.
D. fertilize eggs to produce offspring.
62
New cards
List the five main pieces of evidence supporting evolution.
* **Paleontology**: paleontology revealed the various organisms and the major lines of evolution. Fossils can be dated by:
i. The age of the rocks where a fossil is found
ii. The rate of decay of isotopes including carbon-14
iii. Geographical data
* **Biogeography**, or the study of the distribution of flora (plants) and fauna (animals) in the environment: scientists found related species in widely separated regions of the world.
* **Embryology**, or the study of development of an organism: All the vertebrates—including fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and even mammals such as humans—show fishlike features called gill slits.
* **Morphological homologies**, or the study of the anatomy of various animals: scientists discovered that some animals have similar structures that serve different functions. Homologous structures, also point to a common ancestor. Analogous structures evolved totally independently of one another.
* **Molecular Biology**: Similar DNA sequences suggest closer relationships between organisms
i. The age of the rocks where a fossil is found
ii. The rate of decay of isotopes including carbon-14
iii. Geographical data
* **Biogeography**, or the study of the distribution of flora (plants) and fauna (animals) in the environment: scientists found related species in widely separated regions of the world.
* **Embryology**, or the study of development of an organism: All the vertebrates—including fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and even mammals such as humans—show fishlike features called gill slits.
* **Morphological homologies**, or the study of the anatomy of various animals: scientists discovered that some animals have similar structures that serve different functions. Homologous structures, also point to a common ancestor. Analogous structures evolved totally independently of one another.
* **Molecular Biology**: Similar DNA sequences suggest closer relationships between organisms
63
New cards
A scientist is trying to determine how closely related two species of plants are. What would be useful for the scientist to compare?
A. Consumers of the plants
B. Oxygen production levels of the plants
C. The genetic sequences of the plants
D. The size of the plant
A. Consumers of the plants
B. Oxygen production levels of the plants
C. The genetic sequences of the plants
D. The size of the plant
C. The genetic sequences of the plants
64
New cards
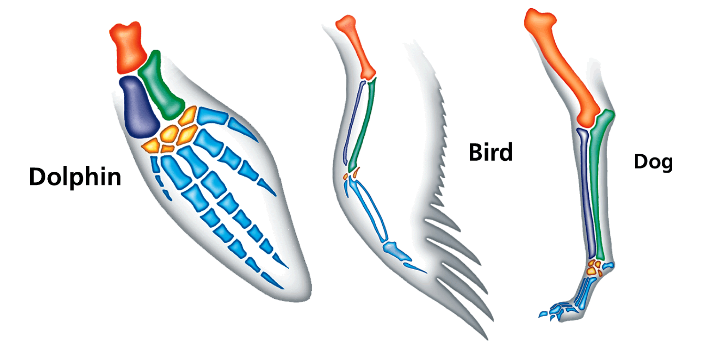
What are homologous structures? Provide an example.
Structures that are similar and are inherited from a common ancestor but have different functions
Example: The forelimb (arm) of different organisms are adapted for different uses, but they all have similar bones
Example: The forelimb (arm) of different organisms are adapted for different uses, but they all have similar bones
65
New cards
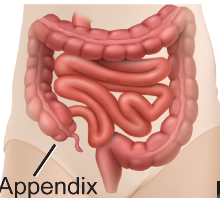
What are vestigial structures? Provide an example.
Body parts left behind that used to have important functions in common ancestors but are now useless
Example: The appendix is a structure important in digestion in most mammals, but has no use in humans
Example: The appendix is a structure important in digestion in most mammals, but has no use in humans
66
New cards
What are analogous structures? Provide an example.
Structures that have the same function but are not inherited from a common ancestor
Example: The wings of an eagle and wings of a beetle both allow the organisms to fly. This shows that similar features can evolve separately in a similar environment.
Example: The wings of an eagle and wings of a beetle both allow the organisms to fly. This shows that similar features can evolve separately in a similar environment.

67
New cards
There are two types of modern whales: toothed whales and baleen whales. Baleen whales filter plankton from the water using baleen, plates made of fibrous proteins that grow from the roof of their mouths. The embryos of baleen whales have teeth in their upper jaws. As the embryos develop, the teeth are replaced with baleen. Which of the following conclusions is best supported by this information?
A. Primitive whales had teeth as adults.
B. Toothed whales descended from baleen whales.
C. Baleen whales are evolving into toothed whales.
D. Descendants of modern baleen whales will have both teeth and baleen as adults.
A. Primitive whales had teeth as adults.
B. Toothed whales descended from baleen whales.
C. Baleen whales are evolving into toothed whales.
D. Descendants of modern baleen whales will have both teeth and baleen as adults.
A. Primitive whales had teeth as adults.
68
New cards
In 2006, scientists discovered fossilized skeletons of an animal with several interesting features. Fossil evidence indicated that the animal not only had scales, fins, and gills, but also had lungs, a full set of ribs, and limb bones arranged to support the animal’s weight. The illustration below shows what the animal, called Tiktaalik, probably looked like based on the fossil evidence.Which of the following statements best explains why the Tiktaalik fossils are an important piece of evidence for evolution?
A. They include skeletons of both males and females.
B. They are complete skeletons of a carnivorous animal.
C. They allow scientists to estimate the animal’s lifespan.
D. They show a transitional form between fish and land-dwelling vertebrates.
A. They include skeletons of both males and females.
B. They are complete skeletons of a carnivorous animal.
C. They allow scientists to estimate the animal’s lifespan.
D. They show a transitional form between fish and land-dwelling vertebrates.
D. They show a transitional form between fish and land-dwelling vertebrates
69
New cards
What are the eight taxa? (Hint: **D**ear **K**ing **P**hilip **C**ame **O**ver **F**or **G**reen **S**paghetti)
1. Domain
2. Kingdom
3. Phylum
4. Class
5. Order
6. Family
7. Genus
8. Species
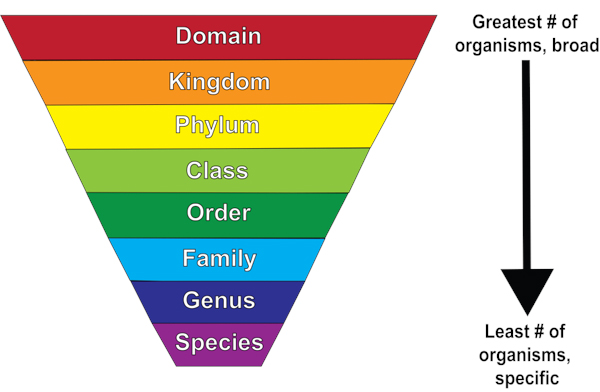
70
New cards
List and describe the six kingdoms.
1. Archaebacteria: bacteria that live in extreme environments
2. Eubacteria: common bacteria
3. Protista: Unicellular or multicellular organisms that do not belong in the other kingdoms
4. Fungi: Mushrooms, yeasts, molds
5. Animalia: animals
6. Plantae: plants
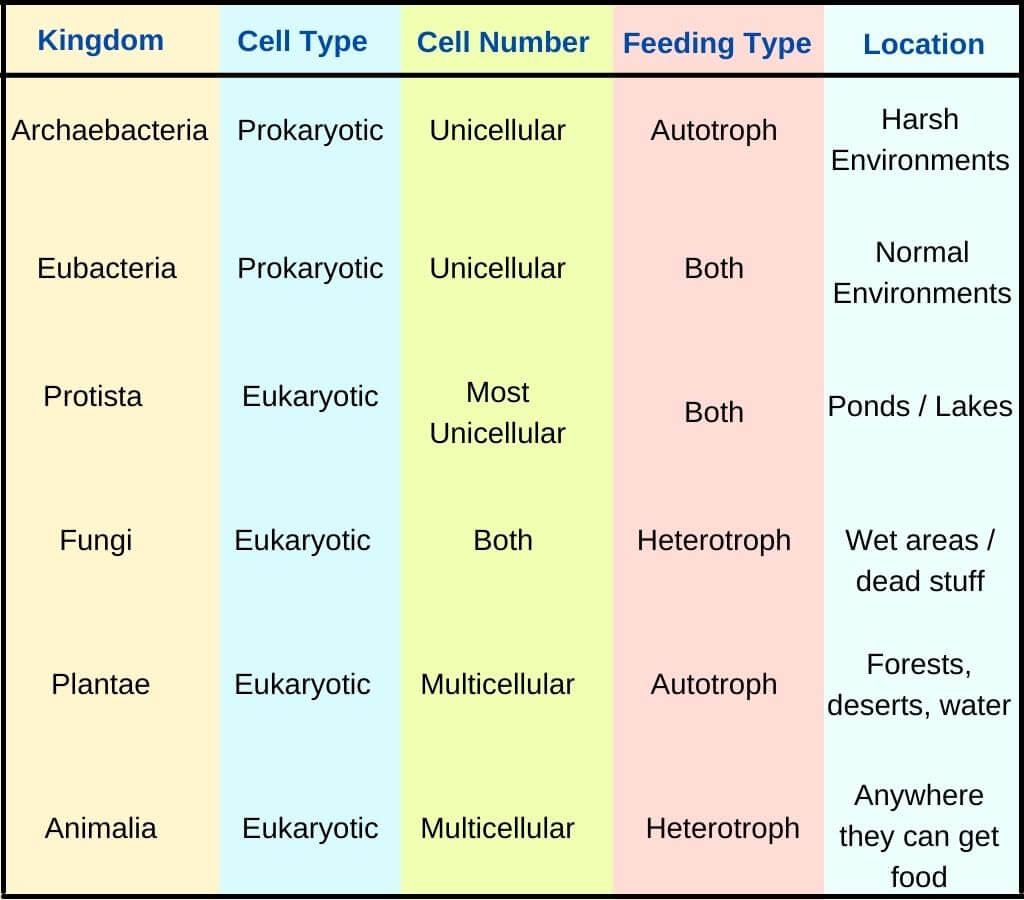
71
New cards

According to the rules of binomial nomenclature, what is the scientific name of an orangutan? (See photo)
*Pongo borneo*
72
New cards
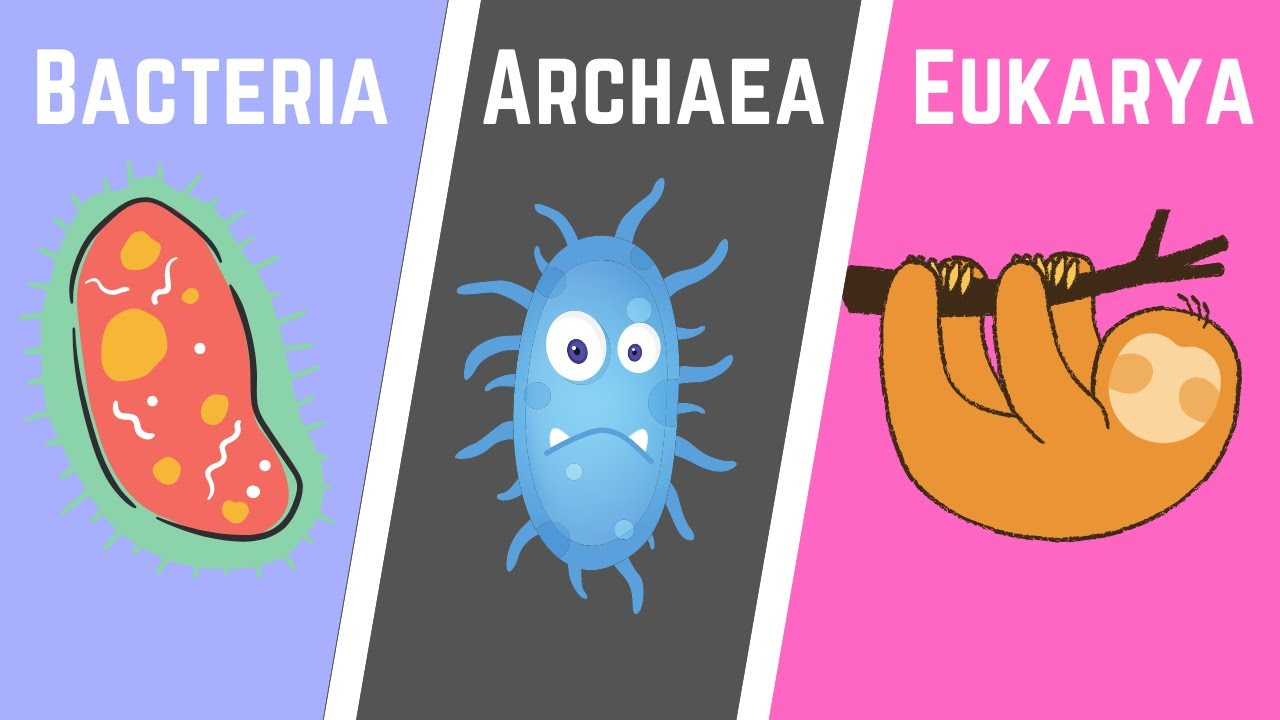
List the 3 domains. Describe each.
1. Archaea: Bacteria that live in extreme environments – **NO nucleus**
2. Eubacteria: Common bacteria – **NO nucleus**
3. Eukarya: Organisms that **HAVE A NUCLEUS!**

73
New cards
Ecosystem
A collection of organisms and their physical environment
74
New cards
The biodiversity of an ecosystem measures _____________.
the number of species living there.
75
New cards
What is the difference between autotrophs and heterotrophs?
Autotrophs: Organisms that make their own food, like plants and some bacteria
Heterotrophs: Organisms that cannot make their own food, like animals
Heterotrophs: Organisms that cannot make their own food, like animals
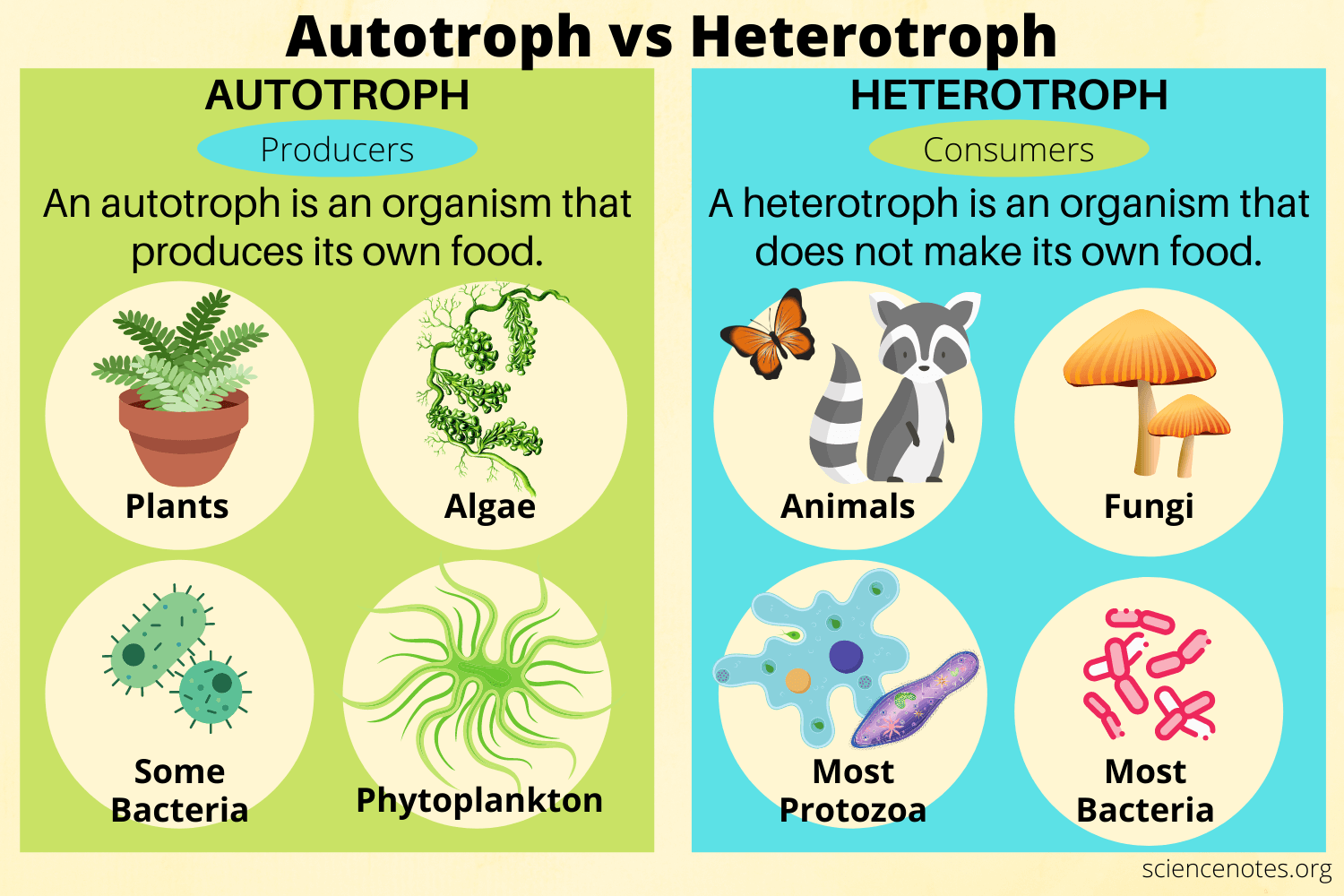
76
New cards
Name and describe the diet of the five types of heterotrophs.
* Herbivores: Eat plants
* Carnivores: Eat animals
* Omnivores: Eat plants and animals
* Decomposers: Special type of consumer that breaks down waste products and recycles dead organisms for energy
* Detritivores: Feed on dead organisms
* Carnivores: Eat animals
* Omnivores: Eat plants and animals
* Decomposers: Special type of consumer that breaks down waste products and recycles dead organisms for energy
* Detritivores: Feed on dead organisms

77
New cards
What is the difference between biotic and abiotic factors?
Abiotic factors are **nonliving** things, such as the sun, water, rocks, and climate
Biotic factors are **living** things, such as
* Producers: Organisms that take in energy from the sun to make food (plants)
* Consumers: Organisms that eat other organisms for energy
Biotic factors are **living** things, such as
* Producers: Organisms that take in energy from the sun to make food (plants)
* Consumers: Organisms that eat other organisms for energy
78
New cards
How much energy is transferred when moving up a trophic level?
10%
79
New cards
Where is the rest of the energy that is not transferred when consumed?
90% of the energy is used for body functions or is not eaten.
80
New cards
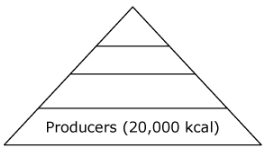
Based on the energy pyramid, how much energy would be stored in the tertiary consumers in this ecosystem?
A. 2,000 kcal
B. 200 kcal
C. 20 kcal
D. 2 kcal
A. 2,000 kcal
B. 200 kcal
C. 20 kcal
D. 2 kcal
C. 20 kcal
81
New cards
Which of the following would most likely happen if grasses and shrubs were removed from a rural Massachusetts ecosystem?
A. There would be an increase in consumers in the ecosystem.
B. There would be an increase of photosynthesis in the ecosystem.
C. There would be a decrease in food energy produced by the ecosystem.
D. There would be a decrease of carbon dioxide available to the ecosystem.
A. There would be an increase in consumers in the ecosystem.
B. There would be an increase of photosynthesis in the ecosystem.
C. There would be a decrease in food energy produced by the ecosystem.
D. There would be a decrease of carbon dioxide available to the ecosystem.
C. There would be a decrease in food energy produced by the ecosystem.
82
New cards
A caterpillar eats an oak leaf. Which of the following best describes the energy transfer in this situation?
A. Both the caterpillar and the leaf gain energy.
B. Energy is transferred from the leaf to the caterpillar.
C. Decomposers in the leaf obtain energy from the caterpillar..
D. The oak tree gains energy when the caterpillar eats the leaf.
A. Both the caterpillar and the leaf gain energy.
B. Energy is transferred from the leaf to the caterpillar.
C. Decomposers in the leaf obtain energy from the caterpillar..
D. The oak tree gains energy when the caterpillar eats the leaf.
B. Energy is transferred from the leaf to the caterpillar
83
New cards
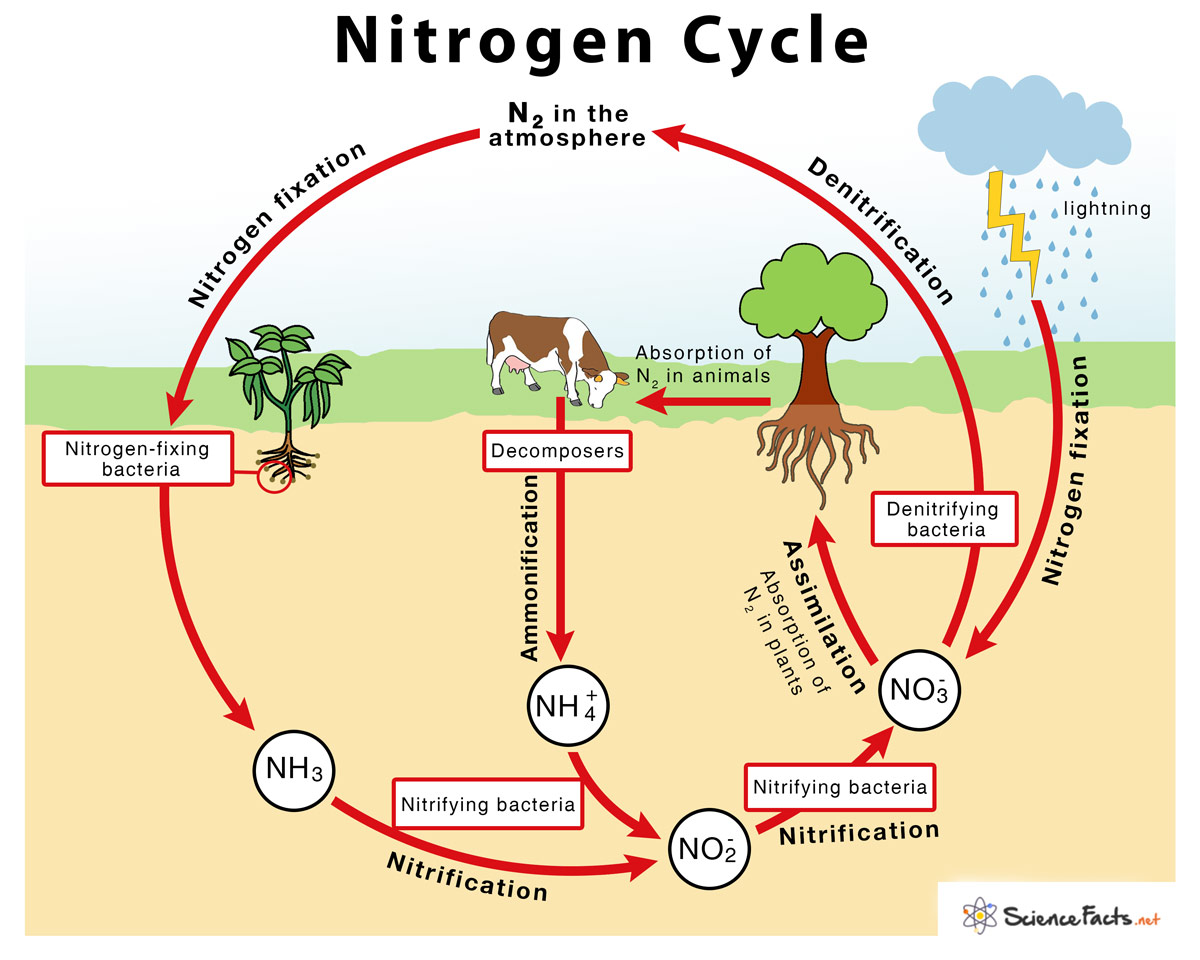
Describe what happens in the nitrogen cycle.
* Nitrogen in the atmosphere is taken in by bacteria that live in plant roots (nitrogen fixation)
* The nitrogen is passed onto the plants and any animals that eat the plants
* Once the plant or animal has died, decomposers (bacteria) again eat the nitrogen in the dead material and send it back to the atmosphere (denitrification)
* The nitrogen is passed onto the plants and any animals that eat the plants
* Once the plant or animal has died, decomposers (bacteria) again eat the nitrogen in the dead material and send it back to the atmosphere (denitrification)
84
New cards
Which of the following correctly explains how atmospheric nitrogen is converted to nitrogen compounds used by living organisms?
A. Sunlight converts atmospheric nitrogen to a form usable by protists.
B. Plant leaves convert atmospheric nitrogen to a form usable by animals.
C. Bacteria in soil convert atmospheric nitrogen to a form usable by plants.
D. Invertebrate animals in soil convert atmospheric nitrogen to a form usable by fungi.
A. Sunlight converts atmospheric nitrogen to a form usable by protists.
B. Plant leaves convert atmospheric nitrogen to a form usable by animals.
C. Bacteria in soil convert atmospheric nitrogen to a form usable by plants.
D. Invertebrate animals in soil convert atmospheric nitrogen to a form usable by fungi.
C. Bacteria in soil convert atmospheric nitrogen to a form usable by plants
85
New cards
Fertilizers can enable farmers to grow the same crop in a field for several years in a row. Farmers who use less fertilizer often rotate their crops by planting the crop one year and legumes, such as beans and clover, the following year. Fertilizer use and crop rotation with legumes both increase the availability of which of the following nutrients in soil?
A. calcium
B. nitrogen
C. oxygen
D. protein
A. calcium
B. nitrogen
C. oxygen
D. protein
B. nitrogen
86
New cards
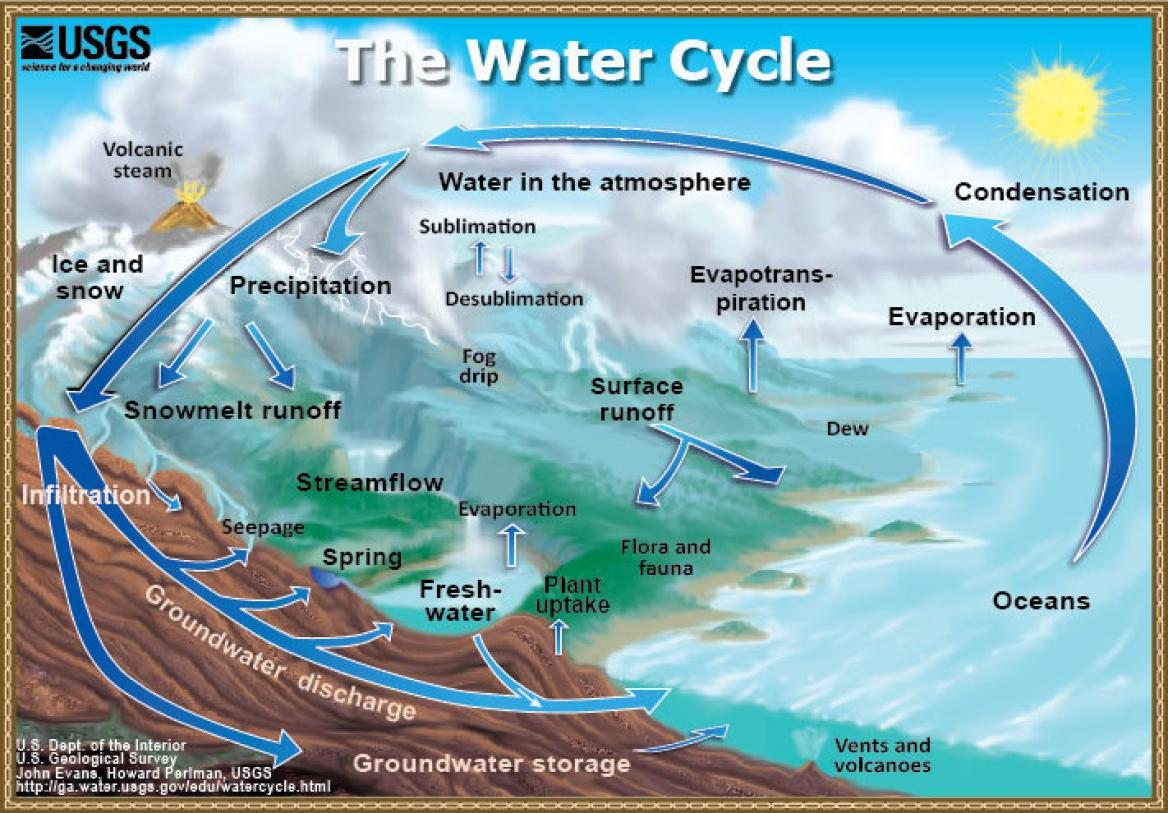
Describe what happens in the water cycle.
* Precipitation, such as rain and snow, fall to the earth
* The water either
* goes into the ground for plants to use and the plants give off excess water back to the atmosphere (transpiration)
* or runs off the land to lower-lying bodies of water where it evaporates back into the atmosphere and then forms clouds during condensation
* The water either
* goes into the ground for plants to use and the plants give off excess water back to the atmosphere (transpiration)
* or runs off the land to lower-lying bodies of water where it evaporates back into the atmosphere and then forms clouds during condensation
87
New cards
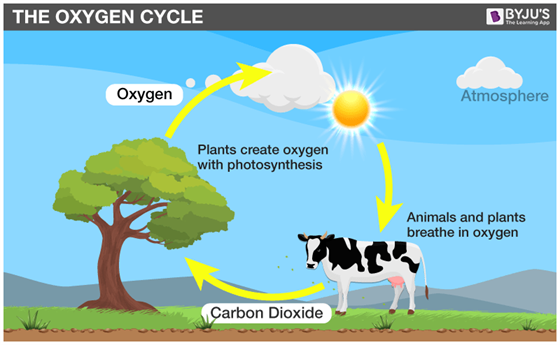
Describe what happens in the oxygen-carbon cycle.
* Carbon dioxide from the atmosphere is used by plants who use it during photosynthesis and release oxygen back into the atmosphere
* Oxygen in the atmosphere is taken in by animals and plants who use it during cellular respiration and release carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere
* Oxygen in the atmosphere is taken in by animals and plants who use it during cellular respiration and release carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere
88
New cards
Which of the following explains why elements, such as carbon and oxygen, that are used in organic molecules are not permanently removed from the environment?
A. They are replenished by sunlight.
B. They are cycled through ecosystems.
C. They are replaced by volcanic eruptions.
D. They are produced constantly from nutrients.
A. They are replenished by sunlight.
B. They are cycled through ecosystems.
C. They are replaced by volcanic eruptions.
D. They are produced constantly from nutrients.
B. They are cycled through ecosystems
89
New cards
In one of the steps of the carbon cycle, a person exhales a molecule of carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere. Which of the following is most likely to happen next to the atom of carbon in this molecule?
A. It may be used as part of a sugar in a plant.
B. It may become part of a protein in an animal.
C. It may be consumed as a fossil fuel is burned.
D. It may be decomposed into carbon and oxygen by a bacterium.
A. It may be used as part of a sugar in a plant.
B. It may become part of a protein in an animal.
C. It may be consumed as a fossil fuel is burned.
D. It may be decomposed into carbon and oxygen by a bacterium.
A. It may be used as part of a sugar in a plant
90
New cards
How do animals get their carbon and nitrogen?
Consumption

91
New cards
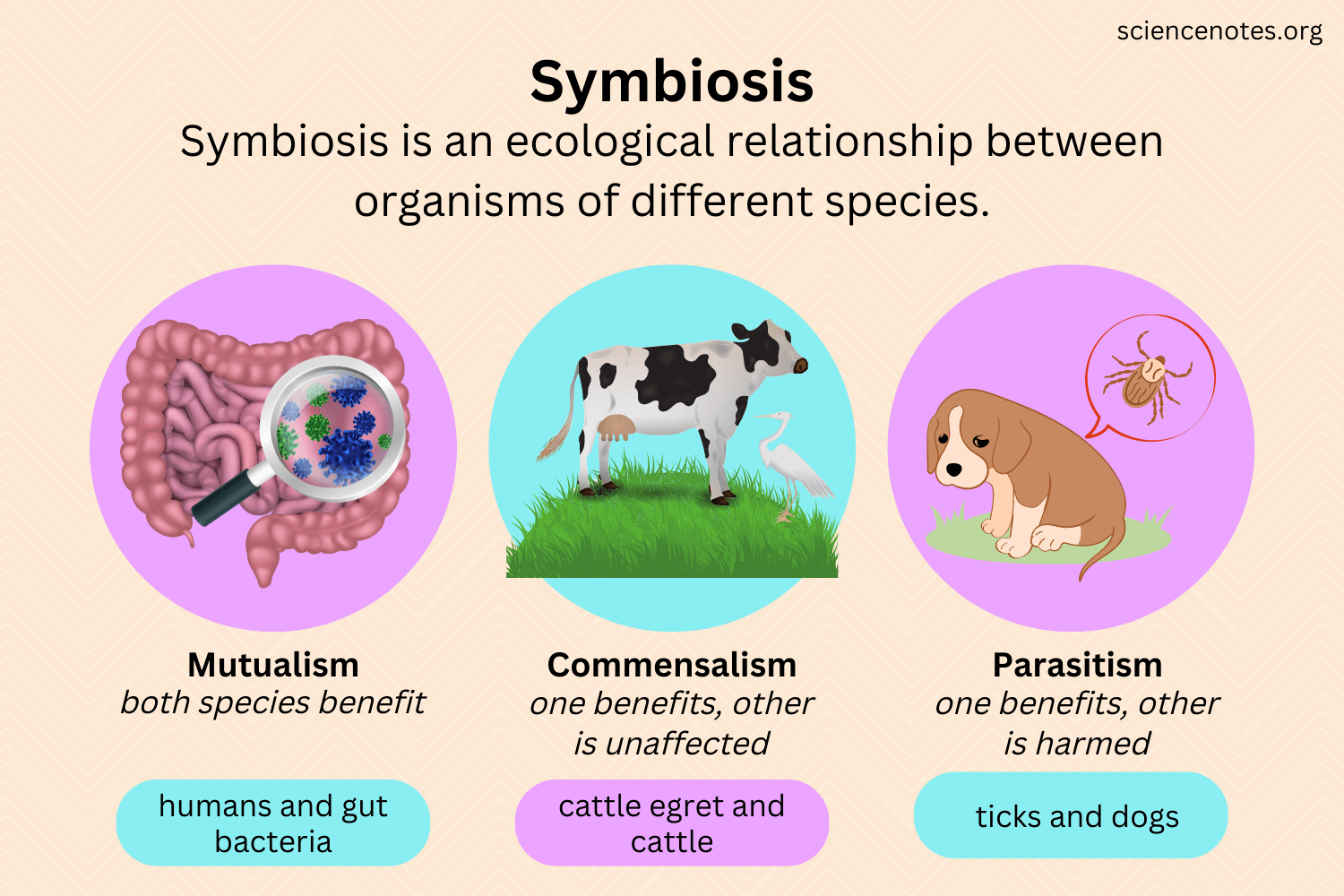
List and describe the 3 symbiotic relationships.
1. Commensalism is when one of the 2 organisms benefits from the symbiosis
2. Mutualism is when both organisms benefit from the symbiosis
3. Parasitism is when one organism benefits (parasite) and the other organism is harmed (host) from the symbiosis
92
New cards
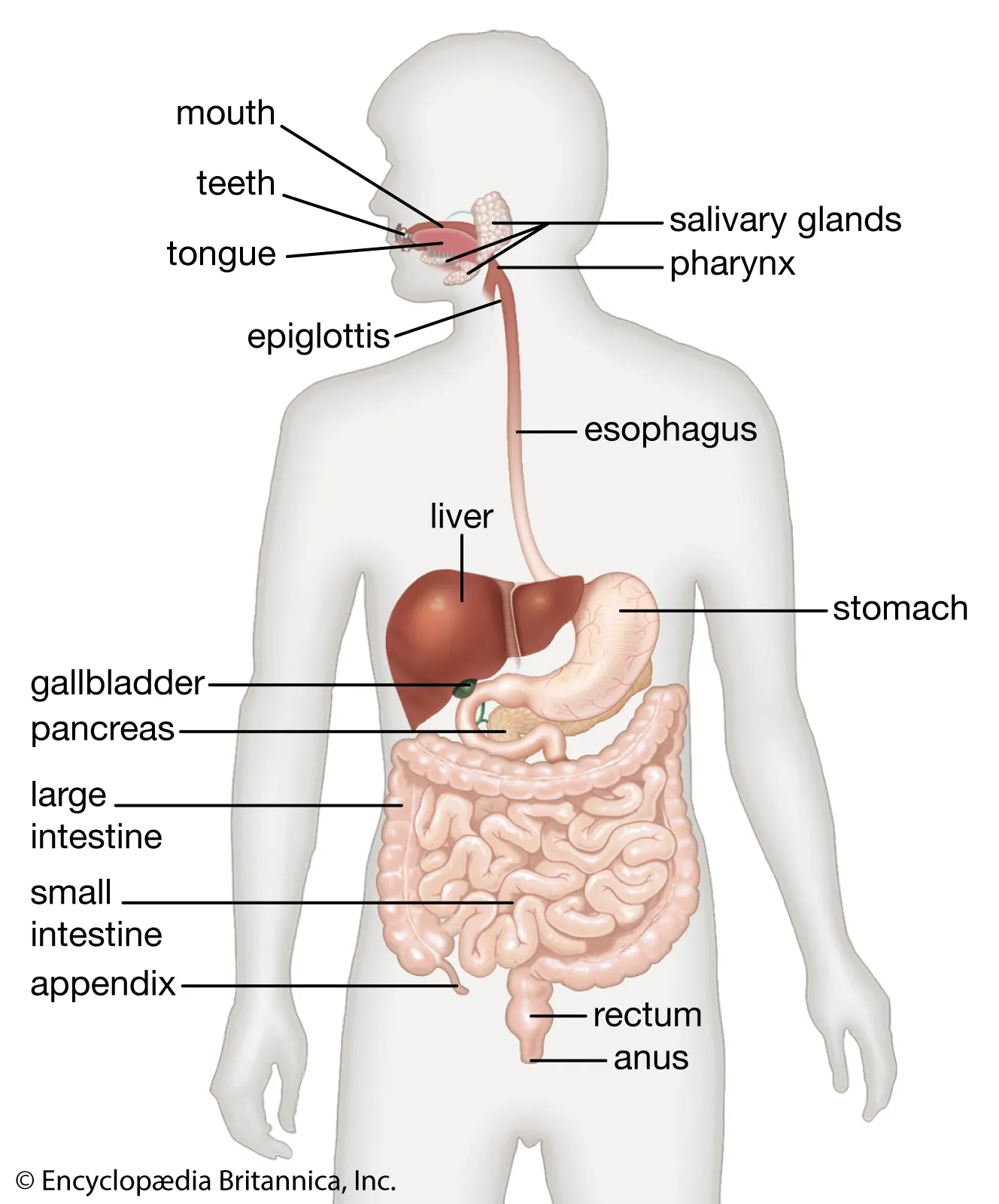
What is the function of the digestive system?
To break down food into nutrients (digestion) and to absorb them into the blood for energy (absorption).
93
New cards
Describe the function of each part of the digestive system.
* **Mouth**: chemical and mechanical digestion start here using teeth to chew and saliva to break down carbohydrates
* **Pharynx**: the throat, where food and air pass through
* **Esophagus**: long tube that takes food to stomach
* **Stomach**: strong organ that mechanically (squishes) and chemically (using acid) digests food.
* **Small Intestine:** very long, most chemical digestion happens here using enzymes from pancreas and bile from gall bladder and liver. Most nutrient absorption happens here!
* **Villi**: tiny finger like structures inside the small intestine that help absorb nutrients from food.
* **Gall bladder**: stores bile to be released into small intestine
* **Bile**: green liquid that helps digest fat. Made in liver and stored in gall bladder.
* **Pancreas**: makes enzymes to help with digestion.
* **Liver**: Makes bile.
* **Large Intestine**: absorbs water from undigested food.
* **Rectum**: place at end of large intestine where waste waits to be excreted.
* **Anus**: hole where waste leaves your body.
* **Pharynx**: the throat, where food and air pass through
* **Esophagus**: long tube that takes food to stomach
* **Stomach**: strong organ that mechanically (squishes) and chemically (using acid) digests food.
* **Small Intestine:** very long, most chemical digestion happens here using enzymes from pancreas and bile from gall bladder and liver. Most nutrient absorption happens here!
* **Villi**: tiny finger like structures inside the small intestine that help absorb nutrients from food.
* **Gall bladder**: stores bile to be released into small intestine
* **Bile**: green liquid that helps digest fat. Made in liver and stored in gall bladder.
* **Pancreas**: makes enzymes to help with digestion.
* **Liver**: Makes bile.
* **Large Intestine**: absorbs water from undigested food.
* **Rectum**: place at end of large intestine where waste waits to be excreted.
* **Anus**: hole where waste leaves your body.
94
New cards
Where does mechanical and chemical digestion start?
The mouth
95
New cards
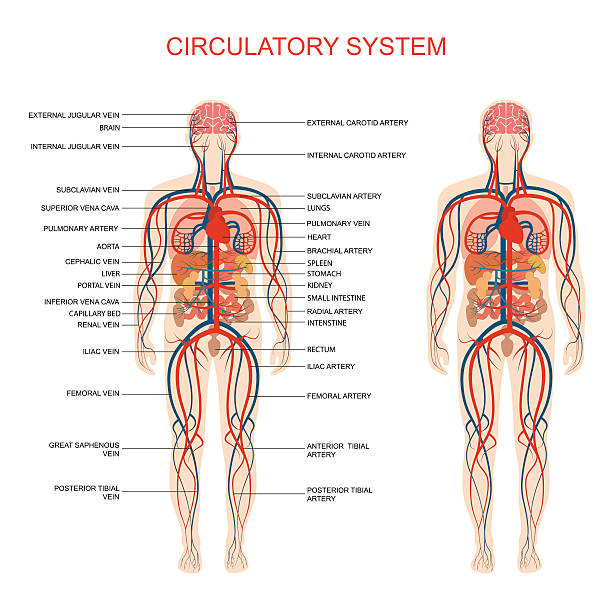
What is the function of the circulatory system?
To transport oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients and wastes around our body (in the blood).
96
New cards
Describe the function of each part of the circulatory system.
* **Heart**: pumps blood to the body and to the lungs
* **Arteries**: send oxygen rich blood away from the body to the cells
* **Veins**: take oxygen poor blood back to heart from the body
* **Capillaries**: tiny tubes on each cell where oxygen and nutrients are given to cell and carbon dioxide and wastes are taken away.
* **Blood**: red liquid that transports oxygen, nutrients, wastes, blood cells and carbon dioxide to and from your cells.
* **Red blood cells**: carry oxygen to body cells.
* **Arteries**: send oxygen rich blood away from the body to the cells
* **Veins**: take oxygen poor blood back to heart from the body
* **Capillaries**: tiny tubes on each cell where oxygen and nutrients are given to cell and carbon dioxide and wastes are taken away.
* **Blood**: red liquid that transports oxygen, nutrients, wastes, blood cells and carbon dioxide to and from your cells.
* **Red blood cells**: carry oxygen to body cells.
97
New cards
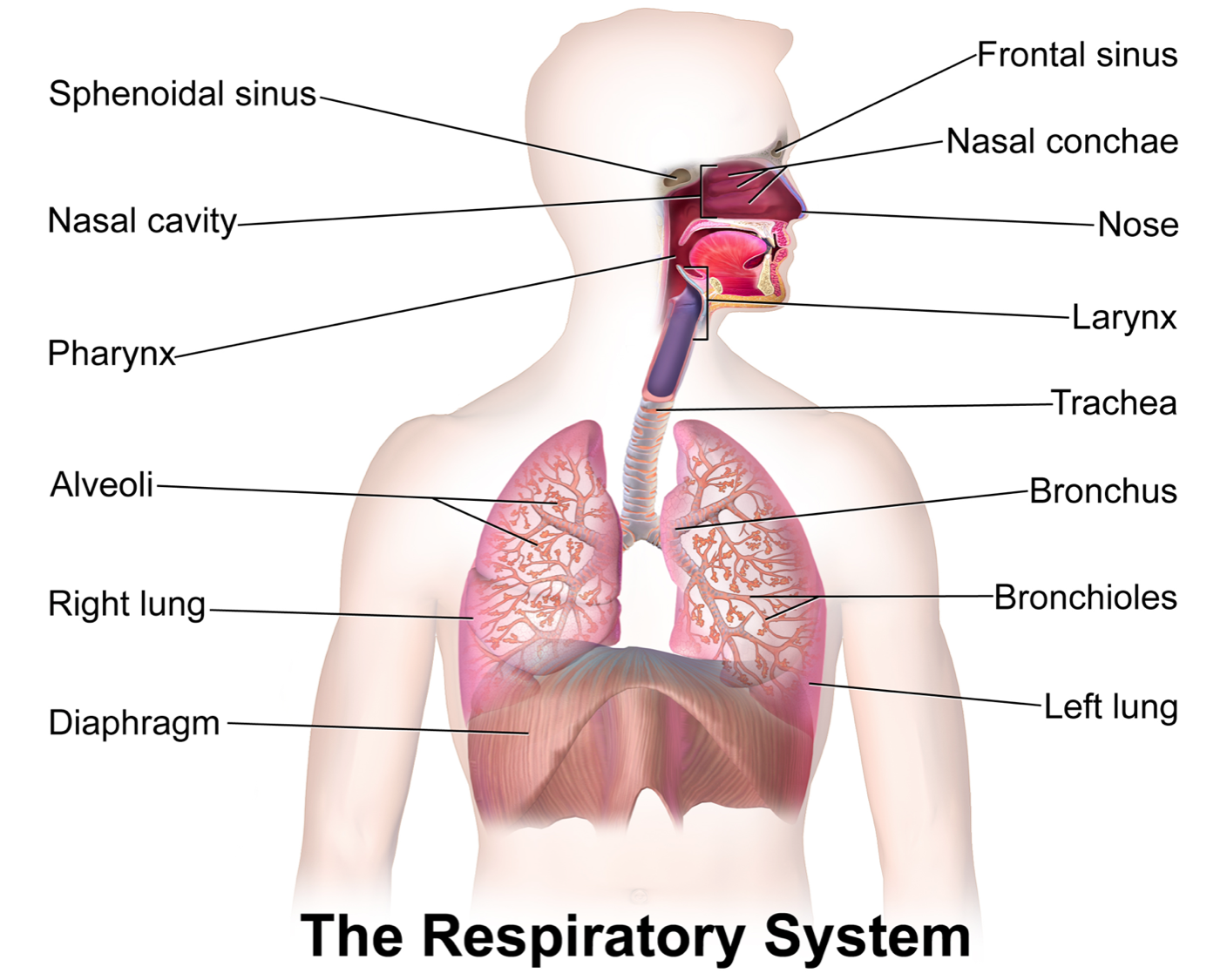
What is the function of the respiratory system?
To transport oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients and wastes in and out of our body.
98
New cards
Describe the function of each part of the respiratory system.
* **Nose**: to bring air in, filter and moisten it
* **Pharynx**: the throat, where food and air pass through
* **Larynx**: the voice box, contains vocal cords
* **Epiglottis**: flap of skin that covers trachea when swallowing so food does not go into lungs
* **Trachea**: windpipe, brings air to bronchi
* **Bronchi**: two tubes that take air to each lung
* **Lungs**: two part organ where oxygen is absorbed
* **Bronchioles**: small tubes that spread air throughout your lungs
* **Alveoli**: tiny air sacs surrounded by capillaries, oxygen diffuses from these sacs into the blood while carbon dioxide fuses from blood into alveoli.
* **Pharynx**: the throat, where food and air pass through
* **Larynx**: the voice box, contains vocal cords
* **Epiglottis**: flap of skin that covers trachea when swallowing so food does not go into lungs
* **Trachea**: windpipe, brings air to bronchi
* **Bronchi**: two tubes that take air to each lung
* **Lungs**: two part organ where oxygen is absorbed
* **Bronchioles**: small tubes that spread air throughout your lungs
* **Alveoli**: tiny air sacs surrounded by capillaries, oxygen diffuses from these sacs into the blood while carbon dioxide fuses from blood into alveoli.
99
New cards
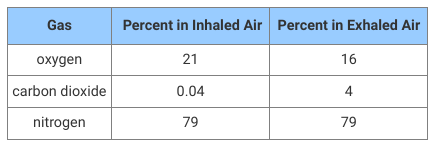
Students learning about the respiratory system collected data on the gases inhaled and exhaled by a classmate. The table shows the data collected.
Which of the following best explains the data in the table?
A. The nose filters out nitrogen gas so only oxygen and carbon dioxide gases enter the lungs.
B. The walls of the trachea allow only carbon dioxide gas and nitrogen gas to move out of the body.
C. As air enters the larynx, it is warmed, causing some oxygen gas to be converted to carbon dioxide gas.
D. As air enters the alveoli, some oxygen moves into the blood and some carbon dioxide moves out of the blood.
Which of the following best explains the data in the table?
A. The nose filters out nitrogen gas so only oxygen and carbon dioxide gases enter the lungs.
B. The walls of the trachea allow only carbon dioxide gas and nitrogen gas to move out of the body.
C. As air enters the larynx, it is warmed, causing some oxygen gas to be converted to carbon dioxide gas.
D. As air enters the alveoli, some oxygen moves into the blood and some carbon dioxide moves out of the blood.
D. As air enters the alveoli, some oxygen moves into the blood and some carbon dioxide moves out of the blood.
100
New cards
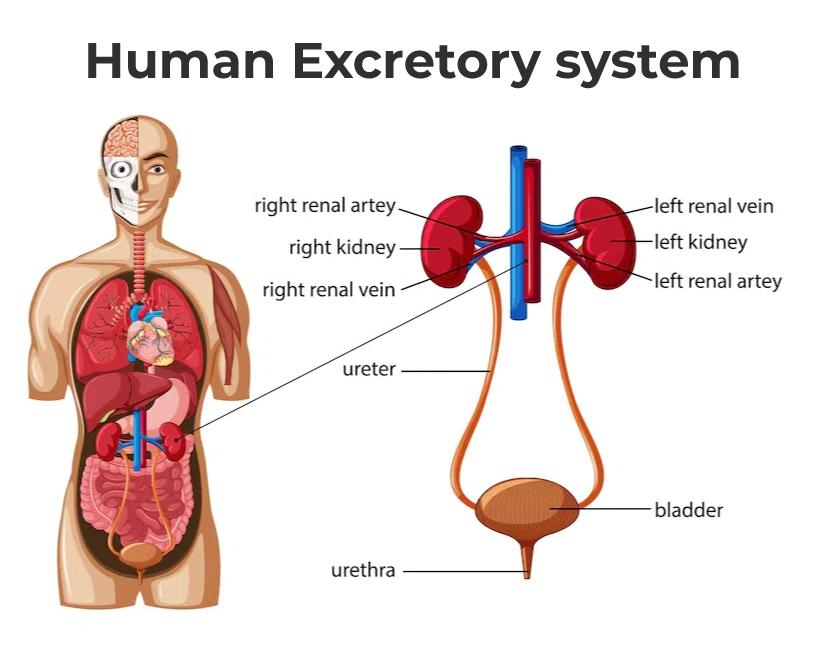
What is the function of the excretory system?
To maintain homeostasis by excreting (removing) the extra water and waste in your blood, and therefore your body, through **liquid** waste or urine.