2.4.1. Electron Structure
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
define electron configuration
the arrangement of electrons in an atom
define principal energy evels
used to number the energy levels i.e. the lower the number the closer the shell is to the nucleus
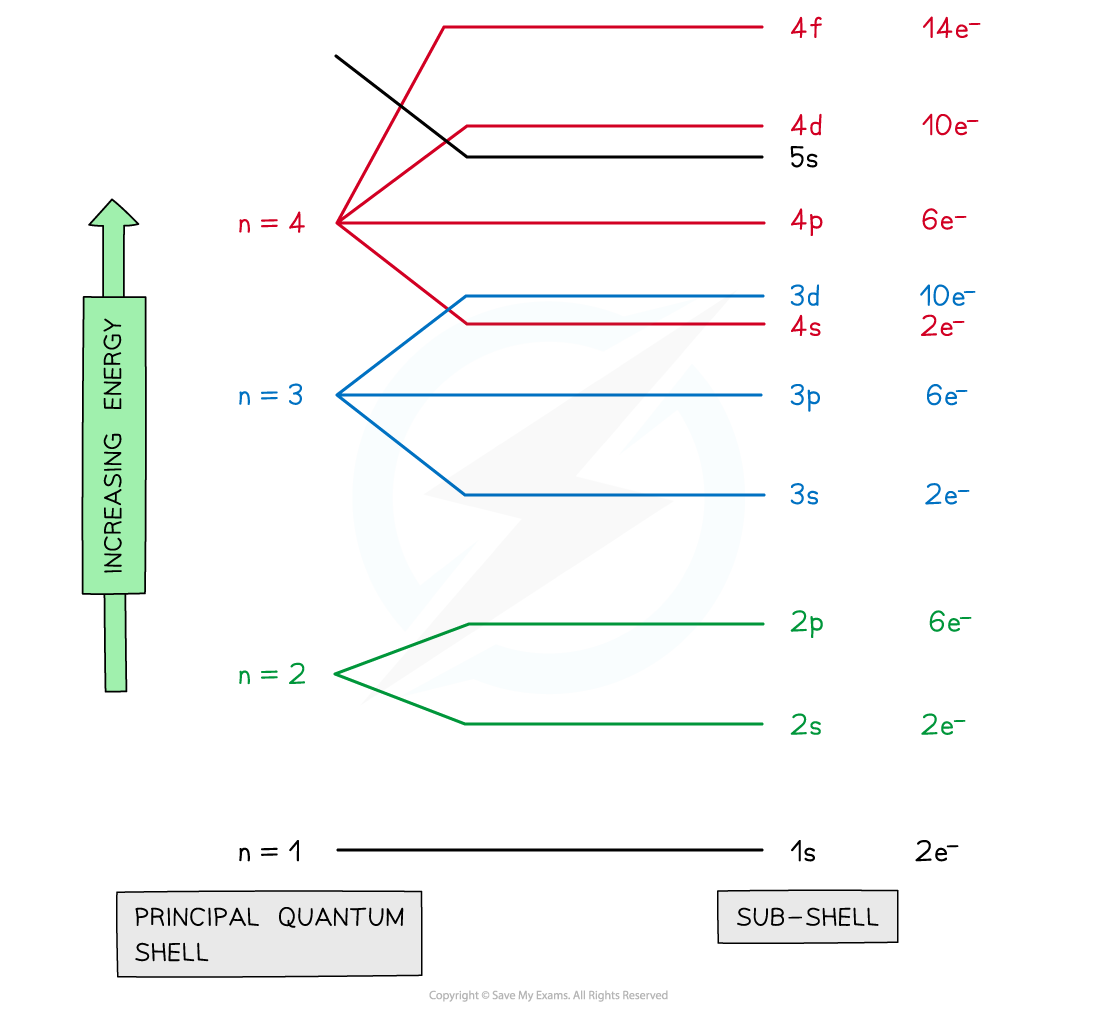
show the fixed number of electrons in each principal quantum number
→n = 1 : up to 2 electrons
→n = 2 : up to 8 electrons
→n = 3 : up to 18 electrons
→n = 4 : up to 32 electrons
label the layout for subshells
define orbitals
they exist at certain energy levels and electrons can only be found at these levels
maximum of 2 electrons
show how many orbitals goes in each subshell
→s : one orbital (1 x 2 = total of 2 electrons)
→p : three orbitals ( 3 x 2 = total of 6 electrons)
→d : five orbitals (5 x 2 = total of 10 electrons)
→f : seven orbitals (7 x 2 = total of 14 electrons)
describe s orbitals
are spherical in shape and the size of the orbitals increase with increasing shell number
describe p orbitals
have a dumbbell shape and every shell has 3 of them [except n=1] which occupy the x y and z axes perpindicular to each other
why do electrons occupy separate orbitals in the same subshell initally
to minimise the spin pair repulsion but if another eletron enters they will pair up spinning in opposite directions
define Hund’s rule
every orbital in a sublevel is singly occupied before any orbital is doubly occupied

define Pauli’s exclusion principle
no two electrons in the same atom can have identical values for all four of their quantum numbers
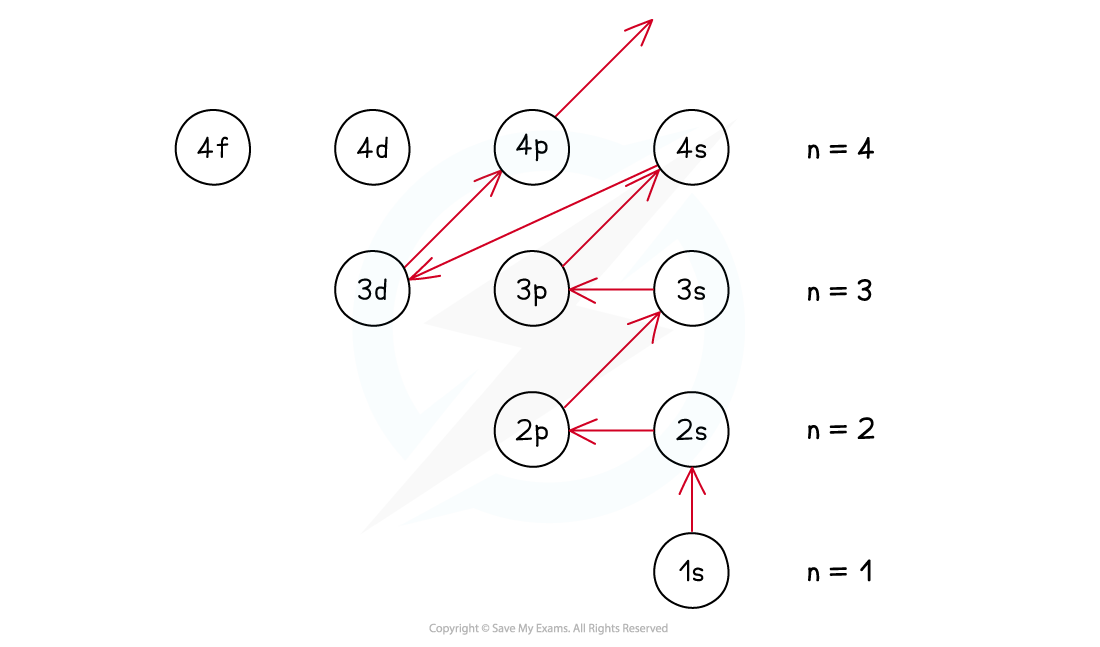
as energy required to jump to a higher empty orbital is greater than the inter-electron repulsion so they pair up and occupy the lower energy levels first
explain ground state
the most stable electronic configuration of an atom which has the lowest amount of energy and is achieved by filling the lowest energy subshells first
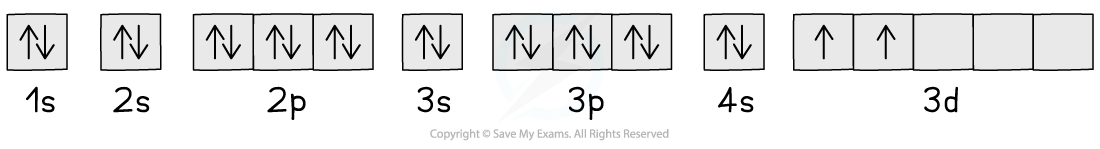
describe orbital spin diagrams
→each box represents an atomic orbital and are arranged in order of increasing energy
→ the arrows represent the electron spin
explain the difference using the full electron configuration or the shorthand version
→full electron configuration describes the arrangement of all electrons from the 1s subshell up
→ shorthand electron configuration uses symbol of the nearest preceding noble gas followed by the rest of the electron configuration
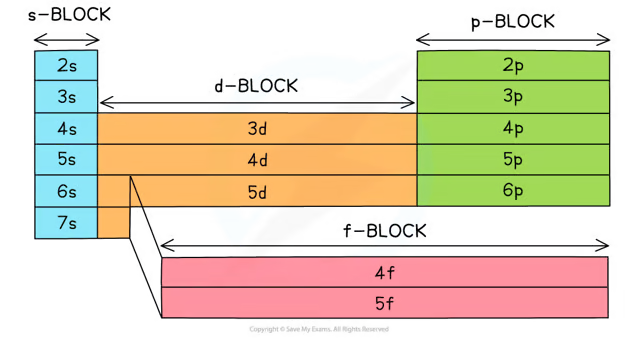
label how the Periodic Table is split up depending on their electronic configuration
exceptions to the aufbau principle
→Cr is [Ar] 3d5 4s1 not [Ar] 3d4 4s2
→Cu is [Ar] 3d10 4s1 not [Ar] 3d9 4s2
this is because those configurations are more energetically favourable