Biology - Unit 8 {Evolution}
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/40
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
1
New cards
Punctuated equilibrium
Short periods of rapid evolutionary change
2
New cards
Gradualism
Slow, steady, and gradual change into another species
3
New cards
Allopatric speciation
Turning into different species due to being in separate areas, “*aloha*”
4
New cards
Sympatric speciation
Turning into different species while being in the same area, “*same*”
5
New cards
Ecological isolation
When species live in the same region but occupy different habitats
6
New cards
Reproductive isolation
When the members of two populations cannot interbreed and produce fertile offspring
7
New cards
Temporal isolation
When species reproduce at different times
8
New cards
Geographic isolation
When two populations are separated by geographic barriers such as rivers or mountains
9
New cards
Behavioral isolation
When two populations are capable of interbreeding but have differences in courtship rituals that involve behavior
10
New cards
Adaptations
the biological mechanism by which organisms adjust to new environments or to changes in their current environment. {Adaptations arise from random mutations}
11
New cards
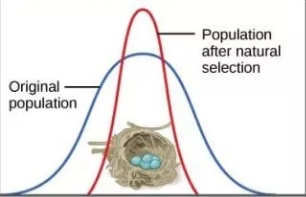
Stabilizing Selection
When genetic diversity decreases and a population stabilizes on a particular trait {EX: Robins lay only four eggs because too many eggs = malnourished chicks & too little chicks = no viable offspring}
12
New cards
Divergent evolution
Interbreeding species are diverged into two or more evolutionary groups {two species evolving from the same organism}
13
New cards
Natural Selection
The process through which populations of living organisms adapt and change throughout the changes the environment faces.
14
New cards
Evolution
Species adapting over time in response to changing in the environment.
15
New cards
Population Genetics
The study of the genetic composition of populations. Distributions and changes in genotype & phenotype frequency.
16
New cards
Convergent evolution
distantly related organisms evolving similar traits to adapt to similar environments & necessities.
17
New cards
Analogous Structures
Features of different species that are similar in function but not similar in structure {Don't evolve from common ancestors}
18
New cards
Homologous Structures
similar physical features in organisms that share common ancestors but serve for different functions.
19
New cards
Genetic Drift
Migration / variation in genotypes within a small population, allowing it to disappear. {Smaller populations, random events, sudden.}
20
New cards
Selection Pressures
Factors that contribute to natural selection, {which traits will survive better than other traits and why?}
21
New cards
Sexual Selection
the evolution of certain conspicuous physical traits \[such as pronounced coloration, increased size, or striking adornments\] in animals may grant the possessors of these traits greater success in obtaining mates. {Phenotype / behaviors}
22
New cards
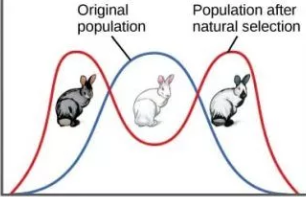
Disruptive Selection
When extreme versions of a trait are favored over normal versions of a trait {EX: Gray & Gray and White rabbits are able to blend into rocky entrances better than white rabbits, so white rabbits die off}
23
New cards
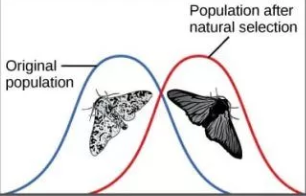
Directional Selection
When a single phenotype is favored, causing the allele frequency to continually move in one direction {EX: light colored moths are better camouflage against pristine environment, dark colored moths are better in sooty environment. When england because darker the population shifted from light to dark.}
24
New cards
Fitness
The ability of an animal to survive and reproduce {The quantity of offspring had doesn’t really matter if none of them survive to reproduce themselves}
25
New cards
Charles Darwin
An English naturalist and biologist who transformed the way that humanity thinks about life
26
New cards
Antibiotic Resistance
when germs like bacteria and fungi develop the ability to defeat the drugs designed to kill them.
27
New cards
Transitional Forms
A fossil that shows an intermediate state between an ancestral trait and that of its later descendants is said to bear a transitional feature.
28
New cards
Homologies
similarity of the structure, physiology, or development of different species of organisms based upon their descent from a common evolutionary ancestor.
29
New cards
Vestigial structure
Various cells, tissues, and organs in a body which no longer serve a function.
30
New cards
Artificial Selection
identification by humans of desirable traits in plants and animals, and the steps taken to enhance and perpetuate those traits in future generations.
31
New cards
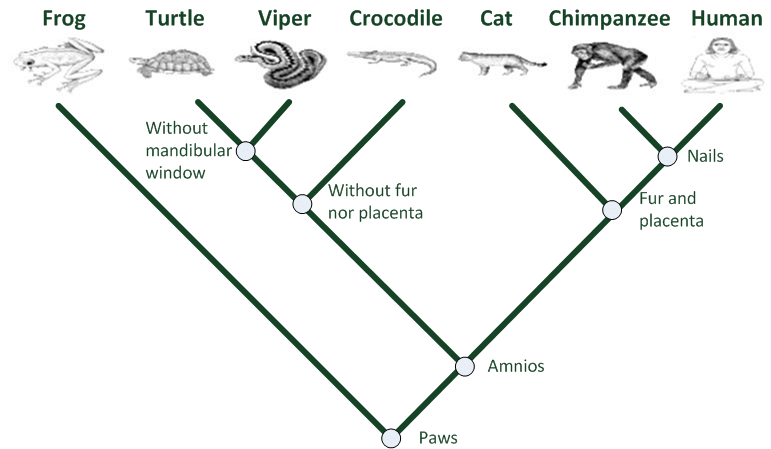
Cladogram
A diagram used to represent a relationship between a group of animals {Most often based on traits… number of limbs, presence of fur or hair, wings, etc.}
32
New cards
Hardy Weinberg Conditions
Environment having no mutation, random mating, no gene flow, infinite population size, and no selection.
33
New cards
Hardy Weinberg formulas
p^2 + 2pq + q^2 = 1
p + q = 1
p + q = 1
34
New cards
Bottleneck effect
Events that limit genetic variation in a population and result in founding populations can lead to genetic drift. {Ex: a lot of rabbits die in a fire, and the remaining rabbits aren’t as genetically diverse.}
35
New cards
Founder effect
the reduced genetic diversity which results when a population is descended from a small number of colonizing ancestors. {When a few individuals find a new area.}
36
New cards
Genetic flow
Any movement of individuals, and/or the genetic material they carry, from one population to another. {Larger population, through migration.}
37
New cards
biogeography
Studies where species live now and where their ancestors lived in the past.
38
New cards
Comparative Anatomy
The study of similar body structures indicating common ancestry.
39
New cards
Comparative Embryology
The study of similarities in developmental stages from fertilization to birth.
40
New cards
Paleontology
Studying fossils that document the intermediate evolutionary stages of many different species groups.
41
New cards
Molecular Biology
The study of all living things on Earth sharing the same universal code in DNA and RNA molecules, which indicates that they share a common ancestor.