Histopath stains
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Alcian Blue
Stains glycosaminoglycans and mucopolysaccharides blue.
(If counterstained with H&E that will color nuclei black and cytoplasm pink or red)
Think of MV disease
Orcein
Elastin Fibers – Stain Black

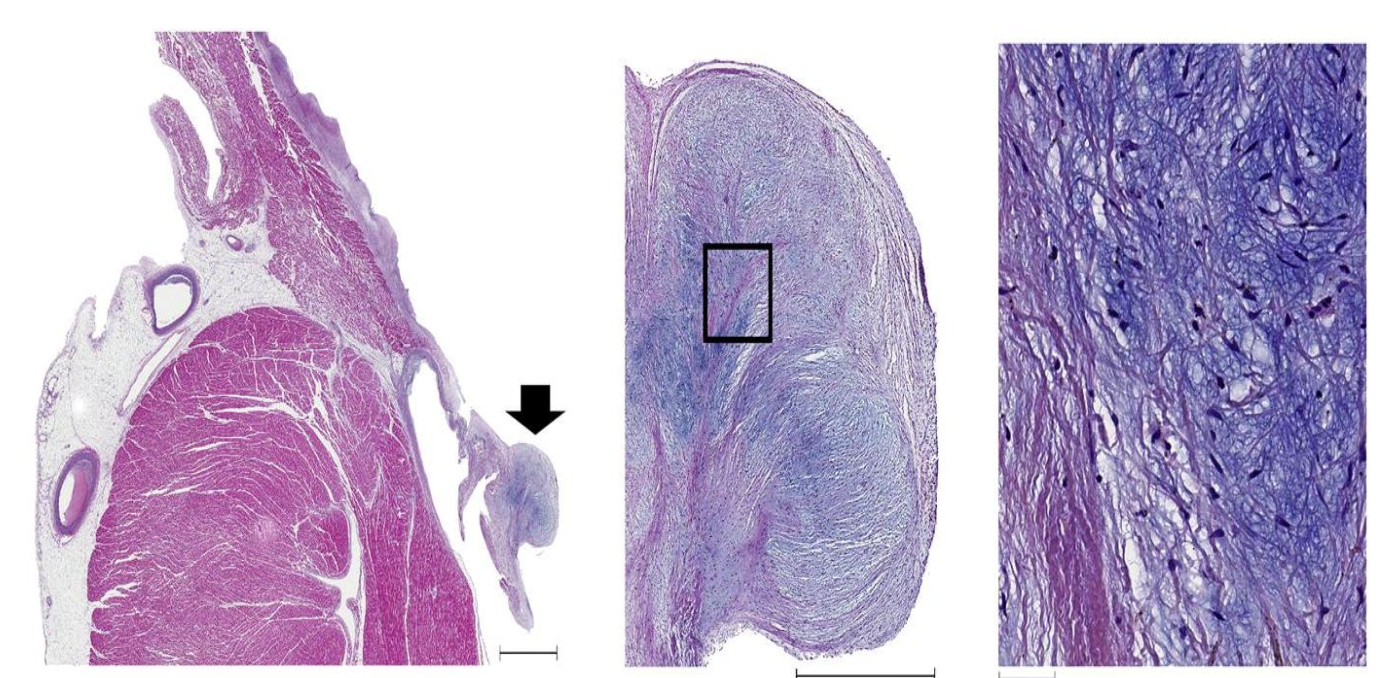
Hematoxylin & Eosin
Stains nucleic acids and cytoplasm blue brown or black. Stains proteins within cytoplasm and extracellular matrix pink to red. In the myocardium, nuclei are blue-black and muscle fibers are pink- red.
Upper Image Left: Normal coronary artery.
Upper Image Right: Subendocardial fibrosis (arrows) in the papillary muscle of a dog with DMVD.
Bottom Image: Mitral valve leaflet
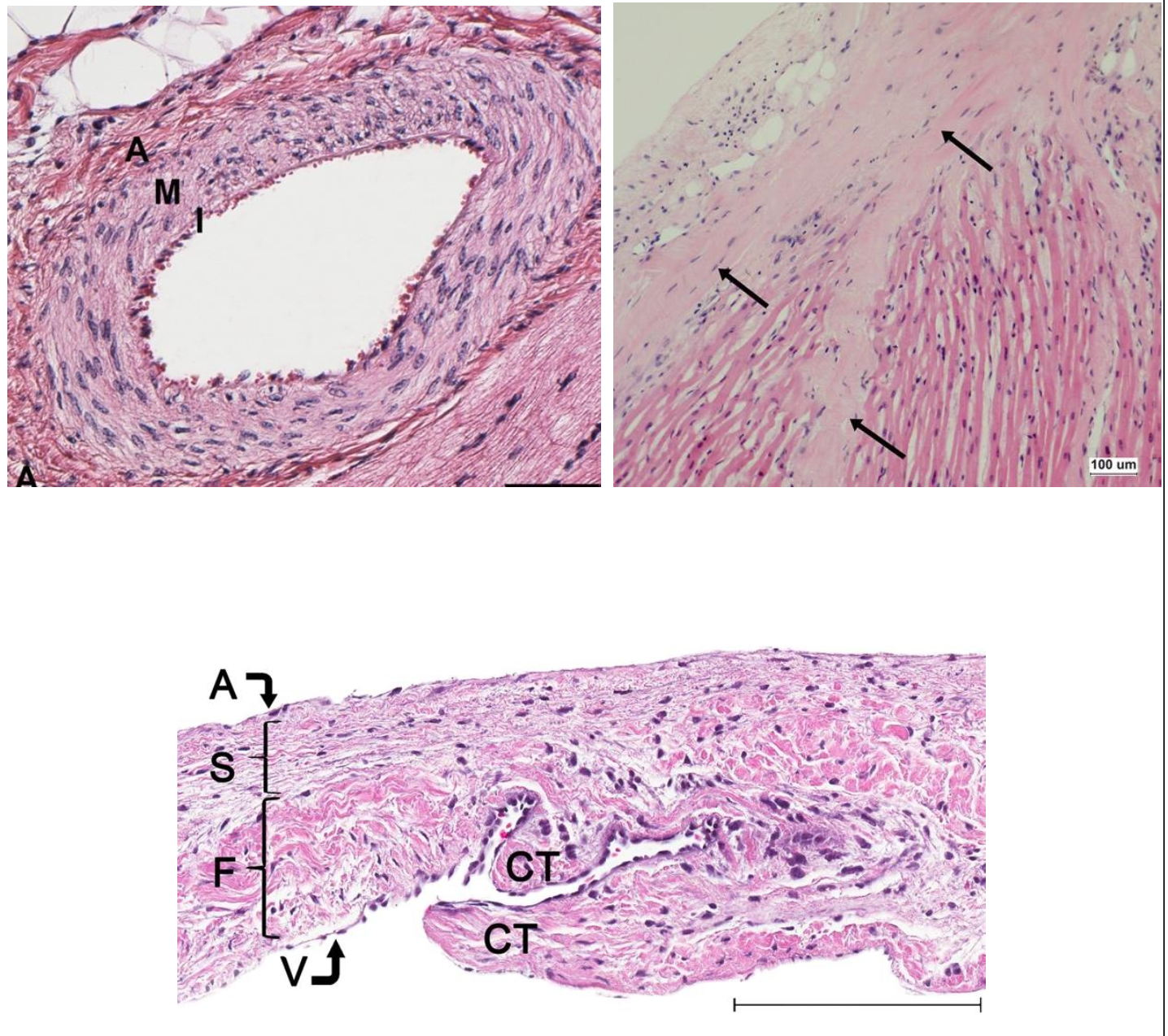
Masson’s Trichrome
Helpful for differentiating between collagen fibers (stain blue or green) and smooth muscle (stains bright red).
Upper image (left): Subendocardial fibrosis (collagen deposition, stained blue) in a dog with DMVD.
Upper image (right): Endocardial fibroelastosis with thickened endocardium with excess collagen deposition (stained blue).
Bottom Image: Multifocal severe replacement fibrosis (stained blue)
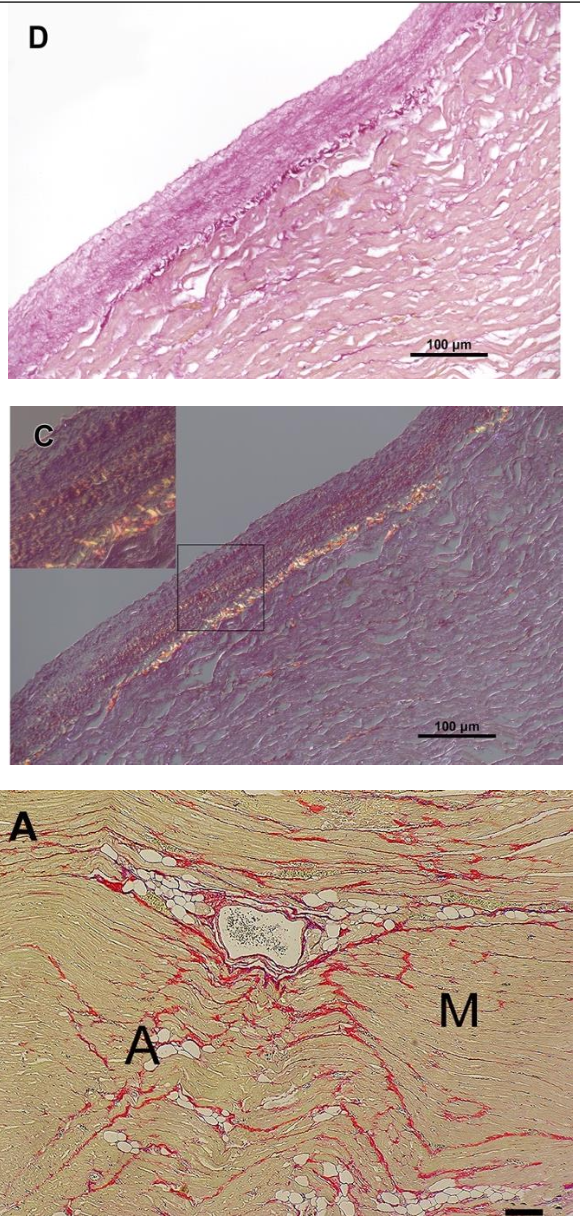
Picrosirius Red Stain
Collagen fibers stain dark red in normal light and myocardium is stained a shade of yellow. If using polarized light collagen bundles are birefringent.
Upper Image: Normal light, collagen fibers stain red.
Middle Image: Polarized light, collagen bundles are birefringent.
Bottom Image: Dog with lone AF. Mild interstitial fibrosis (stained red) and mild adipocyte infiltration in the myocardium. Often this stain will stain myocardium yellow as seen in this example.
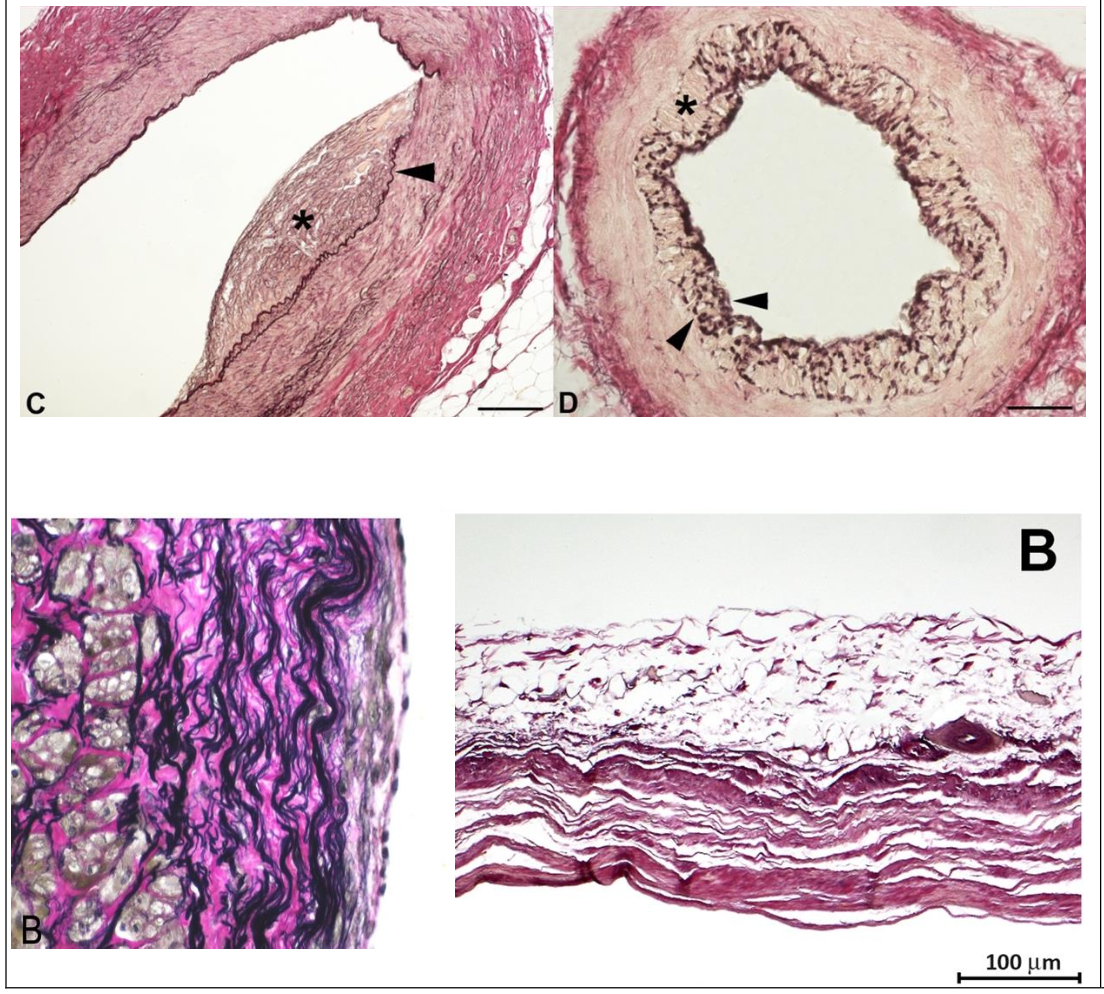
Van Gieson’s Trichrome Stain
Most useful for highlighting elastic fibers in connective tissue. Elastin fibers stain blue-black, collagen fibers stain red, nuclei stain black and cytoplasm turns a background yellow.
Top Image (Left): Coronary artery, arrow head indicates the internal elastic lamina (stained black due to the Stain. Note the red-staining collagen in the tunica adventitia.
Top image (Right): Coronary artery with black staining of a fragmented internal elastic lamina. Note the red staining collagen in the tunica adventitia.
Bottom Image (Left): Histopath image of an aneurysm wall showing black staining elastin fibers within the tunica media.
Bottom Image (Right): Section of myocardium completely replaced by fibrous tissue (staining blue-black) and scattered groups of epicardial adipocytes.
Immunohistochemical Staining Chromogranin A
Marker for neuroendocrine tumors. Chromogranin A is a protein produced by many neuroendocrine cells and it can be found within these cells as well as secreted in blood.
Immunohistochemical Staining Synaptophysin
Marker for neuroendocrine tumors. Synaptophysin is a membrane glycoprotein present in presynaptic vesicles of the adrenal medulla and neurons and neuroendocrine tumors.
Immunohistochemical Staining CD20
B Cell Marker
Immunohistochemical Staining CD3
T Cell Marker
Immunohistochemical Staining IBA-1
Histiocyte Marker
Immunohistochemical Staining MUM-1
Plasma Cell Marker
Immunohistochemical Staining S-100
Protein marker for lipocytes, melanocytes, Schwann cells and chondrocytes.
Immunohistochemical Staining Desmin
Protein within the intercalated disk. With heart failure, the structure of the cardiomyocyte and intercalated disks become disorganized which leads to loss of myofilaments and their supporting proteins (e.g. desmin). This results in a decrease in positive desmin staining tissue.
Immunohistochemical Staining Vimentin
Marker for mesenchymal cells