ANTH1L final- human evolution
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Relative dating
Comparison/in relation to one another, not exact date
Principle of superposition:
Oldest on the bottom, newest on the top
Fluorine dating:
Two fossils; the one with more fluorine is more likely older
Absolute dating (Chronometric)
“Exact” age
Radio-carbon dating: C14 → N14
5,730 yrs for half the Carbon14 to turn into Nitrogen14
half-life: the amount of time it takes for the parent to turn into the daughter
Radio-potassium dating: K → Ar
Volcanic material
1.3 billion years = one half-life
What epoch are we currently living in?
Holocene (10k ya)
What epoch were the first primates thought to appear?
Paleocene, 60mya
Did dinosaurs coexist with any primates in the Mesozoic era?
No
The first hominids were found toward the end of the Miocene; when was that?
5.3 mya
What time span does the Cenozoic era include?
66mya — present
Characteristics of the genus Australopithecus
Small brain
Ape-like head
Rather human-like body
Small canines and larger premolars/molars (called megadontia)
3 groups:
gracile— smaller, “lighter” than robust species
primitive (same as gracile)
robust— cresting, huge molars, large zygomatics, large mandibles with tall ramus
legs:
angled femoral neck
shorter than our legs
feet:
convergent big toe
double arches
pelvis:
small
somewhat rounded iliac blade shape
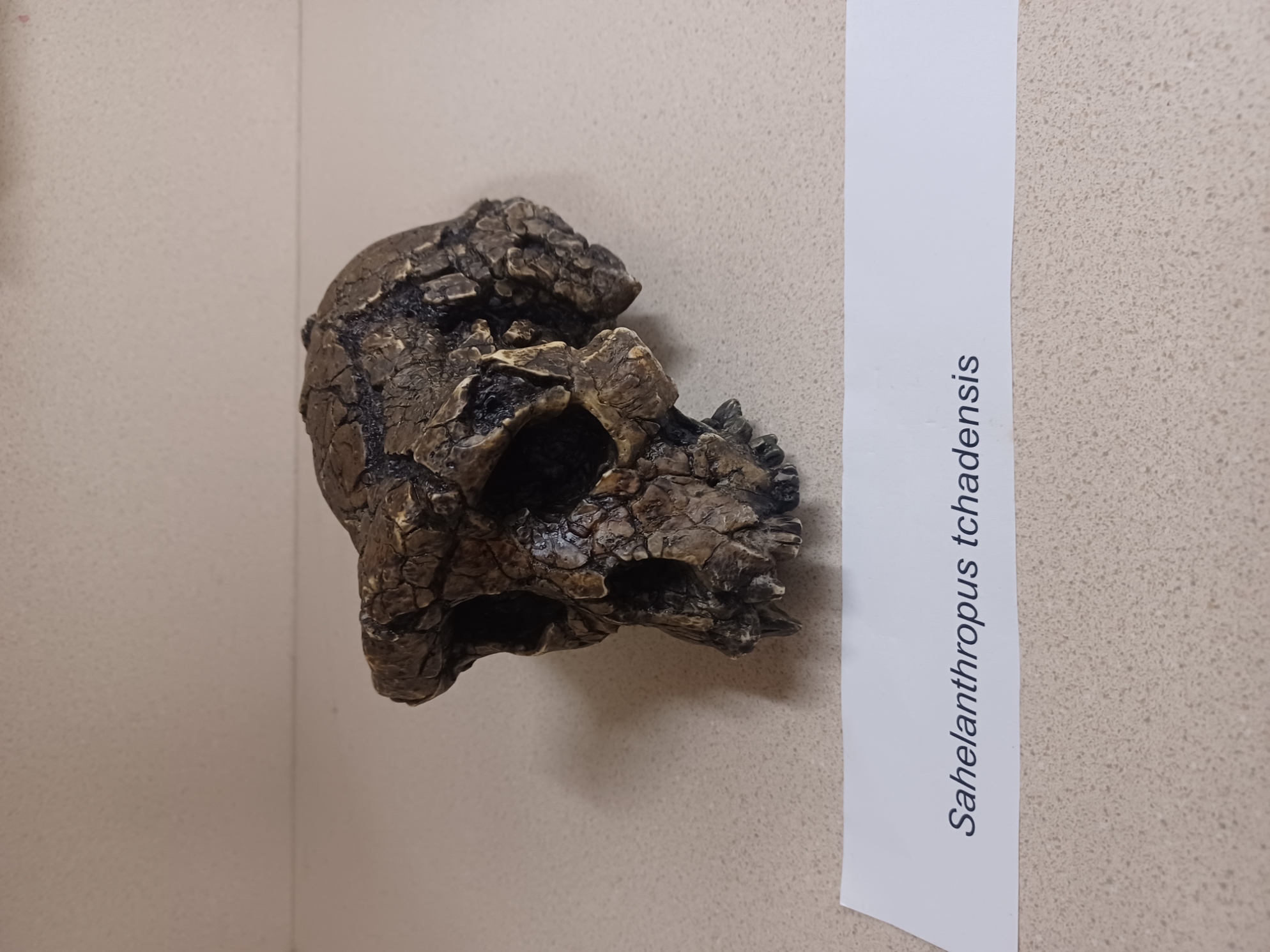
Sahelanthropus tchadensis (S. tchadensis)
Chad, Africa
320cc brain size
6-7mya
considered hominid because of anterior foramen magnum

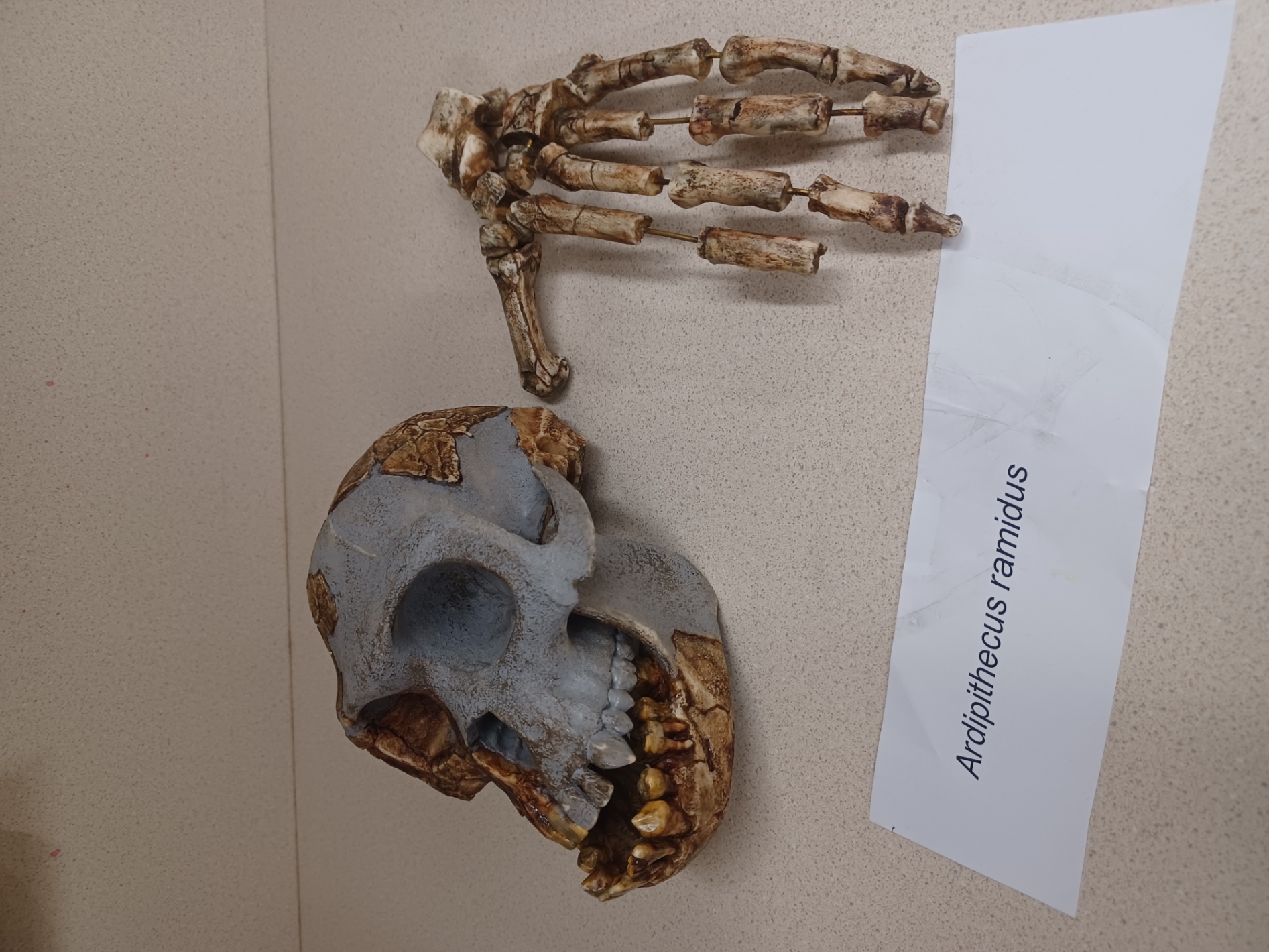
Ardipithecus ramidus— “Ardi”
Ethiopia
380cc brain size
4.4mya
skull:
no cresting
anterior foramen magnum
flaring zygomatics
lower body:
divergent big toe
curved phalanges
angled femur
short & wide iliac blade shape
Paranthropus aethiopicus
Ethiopia, Kenya and Tanzania in east Africa
2.5 mya
Brain size 410 cc
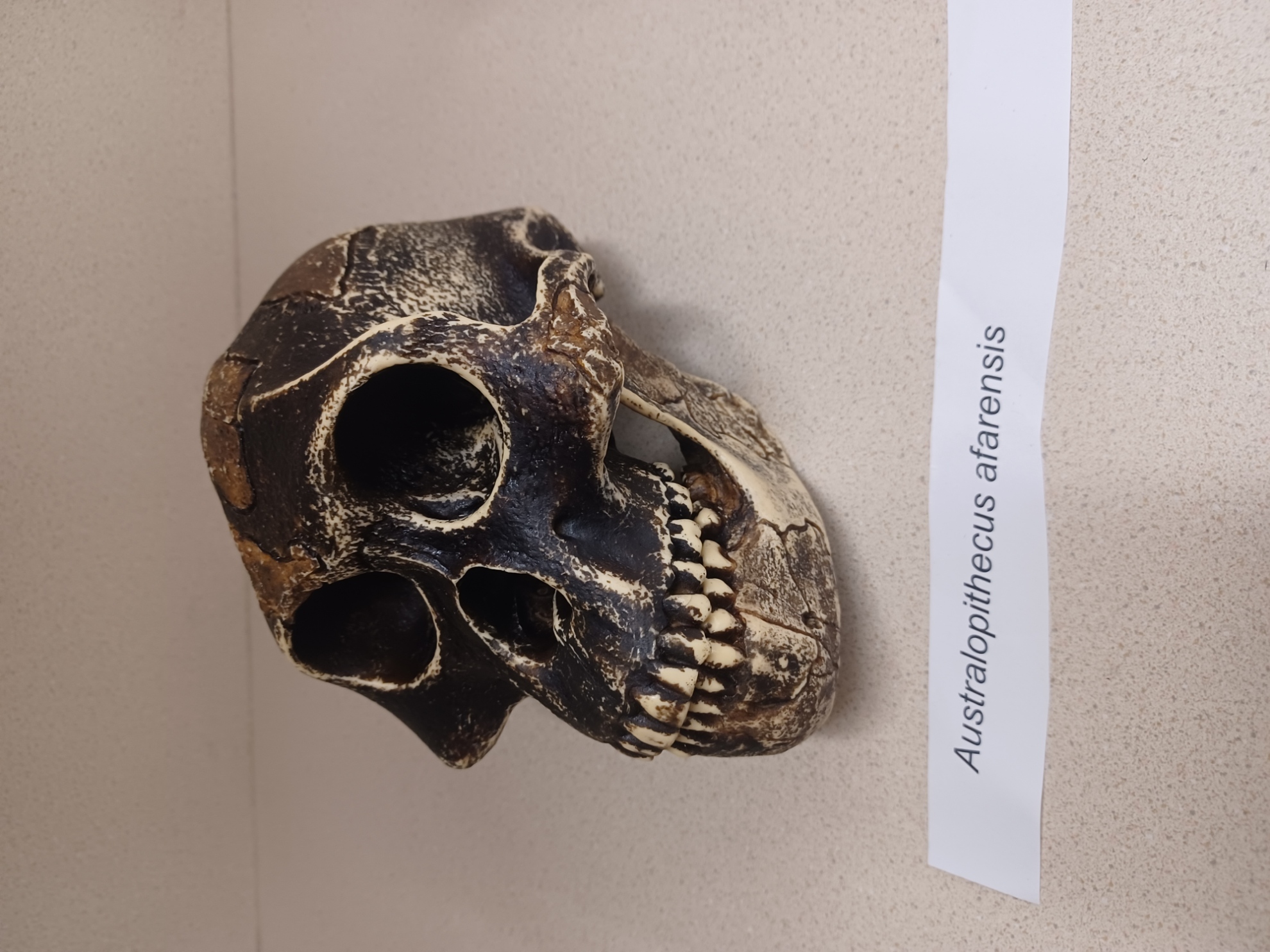
Au. afarensis— “Lucy”
primitive (gracile) Australopithecus
2.9 - 3.9 mya
Ethiopia, Kenya, Tanzania
Brain size:
433—550 cc
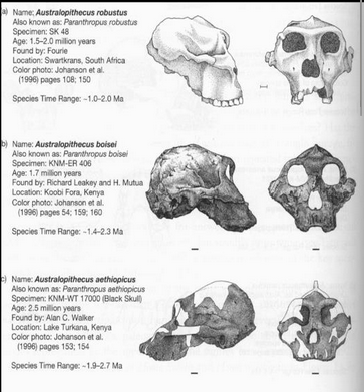
ROBUST Australopiths
Cresting
Large molars
Large zygomatics
Large mandibles with tall ramus
Paranthropus aethiopicus
P. boisei
P. robustus
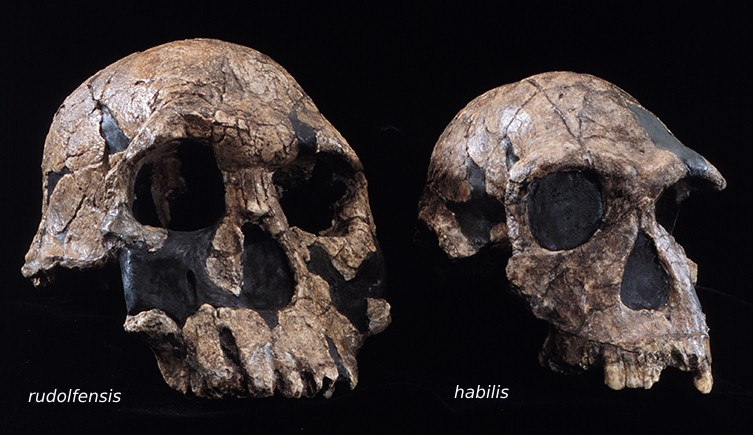

Homo habilis/rudolfensis
short legs, long arms
finger bones suggest a precision grip
H. habilis:
Found in Tanzania
Cranial capacity: 600-700 cc
Time existed: 2.4–1.4 mya
H. rudolfensis:
Found in Kenya
Cranial capacity: up to 775 cc
Time existed: 1.9–1.8 mya
generally larger skull/teeth than habilis
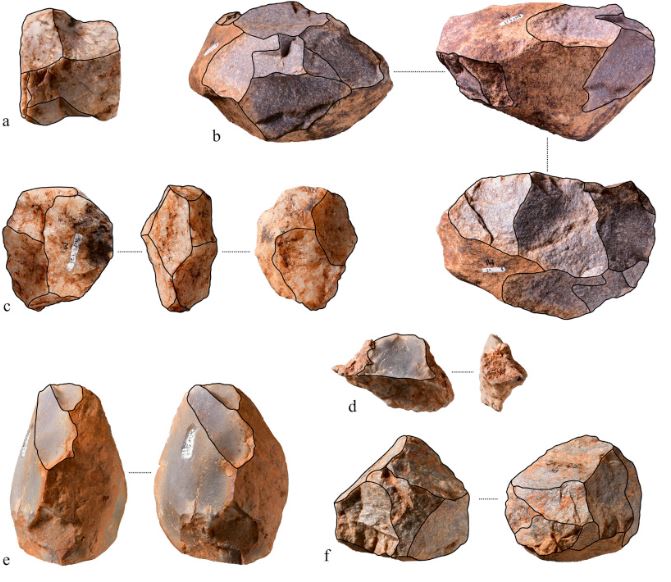
Oldowan Tools

Homo erectus
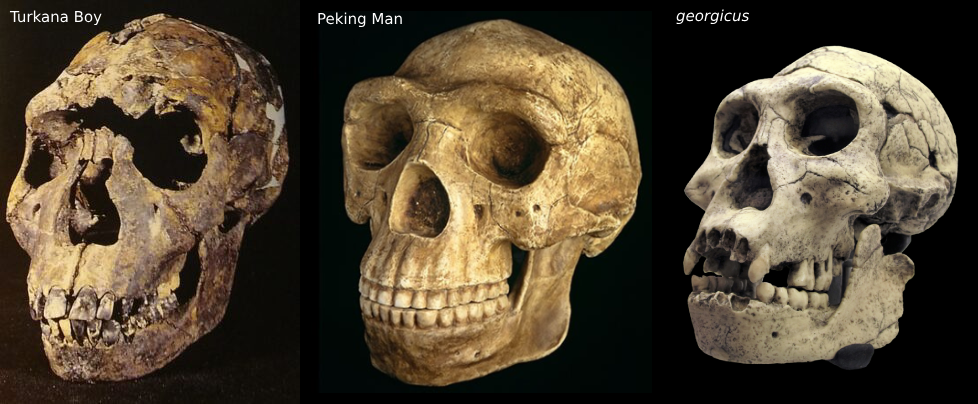
Homo erectus (“Peking Man”)
850–1150cc brain size
Found in Asia
1.6 mya—40k ya
Homo ergaster (“Turkana Boy”)
850–1250 cc brain size
Found in Kenya
1.9 mya — to maybe 400k ya
Homo georgicus
600 cc brain size
Found in Republic of Georgia (Dmanisi)
1.7 mya
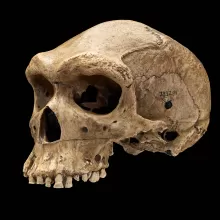
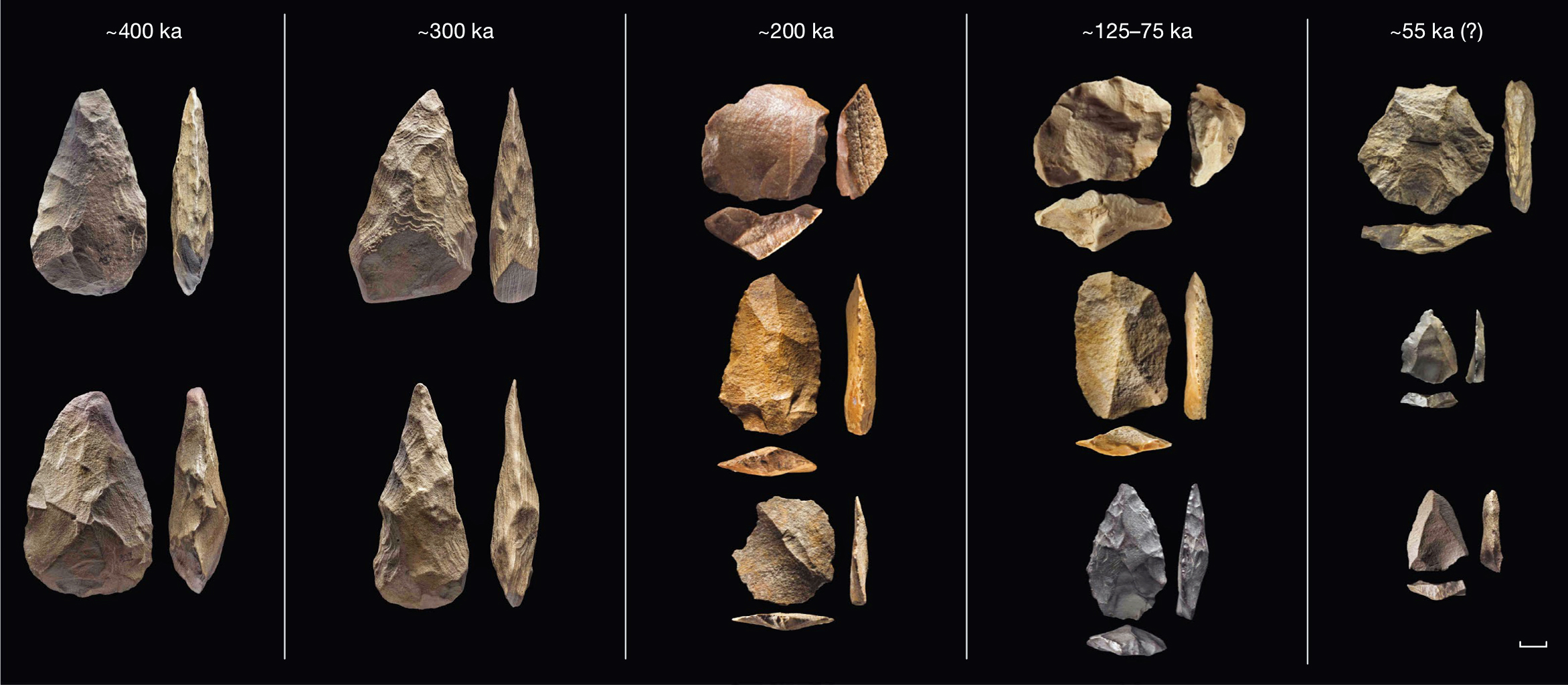
Homo heidelbergensis
800,000 - 200,000 ya
Europe, Africa, possibly Asia
Compared to H. erectus:
Skull is higher and more well-rounded
Brow ridges still large
Less prognathic lower face
Cranial capacity: average of 1206 cc
More diverse than H. erectus
Varied tools (Acheulian)
Primitive shelters
More efficient hunting techniques

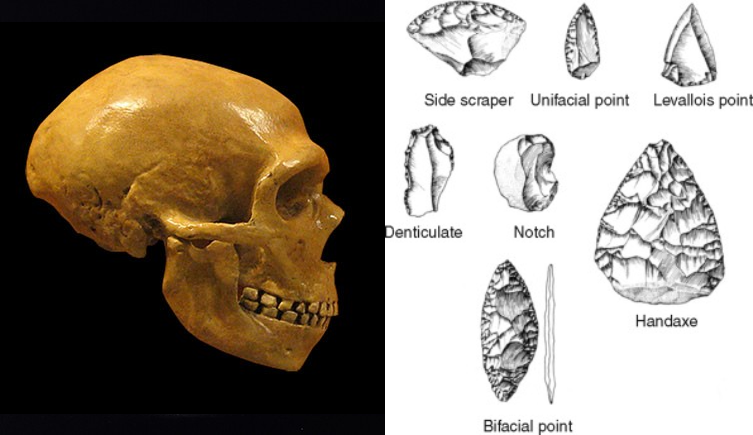
Homo neanderthalensis
Germany, might have extended into Central Asia and Siberia
400-28k ya
More complex stone tools (Mousterian)
1520 cc cranial capacity
Shorter and bulkier than modern humans, more adapted to cold climates:
shorter limbs, barrel-like large ribcages, large skulls & noses
Some modern humans have Neanderthal DNA in their genome
This means that Neanderthals were not a different species than modern humans, interbreeding took place when modern humans left Africa
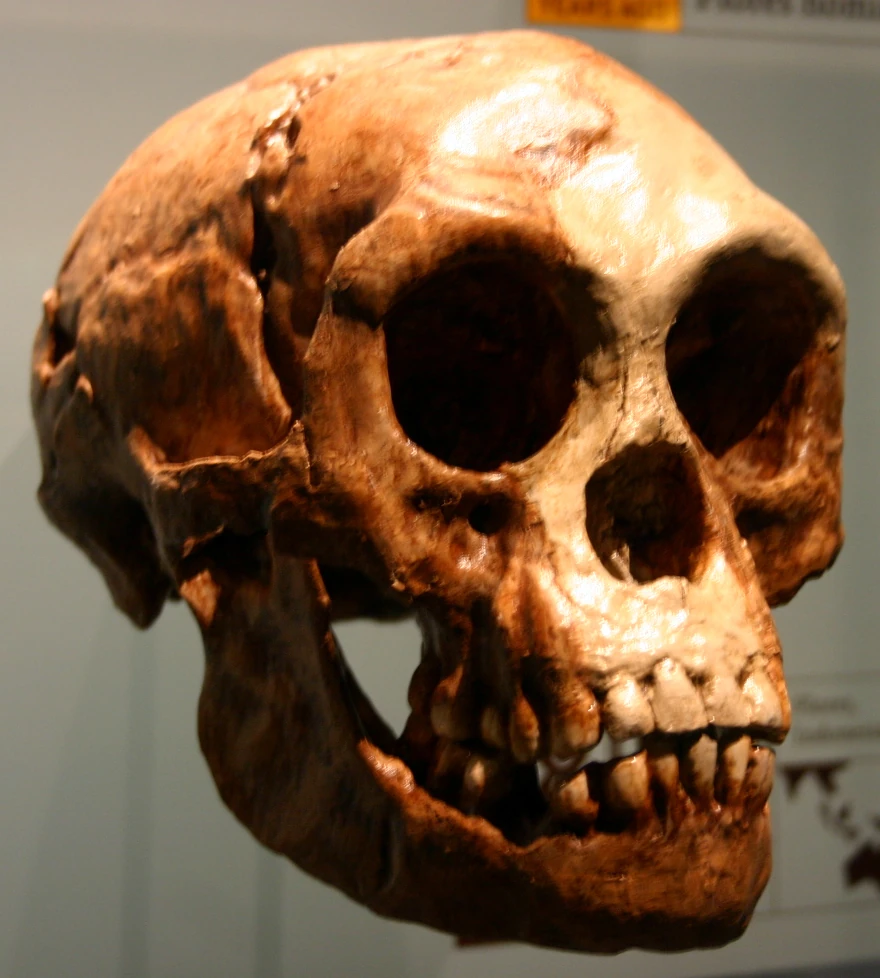
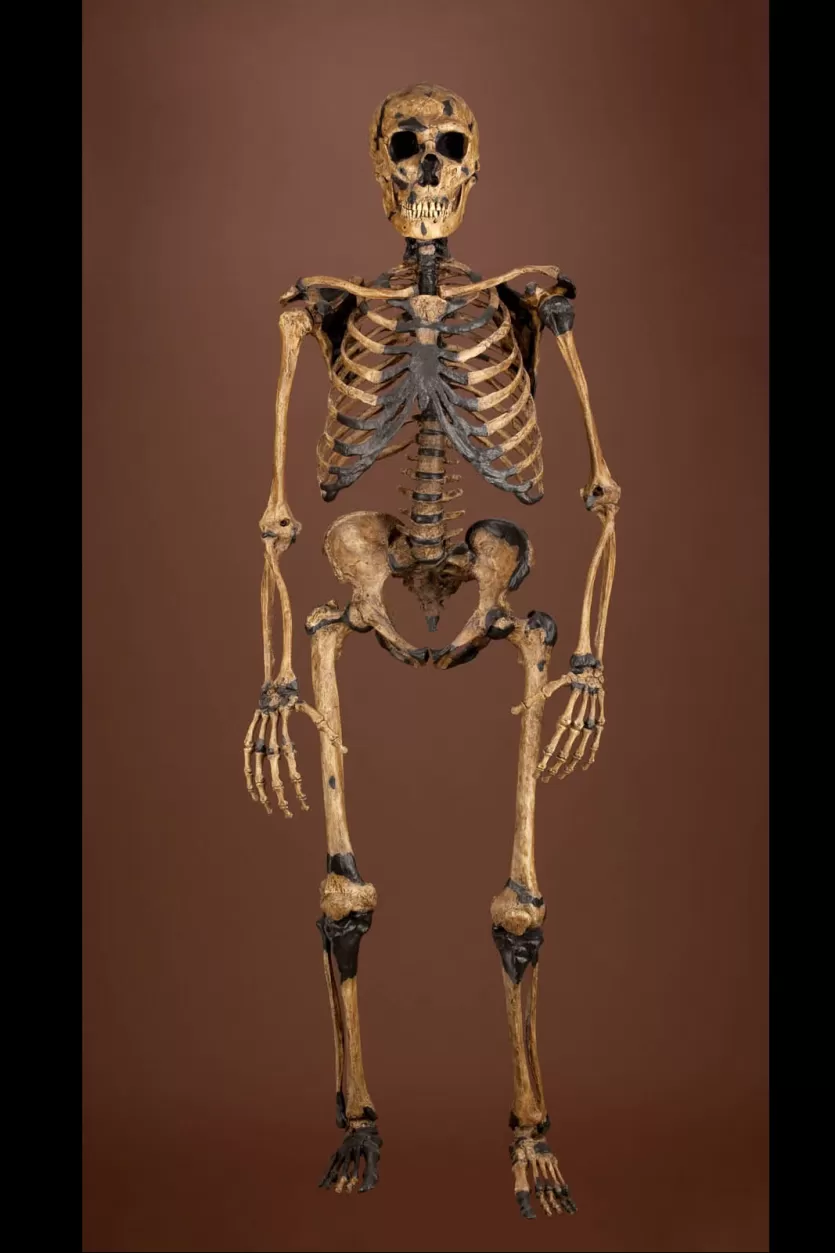

Homo florensiensis
Found in 2003 on the island of Flores in Indonesia
As many as 12 found
94–13kya
~3ft tall
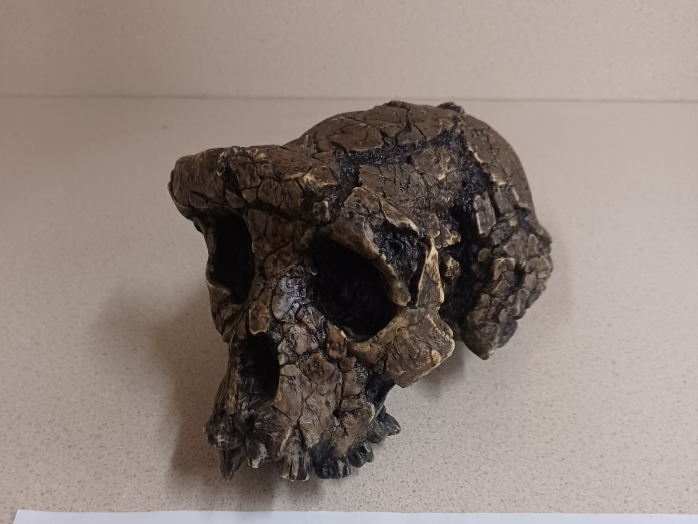

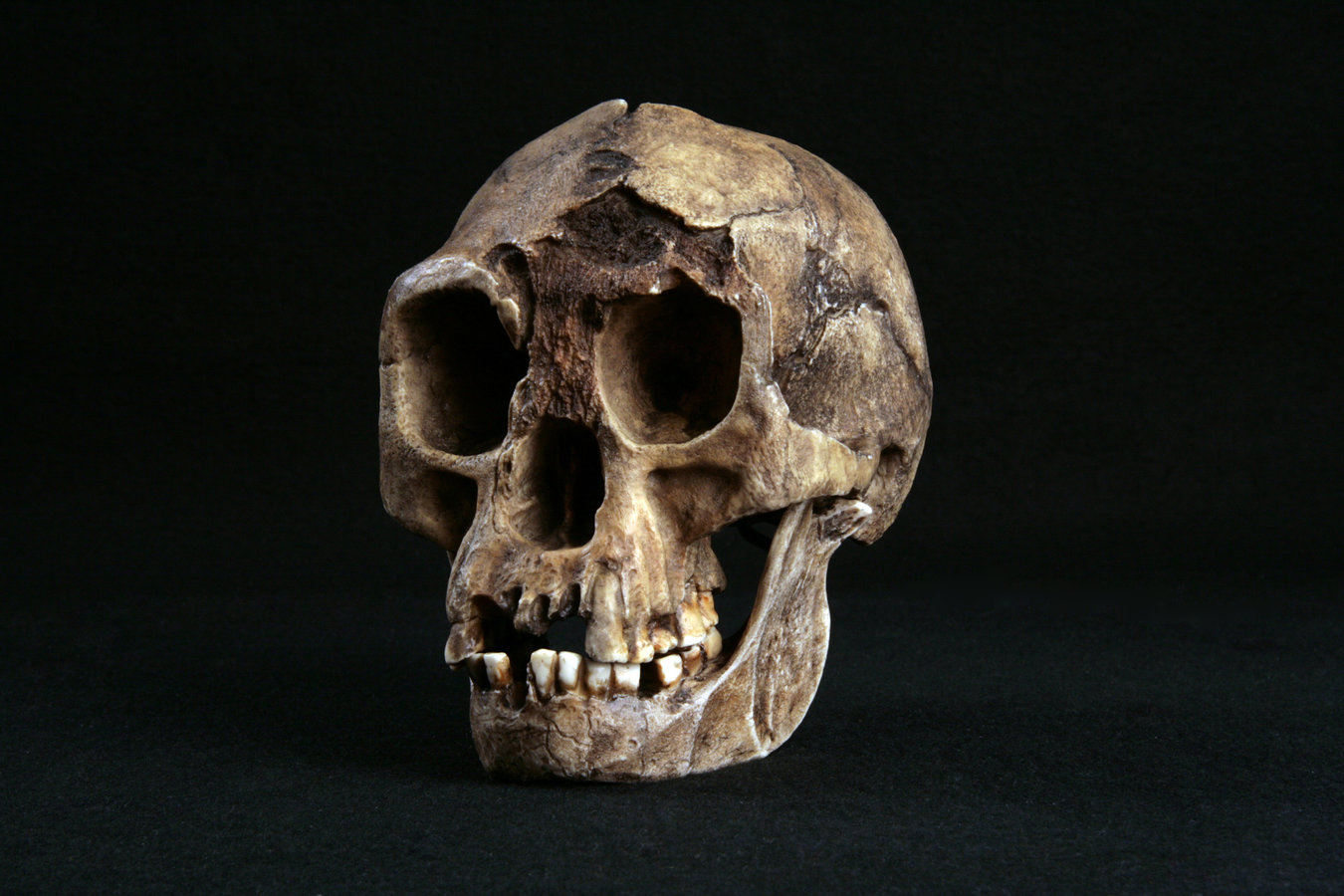
What skull is this?
Sahelanthropus tchadensis (S. tchadensis)
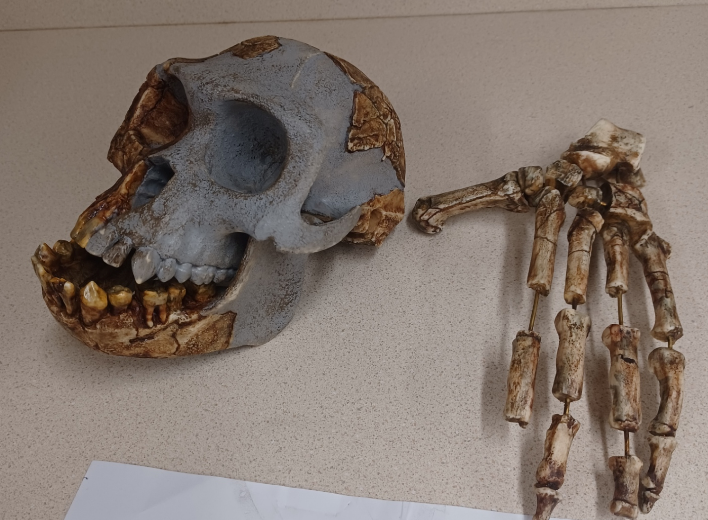

What skull is this?
Ardipithecus ramidus (“Ardi”)
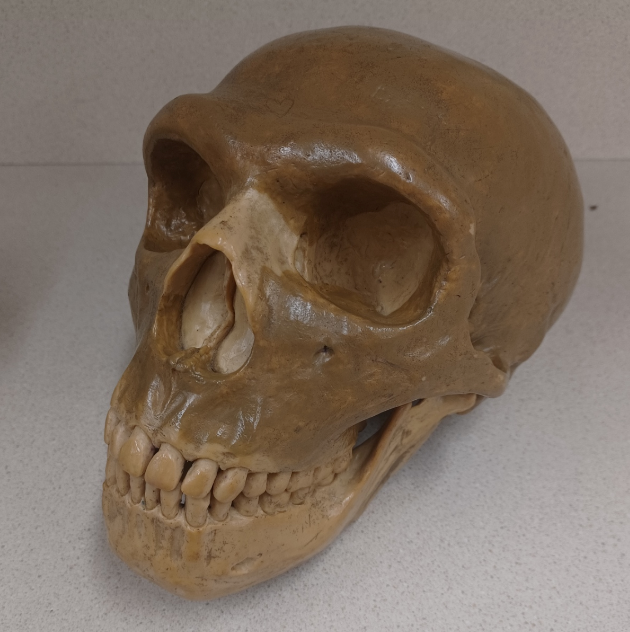

What skull is this?
Homo neanderthalensis (H. neanderthalensis, neanderthal)
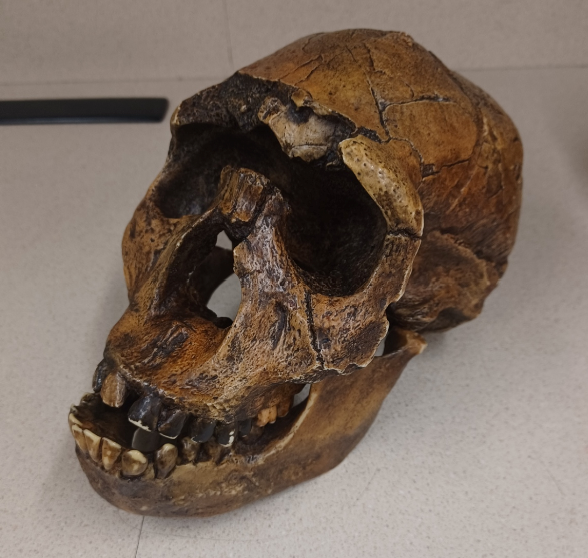

What skull is this?
Homo erectus/ergaster (H. erectus/ergaster, “Turkana Boy”)
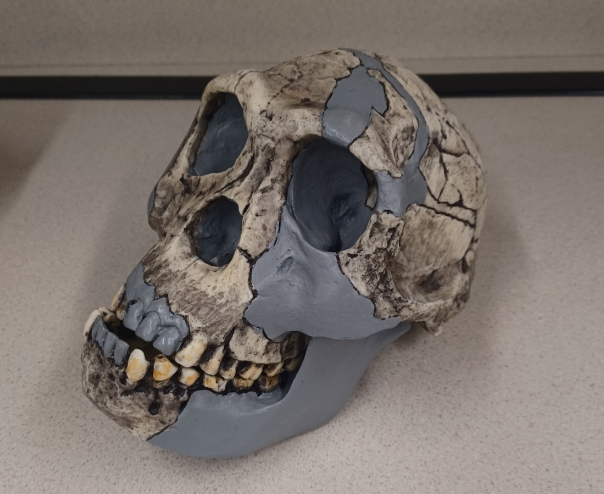

What skull is this?
Homo habilis (H. habilis)
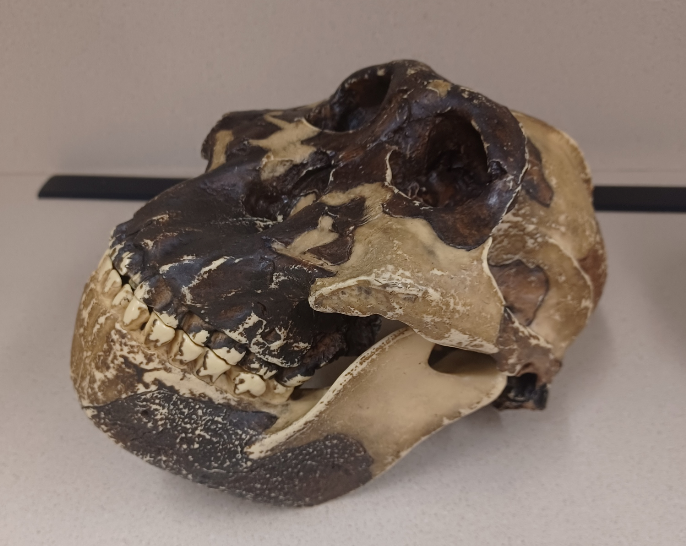

What skull is this?
Paranthropus boisei (P. boisei)
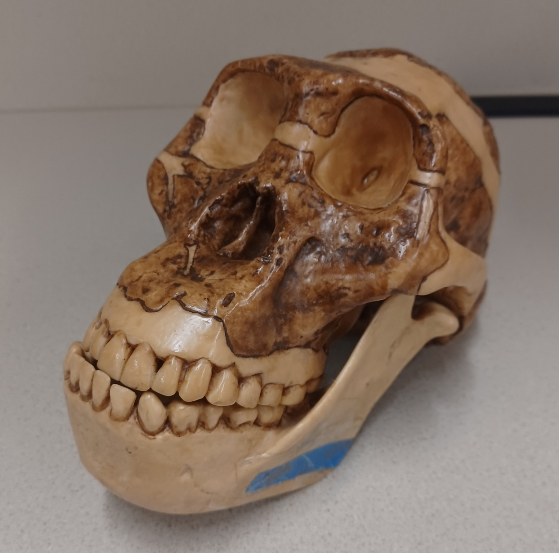
What skull is this?
Australopithecus africanus (A. africanus)
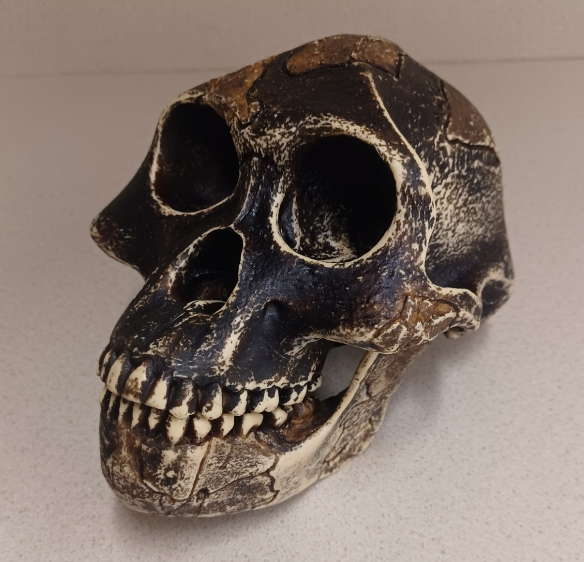

What skull is this?
Australopithecus afarensis (A. afarensis, “Lucy”)
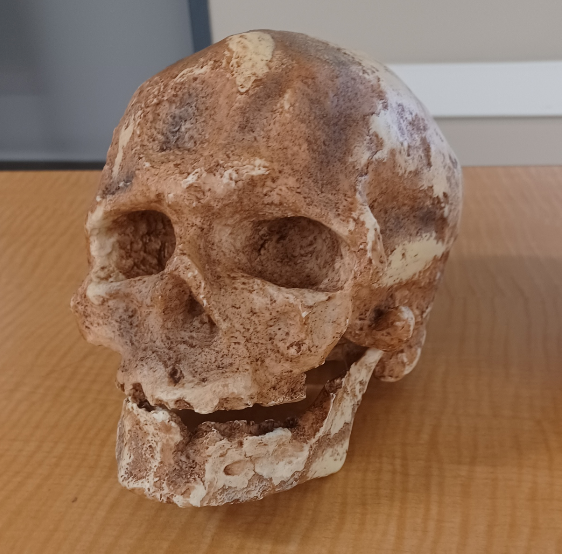

What skull is this?
Cro-Magnon man (anatomically modern human)
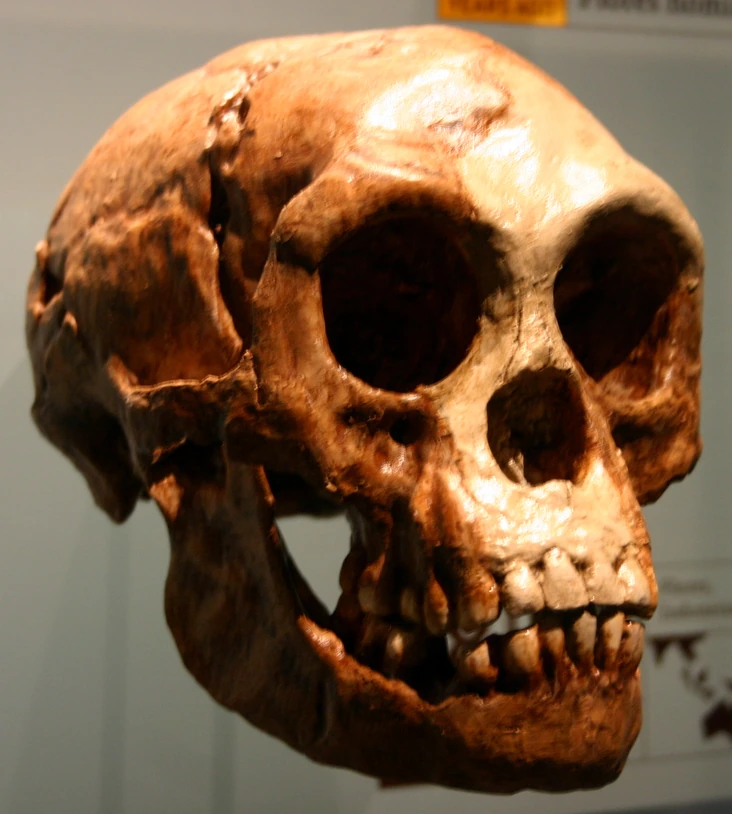

What skull is this?
Homo florensiensis (H. florensiensis)
