9 SCI Ecosystems
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
123 Terms
What happens in capture-mark-recapture?
a sample of species is captured, tagged and then released. sometime later another sample is captured from the same species. the number of that species in the area is then estimated.
What is capture-mark-recapture?
a method used to estimate the population of a highly mobile species.
What do hotter and drier climate mean?
The bush fire seasons are longer and more intense
Why use systematic quadrant sampling?
To prevent errors like choosing areas because it's easier to get to and accidentally studying the same area twice.
What is systematic quadrant sampling?
Grid sampling an area with an order to work quadrants are placed
What is random quadrant sampling?
A random selection of locations for quadrants in an area
What do high ocean temperatures create?
More heat stress and coral bleaching events. Longer and more intense bushfires. Flooding due to intense rain and certain areas. Drought due to lack of rain in other areas. Land ice melting and sea level rising.
How much needs to be sampled if the total area is 100 m²
20 m² at least
What percent of the total area needs to be sampled to get an accurate estimation?
20%
What is renewable energy?
Energy that comes from sources that will never run out or will replenish faster than they are used
Why use a quadrant?
Take less time to estimate the population of plants
The species in quadrants are...
Counted or the percentage is estimated
What are the common quadrant sizes?
0.25 m² 1 m² 9 m² and 100 m²
What is a quadrant?
A shape with a known area for sampling plants, which is normally a square
List some common sampling techniques
Quadrants for plants. And capture - mark - recapture for animals.
Why use a sampling technique?
To estimate the size of a population
What is species abundance?
The number of a particular species in an area
What does diversity of wildlife population mean?
The number of species. The size of local population. The health of population. The amount of introduced species. It's used to see if species are under threat.
What does scientists try to assess when using quadrants and or capture mark recapture?
The diversity of wildlife populations in an area
Introduced species were...
Brought over from other countries by humans
Native species were...
Originally found in Australia
Plastic produced machine machines run on oil and fuel. Why is this bad?
Burning oil and fuel releases carbon dioxide, so as well as being bad itself, the way plastic is made is also bad
What does deforestation do?
Reduces the amount of carbon dioxide being absorbed by trees. This increases the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere and creates an imbalance.
What does solar energy do?
Uses soul energy from the Sun to generate electricity
How does global warming affect us agriculturally
There will be less food and water available and no land to farm
What is the combustion equation? (words)
Carbon based fuels plus oxygen turns into CO2 plus water plus energy
What is the combustion equation? (symbols)
Carbon based fuels + oxygen > carbon dioxide + Water + energy
What do we do by burning fossil fuels
We increase the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere
What happens when a fossil fuel is combusted?
It is quickly reacting with oxygen gas to produce thermal energy
How do humans affect carbon dioxide emission?
By burning fossil fuels. Deforestation. Increased use of plastic. These disturbed the balance of the carbon cycle.
What happens to carbon in the soil?
It gets compressed into minerals, and over millions of years it can turn into fossil fuels such as crude oil, coal, and natural gas.
Where does carbon go when organisms die and decompose?
It is deposited into the soil, which is the lithosphere
How does ocean certification affect coral?
It doesn't cause core bleaching, but the acid dissolves the coral skeletons and makes it harder for them to repair
What does heat stress do?
Cause core bleaching. it causes coral to expel their colourful algae making them look bleached
What is ocean acidification?
When there is too much carbonic acid in the ocean.
What is too much carbonic acid in the ocean called?
Ocean acidification
What does too much carbonic acid in the ocean do?
Dissolves the shells, killing the organisms inside
How is carbonic acid used by marine organisms in the biosphere?
To build shells
How is carbonic acid formed?
Carbon dioxide in the atmosphere can be dissolved into water which forms carbonic acid
Where is carbon in the atmosphere?
Carbon dioxide
What is the energy pathway diagram?
Plants (photosynthesis) goes to glucose and oxygen gas goes to cellular respiration which goes to carbon dioxide and water which goes back to plants.
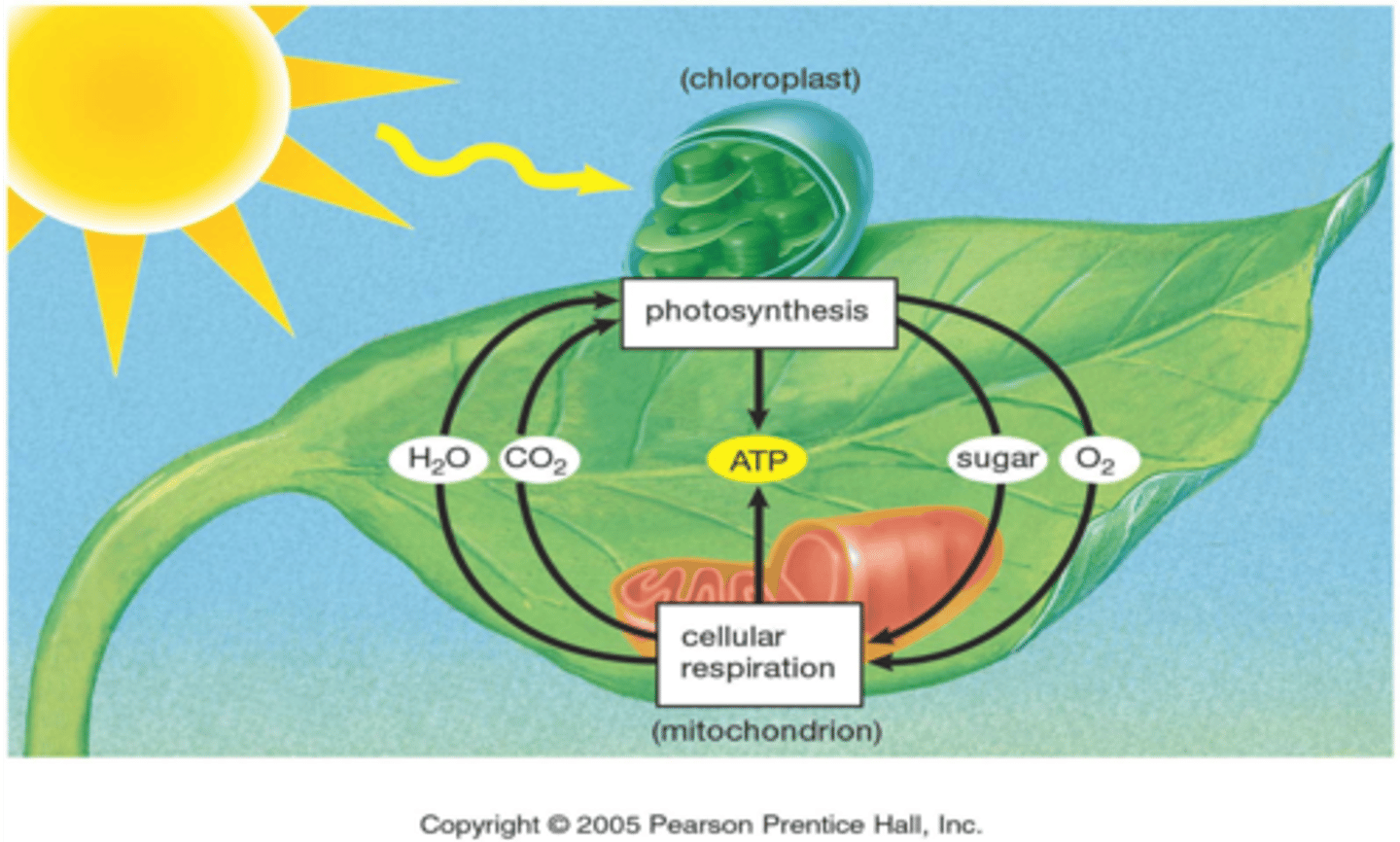
Why do all organisms break down glucose?
To produce energy which can be used in cellular processes
What's the plants do with light energy energy from the Sun?
Absorb it and convert it into the chemical energy of glucose in the chloroplast
What is the word aerobic respiration equation?
Glucose+ oxygen-> carbon dioxide+ water+ Energy

How do organisms produce energy when there is no oxygen gas?
They undergo anaerobic respiration
What is the enhanced greenhouse effect?
Human activities have led to more carbon dioxide and methane produced. This goes into the atmosphere, and traps more heat, which causes earths temperature to rise.
Why do organisms undergo cellular respiration?
To produce energy
What is the symbol for energy?
ATP
What is the equation of photosynthesis?
Carbon dioxide+ water-light and chlorophyll-> glucose+ oxygen
What is chlorophyll?
A grain pigment that captures the light energy of the sun and converts it into glucose and oxygen
Where does photosynthesis take place?
In the chloroplasts of plant cells
What happens when coral is under stress?
They expelled tiny algae that live in their tissues. Without these algae corals look white. This is called coral bleaching.
Finish the sentence. Photosynthesis is the process in which...
Carbon dioxide and water react in the presence of sunlight to produce glucose and oxygen gas
What is the source of energy for most ecosystems?
The Sun
Why is carbon needed?
It's needed to build proteins, glucose and fat. This is stored as long as the organism is alive.
What do almost all organic material store?
Carbon
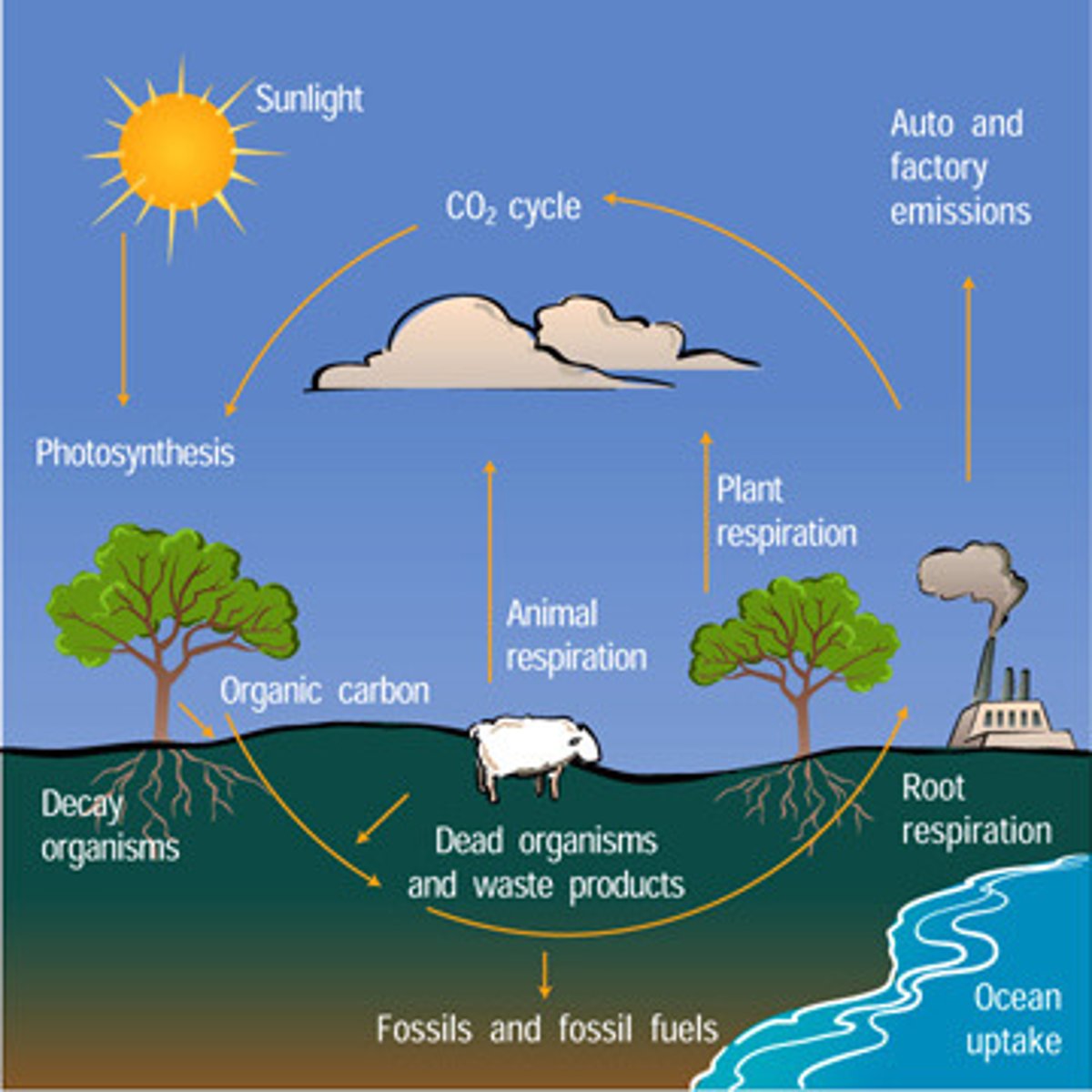
What is the carbon cycle?
Carbon dioxide in the air is absorbed by plants in photosynthesis. Some of this goes back into the atmosphere through plant and animal respiration. When the plants and animals die, the dead organisms and waste products are compressed into carbon which makes fossil and fossil fuels. These fossils and fossil fuels, as well as the dead organisms and waste products go into factory and vehicle combustion emissions, which adds to the carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. Some carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is taken into the ocean.
What are earth's four systems?
The biosphere, atmosphere, lithosphere which is the geosphere, and the hydrosphere.
Finish the sentence. Bacteria and fungi are...
Decomposers
Are decomposers producers or consumers?
Consumers which are also known as heterotrophs
Define population
The members of one species living in an ecosystem
What is a habitat?
The environment in which an organism lives
What are nonliving members of an ecosystem called?
Abiotic factors
What are living factors of an ecosystem called?
Biotic factors
What do ecosystems consist of?
All organisms in a certain community, all nonliving components, and all interactions taking place.
What is inorganic material?
Simple chemicals such as O2, CO2, and H2O
What is organic material?
Ma composed of chemicals made by living things for example, carbohydrates, proteins, and fats
What are cells?
The units of life. All organisms are made up of cells.
What is a species?
A group of organisms which ordinarily reproduce and have fertile offspring
What is an organism?
Any living thing
What do omnivores eat?
Both plants and animals
What do decomposers do?
Break down dead animals in their wastes, releasing nutrients into the soil
Why are decomposers important?
They recycle waste by converting organic material into inorganic material which can be reused by producers
Finish the sentence. Carnivores...
Only eat other animals
What do herbivores do?
Only eat plants
What are the three groups of consumers?
Herbivores carnivores and omnivores
What are consumers (also called heterotrophs)?
Animals that gain their energy by feeding on other living things
What are produ
Organisms that make their own food (organic material) using the process of photosynthesis. Also known as autotroph's and they include all plants and algae.
Define community
A group of all living things in an ecosystem
How does plastic affect the biosphere?
Animals get caught in it
What happens when plastic is burnt?
Carbon dioxide is released into the atmosphere
How is plastic produced?
By crude oil
Is nuclear energy green?
No. It doesn't produce carbon dioxide, but other nuclear wastes are toxic and harmful.
Fill the gaps. Biofuels like... and... are...
Bio feels like a bioethanol and biodiesel biodegradable.
What does biodegradable mean?
The wastes can be introduced into waterways or soil without damaging the environment, because they are decomposed by bacteria
What is bioethanol produced out of?
Plant crops like sugarcane and corn
How long does it take to produce bioethanol?
Hours to days
Bio ethanol producers...
Less CO2 than petrol
What is biodiesel made from?
Animal and plant wastes such as algae, sewage, food waste and plant oils
Why is bio diesel renewable?
Production is fast and waste won't run out quickly
Why wouldn't bioethanol and bio diesel be renewable?
When plants/whites are being replaced more slowly than they're being cut down
Are biofuels green energy
No, they still released carbon dioxide when burned
What would ideally happen with the carbon dioxide produced by biofuels?
It will be absorbed by the new crops grown in photosynthesis
What energy do nuclear power plants use?
Energy from uranium splitting into two other atoms
Is nuclear energy renewable?
No. Uranium will run out in the future.
Disadvantages of hydroelectric dams
They require specific to rain. They disrupt fish migration downstream. They are dependent on rainfall.
What are advantages of hydro power?
It's green energy
What can biodiesel be used for?
Fuel vehicles similar to diesel and to generate electricity
Disadvantages of wind turbines
May disrupt flight parts of birds. Weather reliant
Advantages of wind turbines
Renewable energy. Green energy.