Matter in our Surroundings
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
What is matter?
Matter is any substance that has mass and occupies space.
What is the physical nature of matter?
Matter is made up of particles, which are very-very small.
What are the characteristics of particles of matter?
Characteristics of particles of matter are:-
1. Particles of matter have space between them.
2. Particles of matter are continuously moving.
3. Particles of matter attract each other.
What are the three states of matter?
1. solid,
2. liquid,
3. gas.
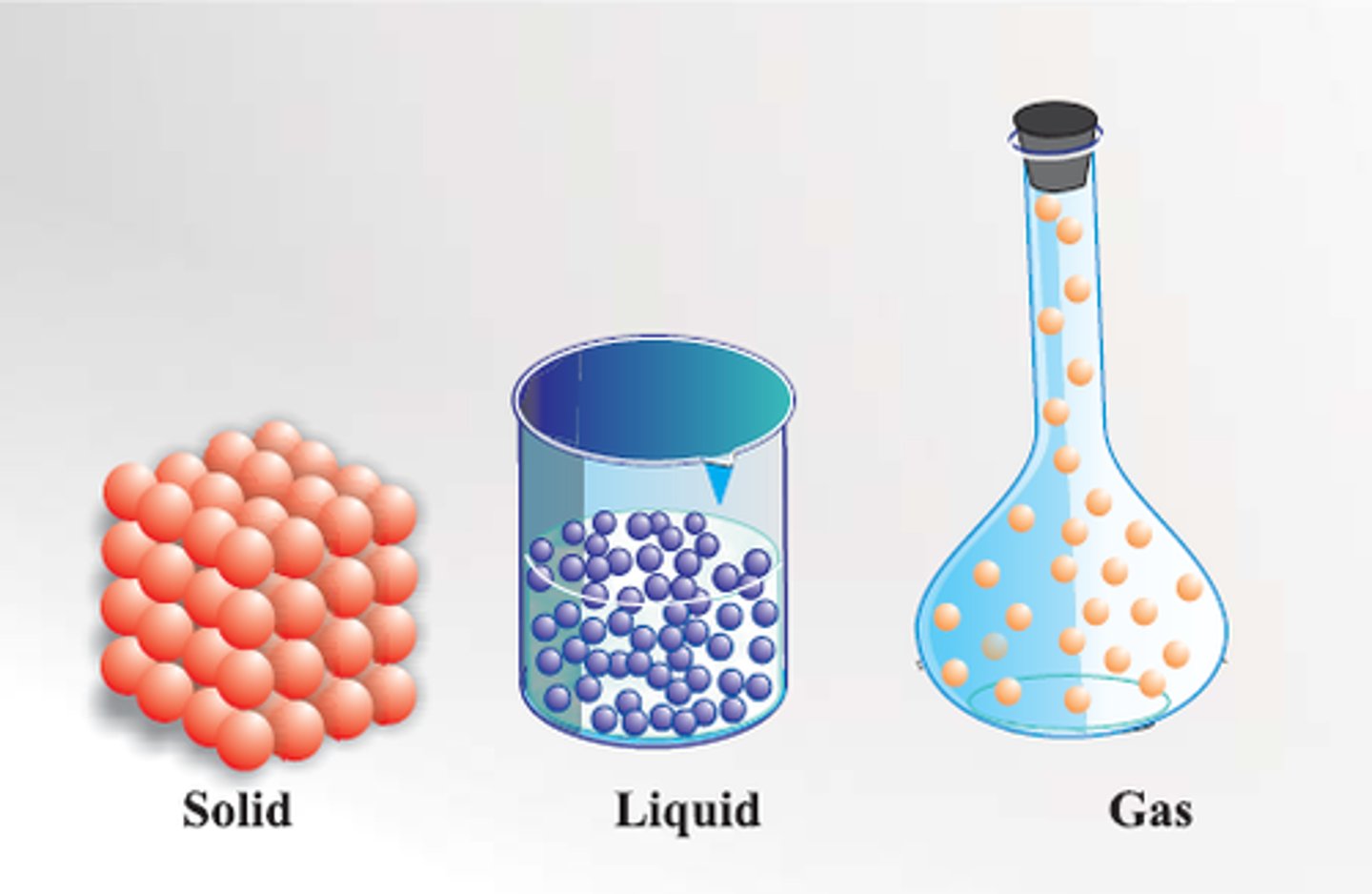
Arrange Inter-particle space and Kinetic Energy in the three states of matter
The space between the particles and kinetic energy of particles is,
Minimum in solids,
Intermediate in liquids,
Maximum in gases.
Arrange the force of attraction in the three state of matter
The force of attraction between the particles is, Strongest in solids,
Intermediate in liquids
Weakest in gases.
What are the characteristics of solid?
Characteristics of solid states are :
(a) Have definite shape.
(b) Have definite volume.
(c) Have rigidity and incompressibility.
(d) Have distinct boundaries.
Why is rubber a solid although we can change its shape?
Rubber changes its shape under force and regains the same shape when force is removed, so they are solid.
Why is sponge a solid although we can compress it?
A sponge has tiny holes in which air is trapped and when we press it the air is expelled out and, we are able to compress it.
Salt and sugar take the shape of the container in which they are placed but are solid. Why?
Salt and sugar take the shape of the container in which they are placed, but shape of their crystals do not change, so they are solids.
What are the characteristics of the liquid state?
The characteristics of the liquid state are :
(a) No definite shape. They take the shape of the vessels.
(b) Have a definite volume.
(c) Have fluidity i.e., they can flow.
(d) Low compressibility

Why do liquids have definite volume?
This is due to a strong force of attraction between the particles of liquid, which keeps its volume definite.
What is diffusion?
The intermixing of particles of different matter on their own is called diffusion.
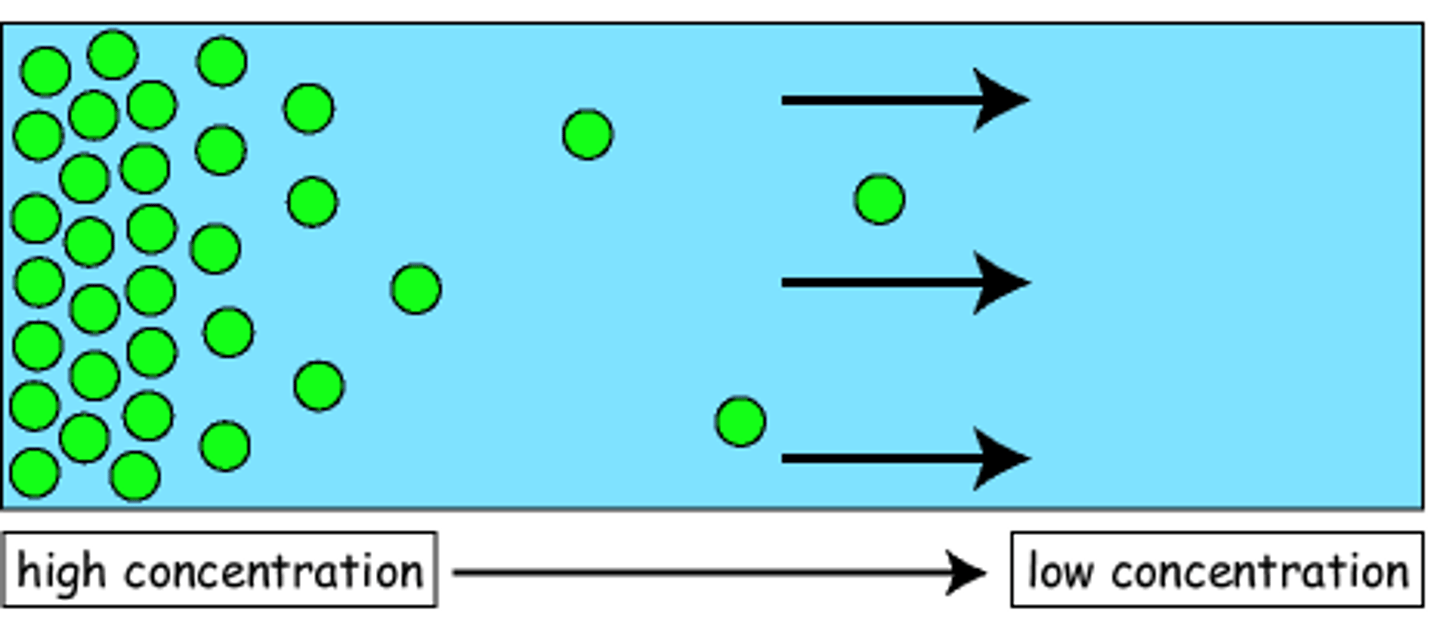
Why do liquids diffuse faster than solids?
Liquid diffuse faster than solids because:
1. Particles of liquid have more space between them as compared to solid.
2. Particles of liquids move faster than particles of solid.
What are the characteristics of the gaseous state?
The characteristics of the gaseous state are :
(a) Have no definite shape.
(b) Have no definite volume.
(c) Have fluidity.
(d) Have high compressibility.
(e) Have no definite boundaries.
Why do gases diffuse faster than liquid and solid?
Gases diffuse the fastest because
1. Highest speed of particles.
2. Largest interparticle space.
Why do the gases flow?
The particles in a gas are free to move in any direction hence gases can flow.
What causes the pressure exerted by gas on the walls of the container?
Particles of gas move randomly at high speed.
Because of this random movement, the particles hit each other and the walls of the container.
This force causes the pressure exerted by gas particles on the wall.
How can we change the state of matter?
Change in the physical state of matter can be done in two ways :
(A) By changing the Temperature.
(B) By changing the Pressure.
What happens when you increase the temperature of solids?
When the temperature of solid is increased:
1. Kinetic energy increases.
2. Particles start vibrating with greater speed.
Define melting point
The temperature at which solid melts to become a liquid at atmospheric pressure.
Melting is also known as
fusion
What is latent heat?
Latent heat is the hidden heat that gets used up in changing the state by overcoming the forces of attraction between the particles.
What is the effect of latent heat?
The temperature does not change until the state change is completed, even when we supply constant heat.
Define latent heat of fusion.
The amount of heat energy required to change 1 kg of solid to liquid at its melting point at atmospheric pressure
Define latent heat of vaporization.
The amount of heat energy required to change 1 kg of a liquid to a gas at its boiling point at atmospheric pressure.
Define boiling point.
The temperature at which a liquid starts boiling at atmospheric pressure. It is a bulk phenomenon.
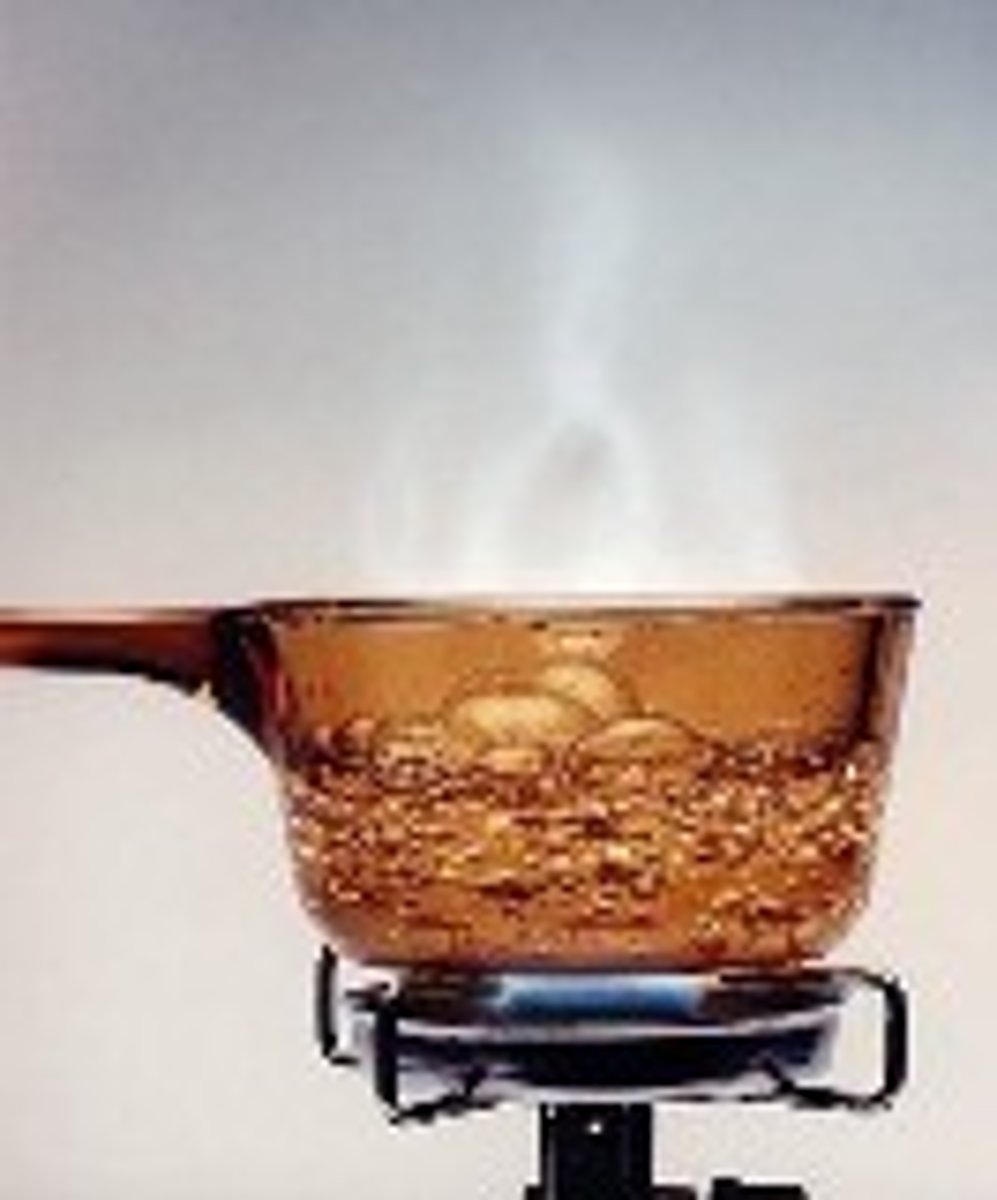

What happens when a liquid boils?
The particles from the bulk of the liquid gain enough energy to change into vapour.
What is sublimation?
A change of state directly from solid to gas without changing into the liquid state.
Eg- the sublimation of camphor, naphthalene, ammonium chloride.
What is the effect of increase in pressure of a gas?
The distance between the particles of gas is reduced.
Explain the effect of change of pressure on dry ice (CO2)
Dry ice gets converted directly into its gaseous state on decrease of pressure to 1 atmosphere.
What is the effect of change in temperature?
With change in temperature the state of matter can be changed.
What is the effect of change in temperature and pressure?
Applying pressure and reducing temperature can liquefy gases.
Pressure and temperature determine the state of a substance.
What is atm?
The unit of measuring pressure exerted by a gas
What is the S.I. unit of pressure?
Pascal (Pa)
What is 1 atm equal to?
1 atm is the atmospheric pressure at sea level at the normal atmospheric temperature.
1 atm = 1.01 x 10^5 Pa
What is atmospheric pressure?
Pressure of air in atmosphere.
Define evaporation
The phenomenon of the change of a liquid into vapours at any temperature

How does evaporation happen?
At any given temperature, in any gas, liquid, solid, there are particles with different amounts of heat energy.
In liquids, a small fraction of particles at the surface that have a higher kinetic energy break away from the forces of attraction of other particles and convert into vapour.
When does the rate of evaporation increase?
1. An increase in surface area- because evaporation is a surface phenomenon.
2. An increase of temperature- because more number of particles have more kinetic energy to change their state.
3. A decrease in humidity- because if the water content in the air is already high, the rate of evaporation decreases.
4. An increase in the wind speed- because particles of vapour can move away with the wind faster, decreasing the amount of water vapour in the surroundings.
How does evaporation cause cooling? Give examples.
Absorption of energy from surroundings keeps the surroundings cool
E.g.- 1. particles of liquid absorb energy from surroundings to regain energy lost from evaporation
2. when you put acetone on your palm it feels cool
3. When you put water on an open ground, it becomes cooler
Why should we wear cotton clothes in summer?
We perspire more during summer. Cotton is a good absorber of water and it exposes it to the atmosphere for easy evaporation.
Why do we see water droplets on the outer surface of a glass containing ice-cold water?
The water vapour present in air, on coming in contact with the cold glass of water, loses energy and gets converted to liquid state, which we see as water droplets.
What is the S.I. unit of temperature?
Kelvin (K)
What is the S.I. unit of Mass?
kilogram (kg)
What is the S.I. unit of Volume?
cubic meter ( m3)
What is the S.I. unit of Density?
Kilogram per cubic metre (kg/m3)
What is the S.I. unit of Pressure?
Pascal (Pa)