geography urban 2 (climate / fogs)
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
geography paper 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
microclimate
a climate in a small or restricted area, especially when it differs to the surrounding areas.
Urban heat island effect
the increased temperature in urban areas compared to surrounding rural areas.
Albdedo effect
the reflectivity of certain services:
black surfaces such as roads and black buildings have low albedo
white surfaces have high albedo
absolute humidity
the mass of water vapour in a given volume of air, regardless of temp
relative humidity
a percentage / ratio of the actual amount of water vapour that is in the air.
different between relative and total humidity
relative - the percentage of water vapur
total - the quantity in the water
venturi effect
two buildings with a gap between them causing a sharp air wind speed
the formation of thunderstorms
ground surface heats and air rises
the air becomes unstable and causes of a ‘chimney’ of condensed air
causes ice crystals and they fall as precipitation
this causes electric charges of the positive crystals
causing thunder and lighting
downdraught effect
tall buildings cause the wind to mostly go down (some go up) and this air picks up speed and causes higher wind speeds.
fog
when visibility is less than 1000mand occurs by water droplets and solid particlses
radiation fog
caused when there is cooling of land by thermal radiation cooling the close to the surface
the cooling reduces the ability to hold moisture and causes the dew point to be reached easier, causing fog
advection fog
caused by warm moist air blowing over a colder area, causing air to reach lower dew point.
Smog
a mixture of smoke and fog which occurs when smoke particulates and sulphur dioxide mix with fog.
photo chemical smog
occurs in drier areas and forms due to fossil fuels, and borning trees and organic waste
particle pollution
pollution which consists of particles suspended. these particles come from natural and human processes
smoke controlled areas: def adv dis
an areas where it is offence to emit smoke from a chimney, normally resulting in a fine.
adv: stops the emissions of gas within urban areas, better air quality, reduces risk of chimney fires
dis: the max offence charge is £1,000 meaning large businesses are mostly unaffected
clean air act: def adv dis:
the clean air act was brought in 1956 and dealt with smog issues, making smog contol areas where smoke is not allowed in domestic properties
adv: improving public health and environmental impact is reduced
dis: may lead to exportation from abroad, worsening the carbon footprint of products and reducing the UK’s economy
vehicle control: def adv dis:
introducing schemes to reduce cars in busy areas, whether that be from the design of cities reducing roads, to low emission zones being introduced
adv: encourages people to have cleaner habits in the way they commute
dis: leads to traffic on the outskirts of the city, with city expansion being an issue
vechile emissions: def adv dis:
car manufacturers have been made to make efficient fuel-burning engines
adv: reduces the impact of vechiles on the road and lowers fuel usage and price
dis: these new standards only apply to new cars, which not many people have
public transport: def adv dis:
introducing more public transport schemes such as bus and train stations and bike paths
adv: reduces traffic, reduces people’s carbon footprint getting to work
dis: can lead to overcrowding of services, can often be unreliable
industry zoning
forcing businesses to emit their pollutants above the immersion layer
adv: decreases fog and smoke, decreasing health issues and keeps businesses still in the city
dis: can have a negative look on a city and the emissions are still being released
the urban water cycle - neame the levels:
source - reservoirs, lakes
water treatment - raw water must be treated with methods such as filtering and disinfection
water distribution - clean water is put into pipes and pumps, where it is transported
use - can be used in many ways such as cleaning, drinking and bathing
wastewater collection - taken back for treatment
wastewater treatment - the physical, chemical and biological treatment processes and discharged into sources
Natural levees: def adv dis:
embankments (turns in the river) are made of concrete and riverbed materials
adv: relatively low costs to maintain and have a nice natural look
dis: can easily be over topped by flash floods
diversion spillways: def adv dis:
emergency areas which are opened when there is flooding
adv: reduce the pressures on the main channel
dis: expensive and can disrupt ecosystems r
river channelisation: def adv dis:
straightening channels with concerete to reduce friction
adv: improved navigation and more efficient flooding
dis: expensive and destroys habitats. can lead to flooding at the bottom of rivers
afforestation: def adv dis:
planting trees to increase interception and reduce water runoff
adv: more natural approach and little construction needed
dis: community not happy, takes long time for them to grow
riverbank conservation: def adv dis:
planting bushes and trees to reduce erosion and roots which stabilise riverbanks
adv: low maintenance and disruption needed
dis: takes a long time and does not reduce major flood impact
floodplain zoning: def adv dis:
restricts land use to a floodplain, allowing it to get flooded
adv: avoids people from being flooded, reducing risk
dis: can be difficult to implement and requires assessment of land
river straightening: def adv dis:
cutting through meanders to create a straight channel
adv: improved navigation, easier maintenance, more space for urban land
dis: can increase floods downstream and can destroy habitats
river restoration definition
removing all hard engineering and adaptations to restore meanders, wetlands and floodplains. this leads to flood management being returned to nature
river conservation
planting vegetation to reduce lateral erosion and riverbank collapse. this can also include introducing native species and awareness to the public
River restoration study - Darlington
the river was straightened in 1850 to accommodate industrialisation
in the 70’s the lake was highly polluted with gas and sewer pipes
in 1995 a plan was made to restore the area into an attractive wetland environment thriving with natural life
this was done to maintain biodiversity and reduce flood risks
river conservation study - Blue Loop Sheffield
throughout the 1800’s, the river was used for industrial purposes such as cooling and exporting coal and goods
this lead to the river becoming derelict, as well as the houses around the canal
this was until 1992 when the Sheffield development co-operation helped to conserve the river Don and canal
the aim was to: encourage biodiversity, create a community to help the river, reducing flood risk and making it a recreational area
SUDS definition
represent the ultimate in realistic yet environmentally friendly replication of natural drainage systems
SUDS: Swale

wide shallow drainage channels which collect and transport water
SUDS: permeable road and pavements

use of porous block paving and concrete
SUDS: infiltration trenches

bioretention basins

gravel / sand filtration beneath reed beds
SUDS: rain garden
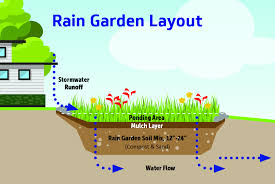
shallow landscape despressions planted with flowers and shrubs
SUDS: green roof

SUDS: adv dis
adv: slow down water runoff, provide wildlife homes i urban areas, reduced flooding risk, prevents water pollution
dis: lowered profit when developing, increased maintenance, high initial costs
Case study: Lamb Drove, Cambourne
this development was apart of a large scale project of introducing SUDS across Europe
this one included introducing methods such as: permeable surfaces for drives, under drained swale, water butts and filter strips
this lead to less metal in their water as well as maintenance being 10% less
however, it did lower profit’s for developers and concerns were made about exposed water
streategy: greener built environment. def adv dis:
initiatives to use energy and water more efficeintly as well as reducing waste in a more greener way
adv: can improve energy consumption in buildings, enhanced appeal of cities
dis: high initial costs, hard to change what is already implemented
strategy: planed expansion def adv dis
encouraging the conservation of historic buildings and green space.
adv: protects open spaces which act as carbon sinks, maintain hsitorical and tourism heritage.
dis: can be costly to maintain older buildings, restrictions on land use take a lot of time to gain
strategy: carbon neutral developments. def adv dis
building structures such as houses that produce as much energy as they need
adv: reduces impact on environment from all settlements, enhanced reputation
dis: can be challenging to maintain due to cost
strategy: economic opportunities. Adv dis
providing a range of economic opportunities outside of the fossil fuel department e.g. Quaternary sector
adv: can lead to a more sustainabel growth in demand and reduce reliance of fossil fuels
dis: can create economic inequalities due to loss of jobs needed
ecological footprint definition
the impact of a person or community on the environment, expressed as the amount of land required to sustain their use fo natural resources
biocapacity definition
refers to the capacity of a given biologically productive area to generate an on-going supply of renewable resources and to absorb its spill ober wastes
ecological defecit and surplus definition
the difference between the bio capacity and ecological footprint tor a region or country
defecit: when the footrpints exceeds the capacity in the area
surplus: when the capacity exceeds the footrprints in the area