Chemistry Final
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 10:10 PM on 6/12/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
1
New cards
isotope notation
ex. C-14 : the number is the same as the mass number
2
New cards
mole
unit for measuring large quantities of atoms/molecules
3
New cards
molecular formula
the number of atoms of each element in a compound
4
New cards
empirical formula
the simplest or most reduced ratio of atoms in a compound
5
New cards
percent composition
the percent by mass of each element in a compound
6
New cards
relative mass
**the mass of an atom or molecule compared to that of 1/12 of a carbon-12 atom**.
7
New cards
avogadro’s hypothesis
At the same temperature and pressure, equal volumes of different gases contain the same number of molecules.
8
New cards
hoffman apparatus
separates water into 2 different gases using electricity
9
New cards
distillation
the process of separating the components of a liquid mixture through selective evaporation and condensation
10
New cards
Matter
anything that has space/takes up space
11
New cards
gases
particles are independent widely separated, with no attractive forces between them. They fill the volume of the container
12
New cards
liquid
particles constantly make and break temporary attractions between each other, particles can slip past one another easily, they take the shape of the container
13
New cards
solid
strong attractions between particles lock them into a fixed arrangement
14
New cards
pure substance
these have fixed compositions, one set of intrinsic physical properties (density etc) can be separated only by chemical means
15
New cards
mixtures
these have variable composition, their physical properties vary depending on the composition, they can be separated by physical means
16
New cards
elements
type of matter where all atoms are the same
17
New cards
compounds
type of matter made from 2 or more elements that have chemically bonded so the new properties are different from the original elements
18
New cards
molecule
two or more atoms that are chemically bonded
19
New cards
homogenous
all samples take from the same mixture are identical
20
New cards
heterogeneous
two samples from the same mixture that are not identical (2-3 phase mixture)
21
New cards
suspension
2 phase mixture where the solids will settle out over time
22
New cards
colloid
2 phase mixture that does not seperate
23
New cards
solution
single phase mixture
24
New cards
decanting
the separation of mixtures of immersible liquids or of a liquid and a solid mixture
25
New cards
mass number
protons + neutrons
26
New cards
atomic size/ atomic radius (volume)
as you go left to right the volume decreases because as you go across you are adding more protons making the attraction strong as you go down a group the volume increases because of the added energy levels
27
New cards
ionization energy
as you go across the rows the energy increases because it takes more energy to remove electrons from levels. going down a group it decreases because the atom is getting bigger
28
New cards
electronegativity
the attraction between the nucleus of an atom and the shared electrons in a chemical bond with another atom (increases left to right because the forces get stronger and decreases down a group)
29
New cards
electron affinity
the energy released when an electron is added to an atom (increase left to right and decreases down a group)
30
New cards
Copper (II) Chloride lab
evidence:
* chlorine gas/bubbles formed on positive electrode
* negative electrode turned orange
* solution started becoming lighter on negative side
Outcome: metals (copper) form positives, nonmetals (chlorine) form negatives
* chlorine gas/bubbles formed on positive electrode
* negative electrode turned orange
* solution started becoming lighter on negative side
Outcome: metals (copper) form positives, nonmetals (chlorine) form negatives
31
New cards
ionic compounds
metal and a nonmetal exchange electrons; high melting and boiling points and conduct electricity, takes more energy to break the bond
32
New cards
covalent compound
nonmetal and nonmetal share electrons; lower melting and boiling point and don't conduct energy
33
New cards
anion
A negatively charged ion
34
New cards
cation
A positively charged ion
35
New cards
ion
An atom or group of atoms that has a positive or negative charge
36
New cards
polyatomic ion
A charged group of covalently bonded atoms (many)
37
New cards
polar molecule
molecule with an unequal distribution of charge, resulting in the molecule having a positive end and a negative end
38
New cards
nonpolar molecule
molecule that shares electrons equally and does not have oppositely charged ends
39
New cards
Law of definite proportions
a given compound always has the same proportion of its constituent elements by mass
40
New cards
law of multiple proportions
when two elements A and B form two different compounds, the masses of element B that combine with a fixed mass of element A can be expressed as a ratio of small whole numbers
41
New cards
polarization of charge
One side of material is charged slightly more positive or negative than the other
\- occurs to neutral conductor when it comes into contact with charged conductor
\- occurs to neutral conductor when it comes into contact with charged conductor
42
New cards
polar bond
any bond between two atoms where the electronegativity difference is between 0.5 and 2.0
43
New cards
non polar bond
a bond between two atoms where the electronegativity difference is less than 0.5
44
New cards
ionic bond
any bond where the electronegativity difference is 2.0 or greater
45
New cards
linear
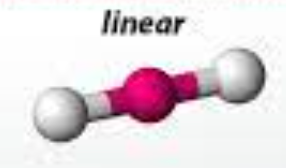
46
New cards
trigonal planar
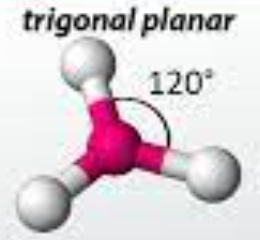
47
New cards
tetrahedral
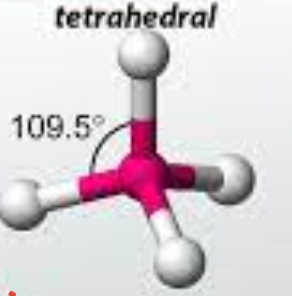
48
New cards
bent
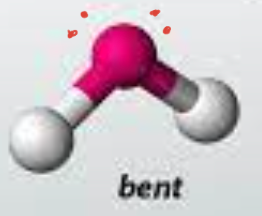
49
New cards
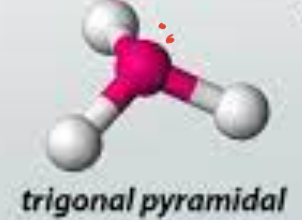
trigonal pyramidal