Lecture 4: Ultrasonography, Computed Tomography, & Magnetic Resonance Imaging
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
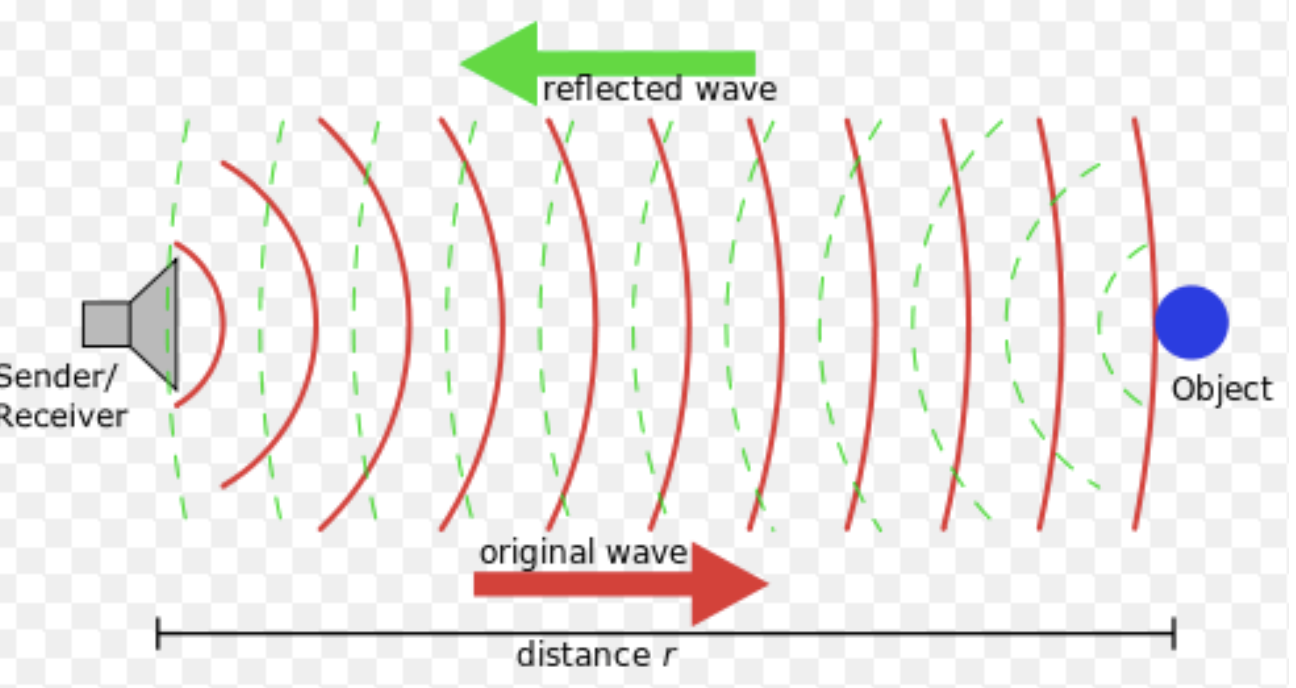
What type of imaging has high frequency sound waves that penetrate tissue and bounce back to the transducer?
Ultrasonography
With ultrasonography, high frequency _____ _____ penetrate tissue and bounce back to transducer
sound waves
What does the ultrasound transducer contain that converts sound waves to electric current?
Crystals
In an ultrasound machine, what converts electric current to an image?
Computer
What are the 2 fates of the sound waves in ultrasonography?
Hint: Acoustic Impedance
Goes through tissues (black arrows)
Bounces back (gray arrows)
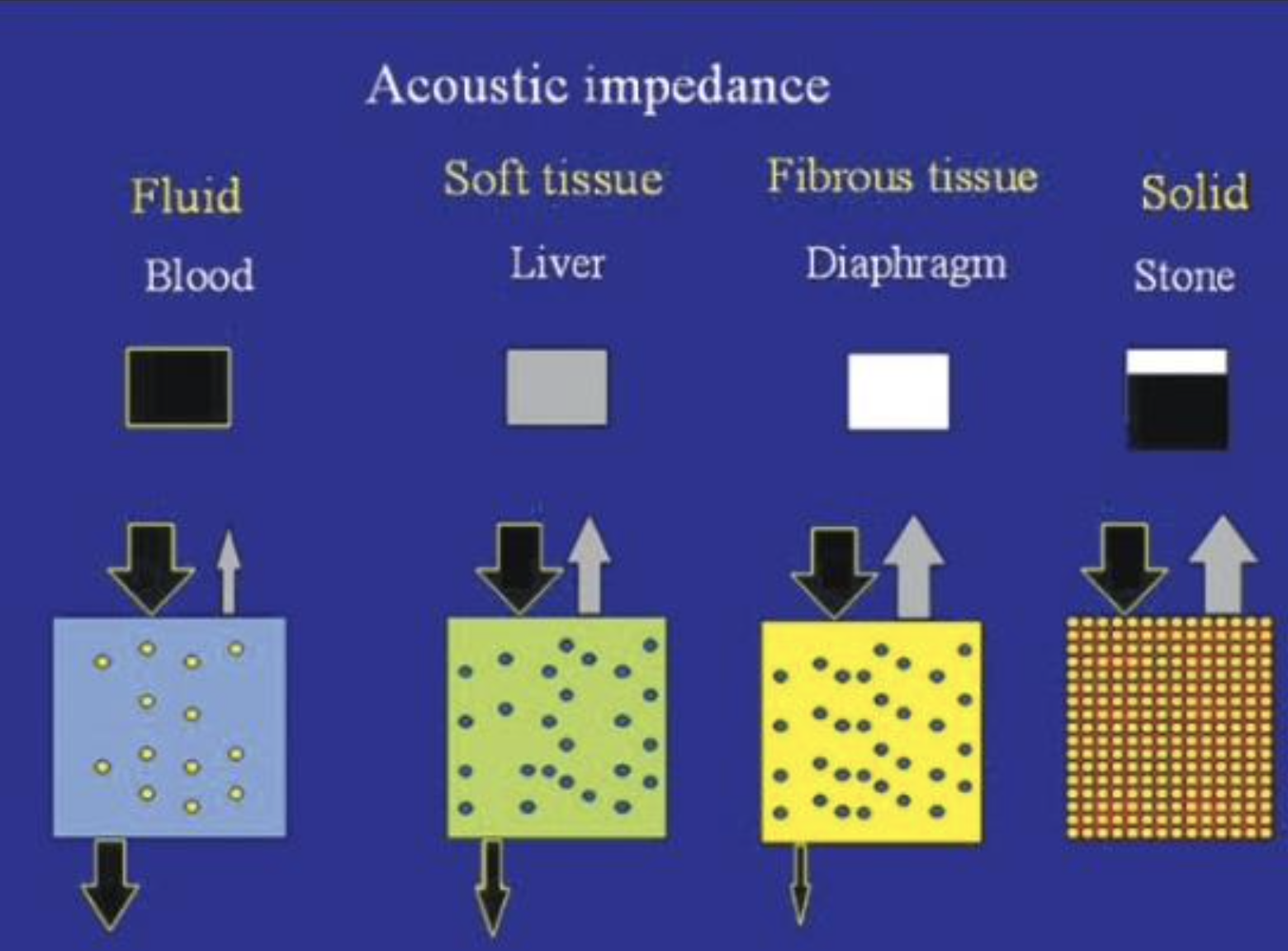
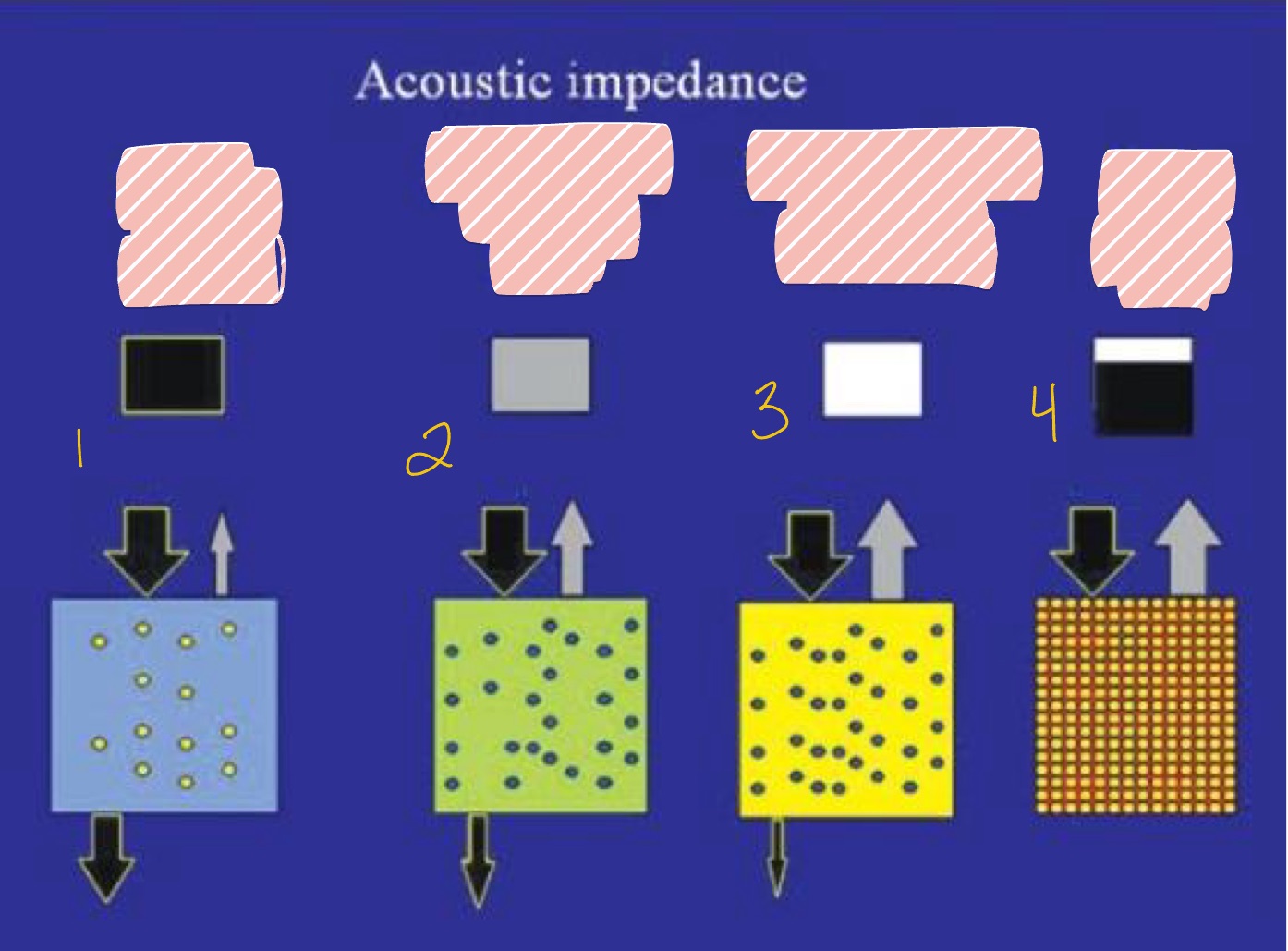
What is seen in #1 with least Acoustic Impedance?
Fluid (blood)
Solid (Stone)
Fibrous Tissue (Diaphragm)
Soft Tissue (liver)
Fluid (blood)
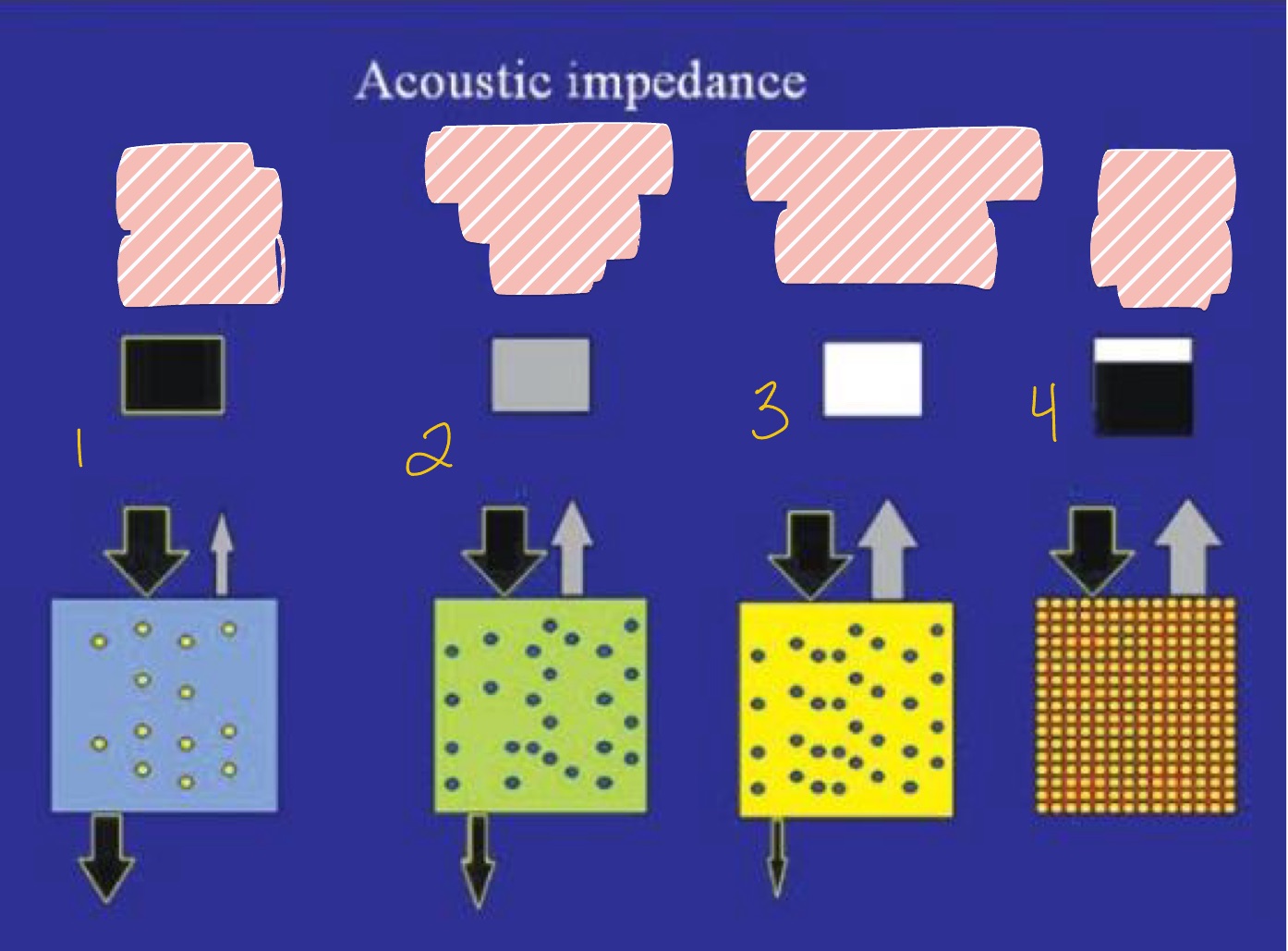
What is seen in #2 regarding Acoustic Impedance with less penetration?
Fibrous Tissue (Diaphragm)
Fluid (blood)
Solid (Stone)
Soft Tissue (liver)
Soft Tissue (Liver)
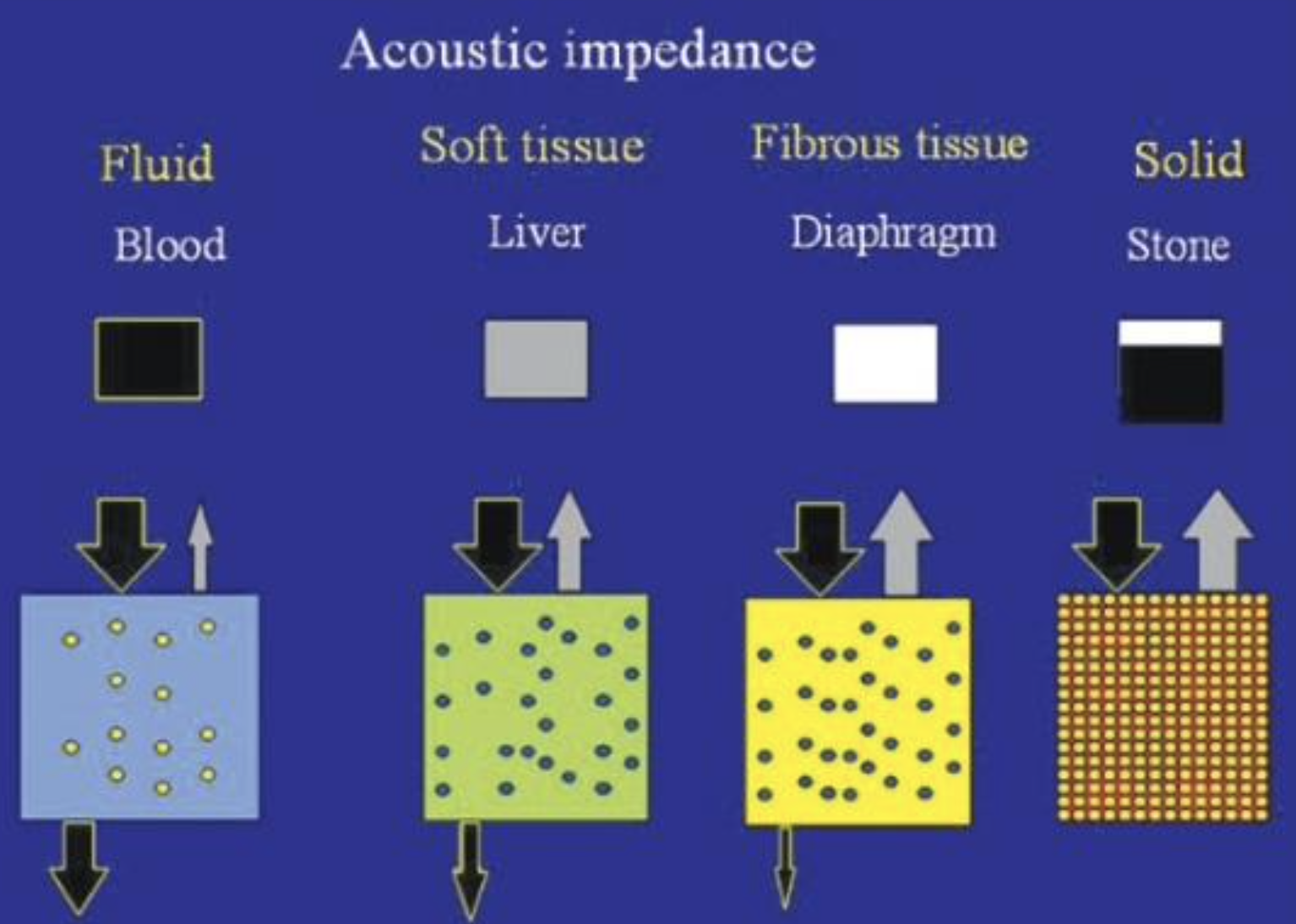
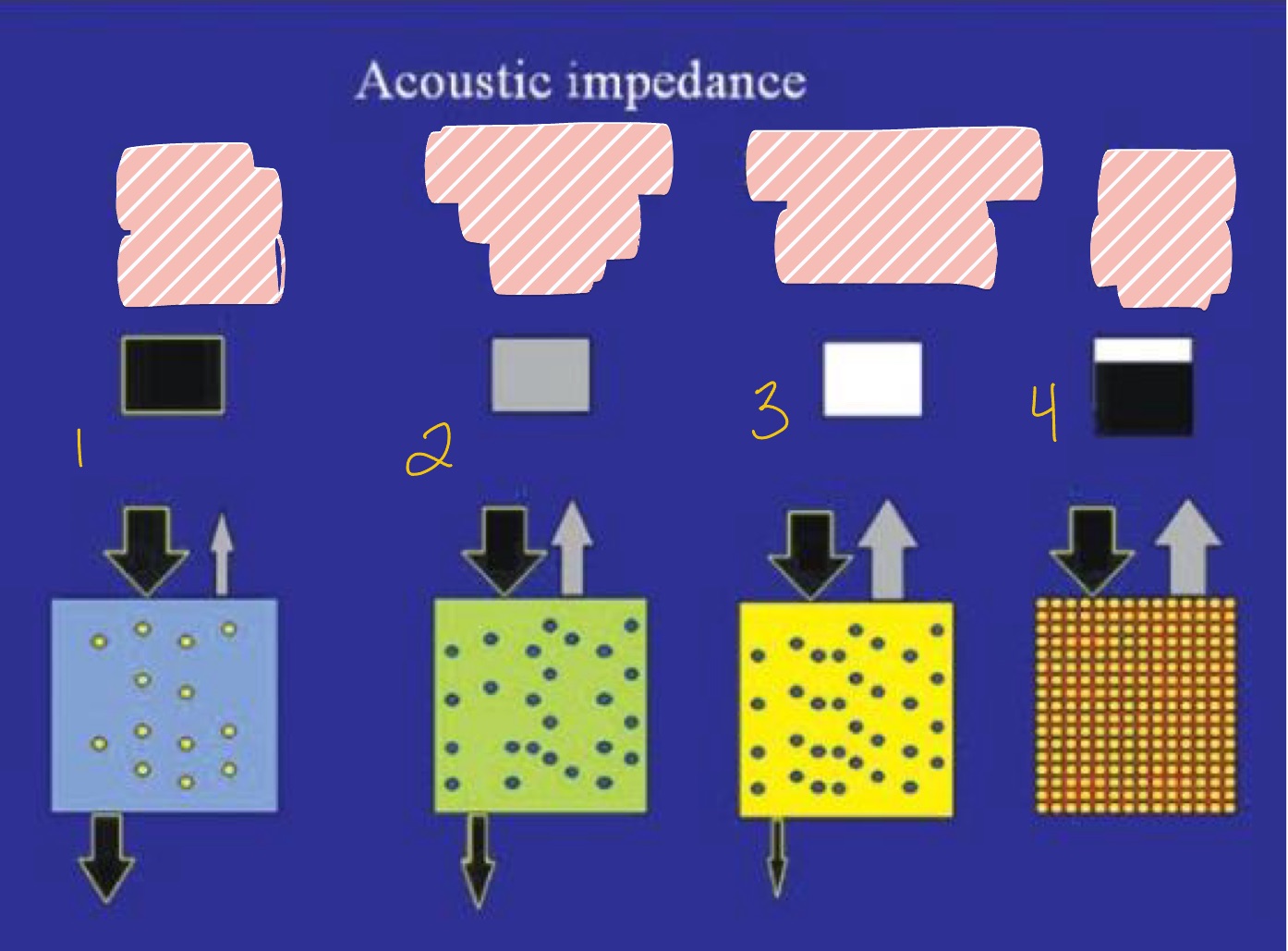
What is seen in #3 regarding Acoustic Impedance with even less penetration?
Fibrous Tissue (Diaphragm)
Fluid (blood)
Solid (Stone)
Soft Tissue (liver)
Fibrous Tissue (Diaphragm)
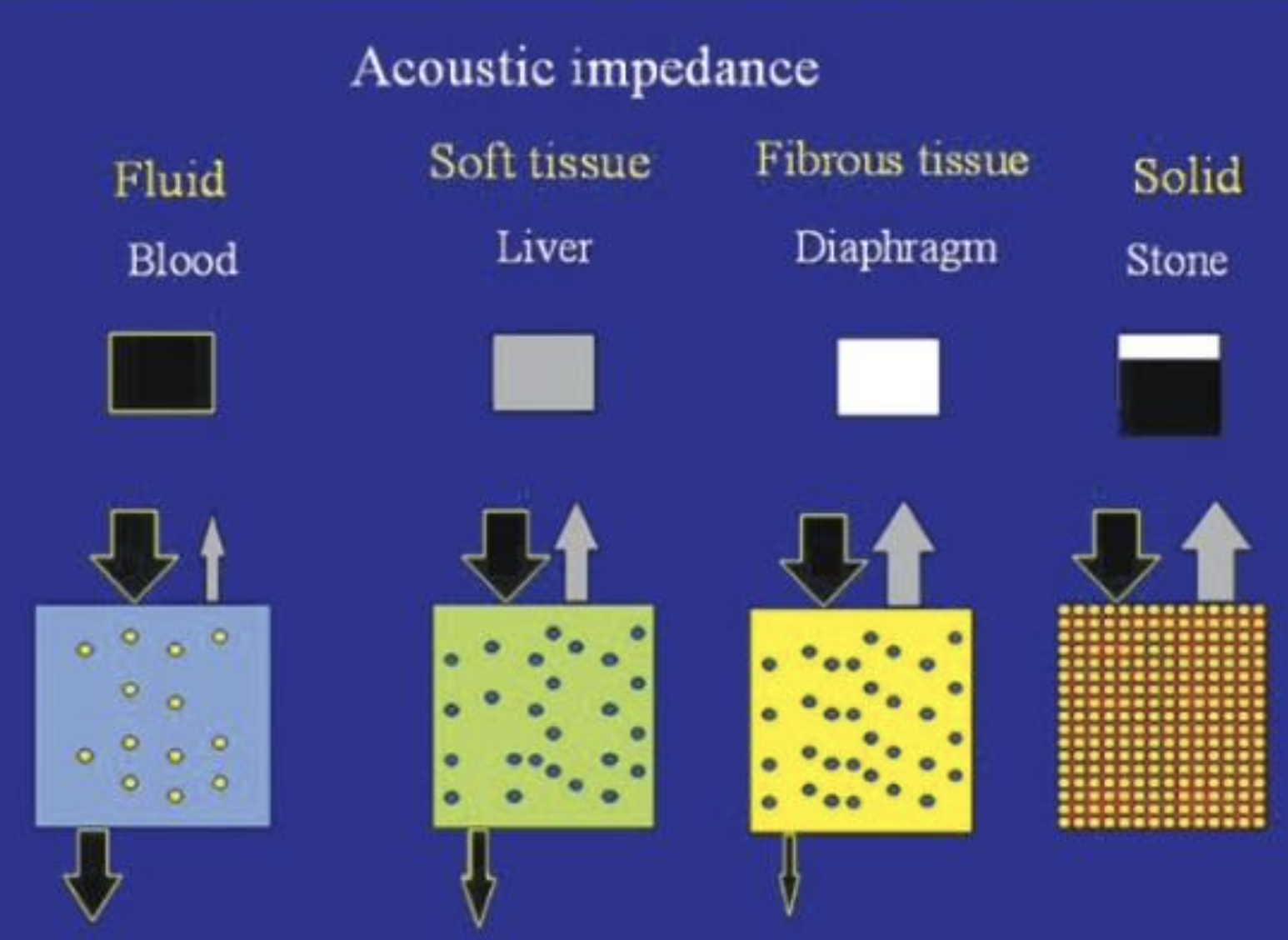
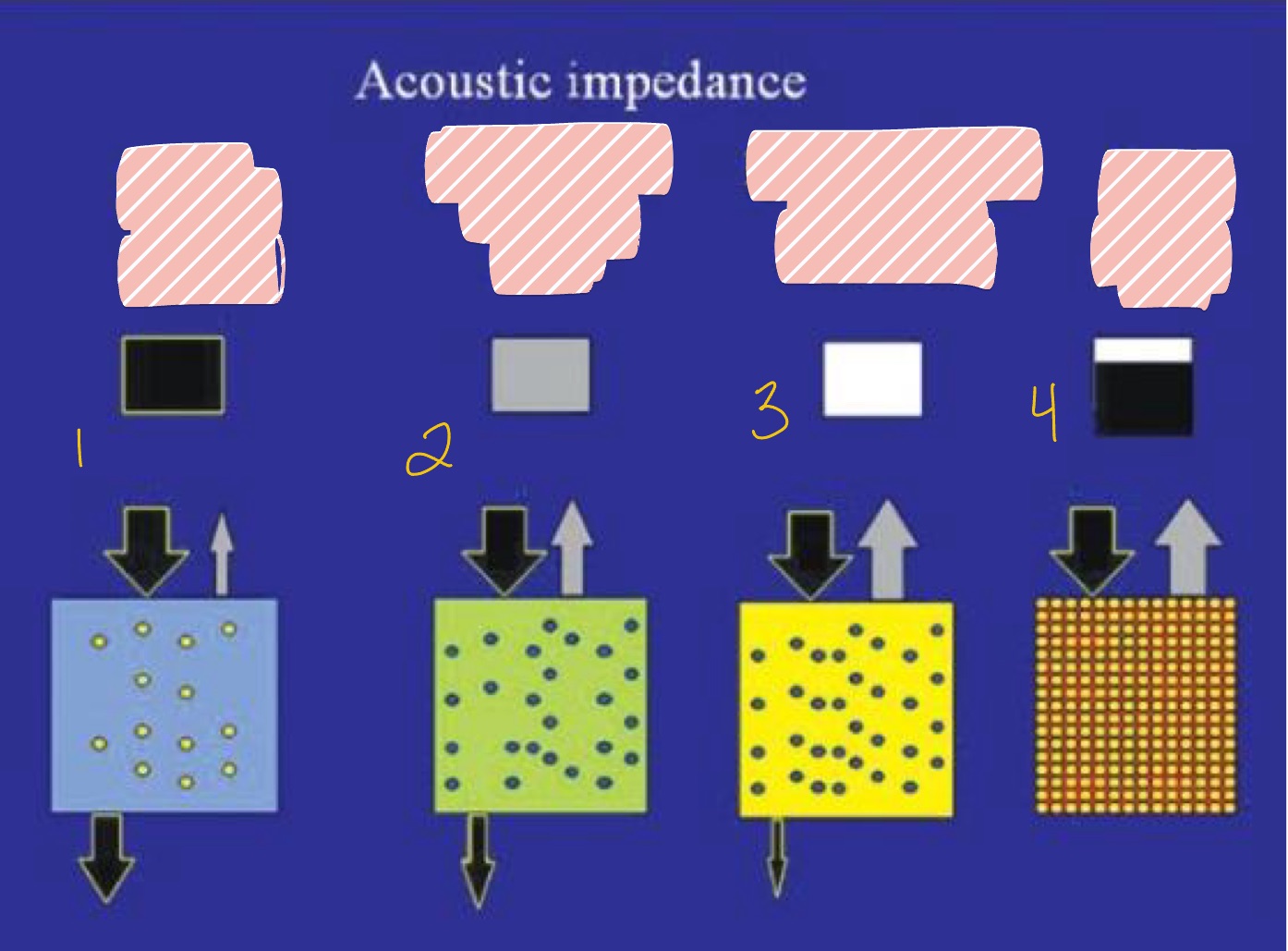
What is seen in #4 with highest Acoustic Impedance?
Fibrous Tissue (Diaphragm)
Fluid (blood)
Solid (Stone)
Soft Tissue (liver)
Solid (stone)
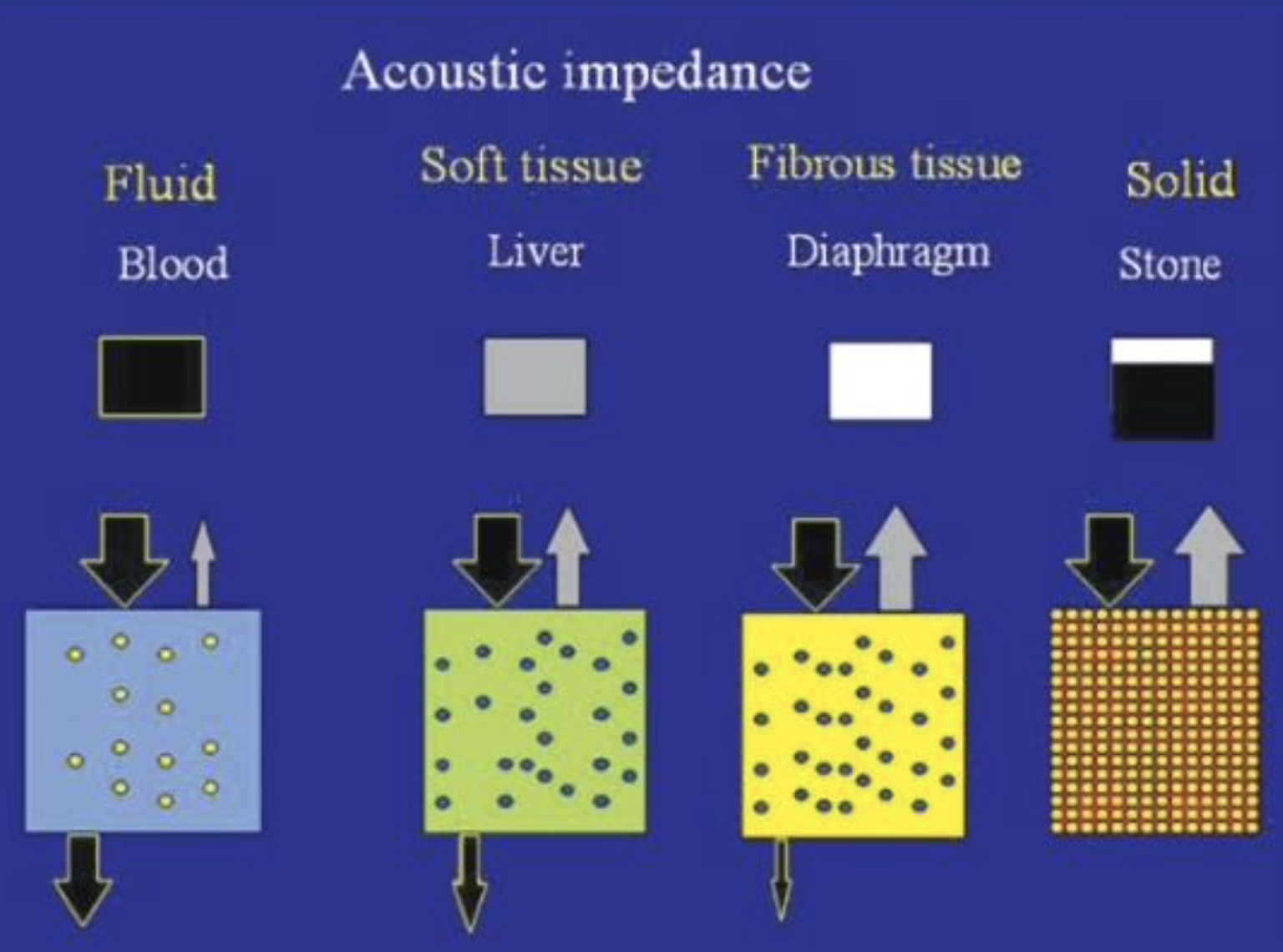
Match:
White, Black, Gray
Some waves back
All waves back
No waves back
Black = no waves back
White = all waves back
Gray = some waves back
What must you keep in mind regarding tissue and wave penetration/bouncing back?
Tissue WATER content
What do ultrasounds HATE? Why?
Air! All waves bounce back & are reflective

T/F - Waves travel in a line
True
Waves traveling through the tissue depends on the tissue’s _____ ______
Water Content
Match:
Anechoic
Hyperechoic
Hypoechoic
Isoechoic
Same/Equal
Black
Brighter/Lighter
Darker
Anechoic: Black
Isoechoic: same/equal
Hyperechoic: brighter/ligher
Hypoechoic: darker

Bone and gas organ boundaries are _____
Hyperechoic
Bile and urine are _____
Hypoechoic
What ultrasound artifact cannot be seen below a structure so reflects back ALL waves?
Acoustic Shadow
ex. ribs
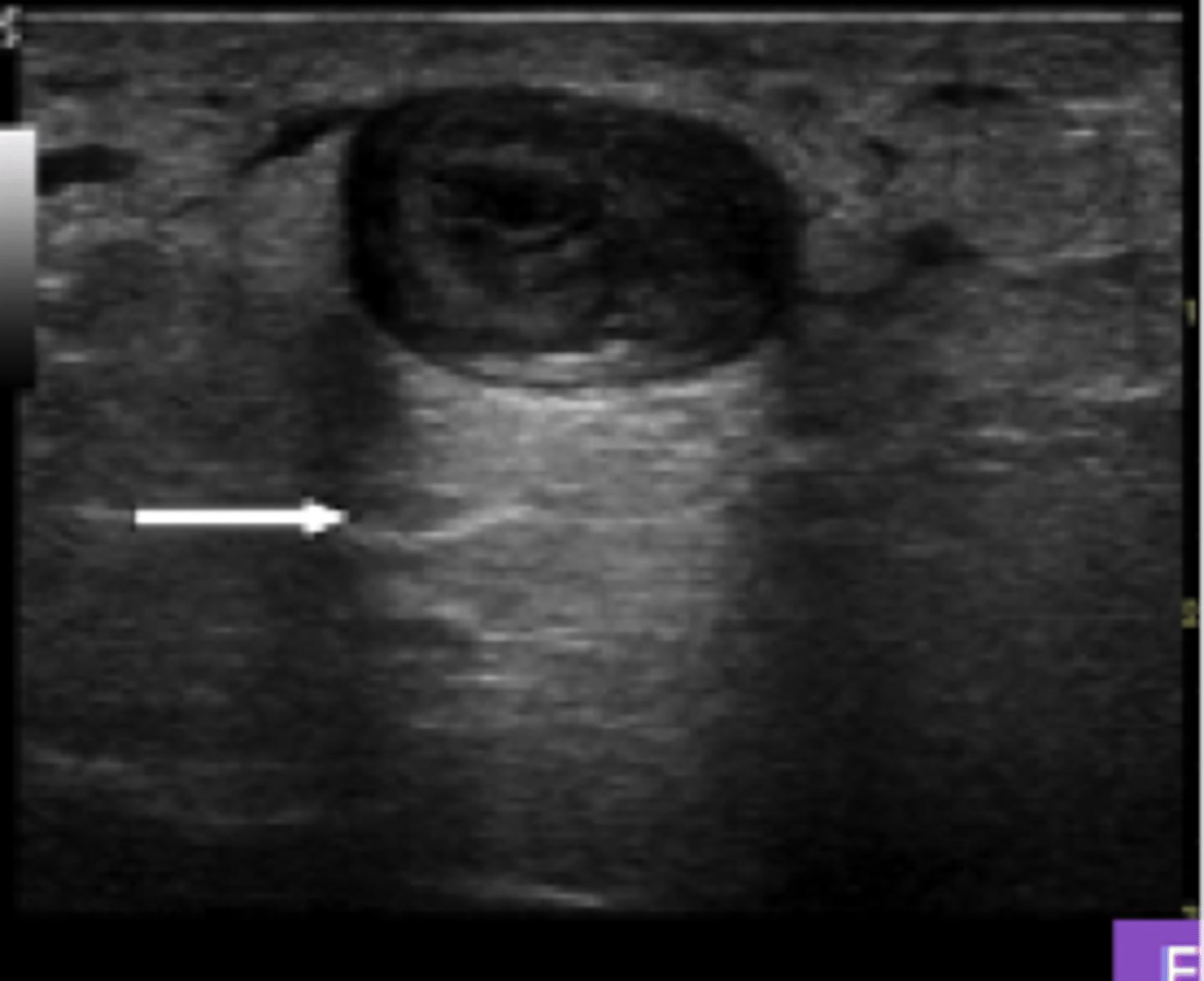
What ultrasound artifact causes (artificial) brightness DEEP to an anechoic structure?
Acoustic Enhancement
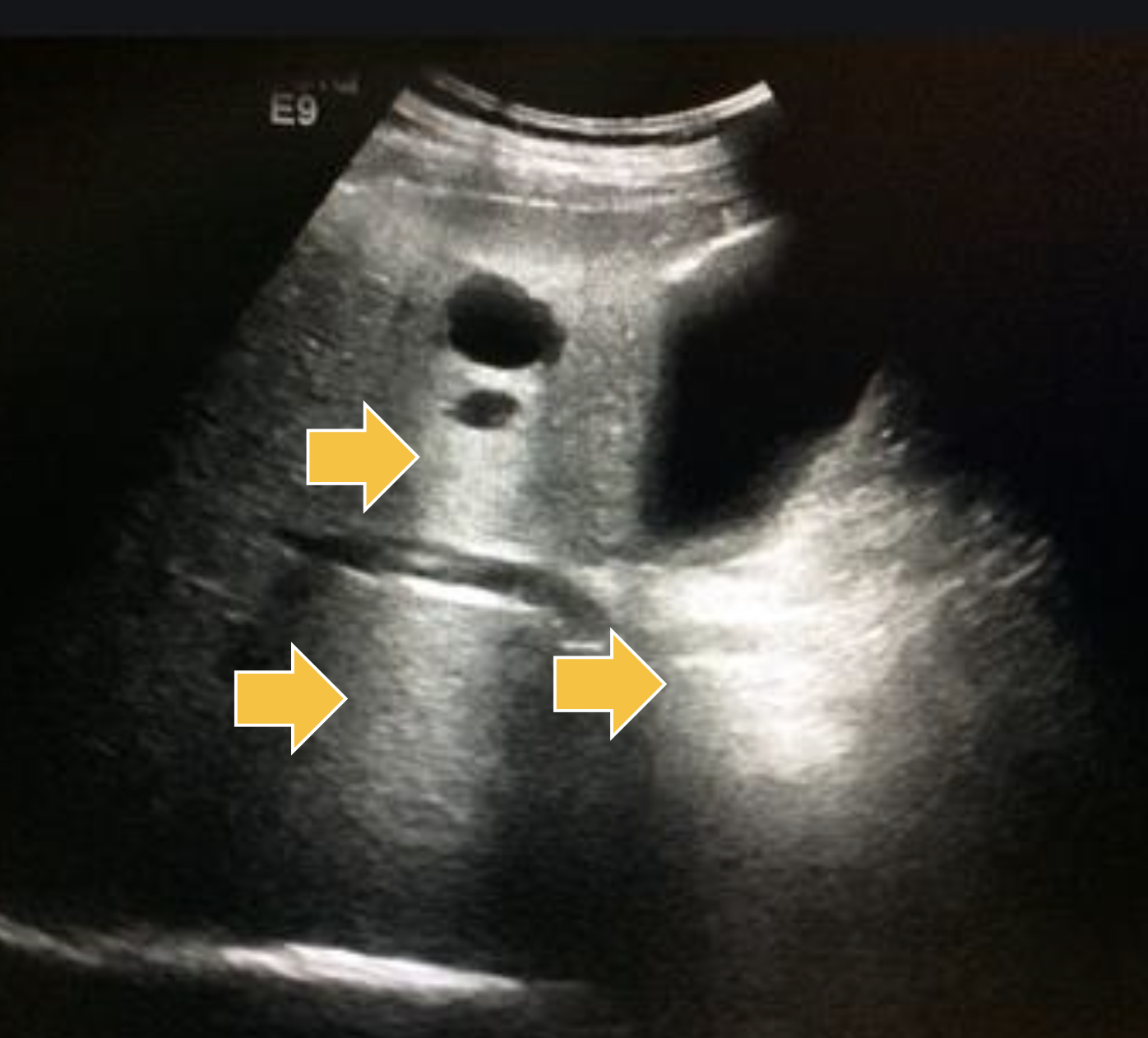
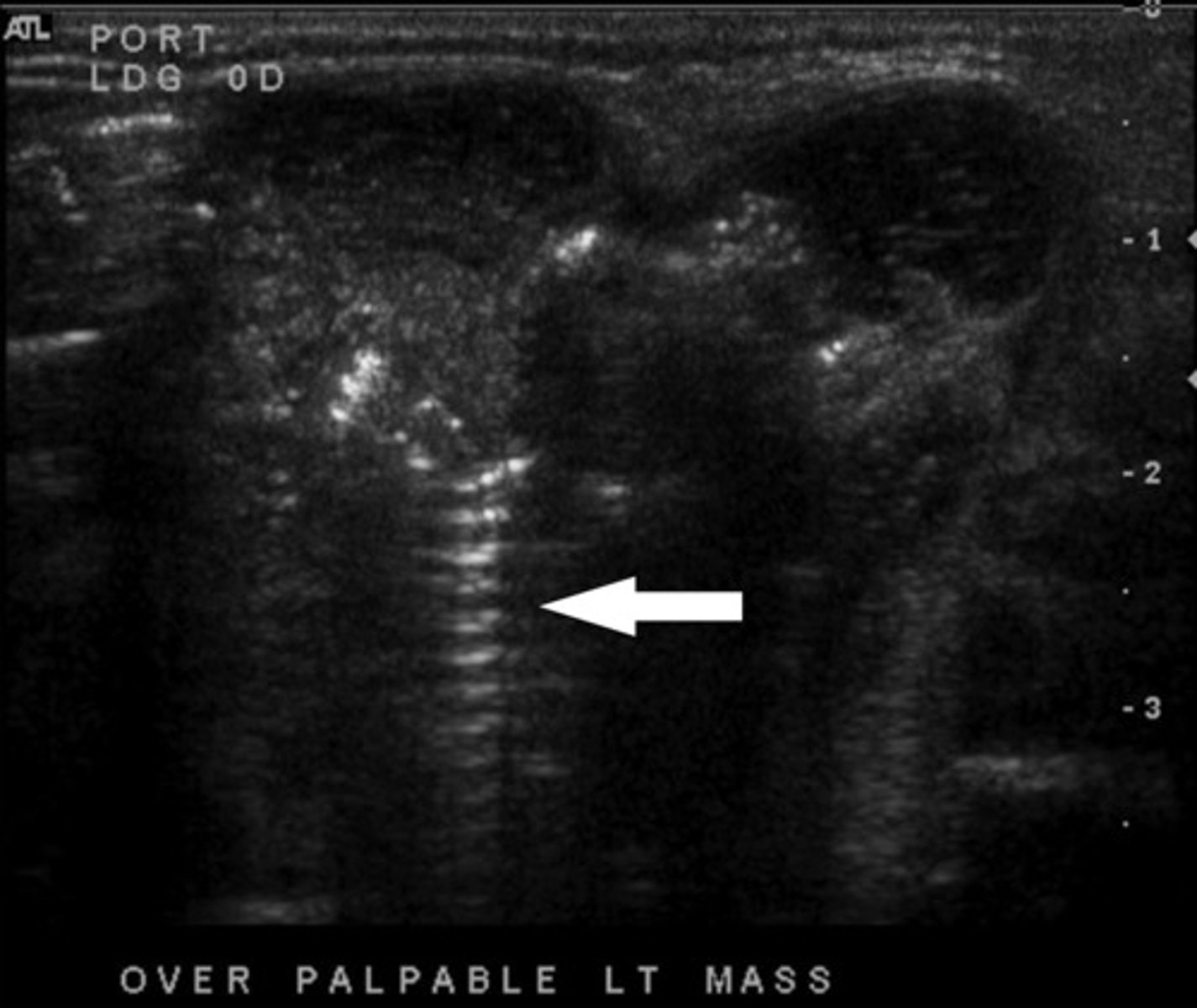
What ultrasound artifact has sound waves reflecting multiple times between strong reflectors?
Reverberation Artifact
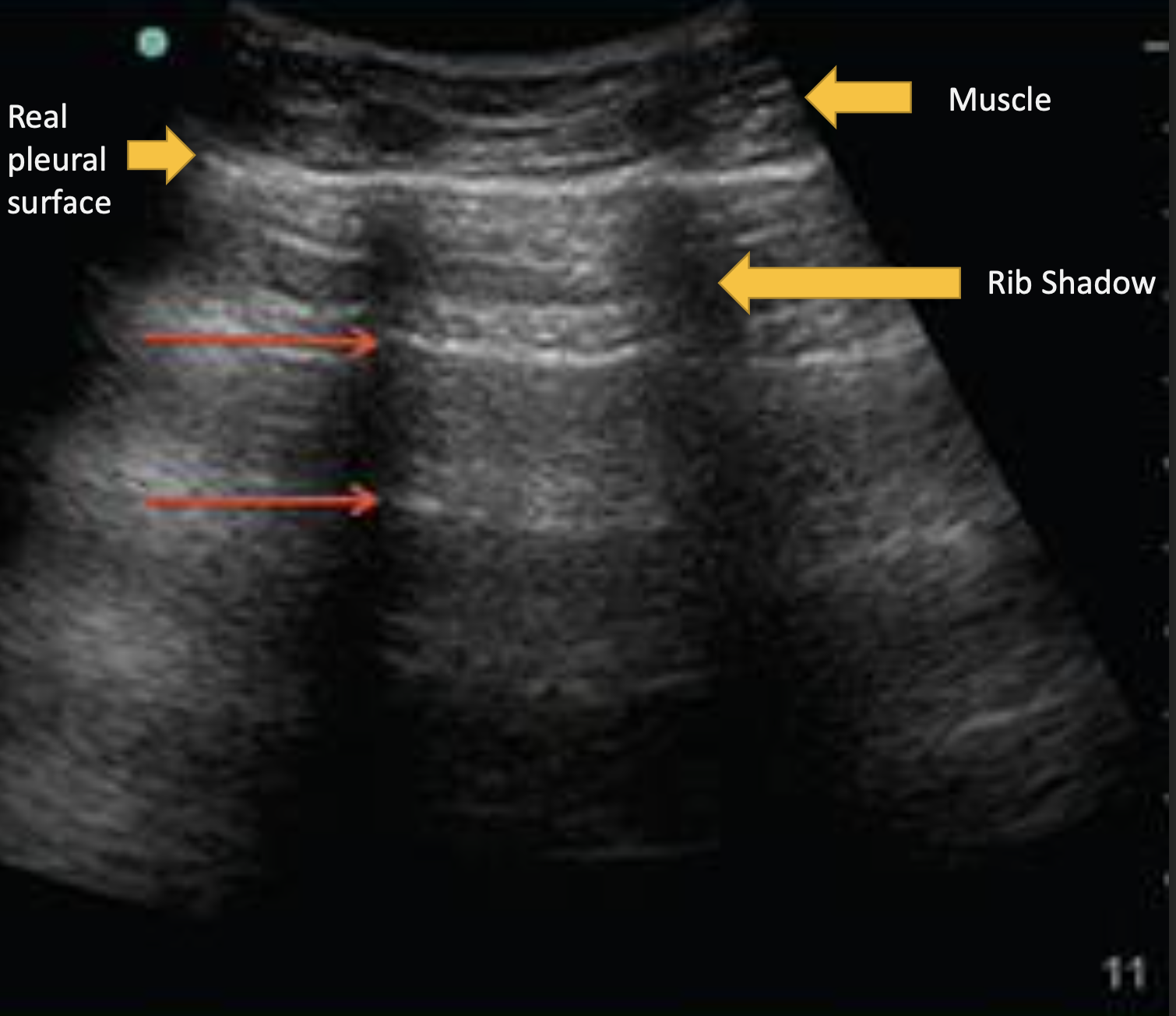
Where is Reverberation Artifact most common?
Lungs
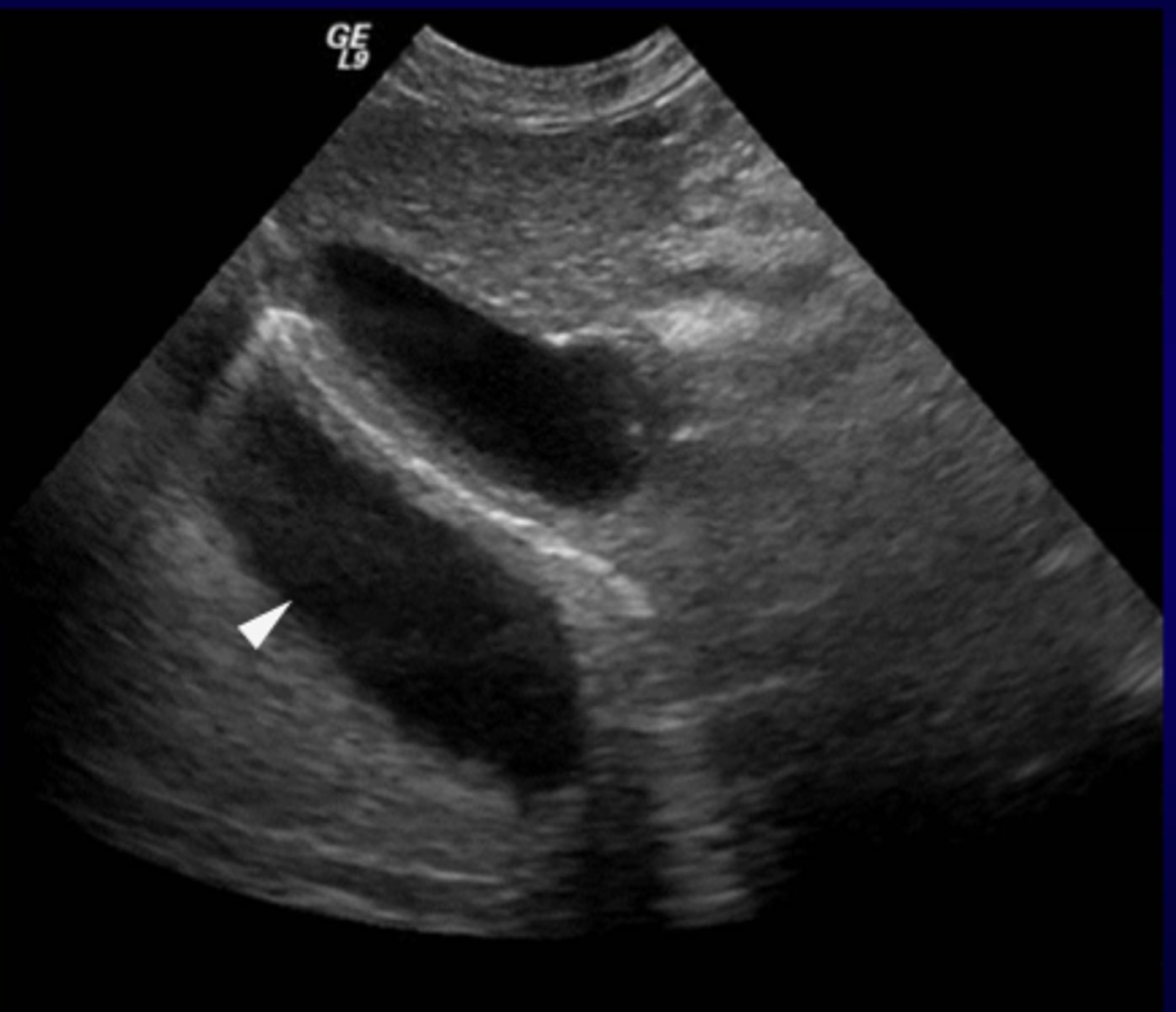
What ultrasound artifact causes the duplication of image of the opposite side of a strong reflector?
Mirror Image Artifact
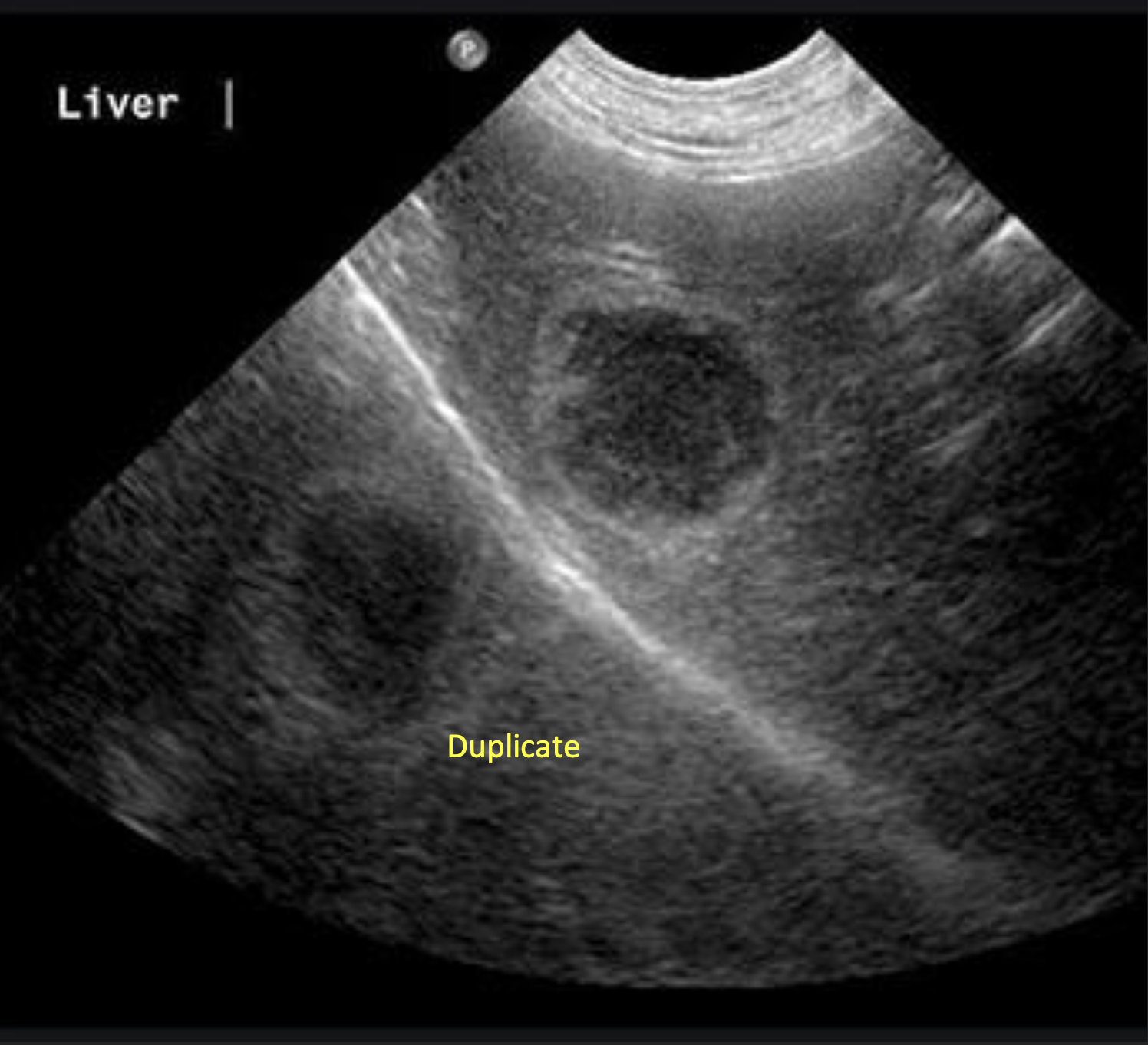
Where is the Mirror Image Artifact most common?
What medium would be the strong reflector?
Thorax/Abdomen Interface
Diaphragm
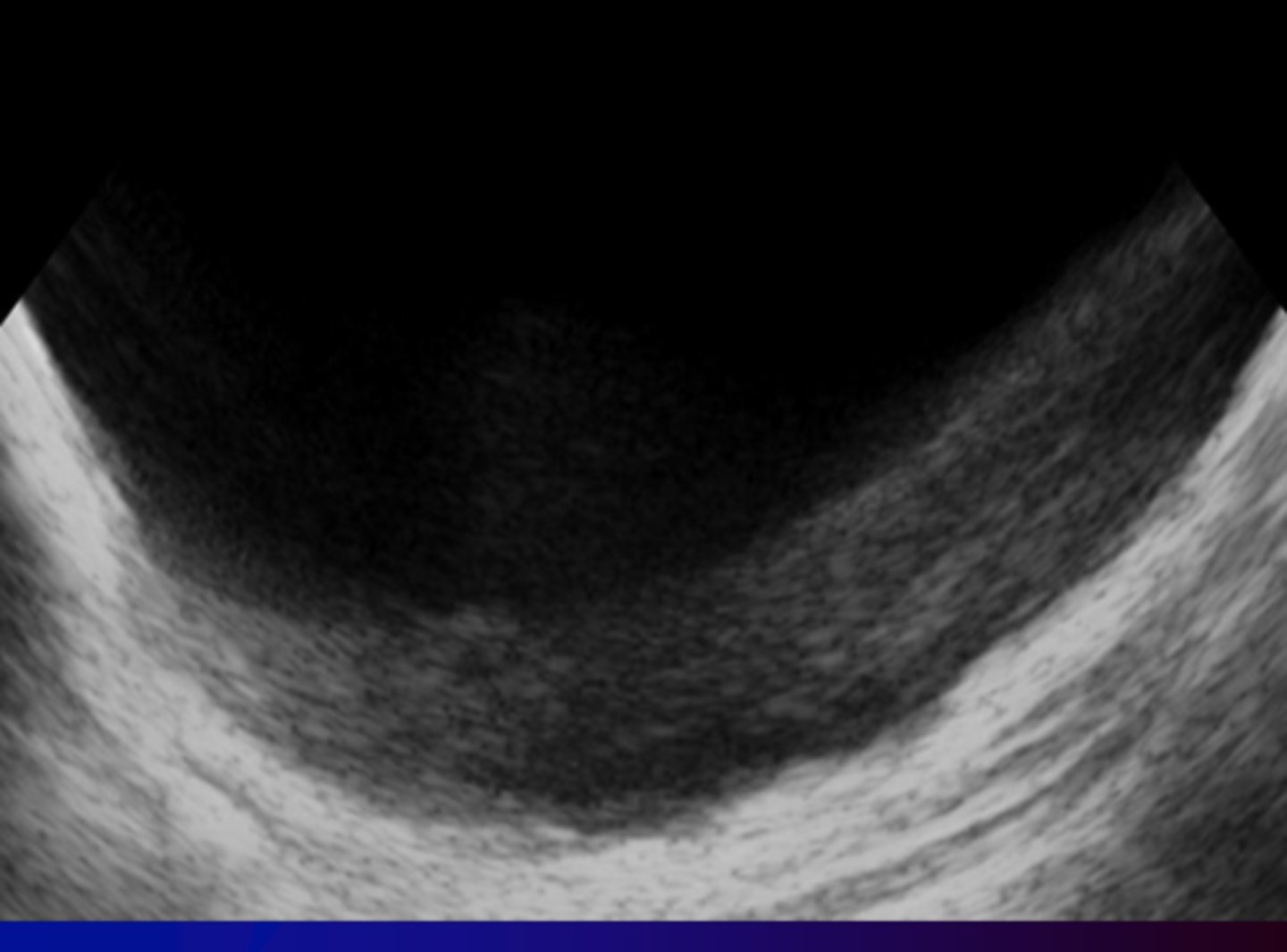
What ultrasound artifact can be seen from imaging a 3D structure with anechoic fluid?
Slice Thickness Artifact
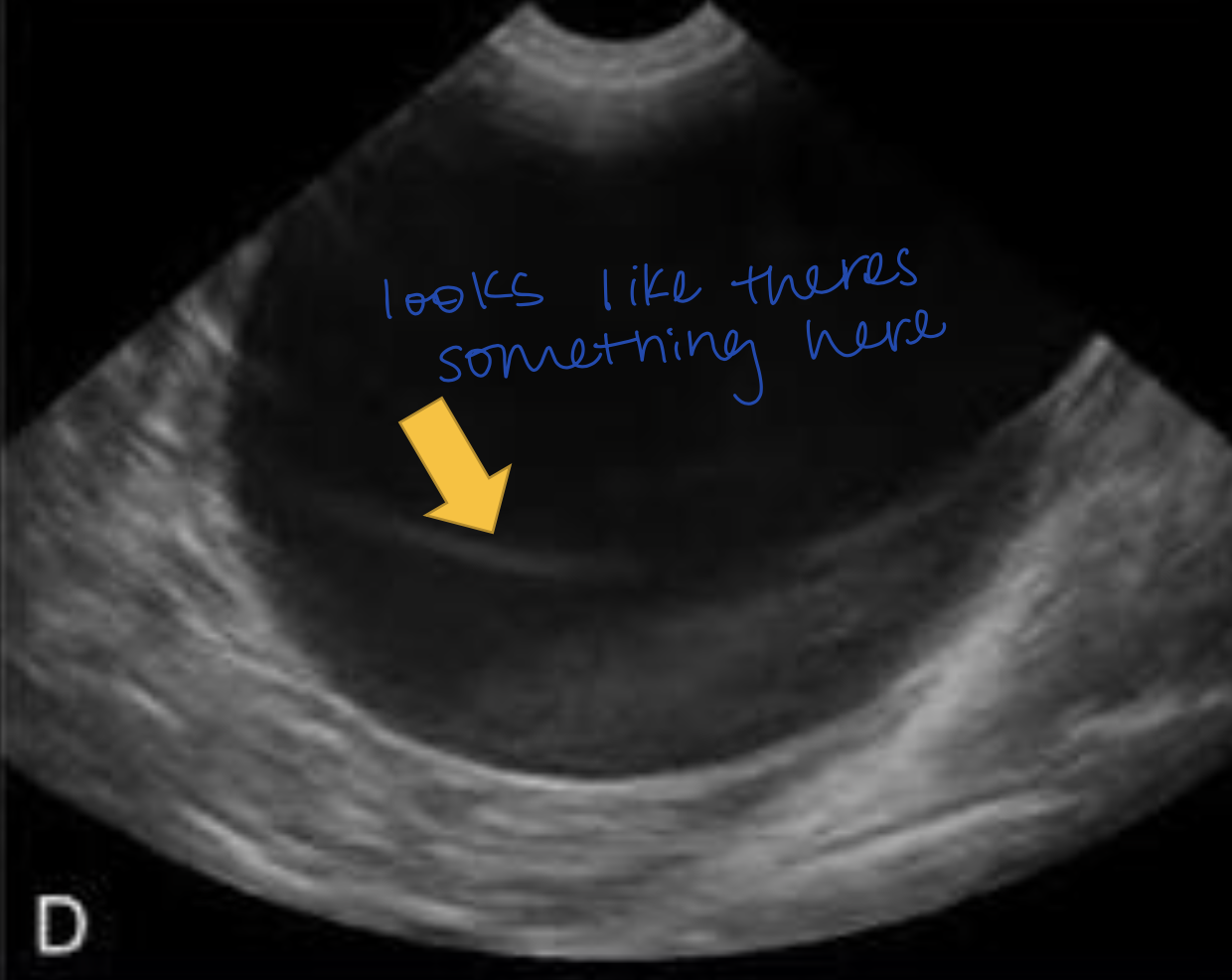
Where does Slice Thickness Artifact most commonly occur?
Gall Bladder and Bladder
can see artificial sludge
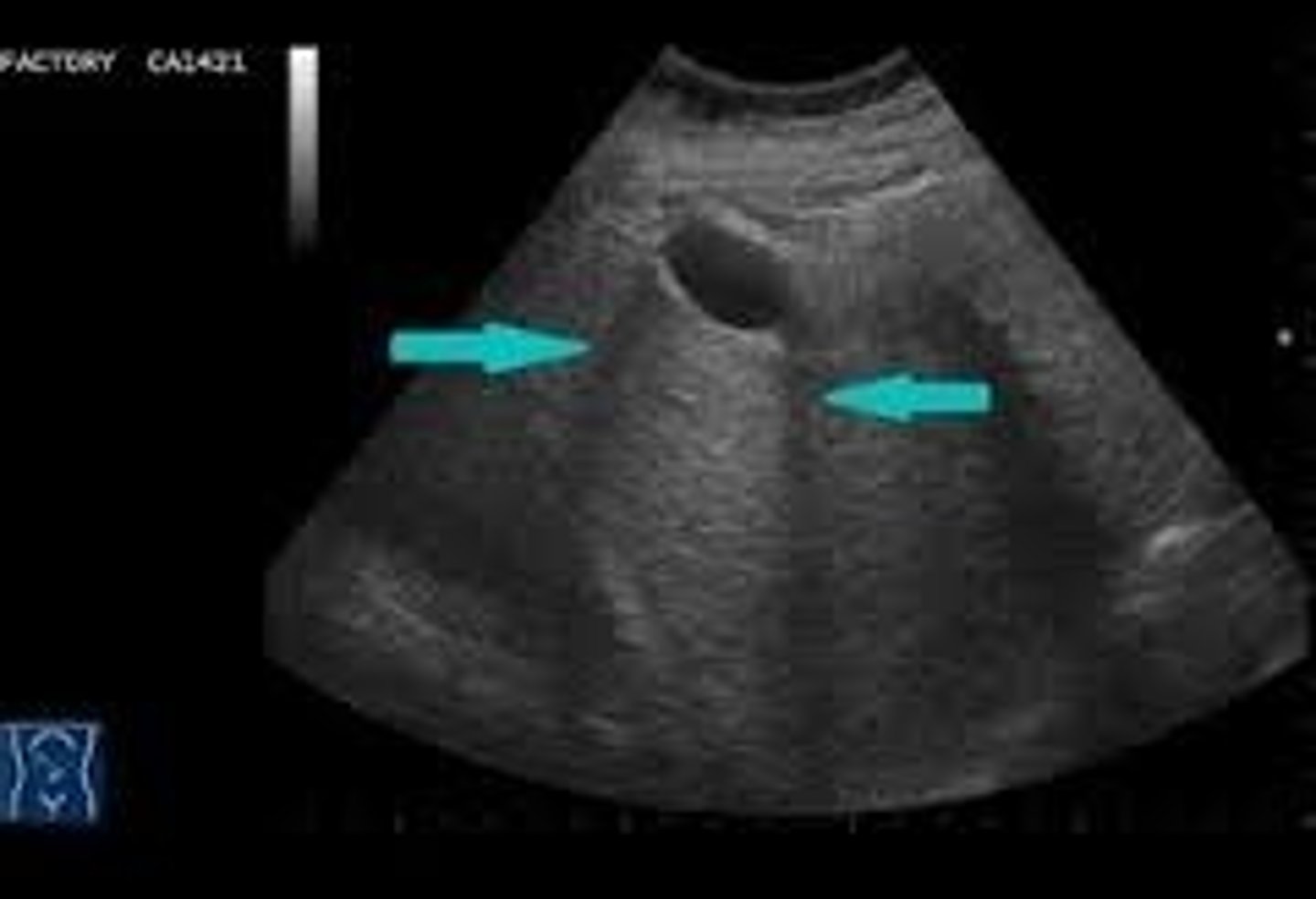
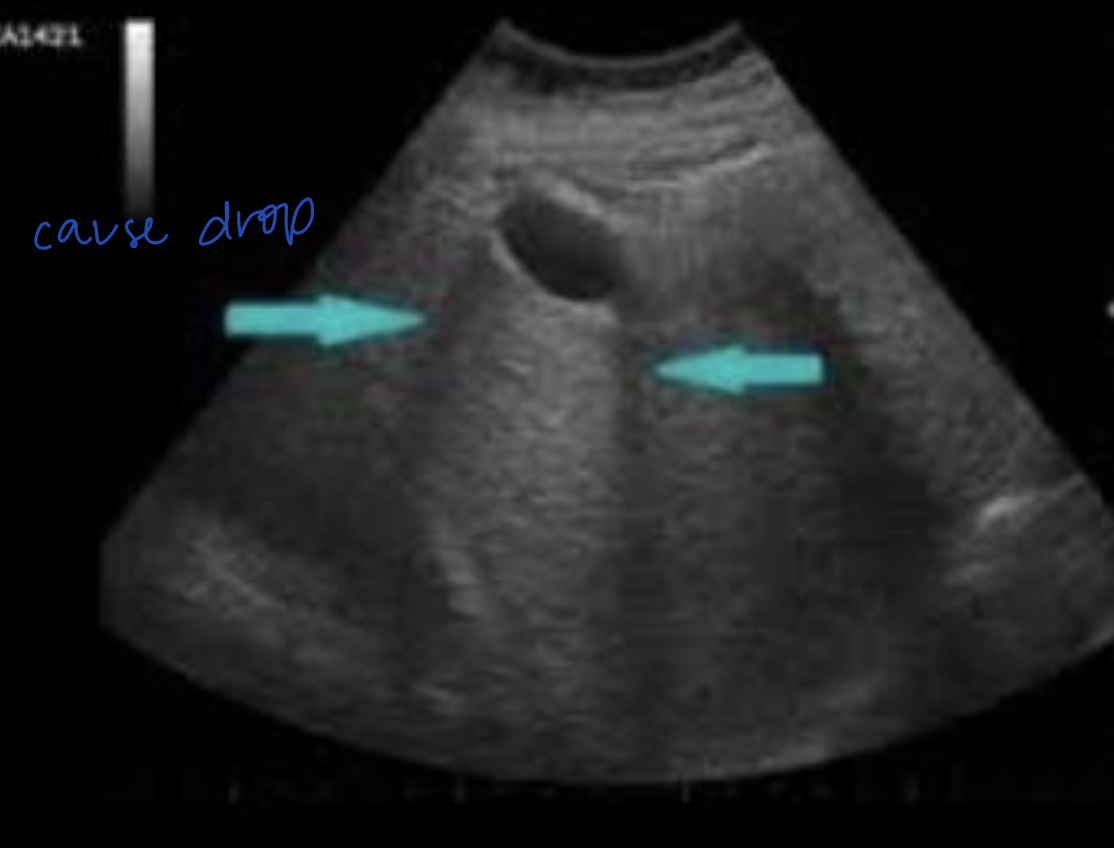
What ultrasound artifact occurs when sound waves bend as they hit a curved surface tangentially?
Edge-Shadowing Artifact
Hypoechoic lines are NOT real
What are the 2 types of ultrasound probes/transducers?
Linear
Curvilinear (sector)
What ultrasound probe is most commonly used for equine tendons?
Linear Probe
What ultrasound probe is most commonly used for LA/SA abdomen and thorax?
Curvilinear (sector) Probe
Can either linear or curvilinear probe be used for SA thorax/abdomen?
Yes
Increased frequency of probe causes greater _____ but less _____
resolution; depth
Decreased frequency - greater _____ but less _____
depth; resolution

What probe frequency would be used for this abdomen? Why?
3-5 mHz = 20-25 cm of depth, low resolution
10-12 mHz = 8 cm of depth, high resolution
3-5 mHz = 20-25 cm of depth, low resolution because of the greater depth

What probe frequency would be used for this abdomen? Why?
Increased or Decreased frequency?
A lower frequency for a greater depth to visualize the abdomen
Any tissue with _____ _____ can be imaged
tendons, ligaments, joints, abdomen, repro tract, heart, thorax
Water content
T/F - You can image the surface of bone and lung for irregularity
True
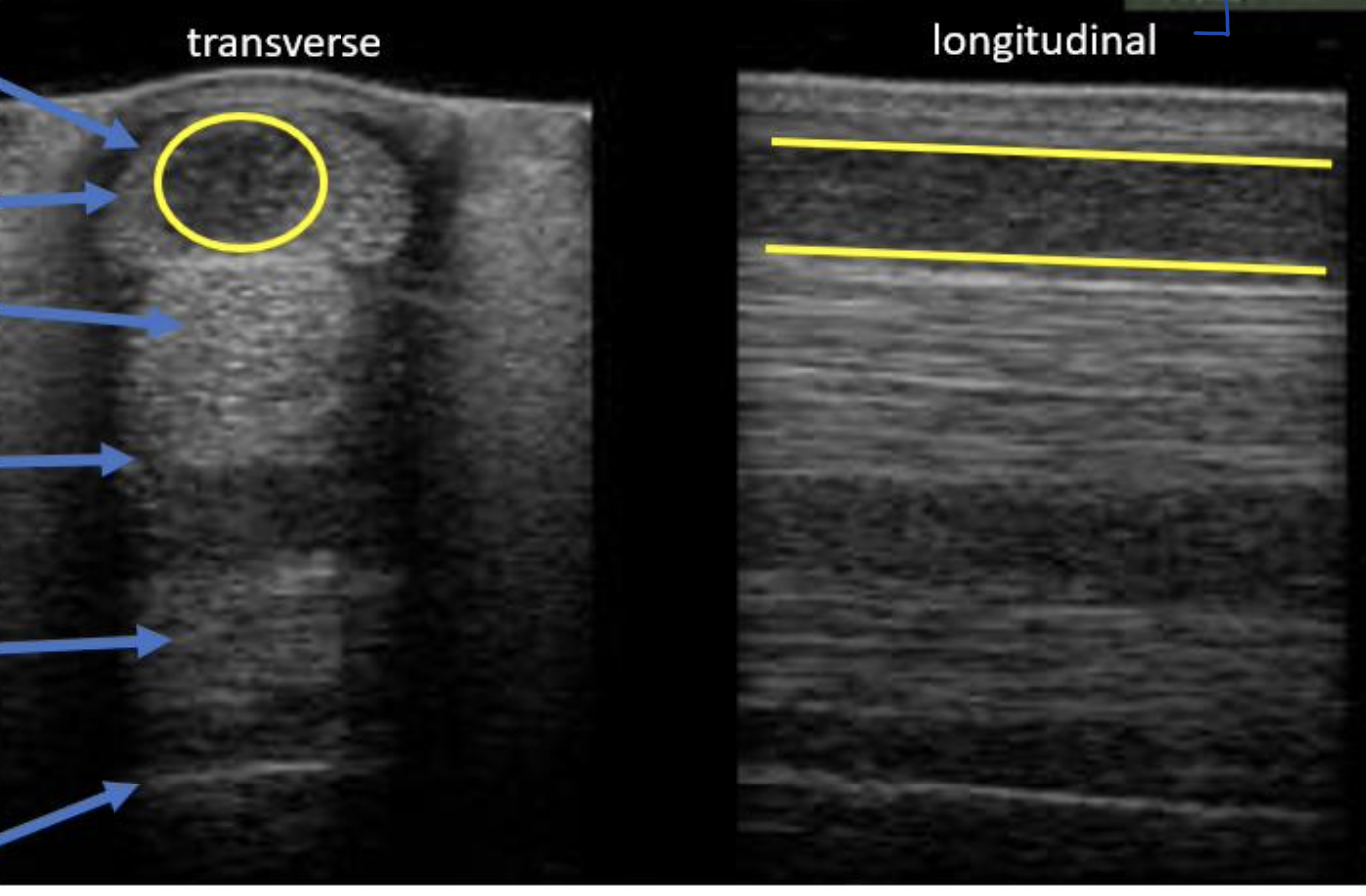
Why does a "core lesion" on the SDF appear dark (hypoechoic to normal)?
Due to loss of collagen fibers and inflammatory edema
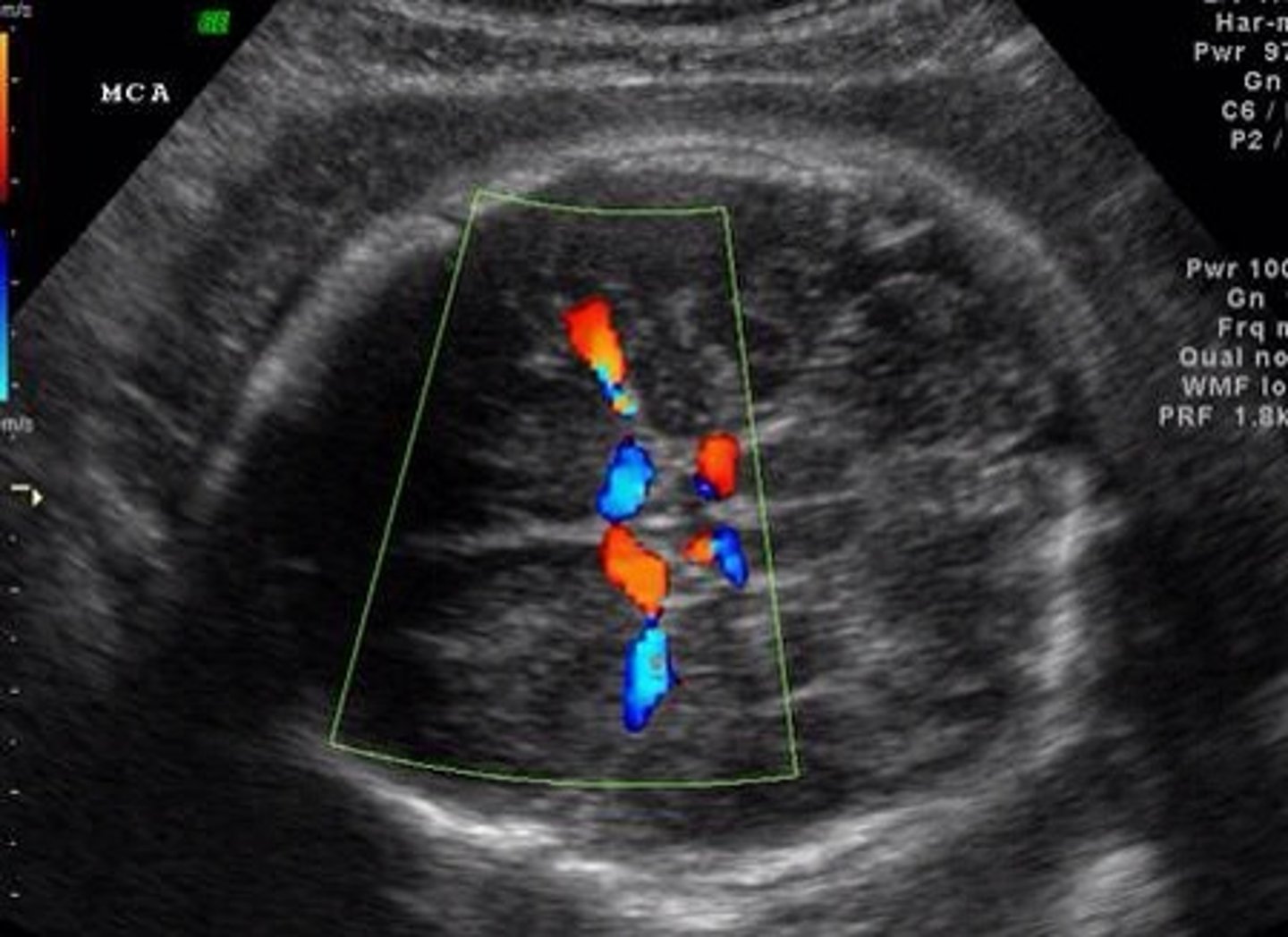
What are the 2 things Real-Time Imaging (doppler mode) can do?
Can measure movement
Ex. heartbeat
Can assess direction of flow
valve regurgitation
What type of diagnostic imaging uses an x-ray tube in circle and rotates at predetermined speed?
Computed Tomography (CT)
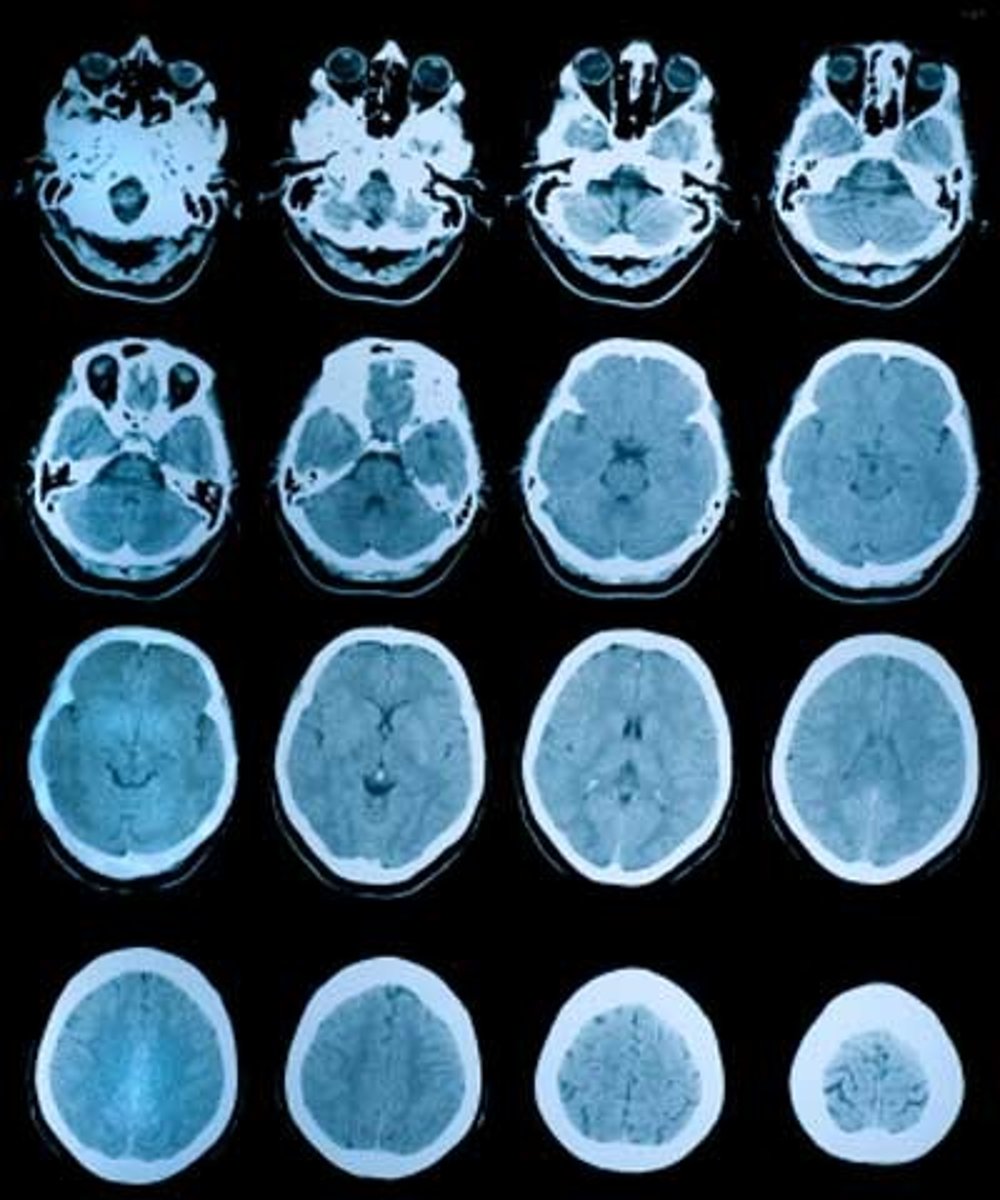
_____ of an x-ray allows for differentiation of structures (like a radiograph) in CT
Intensity
In CT, what reconstructs data acquired from detectors to make a “slice” image?
these sliced images can then be reconstructed into a 3D image
Computer
What term defines when “2D slices allow 3D location by taking MANY views”?
Tomography
What 3 areas is CT imaging in the horse generally limited to?
1. carpus/tarsus
2. digit
3. head
The machine is NOT big enough for the whole body
What are the 4 indications for a CT?
Detailed evaluation of bone
fracture repair planning
Image the head
Image spine
Image the abdomen
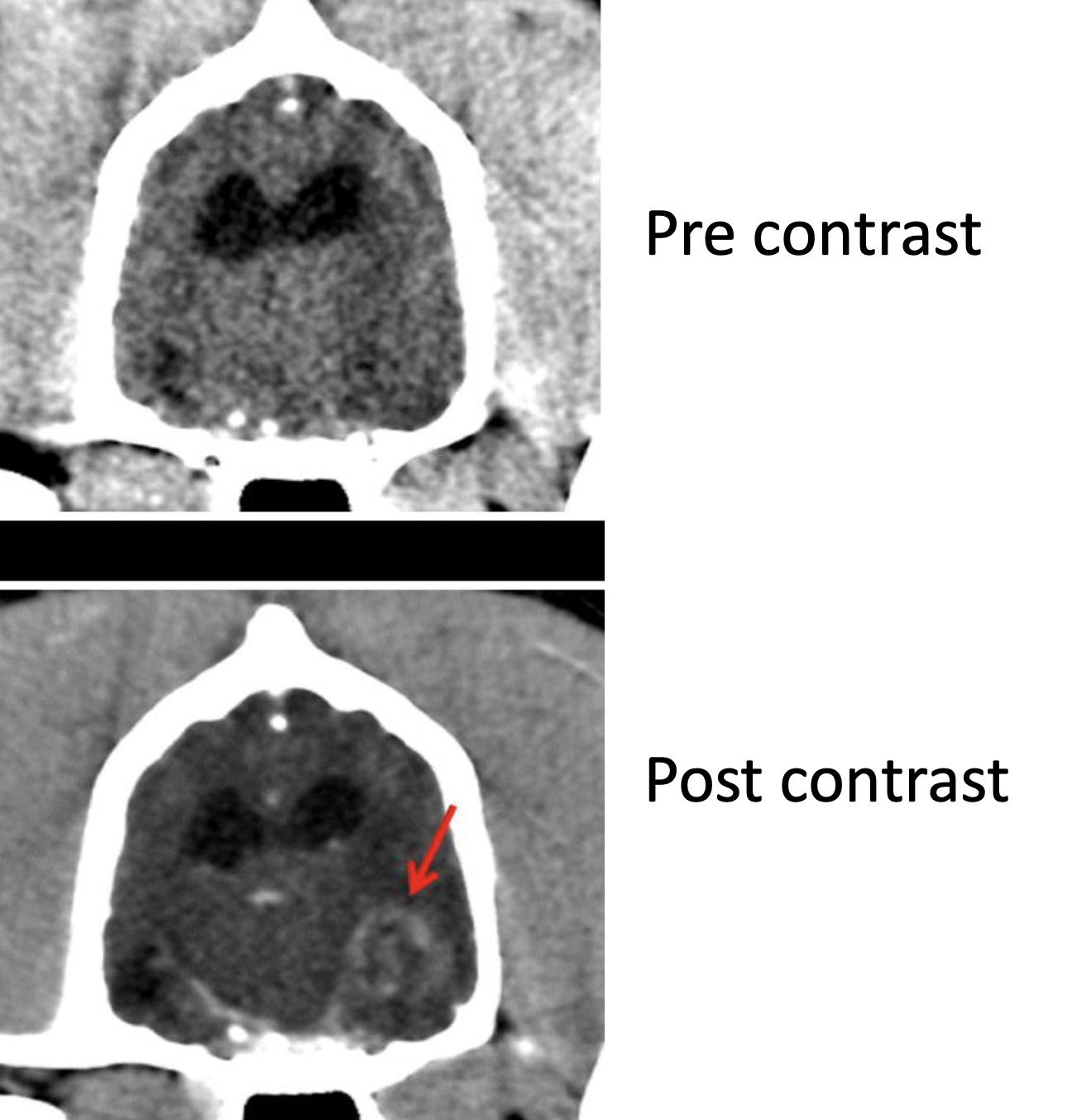
requires injection of contrast solution to enhance contrast of soft tissues
Any imaging of ______ ______ requires injection of contrast solution to _______
Soft tissue
nhance contrast of soft tissues
What diagnostic imaging is described?
All tissues are made of H2O = lots of hydrogen protons
Protons are excited when a STRONG magnet is applied due to radiofrequency pulse
Pulse removed → protons relax → emits signal
Protons in different tissues relax differently
relaxation depends on water content and proton content
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
With what form of imaging must we remove horseshoes and use non-magnetic anesthesia equipment?
MRI
What diagnostic imaging has better contrast resolution and is superior for imaging soft tissues?
MRI
What 2 types of imaging allows for tomography and 3D reconstruction?
MRI & CT
What diagnostic imaging is superior for imaging bone because it doesn't have as much water and is superior for fracture planning?
CT
MRI uses different type of _____ and measure different types of _____ to allow for greater contrast & focus on different types structures (bone vs soft tissue)
pulses; relaxation
When is an MRI indicated in equine?
Imaging areas where ultrasound is NOT possible (foot)
usually used in the foot and for lower limb lesions
What are 4 SA MRI indications?
1. Neuroimaging
2. Musculoskeletal
3. Tumor staging
4. Possible: abdomen and cardiac
What type of imaging is being described?
Inject a drug that is bound to a rapidly decaying radioactive atom called radiopharmaceutical
Gamma camera detects decay of radioactive atom
↑ bone formation → ↑ uptake → ↑ atoms decaying →↑ signal
Nuclear Scintigraphy
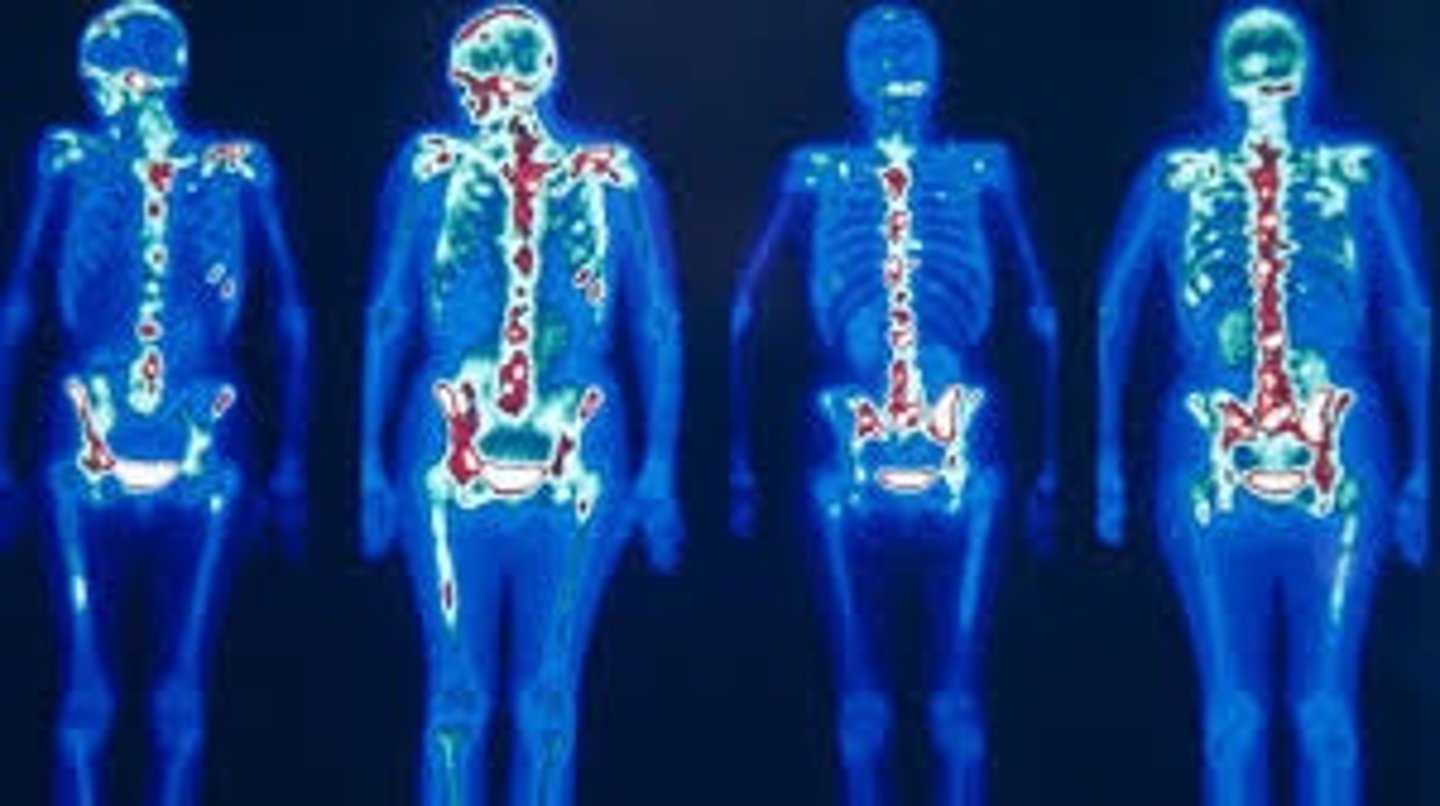
What are these indications for?
Fail to localize lameness with blocks
Localize lameness but no lesions on radiographs or ultrasound
Multiple limb lameness
Upper limb or axial musculoskeletal issue
(Not easily accessible radiographically/Hard to block)
Suspect fracture not imaged on radiographs
Mild, intermittent lameness that precludes blocking
Equine nuclear scintigraphy indications
1. renal function
2. thyroid
3. musculoskeletal
What are the SA nuclear scintigraphy indications?
What imaging modality is associated with the following?
Soft tissue: Minimal
Bone: Good
3D: No
Radiographs
What imaging modality is associated with the following?
Soft tissue: Excellent
Bone: Edge only
3D: No
Ultrasound
What imaging modality is associated with the following?
Soft tissue: Some, need contrast
Bone: Excellent
3D: Yes
CT
What imaging modality is associated with the following?
Soft tissue: Excellent
Bone: Good
3D: Yes
MRI