CVA Nervous
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
Central Nervous Sys
brain + spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous Sys
all other nervous tissue that aren’t the brain or spinal cord
Receptors
cells/ tissues that receive stimuli
Effectors
cells/ tissues that respond to nervous signals
Neurons
nervous cells that transmit information
Neuroglia
support, nourish, protect neurons and bind nervous tissue together
Basic structural and functional unit of the nervous sys
Neuron
How do neurons transmit info?
As nervous impulses/ “action potentials”
Axon
long tail of the neuron that sends signals
Dendrites
part of neuron which branching processes and receive signals
Myelin
Protein covering some axons to speed up transmission
Synapse
Gap @ junction b/w neurons
Neurotransmitter(s)
chemical signals sent from one neuron to another
Peripheral nerves classified by
Innervation
Somatic nerve
serve skeletal muscles, skin, etc.
Visceral nerve
serve int. organs
Afferent (=sensory)
Send signals TOWARD CNS
Efferent (=motor)
Sends signals FROM CNS
Dorsal spinal nerves carry
afferent fibers
Ventral spinal nerve carry
Efferent fibers
Dorsal root ganglia contain
bodies of afferent neurons
Autonomic ganglia contain
bodies of autonomic effector nerves
CN 0 is also known as
terminal nerve
CN I is also known as
Olfactory
CN II is also known as the
Optic
CN III is also known as
Oculomotor
CN IV is also known as
Trochlear
CN O function:
recently discovered but NOT present in birds;
known functions unclear
CN I function:
SENSORY nerve for smell
CN II function:
Not really a nerve, rather an extension of brain;
SENSORY nerve for vision
CN III function:
MOTOR nerve for eye mvmt
CN IV function:
MOTOR nerve for eye mvmt
CN V is also known as
Trigeminal
CN VI is also known as
Abducens
CN VII is also known as
Facial
CN VIII is also known as
Vestibulocochlear
CN V function:
SENSORY + MOTOR nerve to the face;
3 branches: ophthalmic, maxillary, and mandibular
CN VI function:
MOTOR nerve for eye mvmt
CN VII function:
SENSORY nerve for taste and skin + MOTOR (2nd arch);
5 branches to face
CN VIII function
SENSORY nerve for balance (vestibulo—) + hearing (—cochlear)
CN IX is also known as
Glossopharyngeal
CN X is also known as
Vagus
CN XI is also known as
(Spinal) Accessory
CN XII is also known as
Hypoglossal
CN IX function:
SENSORY nerve for taste + MOTOR never (3rd arch)
CN X function:
SENSORY + MOTOR nerve for all over the body
CN XI function:
MOTOR nerve to neck, pectoral girdle, & (maybe) heart
CN XII function:
MOTOR nerve to neck
Cranial nerve evo hypothesis
Each head segment was originally innervated by separate dorsal and ventral roots, similar to modern dorsal and ventral spinal roots
The association b/w CN and branchial arches are
highly conserved across vertebrates
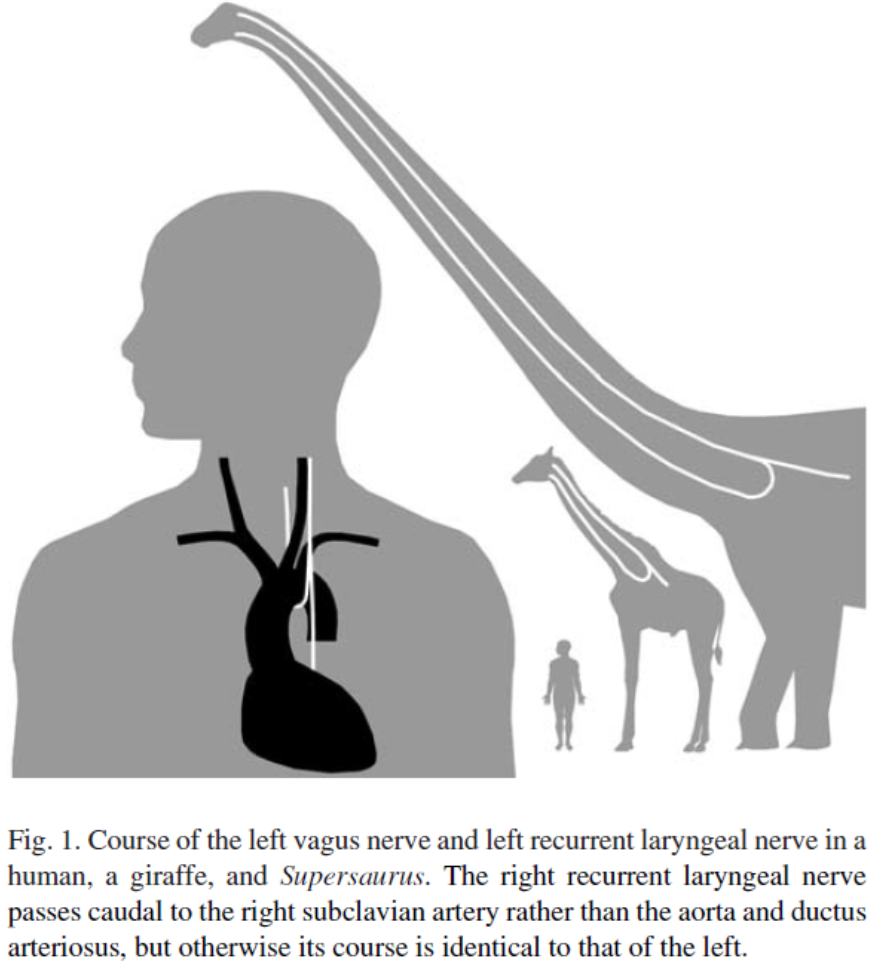
In mammals, the left recurrent laryngeal nerve (RLN) is trapped by
left aortic arch during development
Autonomic nervous sys controls
involuntary, internal processes to maintain homeostasis
Sympathetic nervous sys
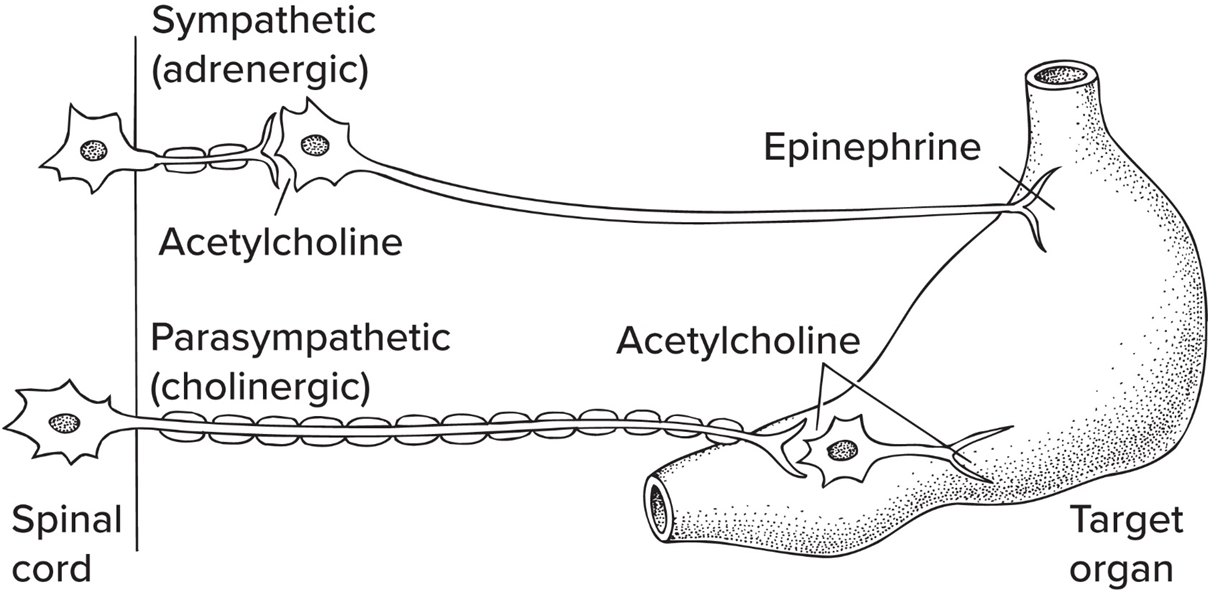
“fight or flight”, prepares for activity, slows digestion
Parasympathetic nervous sys
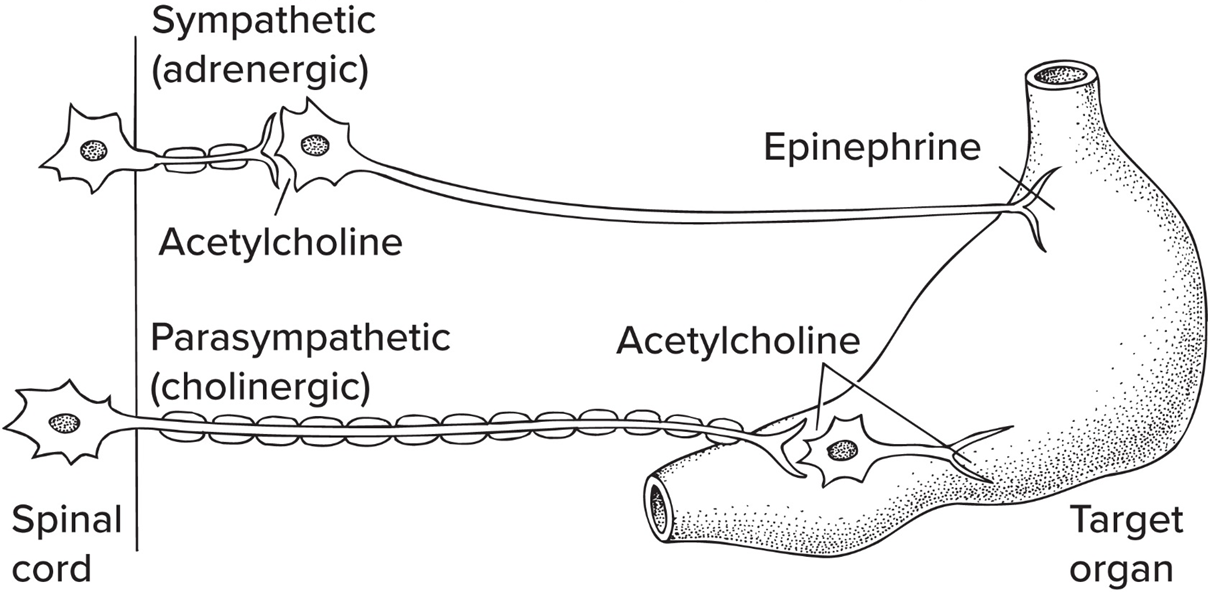
“rest and digest”, lowers activity level, promotes digestion
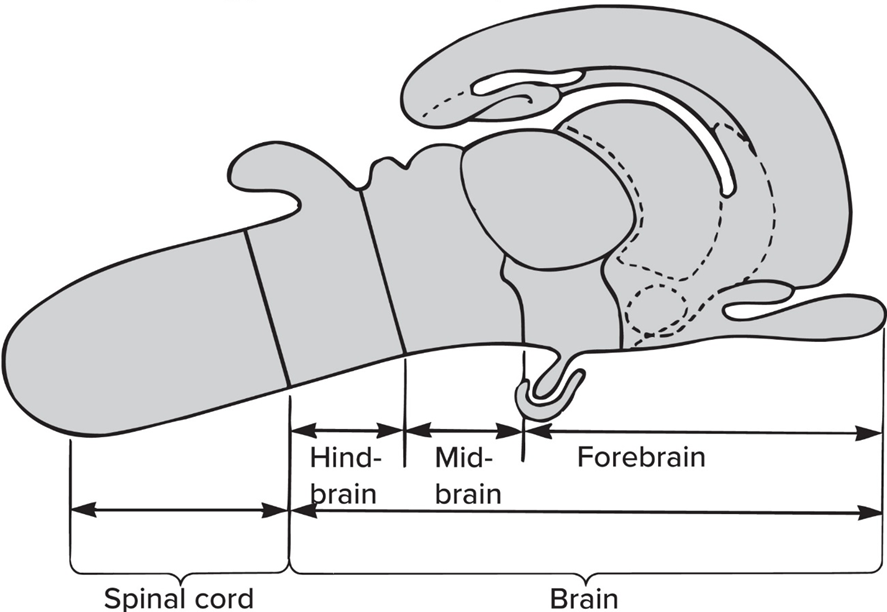
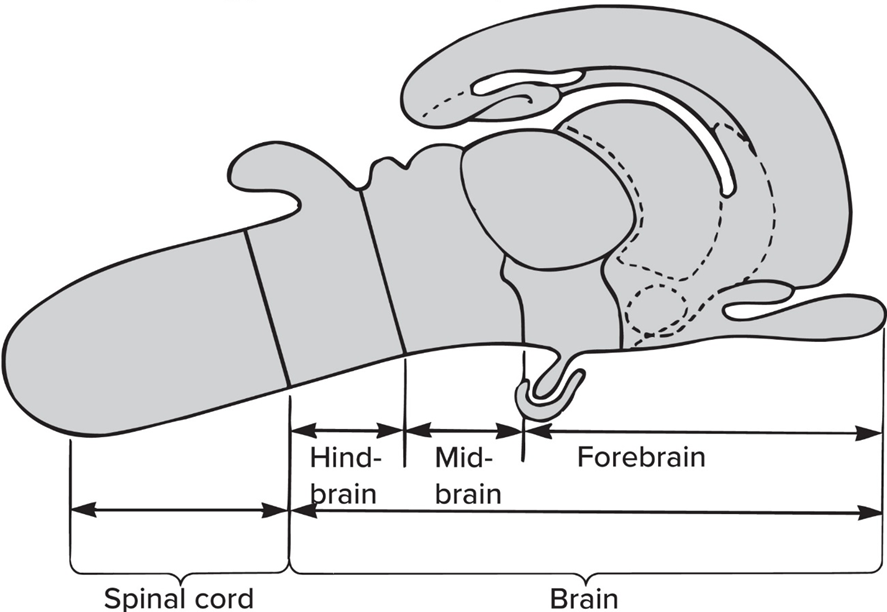
The Hindbrain consist of
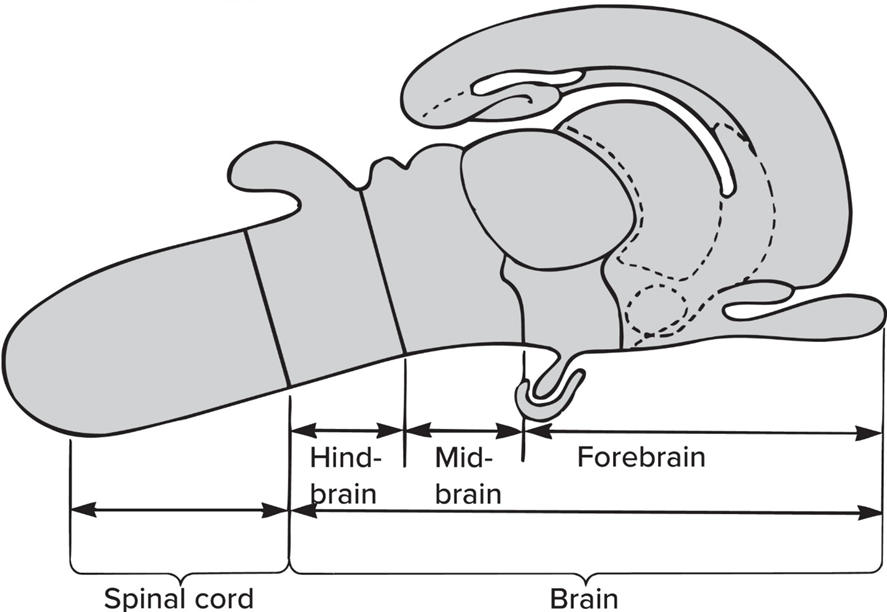
Medulla oblongata + Pons + Cerebellum
The Midbrain consist of
Tectum (SEONSORY) +Tegmentum (MOTOR)
The Forebrain consist of
Cerebrum + Diencephalon
The “brain stem” incl hindbrain + midbrain EXCEPT
Cerebellum + Colliculi
Forebrain enlargement ass. w/
Increased reliance on olfaction (smell);
Complex behaviors and motor control;
Terrestrial posture and locomotion in amniotes
Forebrain enlarges in EVERY vert. group; related to—
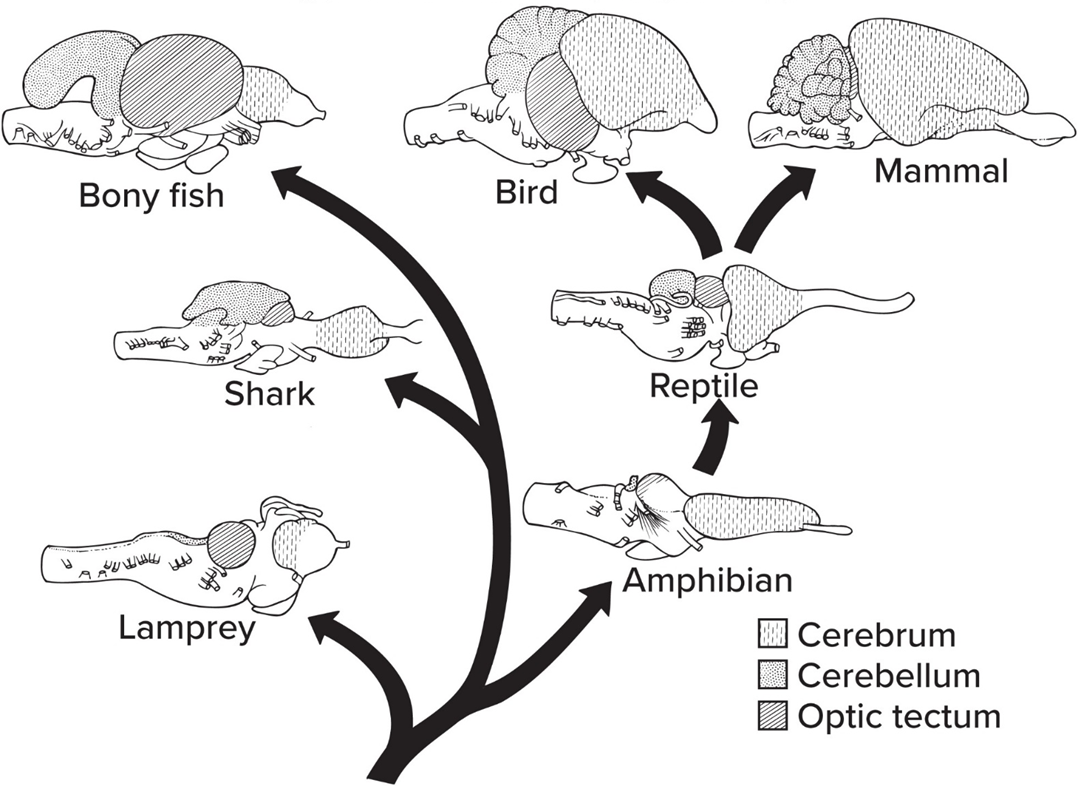
which function are needed for lifestyle
Medulla oblongata function:
manages many autonomic processes
Pons: built + function
enlargement of hindbrain floor in mammals; manages comm. b/w cerebellum and cerebrum
Cerebellum function
manages but does not initiate motor signals
The cerebellum is ABSENT in
agnathans
The cerebellum, is PRESENT in
gnathostomes
Tectum: location and function
dorsal part, processes SENSORY input
Superior and inferior colliculi are
parts of tectum in mammals
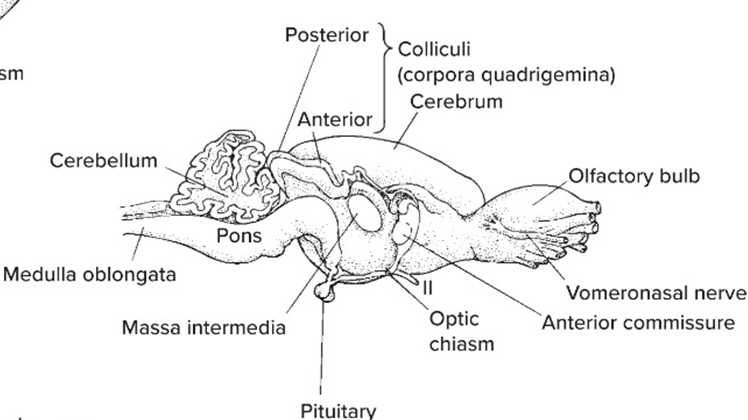
Optic tectum is
visual part of tectum in most vertebrates
Torus semicularis
Lateral line part of tectum in fish
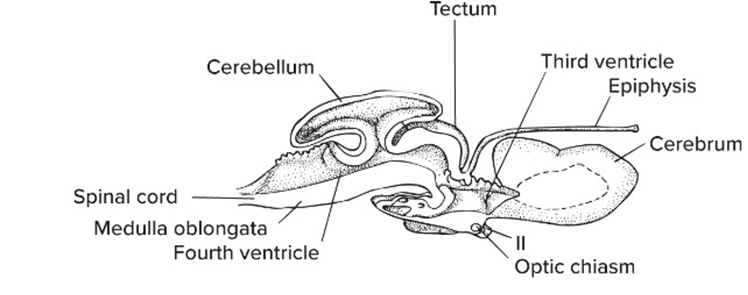
Tegmentum function + location
ventral part, sends MOTOR signals via CN III + IV
Midbrain phylogeny in Fishes & Amphibians
Midbrain usually most prominent part of brain;
Tectum receives direct input from eyes (CN I), skin, and ears/semicircular canals (CN VIII);
Tegmentum also quite large
Midbrain phylogeny in Amniotes
Tectum relays visual and auditory input to cerebrum via thalamus (as in all vertebrates);
Amniotes (esp. mammals) can also get visual information directly from thalamus to cerebrum
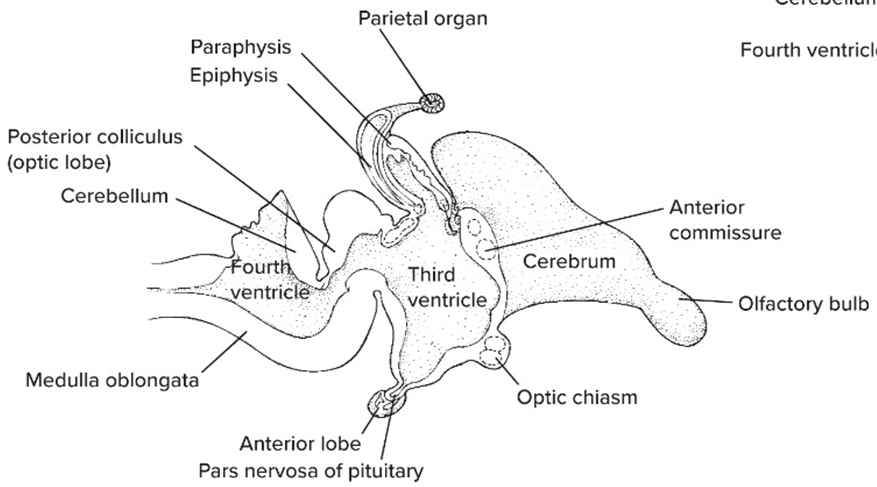
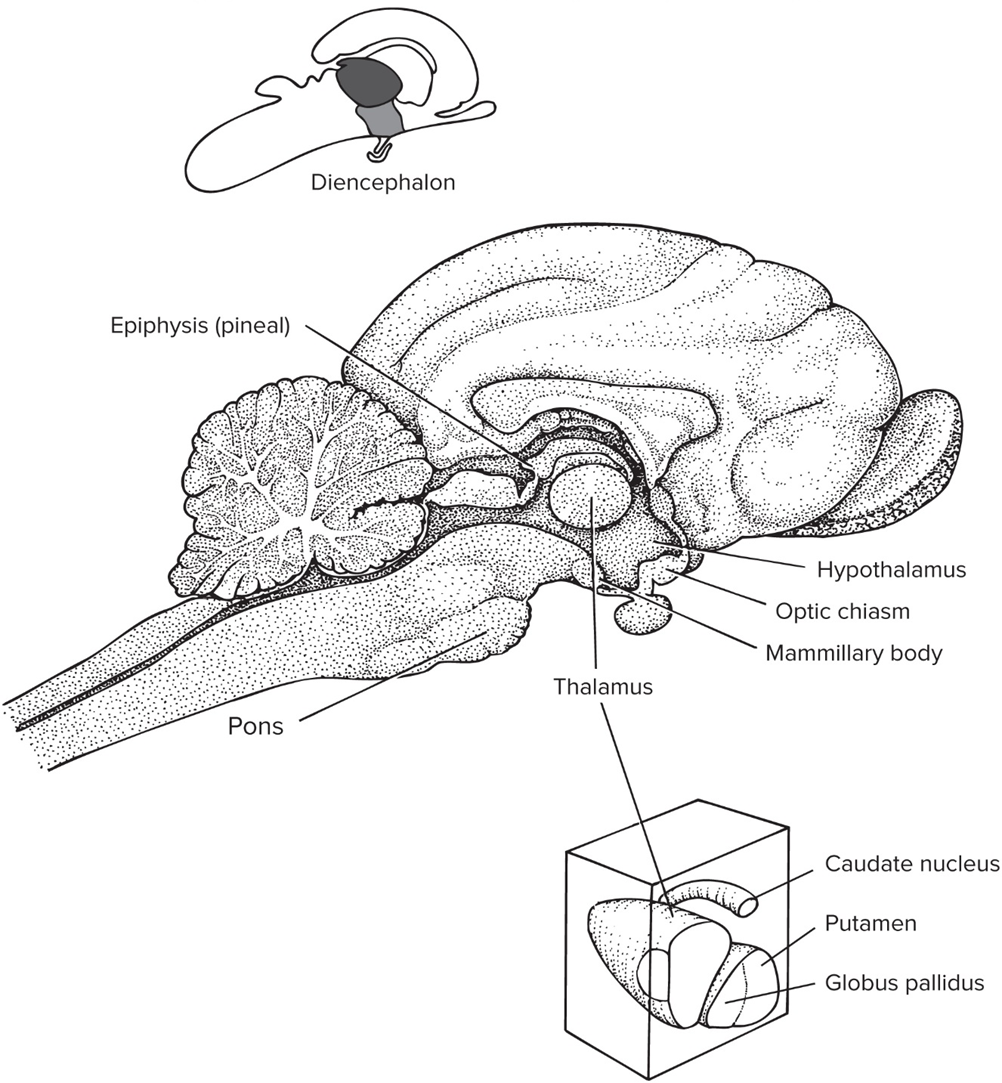
Diencephalon
forebrain outside of cerebrum
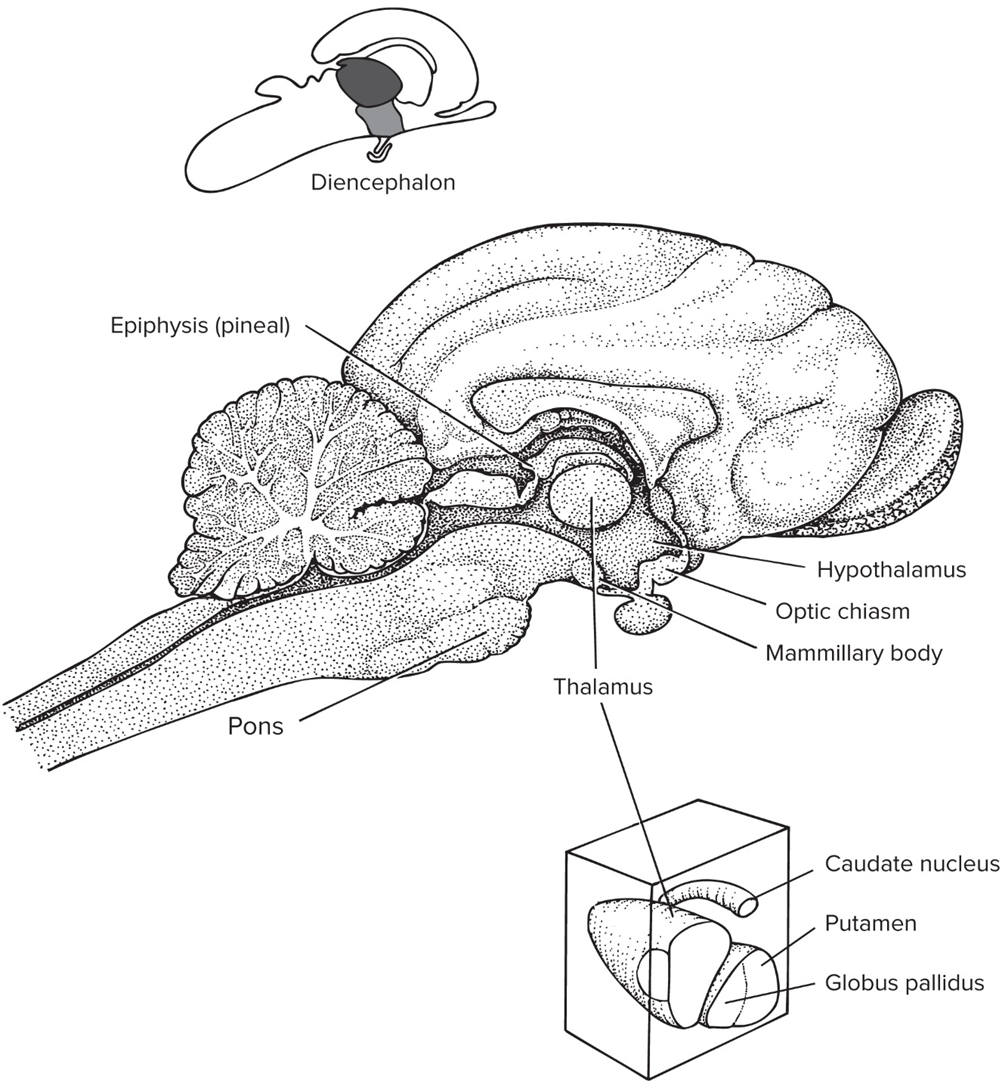
Epithalamus
includes pineal gland that’s involved in circadian rhythms
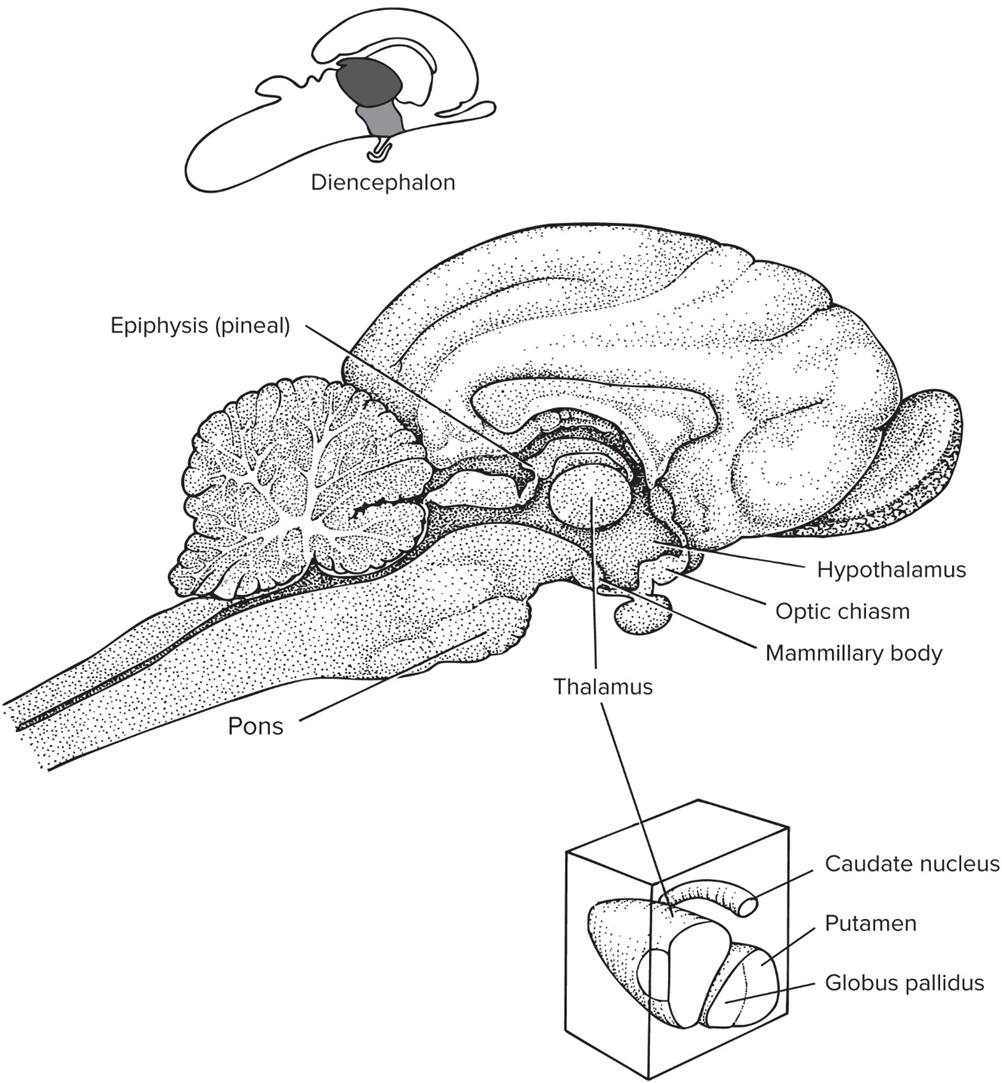
Hypothalamus
manages aspects of homeostasis
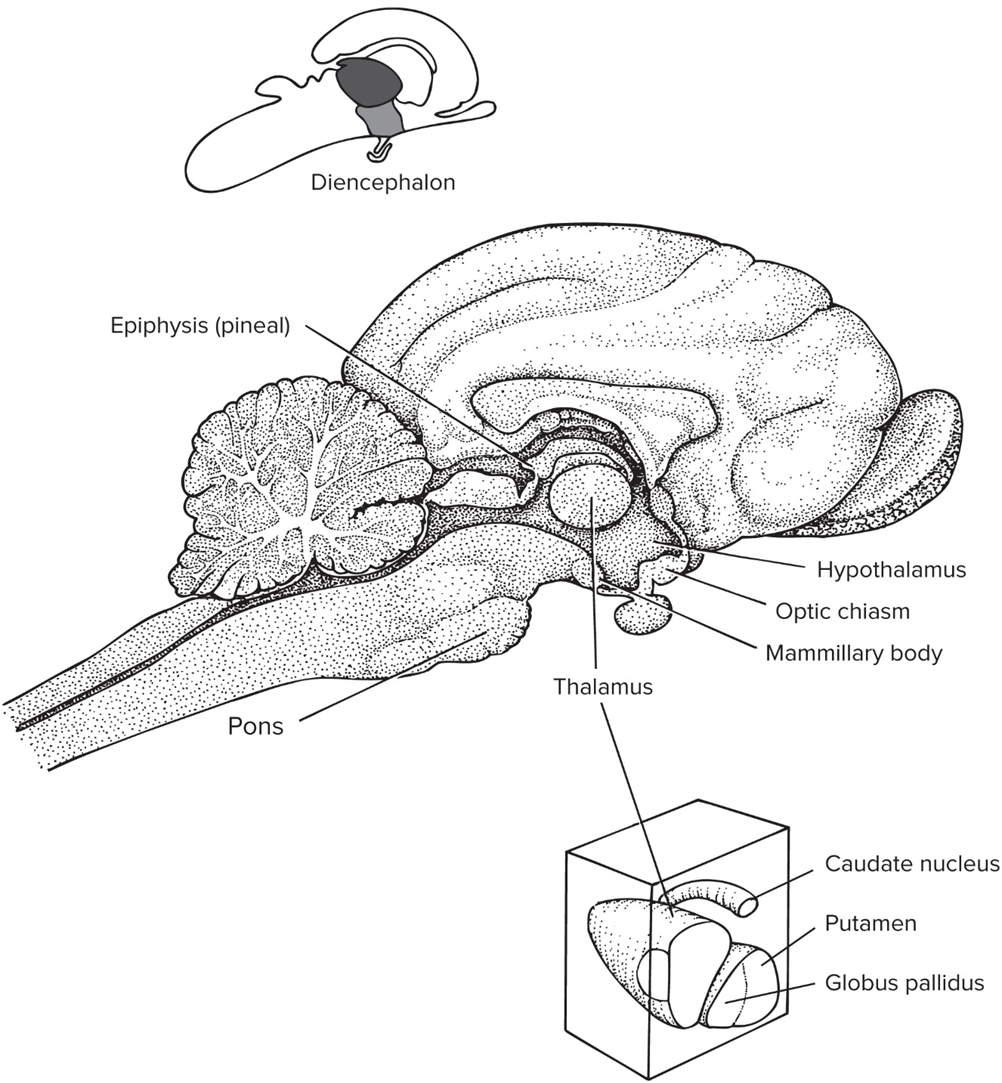
Dorsal thalamus aka Thalamus
coordinates incoming sensory signals to other part of brain
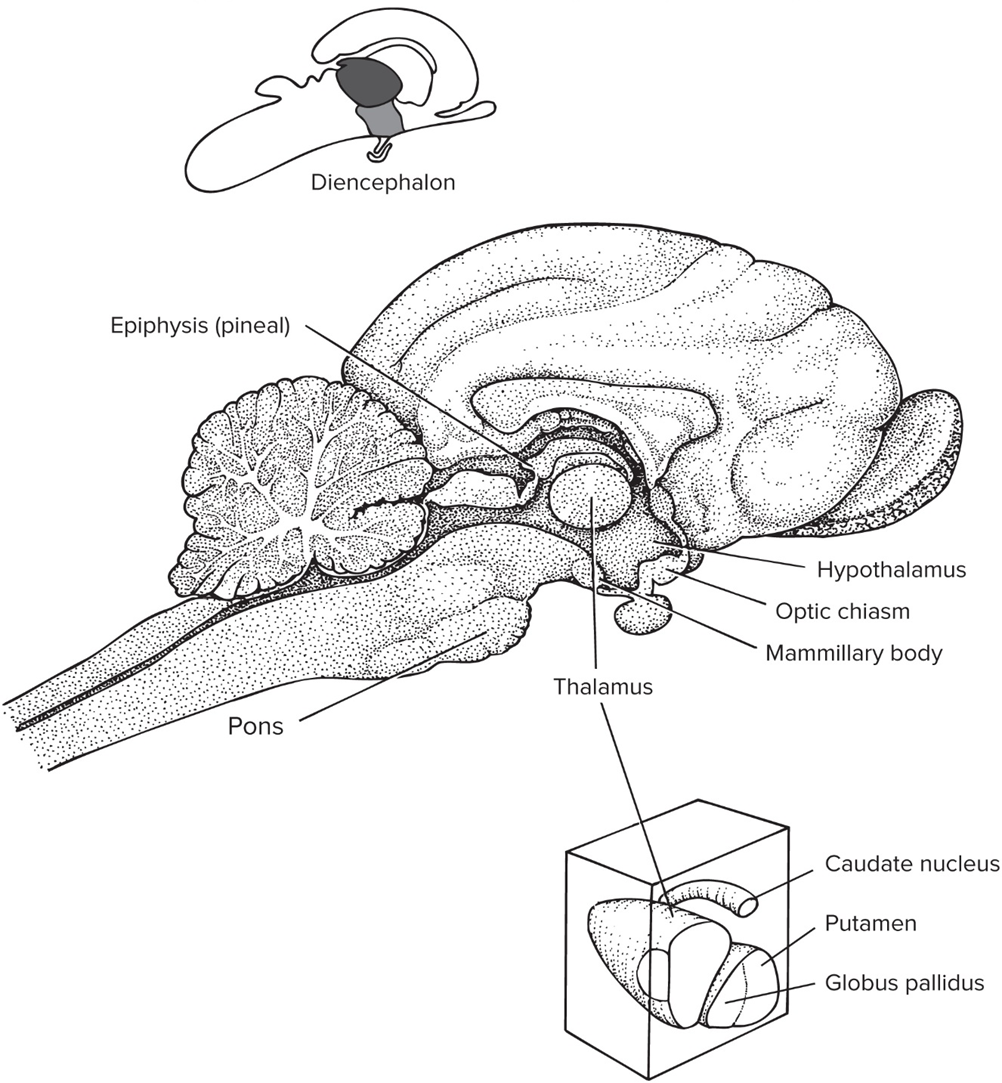
Ventral thalamus
small region b/w midbrain and diencephalon
Cerebral hemispheres are connected via
corpus callosum
SENSORY input is processed in
specific areas of telencephalon