UTA Anatomy & Physiology 1 Exam 1
1/151
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
152 Terms
Anatomy
The study of body structures of an organism an their relationship to each other
Gross Anatomy
large body structures visible without the aid of a microscope
Microscopic Anatomy
Small body structures only visible with the aid of a microscope.
Vital Functions of the organ systems
-separation of internal/external environments
- movement
- responsiveness to stimuli
- digestion/absorption
- metabolism
- excretion
- growth
Non vital to individual, but vital to species
reproduction
Homeostasis
dynamic state of equilibrium and focuses on balance.
Survival Needs for homeostasis
nutrients
ions
water
oxygen
normal body temp
appropriate atompsheric pressure
Homeostasis is maintained by
negative feedback (response to decrease or eliminate the stimulus ex. temp - your temp increases, you sweat to release heat, your body temp decreases. As your body temp decreases, the amount of sweat decreases)
positive feedback (stimulus causes a response and enhances the response until it stops. ex. bleeding - damage blood vessel, platelets adhere to damaged site, release chemical to attract more platelets, plates adhere to damaged site and so on.)
Standard Anatomical Position
erect body, feet slightly apart, palms forward, thumbs pointing away from body
Superior
top part of the trunk (cranial)
Inferior
toward the bottom
Cranial vs Caudal
Cranial - toward head
Caudal - toward tail or tailbone
Posterior or Dorsal
back
Anterior or ventral
belly region
proximal
Closer to the point of attachment
distal
farther from the origin of a body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
deep
below the muscle
ex. knife cut into the muscle
superficial
above the muscle
ex. papercut
medial
toward the midline
lateral
away from the midline
Regional Terms
Anatomical terms that refer to specific visible landmarks on the surface of the body
frontal
forehead
Orbital
eye
occipital
back of head
otic
ear
nasal
nose
buccal
cheek
oral
mouth
Cephalic
head
cervical
neck
thoracic
chest
sternal
breastbone
axillary
armpit
mammary
breast
abdominal (umbilical)
navel
Pelvic
pelvis
Inguinal
groin
Pubic
genital region
Acromial
point of shoulder
Brachial
arm (bicep area)
Antecubital
anterior surface of elbow
Olecranal
elbow (Posterior)
Antebrachial
forearm (both anterior and posterior)
Carpal
wrist
palmar
palm
digital
fingers, toes
femoral
thigh
Patellar
anterior knee
Popliteal
posterior knee area
Crural
leg (shin)
Sural
Calf or posterior surface of the leg
Fibular
lateral part of leg
tarsal
ankle
Calcaneal
heel
plantar
sole of foot
Scapular
shoulder blade
Vertebral
spinal column
Lumbar
lower back
Sacral
Posterior region between the hip bones
Gluteal
buttock
perineal
posterior region between the anus and external genitalia
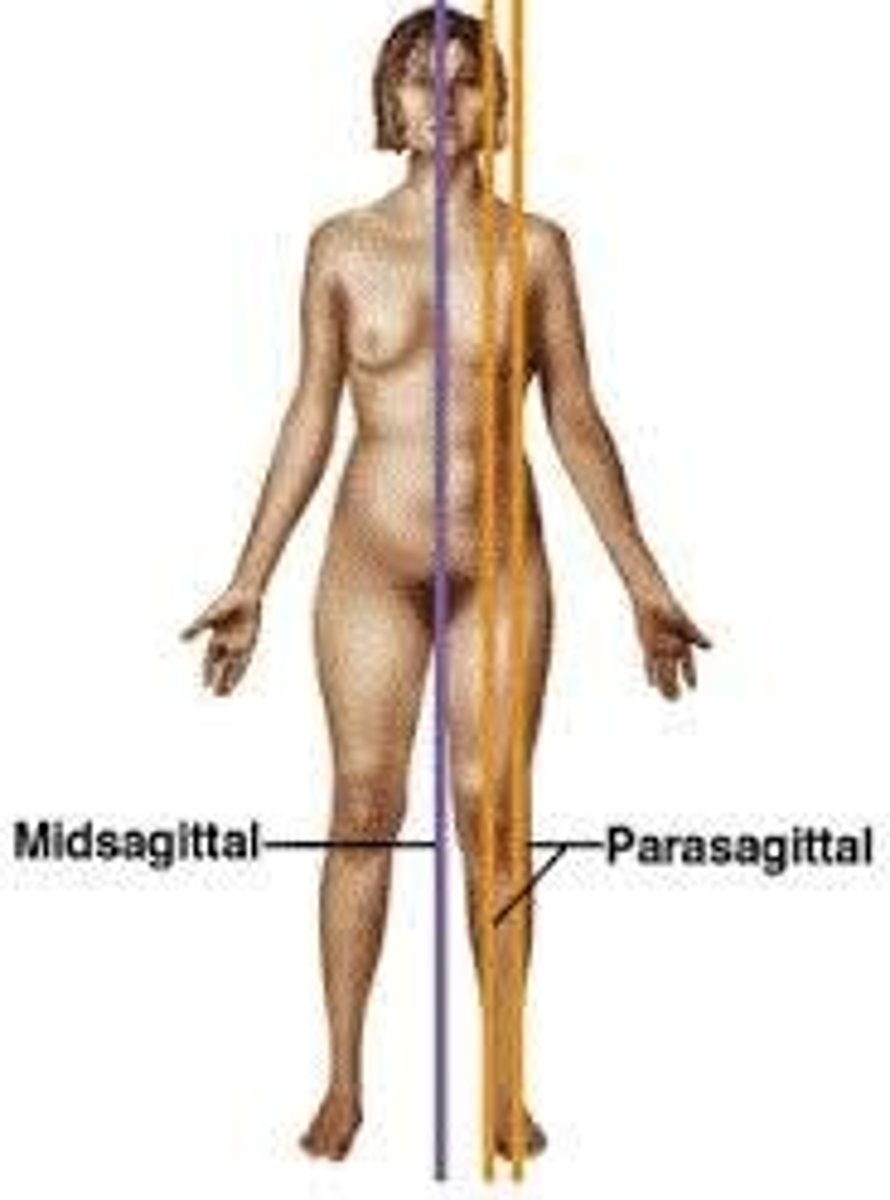
Median (midsagittal) plane
vertical plane that divides the body into right and left halves
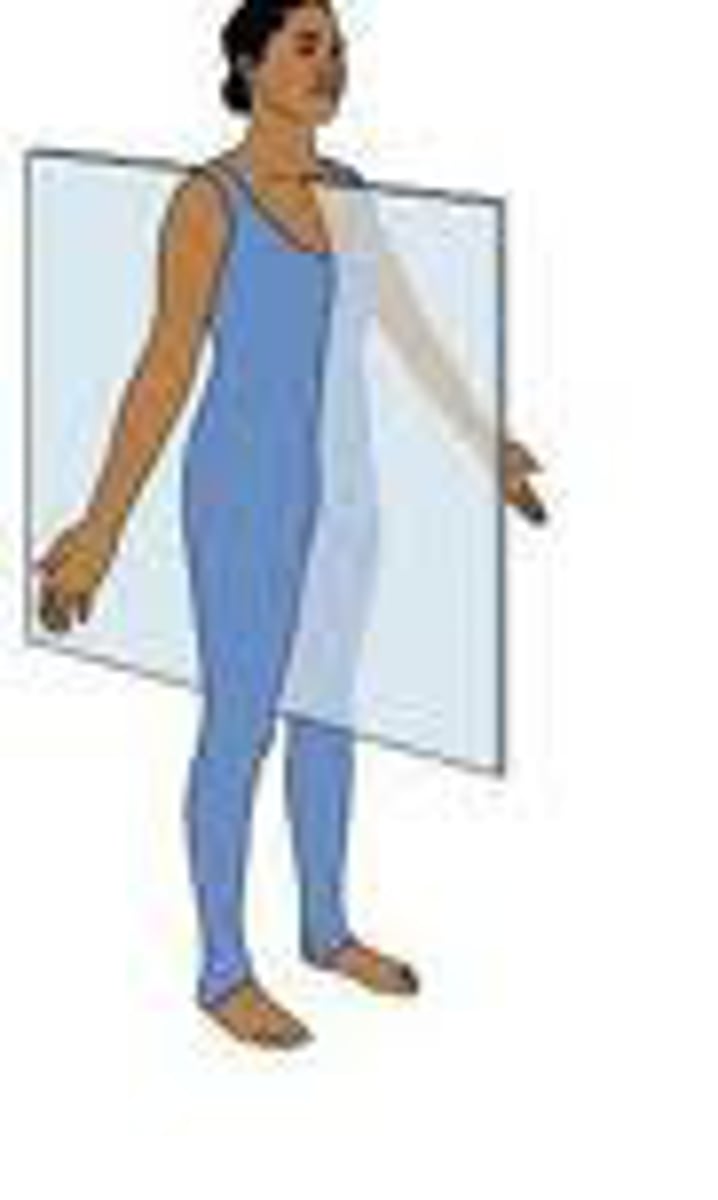
Parasagittal plane
Divides body into unequal right and left sides
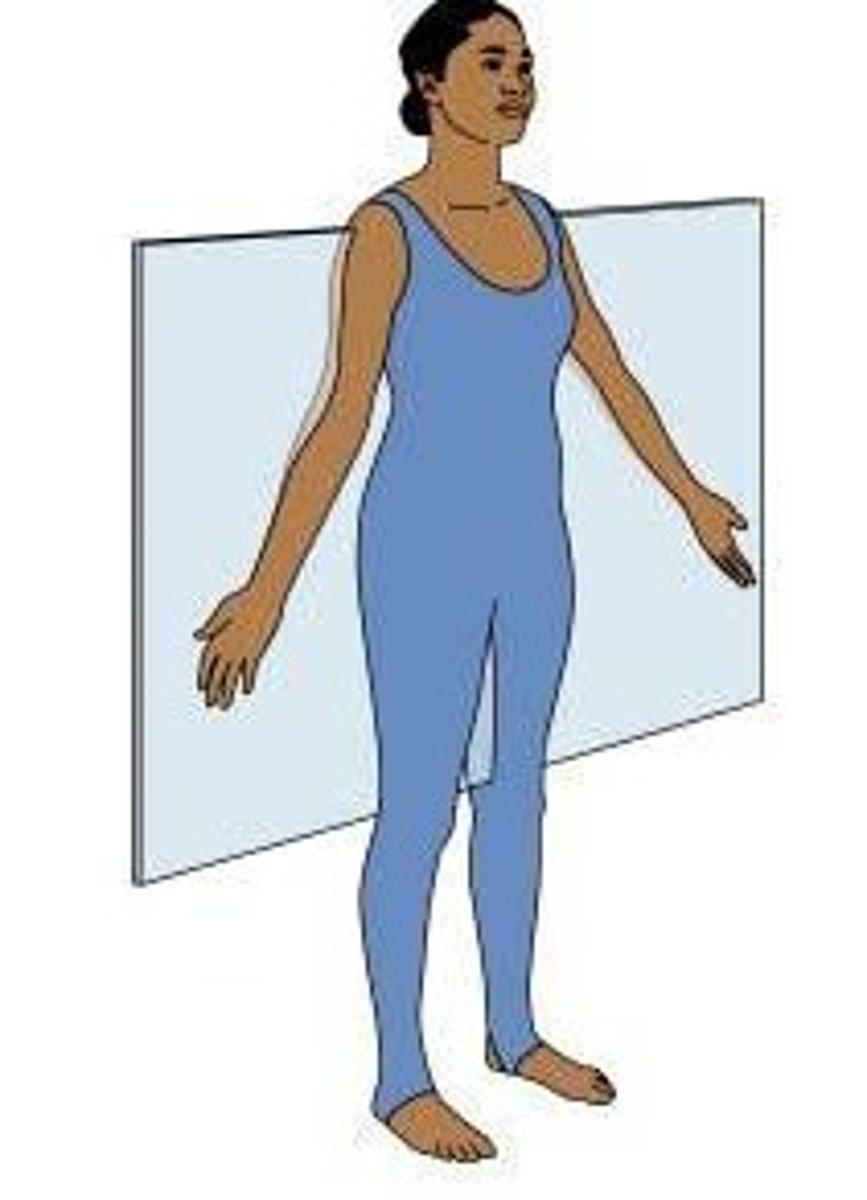
frontal plane (coronal plane)
Divides the body into front and back portions.
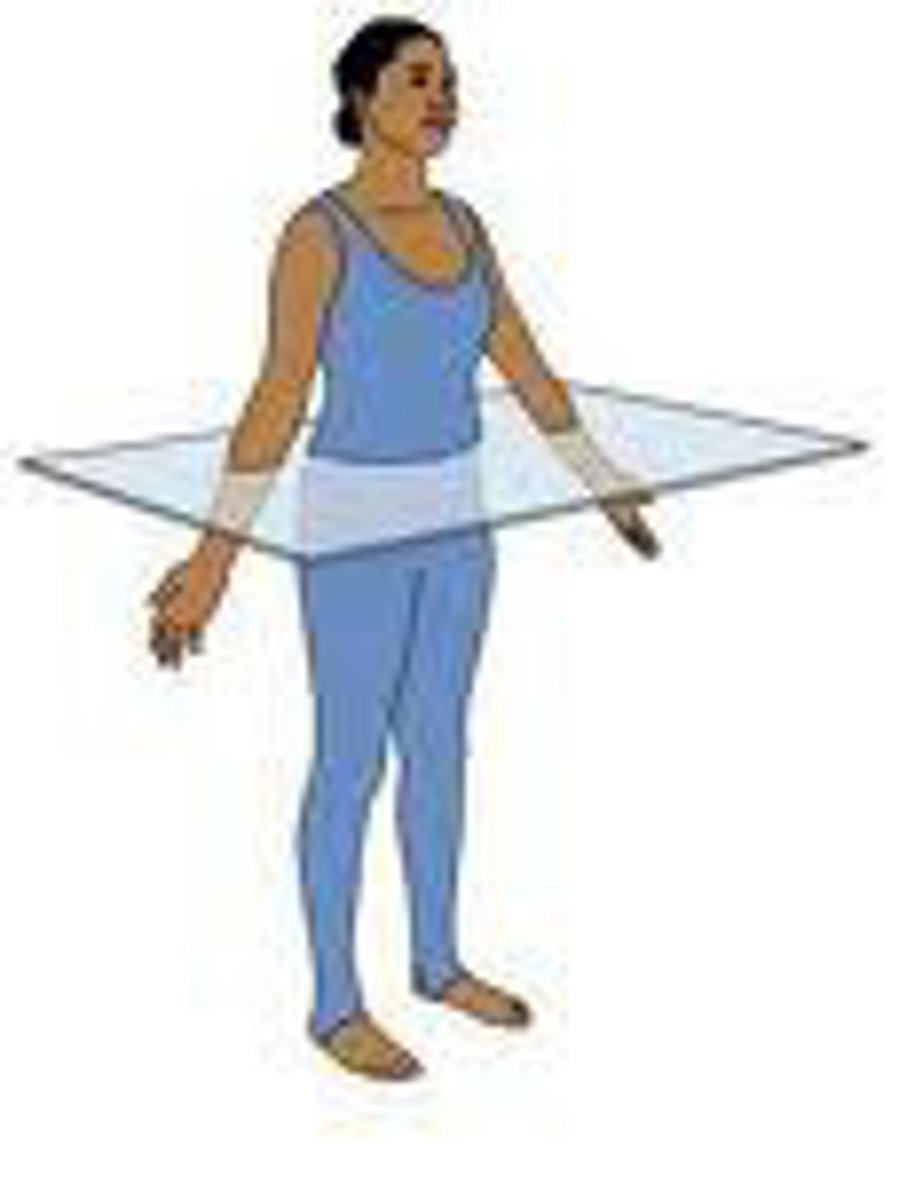
Transverse Plane
horizontal division of the body into upper and lower portions
dorsal cavity
includes the cranial and spinal cavities.
mental
chin
Pollex
thumb
Dorsal body cavity
cranial cavity and vertebral cavity
protects nervous system organs
Ventral body cavity
thoracic, abdominal, and pelvic cavity
cranial cavity
contains the brain
Vertebral Cavity (Spinal Cavity)
contains the spinal cord
thoracic cavity
cavity housing lungs and heart
ribs help protect
pleural cavity
space around each lung
precardial cavity
space around the heart
abdominal cavity
not heavily protected. vulnerable.
stomach, liver, kidney. Adipose provides protection
pelvic cavity
ovaries, testes, urinary bladder.
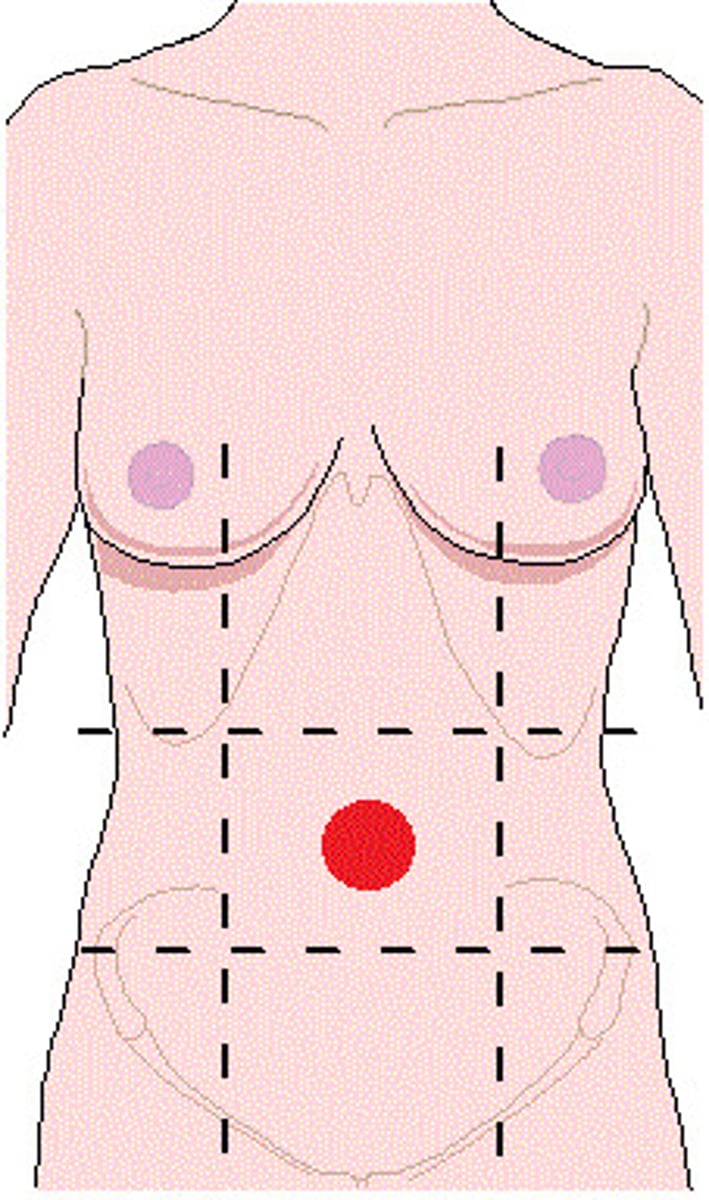
umbilical region
region of the navel
Tissues
Groups of cells with a common structure and function.
Organs
Groups of tissues that work together to perform a specific function or related functions
Integumentary system
skin and its derivatives; provides the external protective covering of the body
skeletal system
system of protection and support composed primarily of bone and cartilage
muscular system
organ system consisting of skeletal muscles and their connective tissue attachments
nervous system
the network of nerve cells and fibers that transmits nerve impulses between parts of the body.
endocrine system
body system that includes internal organs that secrete hormones
cardiovascular system
Organ system that distributes the blood to deliver nutrients and remove wastes.
lymphatic system
system consisting of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, and lymph; drains excess tissue fluid from the extracellular space. The nodes provide sites for immune surveillance.
respiratory system
organ system that carries out gas exchange; includes the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs
digestive system
system that processes food into absorbable units and eliminates indigestible wastes
urinary system
system primarily responsible for water, electrolyte, and acid-base balance and the removal of nitrogen-containing wastes from the blood
reproductive system
organ system that functions to produce offspring.
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
creates lipids or fat
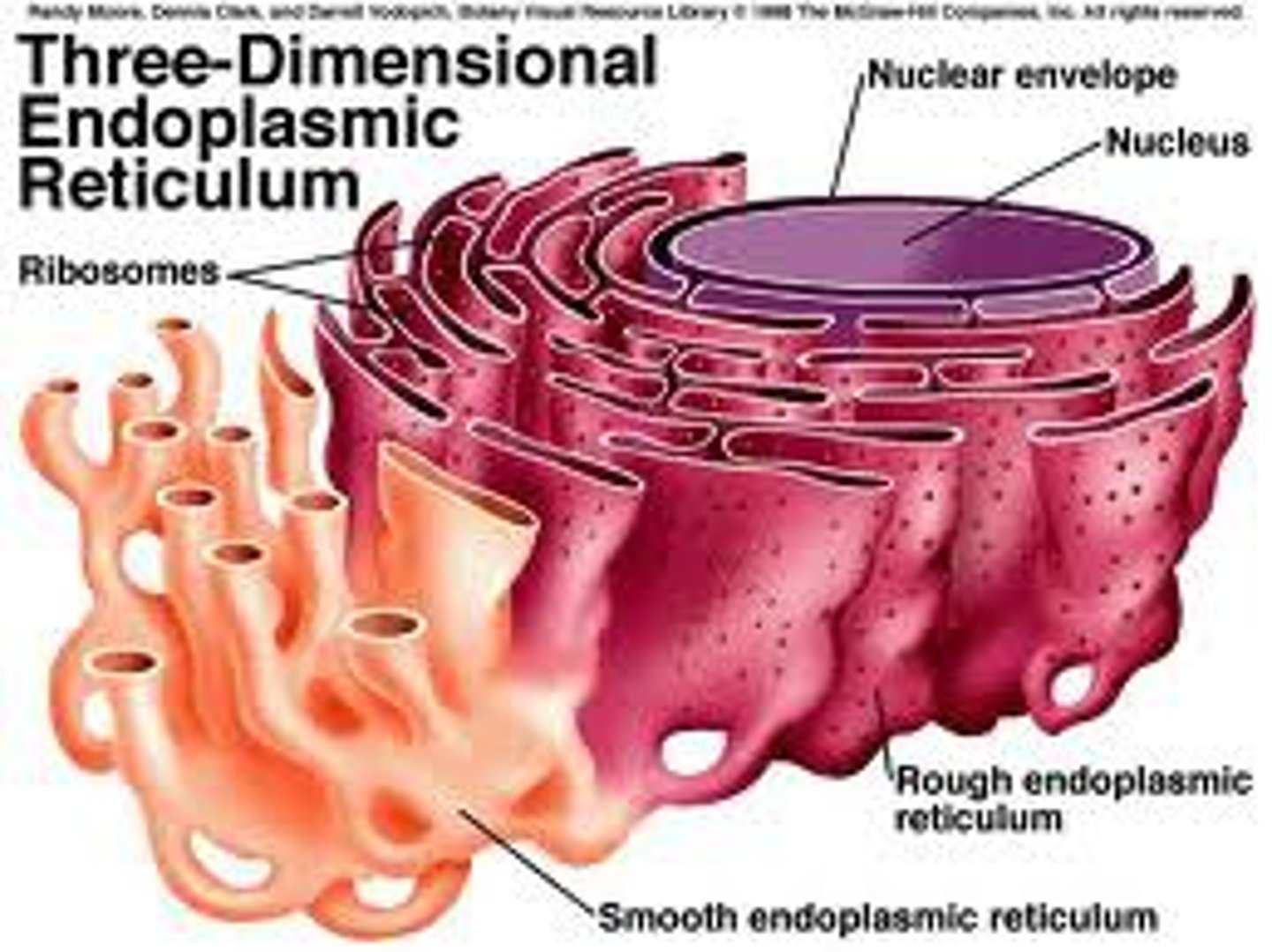
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
transport and storage
ribosomes
Cytoplasmic organelles at which proteins are synthesized.
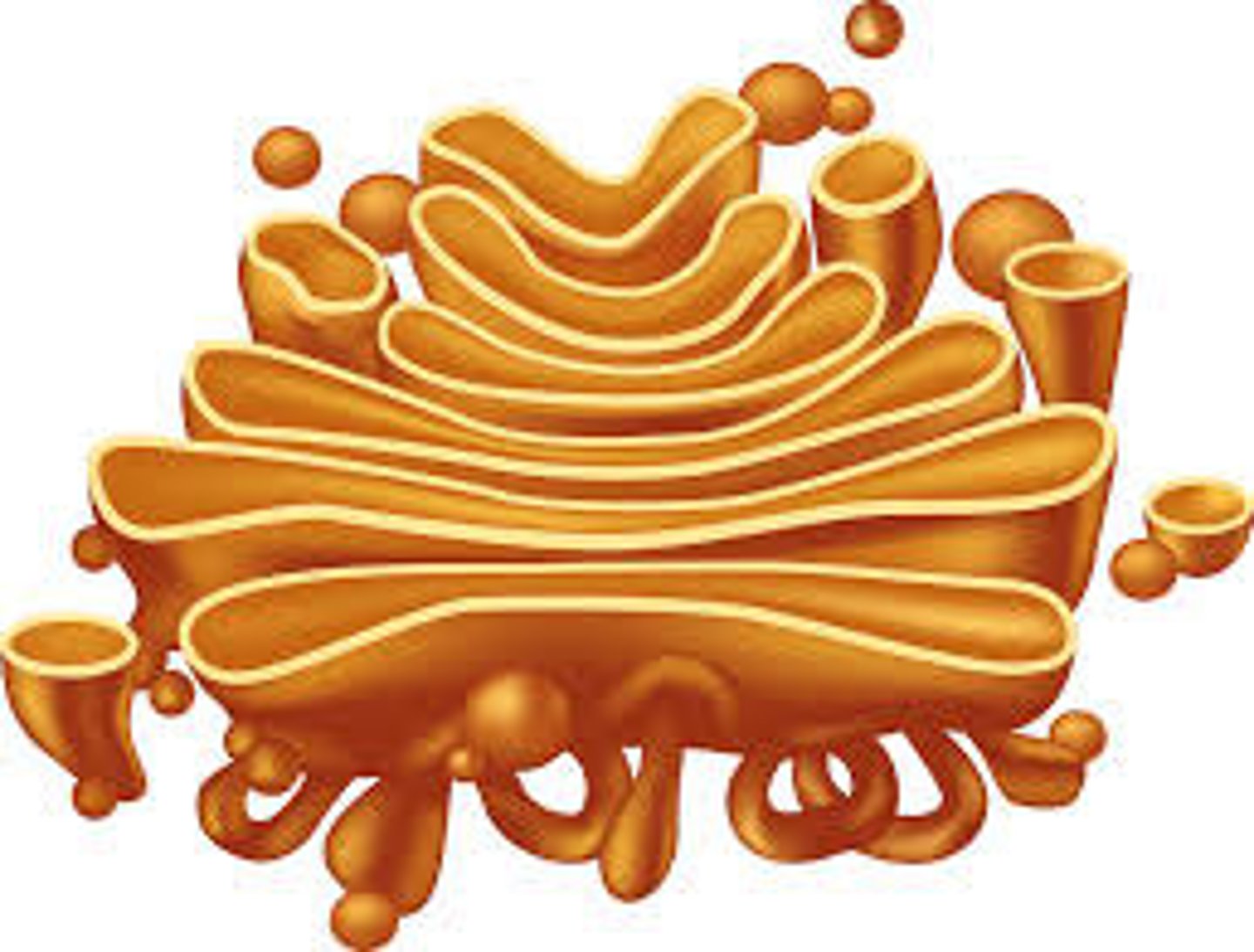
Golgi apparatus
Membranous system close to the cell nucleus that packages protein secretions for export, packages enzymes into lysosomes for cellular use, and modifies proteins destined to become part of cellular membranes.

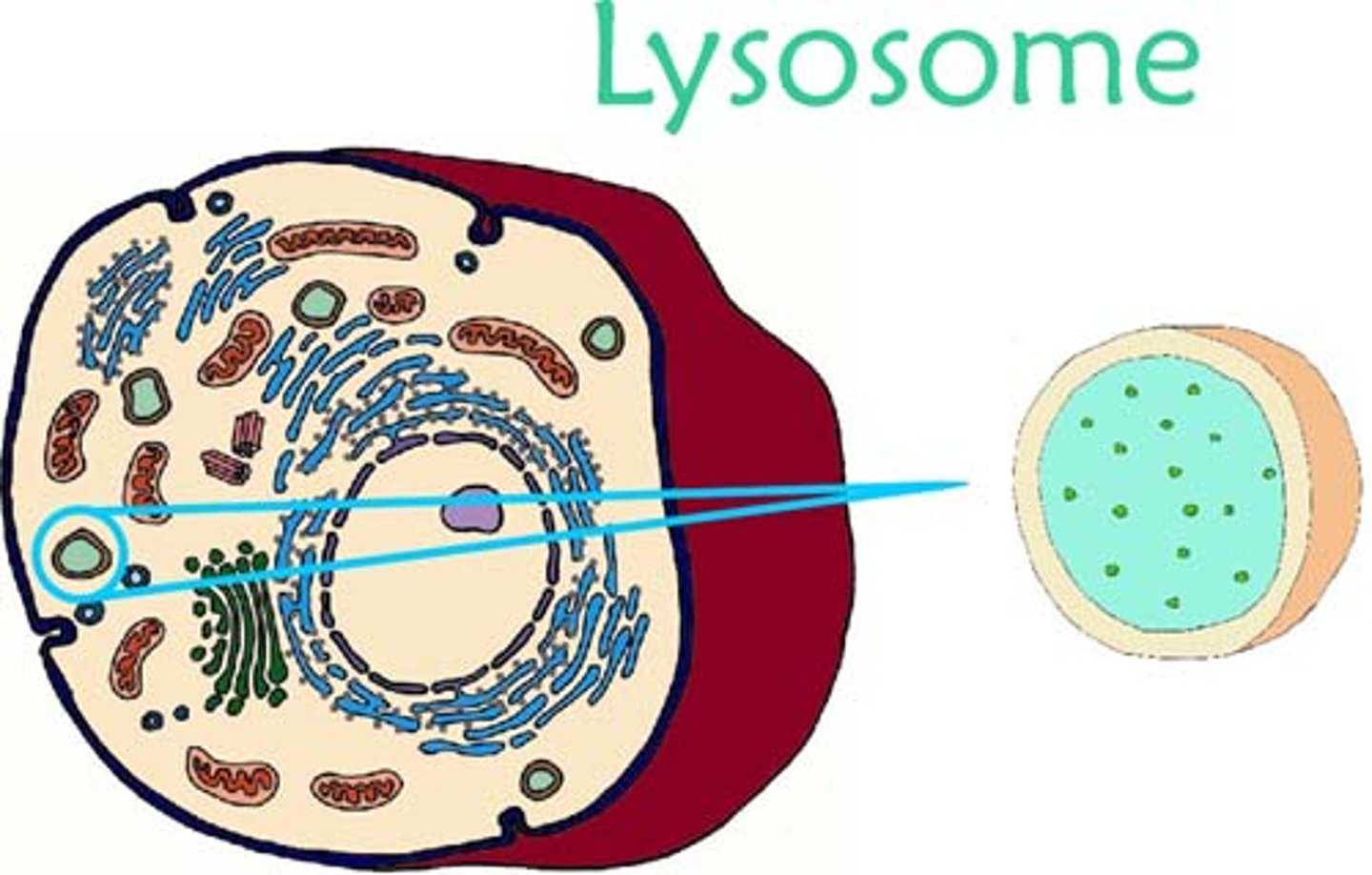
Lysosomes
An organelle used for intracellular digestions, protein synthesis, and breaking down dead cells
Peroxisomes
Membranous sacs in cytoplasm containing powerful oxidase enzymes that use molecular oxygen to detoxify harmful or toxic substances, such as free radicals.
Mitochondria
Cytoplasmic organelles responsible for ATP generation for cellular activities.
powerhouse of cell
nucleus
Control center of the cell; contains genetic material. Clusters of neuron cell bodies in the CNS. Center of an atom; contains protons and neutrons
epithelial tissue
Pertaining to a primary tissue that covers the body surface, lines its internal cavities, and forms glands.