AP Microeconomics Imperfect Competition (Unit 4)
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
a monopoly
What market is this a graph of?
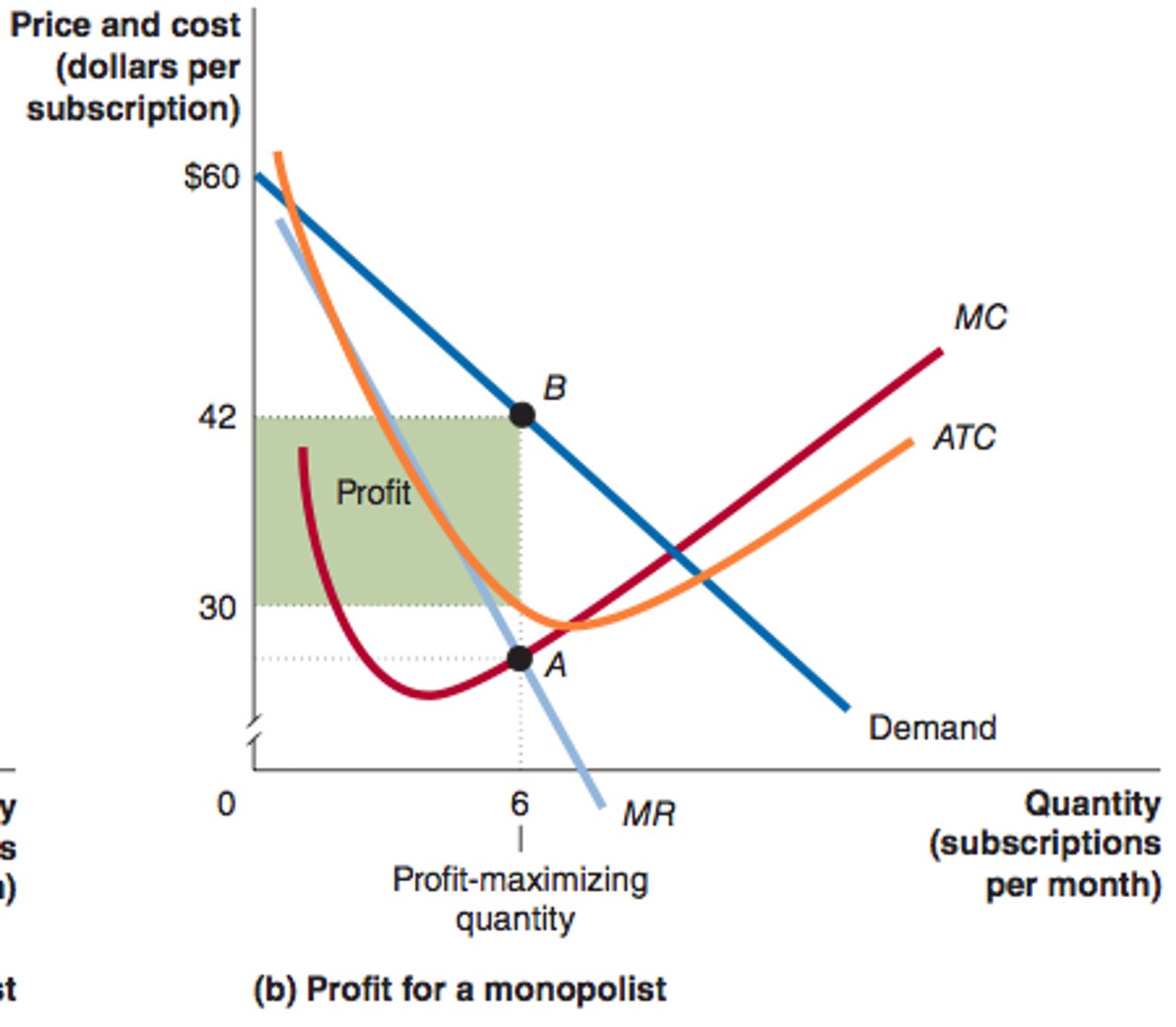
one firm, unique product, and high barriers to entry
What are the characteristics of a monopoly?
economies of scale
A proportionate saving in costs gained by an increased level of production
natural monopolies
It is natural for only one firm to produce because they can produce at the lowest cost
it is at it's peak
What happens to total revenue when marginal revenue hits zero in a monopoly?
when price falls and total revenue increases (before MR hits 0)
What range of a monopoly is elastic?
when price falls and total revenue falls (when MR is negative)
What range of a monopoly is inelastic?
they charge a higher price, and aren't allocatively or productively efficient
Why are monopolies inefficient?
allocatively efficent
When price equal marginal cost (produces at max efficiency)
productively efficient
When a firm produces at the lowest costs (minimum of ATC curve)
consumer surplus falls and there is deadweight loss
What happens to surplus in a monopoly?
average total cost is always decreasing
What does a graph with a natural monopoly look like?
elastic range of demand curve
Where should a profit maximizing monopolist put its output level?
to keep prices low and make monopolies efficent
Why would the government regulate monopolies?
price ceilings - taxes only limit supply
How does the government regular monopolies?
price = marginal cost (allocative efficiency)
What is the socially optimal price?
price = average total cost (normal profit)
What is the fair-return (break even) price?
give the firm a subsidy
If the government were to set a price ceiling to get the socially optimal quantity in a natural monopoly, what would they have to do?
must have monopoly power, be able to segregate the market, and consumers can't resell the product
What conditions are required to make price discrimination work?
demand
What does marginal revenue equal when price discriminating?
advertising (brand names, service, locations, etc)
What is an example of non-price competition?
0
What is the economic profit of monopolistic competition in the long run?
price/quantity falls and demand = ATC = price
What happens in monopolistic competition when new firms enter the market?
price = ATC, and ATC intersects marginal cost at its lowest point
What are some rules for monopolistic-ly competitive graphs in the long run?
excess capacity
Given current resources, the firm can produce at the lowest costs (minimum ATC) but they decide not to
gap between minimum ATC output and profit maximizing output
What is excess capacity on a graph?
mutual interdependence
This is when firms can't legally work together, but are heavily influenced by other firms (oligopoly)
strategic pricing
This sets a product's price based on the product's value to the customer, or on competitive strategy, rather than on the cost of production
economies of scale, high start-up costs, and ownership of raw materials
What are the typical barriers to entry in an oligopoly?
game theory
The study of how people behave in strategic situations
dominant strategy
The best strategy for a player to follow regardless of the strategies chosen by the other players
the Nash equilibrium
A situation in which economic actors interacting with one another each choose their best strategy given the strategies that all the others have chosen (self interest/confess)
no!! (cooperation is)
Is the Nash Equilibrium the best outcome?
price leadership, colluding oligopoly, and non-colluding oligopoly
What are the three types of oligopolies?
price leadership oligopoly
A oligopoly where the "dominant firm" initiates a price change, and the other firms follow the leader (temporary price wars may occur)
there isn't one
What does a price leadership oligopoly graph look like?
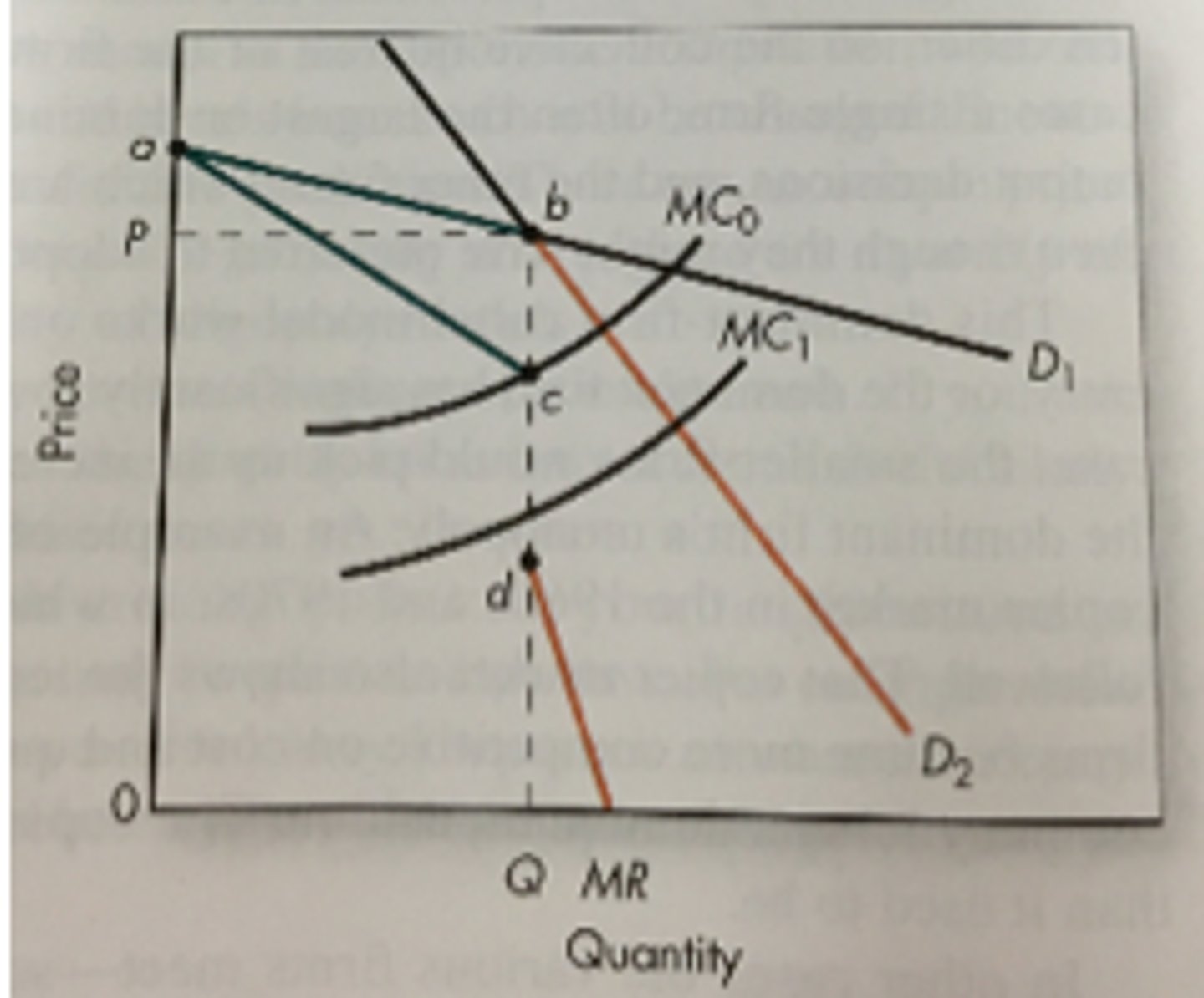
cartel (colluding oligopoly)
A group of producers that create an agreement to fix prices high
monopoly graph
What does a colluding oligopoly graph look like?
match price (inelastic demand) or ignore change (elastic demand)
What are the two ways in which a oligopolistic firm can react to their competitor's pricing?
right
Which side of a non-colluding oligopoly is elastic?
efficient scale
The quantity that minimizes ATC
product-variety externality
Consumers get consumer surplus, so entry of a new firm conveys a positive externality on consumers
business stealing externality
Existing firms lose customers/profits - entry of a new firm has a negative impact on existing firms
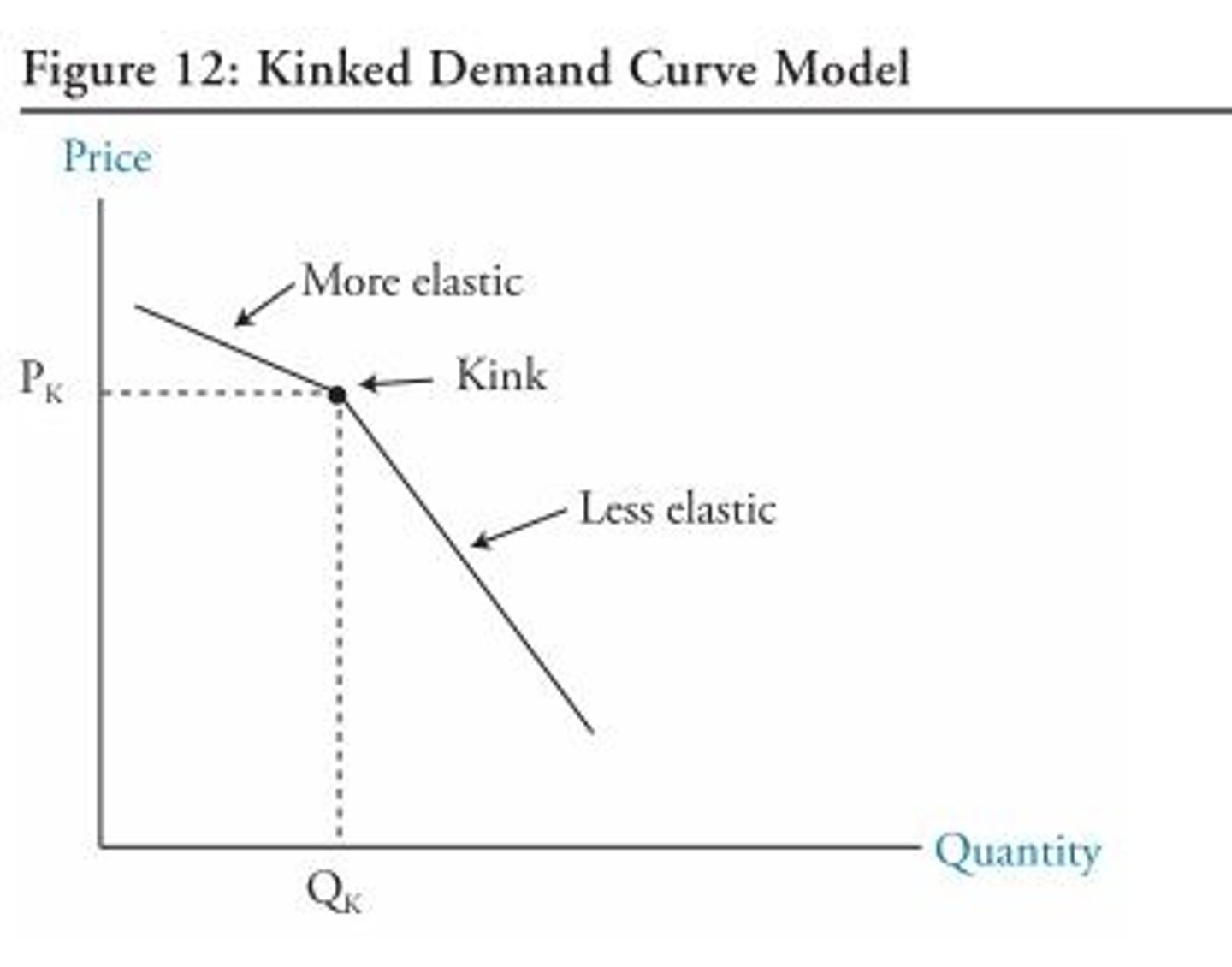
the kinked demand curve (oligopoly non-colluding)
What is this?
vertical gap
What happens to marginal revenue at the kink of the kinked demand curve of an oligopoly?