ch 1 kms
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
health
state of complete physical, mental, and social well-being, and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity
all systems of the human body are functioning normally, and are in balance with each other
homeostasis
stable/dynamic internal conditions under fluctuating environmental conditions
body organs normally do what under homeostasis
maintain temp, pH, blood comp, fluid levels
disease
deviation from normal structure or function in the body that interrupts or modifies the performance of vital functions
insulin
chemical messenger that maintains level of glucose in blood
pathology
study of disease
study of disease includes
causes, mechanisms, signs, symptoms
pathologist
physician who studies and interprets the changes caused by disease
signs
evidence of disease
symptoms
indication of disease reported by patient (NOT REAL)
symptoms ex
pain, dizziness, itching
signs ex
abnormal pulse, abnormal respiratory rate, fever, sweating
syndrome
abnormal structure or function characterized by group of signs and symptoms that occur together
syndrome ex
AIDS, malabsorption syndrome, down syndrome
disorder
functional abnormality not necessarily linked to a specific cause or physical abnormality
disorders ex
ADHD, premenstrual dysphoric disorder, hemorrhoids
is prescence of signs and symptoms required for condition to be termed as a disorder
no
diagnosis
process of identifying disease or disorder
physical exam ex
inspection, palpation, auscultation, percussion, vital signs,
inspection
visual examination of external surface of the body, movements, and posture
for abnormalities or evidence of disease
palpation
feeling the body with fingers or hands
examination of size, consistency, texture, location, and tenderness of organ or body part
auscultation
listening to the lungs, heart, and intestines
evaluation of frequency, intensity, duration, number, and quality of sounds originating in the body
percussion
producing sounds by tapping on specific areas of the body with fingers, hands, or a small instrument
evaluation of size, consistency, and borders of organs and presence/absence of fluid in body areas
vital signs
pulse, respiratory rate, blood pressure, temp
assess most basic body functions
vary with age, sex, weight, exercise tolerance, physical condition
laboratory tests
analyze composition of urine, blood, throat swabs, stool, sputum, and other patient samples
biopsy
surgical removal and analysis of tissue samples
yields info about changes at cellular level
electrocardiography
reads heart electrical impulses
radiography
uses x-rays to visualize internal structures
computed tomography (CT) scan
computers and x-rays to create 3D images of internal structures
magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
analyzes tissue responses to a strong magnetic field to create images of internal structures
ultrasound
analyzes interaction of low-frequency sound waves with tissues to create moving images of internal organs
nuclear medicine
uses radioactive materials to create contrast in the body and help form images of the structure and function of organs
prognosis
predicted course and outcome of a disease
acute disease
sudden onset and short duration (flu, measles, common cold)
terminal
diseases ending in death
chronic disease
slower, less severe onset and long duration of months or years (heart disease, cancer, stroke, diabetes, arthritis)
7 in 10 deaths in US due to
chronic diseases
6 in 10 deaths worldwide due to
chronic diseases
top 5 leading causes of death USA 2010
heart disease
cancer
chronic lower respiratory disease
stroke
accidents
remission
signs and symptoms subside or disappear
exacerbation
signs and symptoms grow more severe
relapse
return of a disease weeks or months after apparent cure
complication
related disease/ other abnormal state that develops in a person already suffering from a disease
common complication of leukemia, cancer, chronic kidney disease
anemia
top 5 leading causes of death world 2011
ischemic heart disease
stroke/ cerebrovascular disease
lower respiratory infections
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
diarrheal disease
sequela
aftermath of a disease
sequela of rheumatic fever
permanent damage to the heart
sequela of polio
paralysis
mortality
number of deaths that occur among people with a certain disease
top 5 leading cause of death low income countries 2008
lower respiratory infections
diarrhea disease
hiv/aids
ischemic heart disease
malaria
morbidity
number of cases of a disease in a population
prevalence
percentage of a population that’s affected with a particular disease at a given time
epidemiology
study of the occurrence, transmission, distribution, and control of disease
top 5 leading cause of death high income countries 2008
ischemic heart disease
stroke/ cerebrovascular disease
trachea, bronchus, lung cancers
alzheimer’s and other dementias
lower respiratory infections
pathogenesis
how the cause of a disease leads to anatomical and physiological changes in the body that ultimately result in the disease
idiopathic
cause of disease is unknown
hereditary diseases
hemophilia, sickle cell anemia, cystic fibrosis
congenital diseases
tetralogy of fallot (heart abnormality)
degenerative diseases
arteriosclerosis, osteoarthritis, alzheimer’s
inflammation/autoimmunity/allergy diseases
asthma, systemic lupus erythematosus, hay fever
infectious diseases
tuberculosis, influenza, syphilis
neoplastic diseases
lung cancer, malignant melanoma, breast cancer
metabolic diseases
diabetes, hypothyroidism, gigantism
trauma diseases
burns, frostbite, bone fractures
nutritional-imbalance diseases
iron-deficiency anemia, scurvy, obesity
hereditary cause of disease def
abnormality in an individuals genes or chromosomes
congenital cause of disease def
exist at or date from birth
aquired through hereditary/development in uterus
degenerataive cause of disease def
function or structure of the affected tissues or organs progressively deteriorates over time
inflammatory autoimmune allergic cause of disease def
result of abnormal immune function
caused by pathogens such as bacteria and viruses
neoplastic cause of disease def
result from abnormal growth that leads to formation of tumors
metabolic cause of disease def
disruption of normal metabolis
traumatic cause of disease def
physical or chemical injury
nutritional cause of disease def
over or underconsumption of nutrients
risk factors
increase person’s change of developing a disease
what can risk factors be
environmental, chemical, physiological, psychological, genetic
modifiable risk factors
physical activity, nutrition, tobacco use, alcohol use
4 ways to promote long healthy lives
be physically active, eat wisely, maintain healthy weight, be tobacco free
treatment
aims to cure a disease or reduce severity of signs/symptoms
What is the best definition of health?
the condition in which the human body performs its vital functions normally
What physical assessment technique produces sounds by tapping on specific areas of the body using fingers, hands, or a small instrument?
percussion
What is the study of disease?
pathology
What is the leading cause of death in the United States?
diseases of the heart
What category of disease is sickle cell anemia?
hereditary
What category of disease best describes a disease in which the function or structure of the affected tissues or organs progressively deteriorates over time?
degenerative
What is true regarding risk factors related to disease?
Risk factors increase a person's chance of developing a disease.
According to the United States Health and Human Services, what choice best demonstrates a component of a healthy plate?
green leafy vegetables covering 50% of the plate
The medical assistant is assisting the primary care provider during a client's annual health exam. Which statement will the medical assistant most likely hear the provider tell the client regarding smoking cessation?
"Within three months of quitting, an ex-smokers lung function begins to improve."
The doctor says that with rest and fluids, Maria has a good chance at complete recovery in about 2 weeks. This predicted outcome is called the disease's _______.
prognosis
Lung cancer is an example of a(n) ________ disease
chronic
Maria's disease can be described as ________
acute
Maria has many signs and symptoms of influenza. Which is an example of a sign?
cough
You note that because his father had lung cancer, Carl has a risk factor he cannot modify or control. Which of these is not a modifiable risk factor?
genetics
Carl can modify which risk factor?
cigarette smoking
dynamic equilibrium
maintained by the ever-changing processes of feedback, and then regulation in response to external and internal feedback changes
trisomy 21 aka
down syndrome
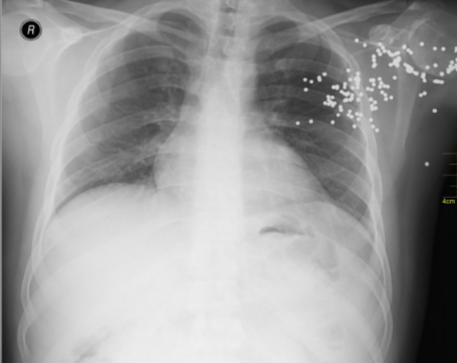
x-ray
dark = less dense
bright = more dense
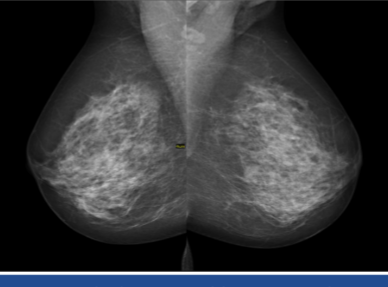
mammography
radiographic technique used to screen for breast cancer
can reveal cancer before even palpable
incidence of breast cancer in women
1 in 8
women diagnosed w/ breast cancer in 2021
284,000
breast cancer screening recommendations
every year for women 40+
self-examination once a month
clinical breast exam 19+