2(j) Coordination and Response in humans (copy)
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Syllabus statements 2.80-2.82, 2.86-2.94
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Stimulus
A change in the environment that can be detected by an organism, e.g.
light
temperature
sound
touch
chemicals
How do organisms respond to stimuli and why is this necessary?
They need to respond to stimuli in order to survive.
Organisms have receptors that allow them to detect stimuli.
In humans, receptors are found in sense organs
In plants, specialised cells detect stimuli such as light, gravity or water
They then coordinate the required response.(e.g. move away, secrete chemicals,…)
The response increases the organisms chance of survival
Homeostasis
The maintenance of a constant internal environment.
body temperature (37oC in humans to provide an optimum To for enzymes)
body water content (ensures that cells function correctly, preventing them from bursting or shrivelling due to osmosis)
pH level
CO2 level
glucose level
What 3 elements does a coordinated response require? + their definition
A stimulus, a change in the environment that can be detected by an organism(light, temperature, touch,…)
Receptor cells to detect the stimulus and to transduce the stimulus energy into electrical impulses(found in sense organs in humans, such as the skin on the fingertip, eyes,…)
Effector cells to bring about the required response to the stimulus(usually muscle cells or a gland)
2 Systems involved in coordination&response in humans
Nervous(hormonal) system
Endocrine system
Both systems require a stimulus, receptor and effector and chemicals are involved in both.
Key differences between the nervous and endocrine(homonal) system
The nervous system is made up of nerve cells(neurons) that carry electrical impulses around the body.
The endocrine system consists of glands that produce hormones, which are carried by the bloodstream (plasma) and stimulate changes in the body.
The nervous systems brings about quick responses that last for a short time.
The endocrine system brings about slower responses that last for a longer time.
2 parts of the nervous system:
CNS (Central Nervous System)
PNS (Peripheral Nervous System)
CNS and PNS (components and how they are linked)
The CNS consists of the brain and the spinal chord.
The CNS is linked to sense organs by neurons(nerves).
The neurons form the PNS.
Neurons (+Draw and label one)
Specialised nerve cells that carry electrical impulses (at high speeds).
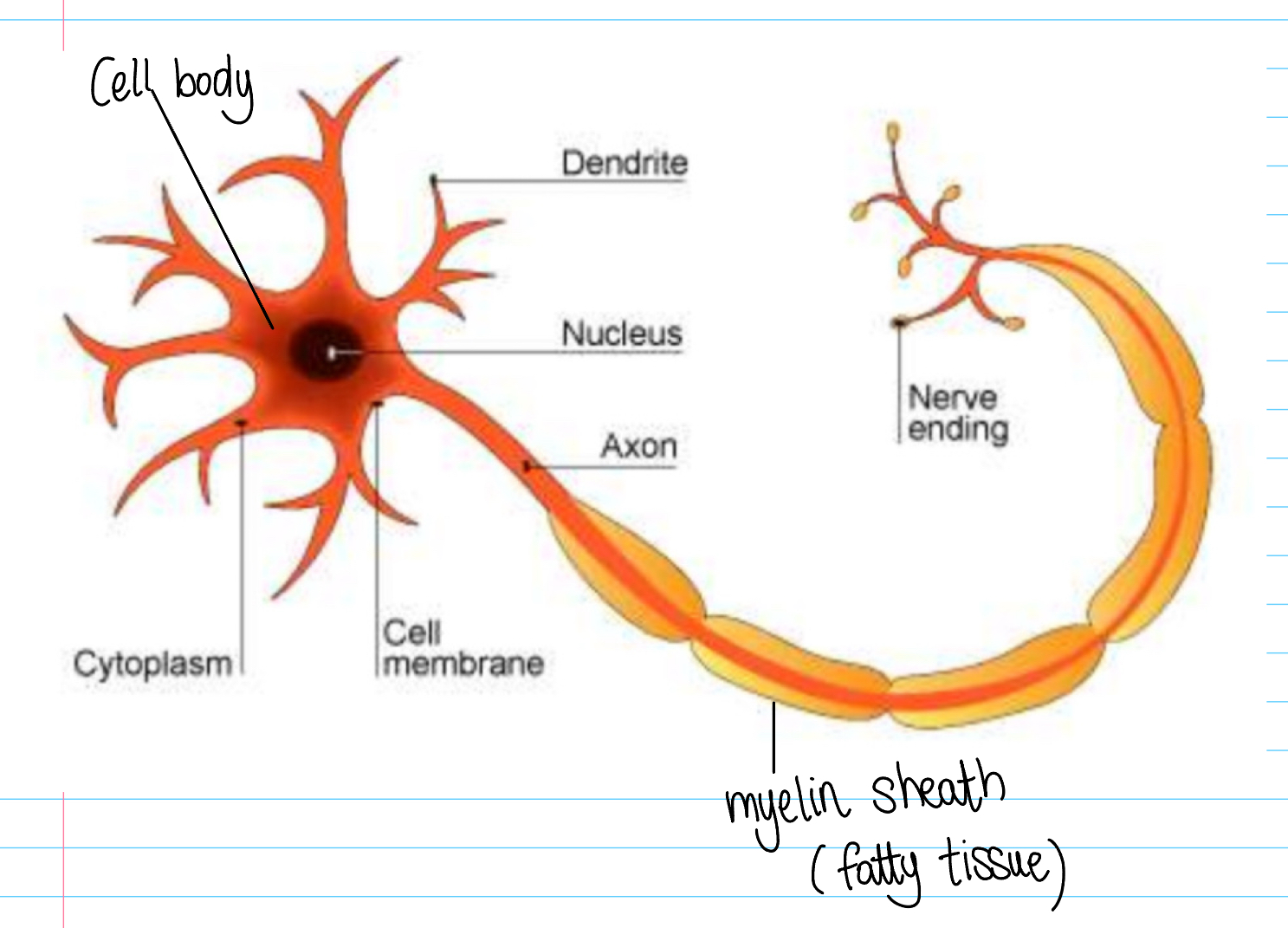
3 types of neurons
Sensory neuron(from receptor to CNS)
Relay neuron(CNS)
Motor neuron(from CNS to effector)
(2.88) Describe the nevous system pathway(including different types of neurons).
A stimulus is detected by a receptor in a sense organ.
The receptor transduces the stimulus energy into an electrical impulse.
This impulse is transmitted from the receptor to the CNS along sensory neurons.(The impulse is transmitted within the CNS to the brain along relay neurons)
The CNS(brain) coordinates this information and sends another impulse in response.
This impulse is transmitted to an effector along motor neurons.
in the exam a specific scenario will be given. Substitution of a specific stimulus, receptor and effector is needed.
Reflex action and reflex arc
A reflex action is a subconscious(automatic)and extremely quick response to a dangerous stimulus. It does not involve the brain. Instead, the impulses pass directly from sensory neurons, along relay neurons in the CNS(spinal cord), to motor neurons. This nervous pathway is known as a reflex arc.
Examples:
Dilation&Constriction of pupils
Contraction of muscles
Salivation
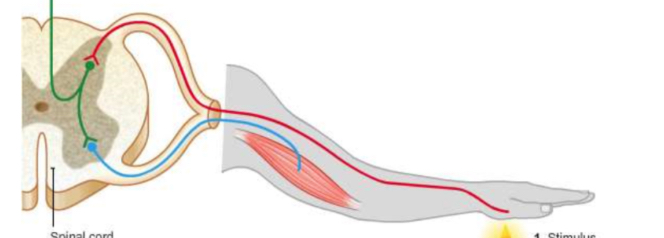
(2.90) Describe the reflex arc : withdrawal of a finger from a hot object
A stimulus(heat) is detected by a receptor (thermoreceptors in fingertips).
The receptor converts/transduces the stimulus energy into an electrical impulse.
This impulse is transmitted from the receptor to the CNS along a sensory neuron.
The impulse is passed to a relay neuron in the CNS.(Pain message is transmitted to the brain)
The impulse is transmitted from the CNS to an effector along a motor neuron(arm muscle).
The effector (arm muscle) brings about the required response, in this case it contracts to pull the hand away from the flame.
(2.89) Synapse and the role of neurotransmitters
A synapse is the gap between two neurons.
When an electrical impulse is carried along an axon,
it triggers the nerve-endings to release a chemical called neurotransmitter so that the signal can travel across the synapse.
The neurotransmitter diffuses across the synapse and binds to a receptor molecule on the next neuron.
This stimulates the second neuron to transmit the electrical impulse.
(2.91) Label the structure of the eye
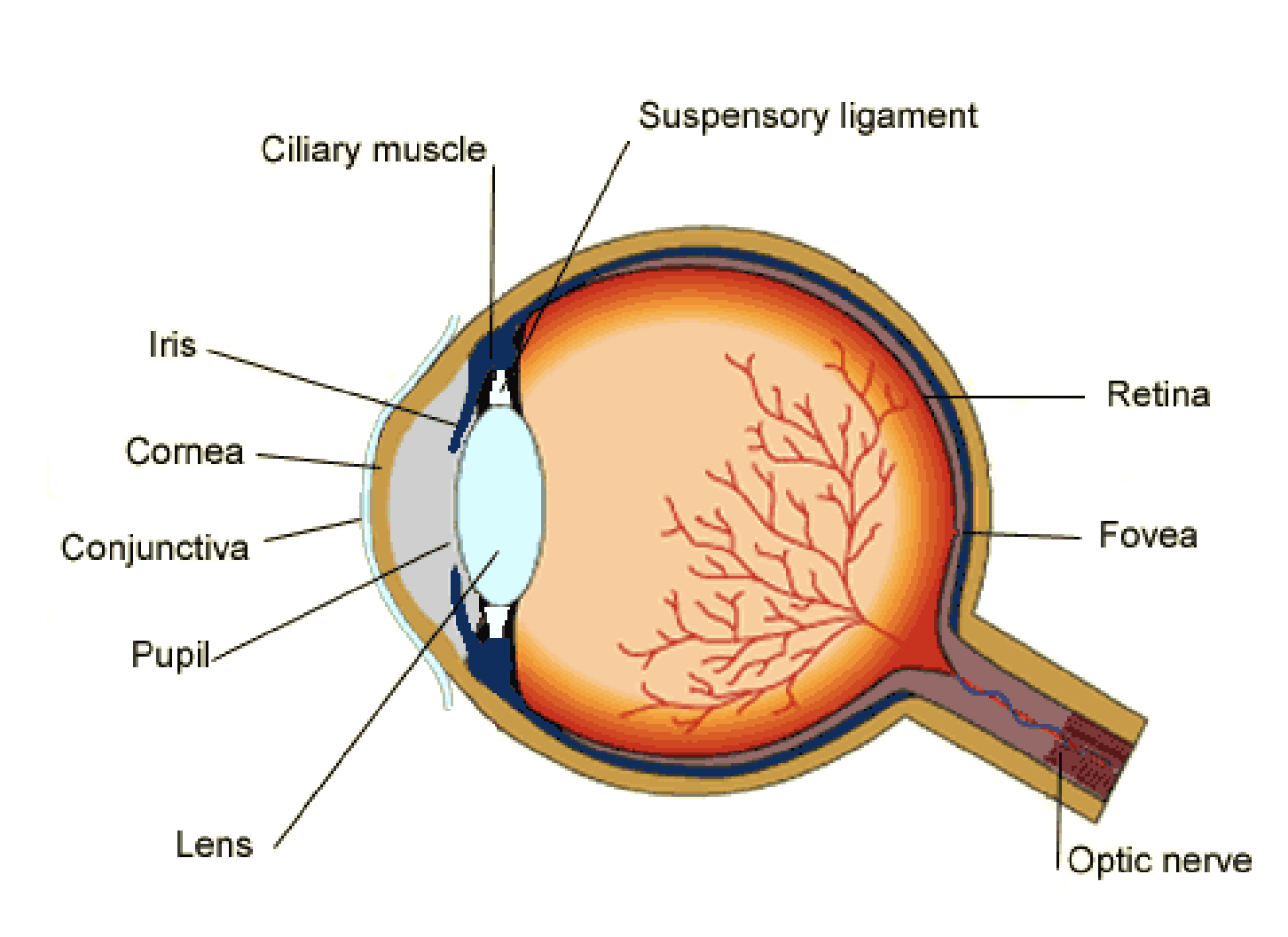
Cornea
the transparent outer part of the eye
refracts light to reach the retina
Conjunctiva
protects eye surface
Iris
the coloured part of the eye that does not allow light go through
controls how much light enters the pupil
has circular and radial muscles to constrict or dilate the pupil
Pupil
Hole allowing light to enter the eye
Lens
transparent, biconvex disc that attaches to ciliary muscles by suspensory ligaments(悬韧带)
focuses light onto retina
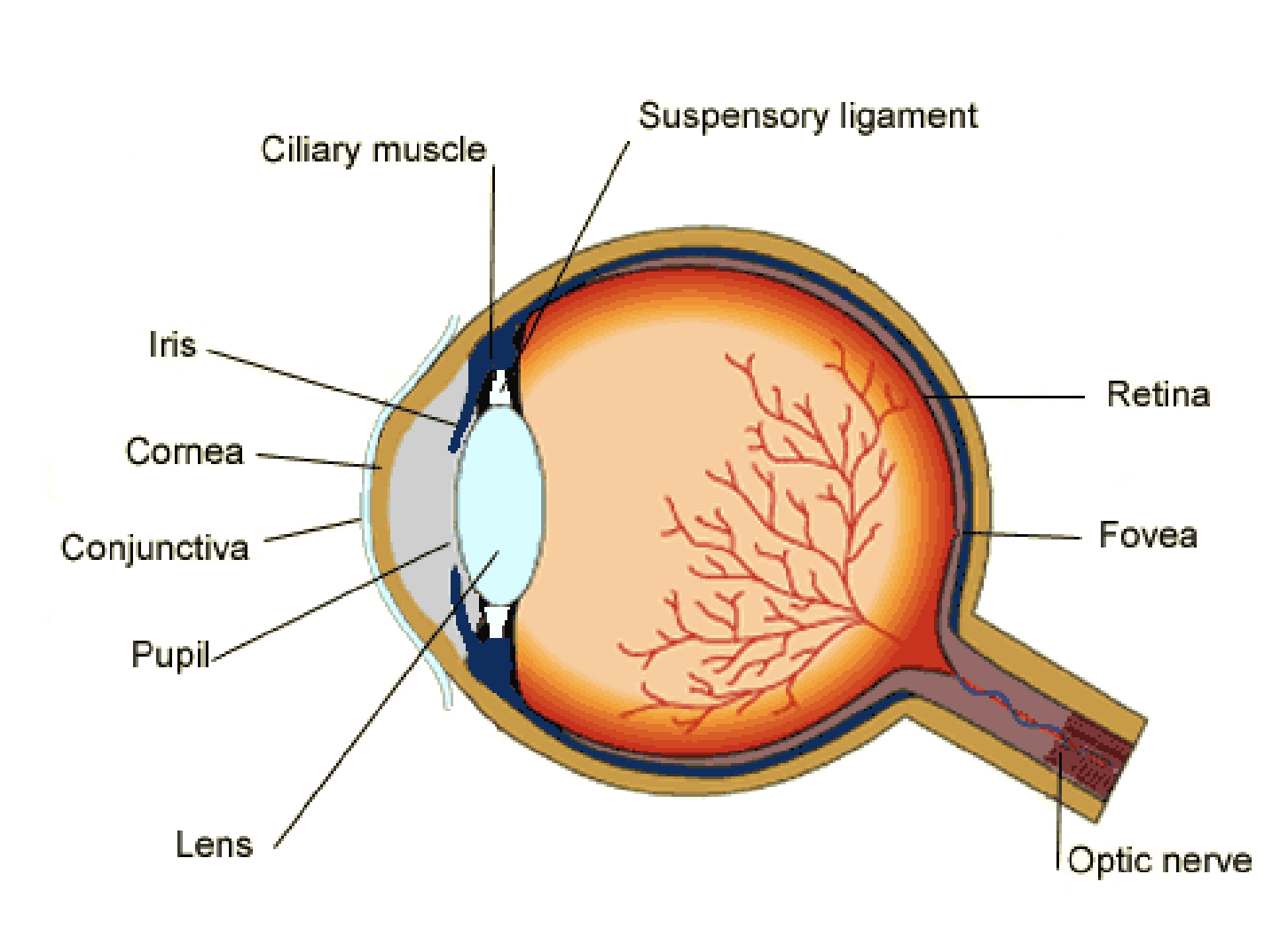
Retina
contains light receptors
Fovea
Area of retina that prpvides the clearest vision
Optic nerve
carries impulses from the eye to the brain
Ciliary muscles
ring of muscle around the eye
involved in changing the shape of the lens
Suspensory ligaments
hold the lens in place
involved in changing the shape of the lens
Accomodation of the eye - distant object
Ciliary muscles relax. (causing…)
Suspensory ligaments tighten.
Lens is pulled thinner(less convex)
Accomodation of the eye - near object
Ciliary muscles contract.
Suspensory ligaments slacken
The lens fattens(more convex)
Response of the eye in bright light
Circular muscles contract.
Radial muscles relax.
The pupil constricts(becomes smaller).
This reduces the amount of light entering the eye to avoid damage to the retina.
Response of the eye in dim light
Circular muscles relax.
Radial muscles contract.
The pupil dilates(becomes bigger).
This allows as much light as possible to enter the eye, falling onto the retina in order to maximise vision (create a better image).