IB English PAPER 1 terminology
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Allegory
A literary or pictorial device in which each literal character, object or event represents a symbol illustrating an idea, a moral or religious principle.

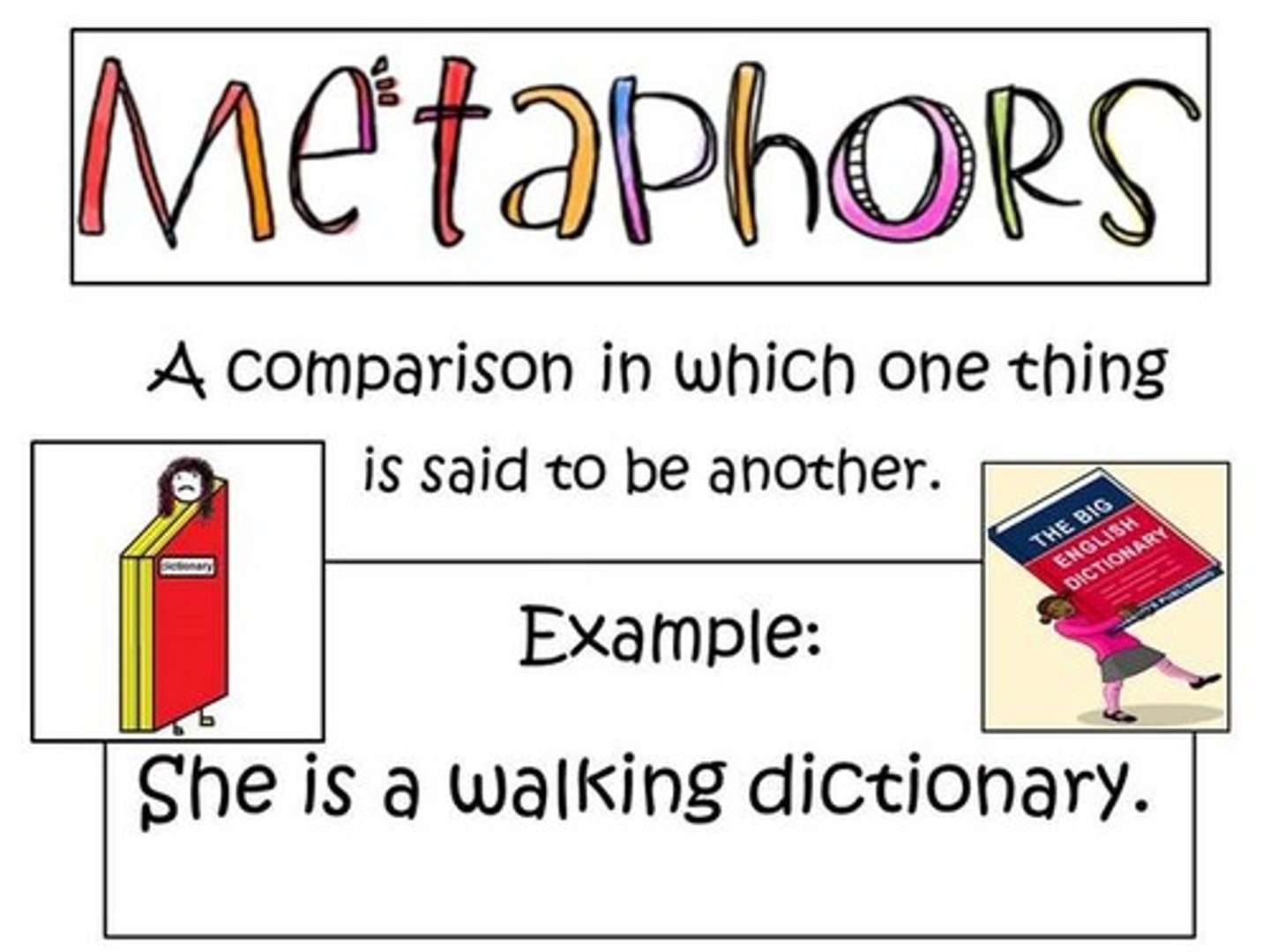
Metaphor
A comparison without using like or as
Simile
A comparison of two unlike things using like or as
Alliteration
Repeated consonant sounds at the beginning of words placed near each other

Allusion
A reference to a well-known person, place, event, literary work, or work of art

Antithesis
A balancing of two opposite or contrasting words, phrases, or clauses.

Aphorism
A brief, cleverly worded statement that makes a wise observation about life.

Assonance
Repetition of a vowel sound within two or more words in close proximity

Aside
A device in which a character in a drama makes a short speech which is heard by the audience but not by other characters in the play

Cacophony
A harsh, discordant mixture of sounds

Connotation
An idea or feeling that a word invokes for a person in addition to its literal or primary meaning.

Consonance
Repetition of a consonant sound within two or more words in close proximity.

Denotation
The dictionary definition of a word

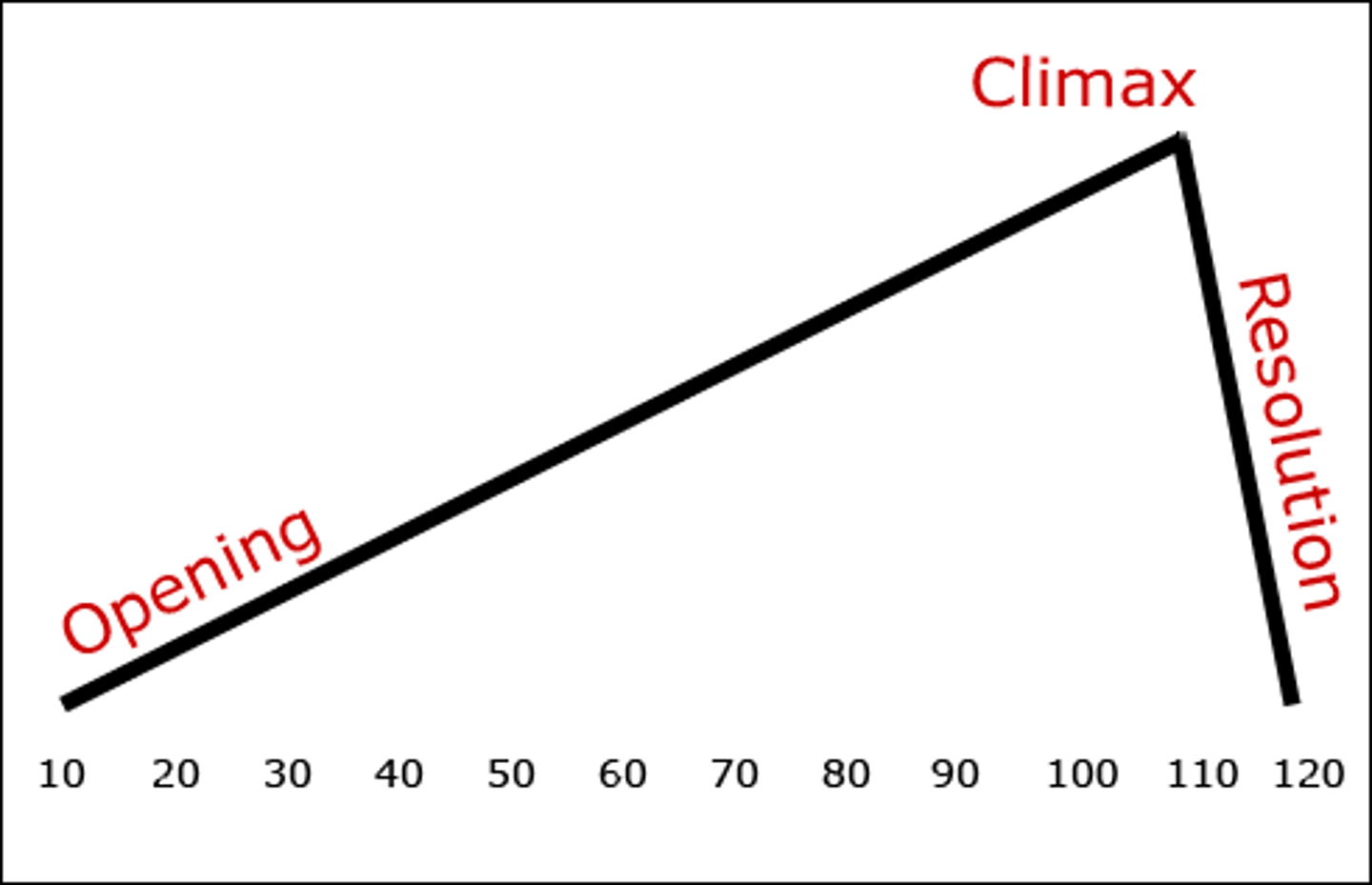
Denouement
an outcome or solution; the unraveling of a plot
Ethos
One of the fundamental strategies of argumentation identified by Aristotle. An appeal to credibility. The writer is seeking to convince you that he or she has the background, history, skills, and/or expertise to speak on the issue. Is the credibility substantiated and valid?

Extended Metaphor
A comparison between two unlike things that continues throughout a series of sentences in a paragraph or lines in a poem.
Euphony
pleasant, harmonious sound

Figurative Language
Language that communicates ideas beyond the ordinary or literal meaning of the words.

Hyperbole
A figure of speech that uses exaggeration to express strong emotion, make a point, or evoke humor

Litotes
A figure of speech consisting of an understatement in which an affirmative is expressed by negating its opposite.

Logos
An appeal to reason; one of the fundamental strategies of argumentation identified by Aristotle. It occurs when a writer tries to convince you of the logic of his argument.
Lyric
A type of poetry that explores the poet's personal interpretation of and feelings about the world.

Metaphor
A comparison that establishes a figurative identity between objects being compared.

Metonymy
A term from the Greek meaning "changed label" or "substitute name," a figure of speech in which the name of one object is substituted for that of another closely associated with it. For example, a news release that claims "the White House declared" rather than "the President declared"

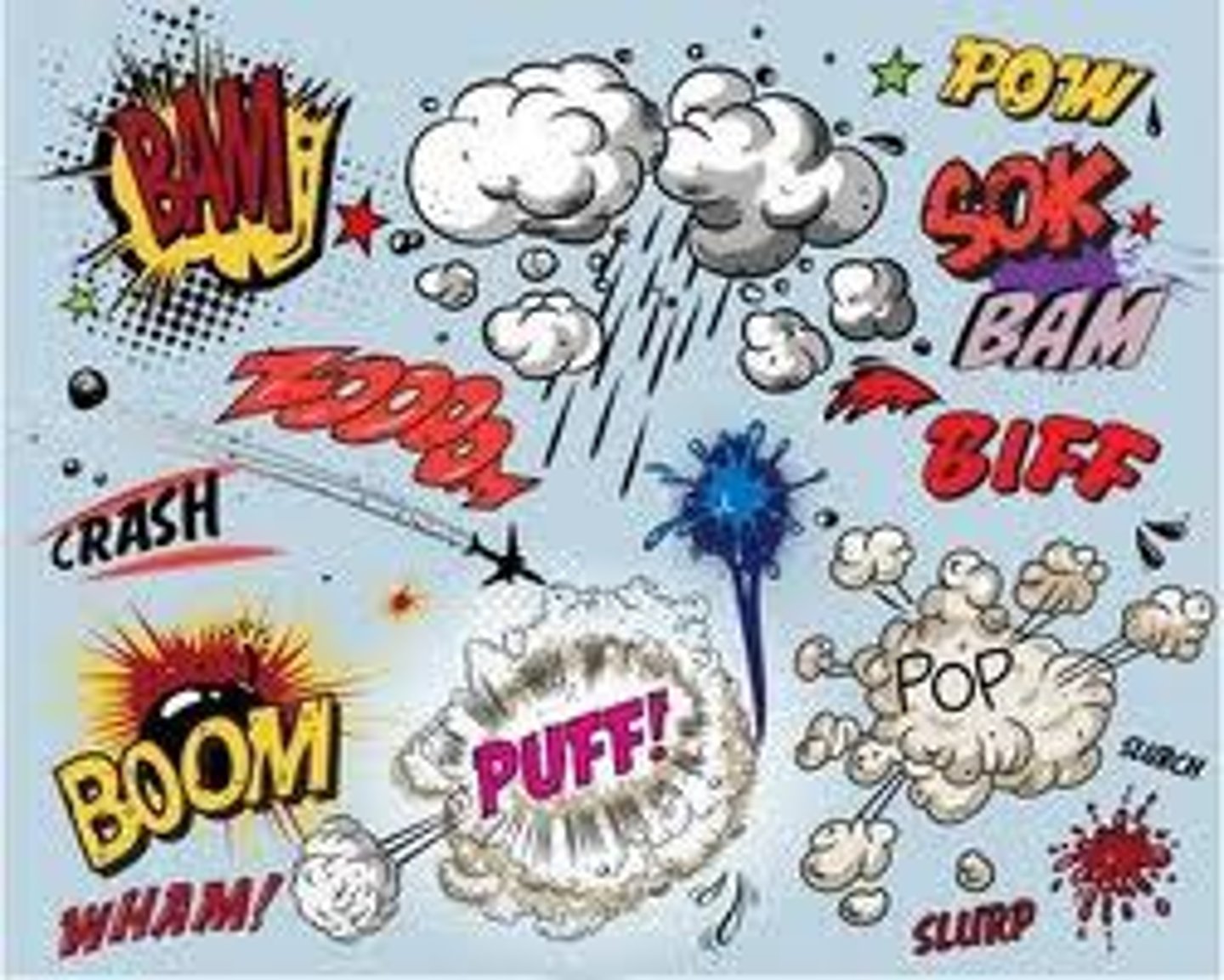
Onomatopoeia
A word that imitates the sound it represents.
Pathos
An appeal to emotion. This is one of the fundamental strategies of argumentation identified by Aristotle. Typically, pathos arguments may use loaded words to make you feel guilty, lonely, worried, insecure, or confused.

Rhetoric
the art or study of persuasion through speaking or writing; language that is elaborate or pretentious but actually empty, meaning little

Soliloquy
A dramatic or literary form of discourse in which a character talks to himself or herself or reveals his or her thoughts without addressing a listener.

Voice
A writer's unique use of language that allows a reader to perceive a human personality in his or her writing.

Bathos
insincere or overly sentimental quality of writing/speech intended to evoke pity