CHE 231 UKY Final Exam Prep FALL 2024
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Recrystalization:
Purpose of recrystallization
A purification technique for impure solids, a process of removing impurities. Dissolved in hot solvent and recovered back in cold solvent
Recrystalization:
Solvent Selection Criteria
insoluble when cold (room T) and soluble when hot (when heated)
Recrystalization:
Solubility Guidelines?
like dissolves like... polar with polar... nonpolar with nonpolar....ex water will be soluble with ehanol because both are polar and have OH groups
ALSO:
Organic compounds with less than 5 carbons and apolar function are water soluble
Recrystalization:
Melting Point effect on impurities
How can it be used to determine purity
f compound is pure, it will melt over a very narrow,reproducible range of temperatures, ~0.5-2.0°C• Presence of impurity causes depression of melting point(M.P.), and melting to occur over wide range• Melting point (M.P.) range can estimate purityMelting points (M.P.)
Impurities decrease the MP and widens the RANGE
Distillation:
What is fractional distillation?
Distillation is a technique used for separating a mixture of two liquids. The separation is based upon the differences in their boiling points as each compound "boils" at a different temperature. Need significant differences of boiling point within the compounds being separated, preferably 30 to 40 degrees.
Distillation:
Relationship between BP and VP?
Inversely related
Distillation:
Cyclohexanone vs Toluene relationship...which has higher BP,...VP?
Cyclohexanone has a higher BP (so lower VP) while Toluene has a higher VP (so lower BP)
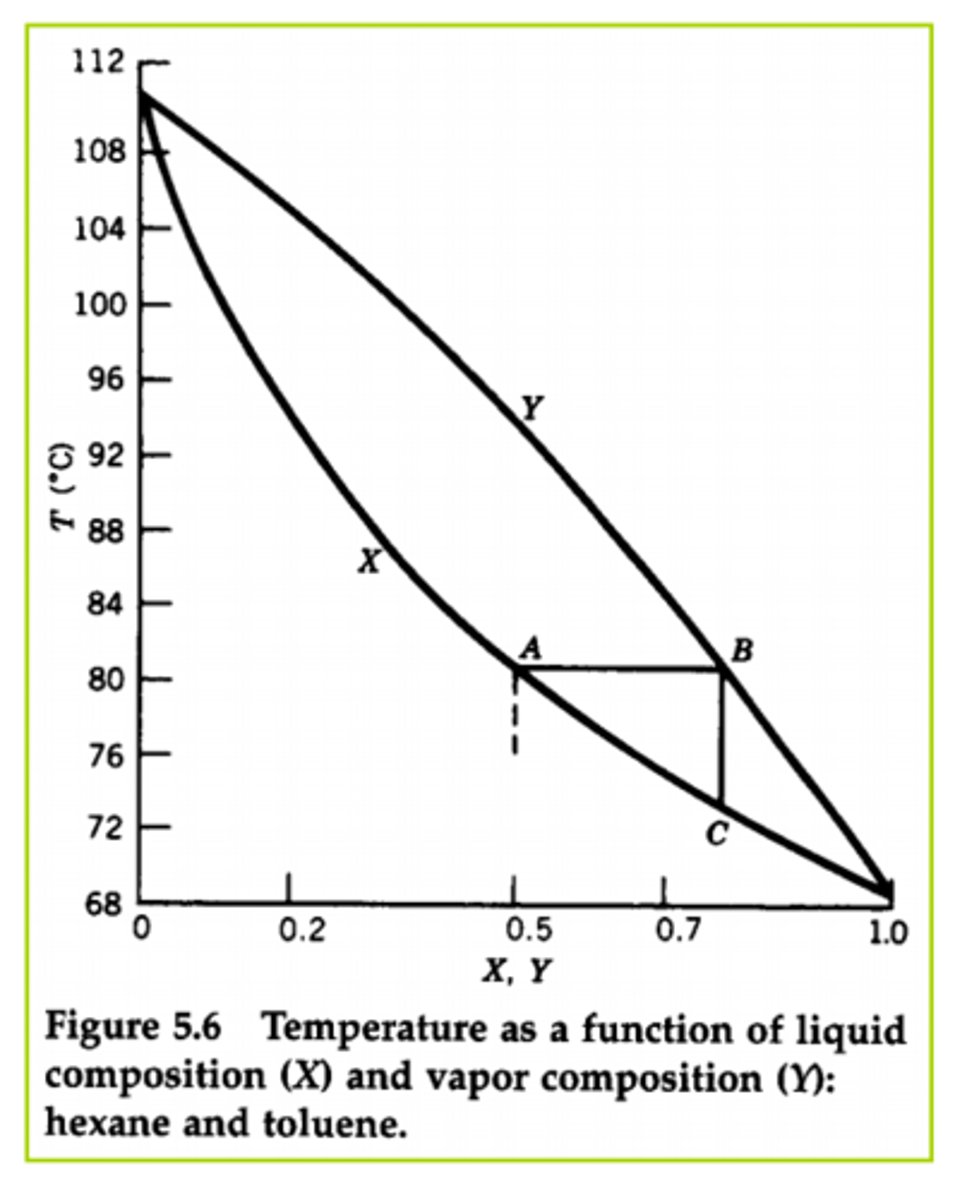
Distillation:
Phase Diagram
.....
Reduction:
General Reations
know the rxn in the lecture ppt
Reduction:
purpose of sodium borohydride
Sodium borohydride is used as the reducing agent and it can reduce aldehydes and ketones, this reducing agent was selected because cyclohexanone contains a ketone which can get easily reduced by this agent
Reduction:
Why dont we use LiAl4 as the reducing agent
We DON'T USE lithium aluminum hydride because its TOO STRONG of a reducing agent and when reacting with a protic solvent it can react with the acidic hydrogen and produce hydrogen gas causing a violent reaction
Reduction
IR PEAKS:
Alcohol?
3300 big gap, broad
Reduction
IR PEAKS:
Carbvonyl (C double bond O)
1700 ish
Reduction
IR PEAKS:
sp3 C-H
2800 ish
Reduction
IR PEAKS:
C-O single bond
1100 ish
Reduction
Which peak disappears from starting material, and which peak is now present in product
In the reactant there is no alcohol peak just a Carbonyl peak (cyclohexanone reactant)
in the product there is a alcohol peak and NO carbonyl peak (cyclohexanol product)
Reduction:
what is the fingerprint section of the IR?
In the IR spectra the fingerprint region is usually between 500 - 1500 this is the region we usually don't pay attention to and are not interested in.
Reduction:
Limiting reagent calculation, how do you do this?
To find the limiting reagent:
- Convert the amounts of all reactants to the moles of the product using the balanced chemical reaction, look for the reactant that produces the least amount of product
this is the theoretical yield (estimated, calculated amount)
so if you start with 26 mg of reactant
26 mg of reactant to g of reactant, g to mols of reactant, change from moles of reactant to mols of product
Column chromatography
Describe it, how does it work?
Column chromatography, also called liquid-solid chromatography, is a technique used to separate and purify compounds in a mixture. It relies on two phases: a liquid mobile phase (organic solvent with varying polarities) and a solid stationary phase. Compounds travel through the column at different speeds based on their affinity for the stationary or mobile phase. Adjusting the polarity of the mobile phase helps separate the compounds by altering their movement rates.
Column chromatography
What is stationary, mobile phase?
stationary phase for Column Chrom. is alumina
mobile phase is liquid solvents
- hexane is used for ferocene
-methylene chloride is used for acetylferocene
Ferrocene, Acetyl Ferrocene get separated based on thedifferences in their polarity, and their interaction with polaraluminaColumn Chromatography Separation
Column chromatography
why is ferocene aromatic?
follows huckels rule (planar strcuture, 10 pi electrons, etc.)
Column chromatography
Which compound elutes first? Which one next? Why?
ferocene elutes first because its nonpolar so travels further down the plate while acetylferocene elutes next (last)
Ferrocene being less polar ELUTES FIRST, travels down faster along the column, acetylferrocene being more polar elutes second when a more polar solvent like methylene chloride is used as the mobile phase
Columnm chromaytrography
How do you determine if the separation issuccessful?
TLC Analsyis
Column chromatography TLC
what is stationary and mobile phase for TLC
stationary is silica gel
mobile is the solvent we use
Column chromatography TLC
What is Rf value?
retention factor, calculates distance traveled...nonpolar compounds travel further down the TLC then polar
distance traveled by the solvent from origin/ total distance from origin to top line
Column chromatography
which compound has higher rf, which lower?
ferocene has higher, acetylferocene has lower
Column chromatography
how do you determine if the seperation is successful
UV light, look for the proper spots that should have dissepared
Solvent Extraction:
what is it?
To separate a mixture containingan acidic, basic, and neutral compound by liquid-liquid solvent extraction
TLC analysis is used to monitor the results of the seperation
Solvent Extraction:
list the 2 methods of extraction and the one we used
Solid-liquid extractionLiquid-liquid extraction
we used liquid liquid for this lab experiment
Solvent extraction
what is bronsted acid
proton donor
Solvent extraction
what is bronsted base
proton acceptor
solvent extraction
example of neutral compounds to know...
hydrocarbons, aldehydes,ketones, ethers, amides, esters
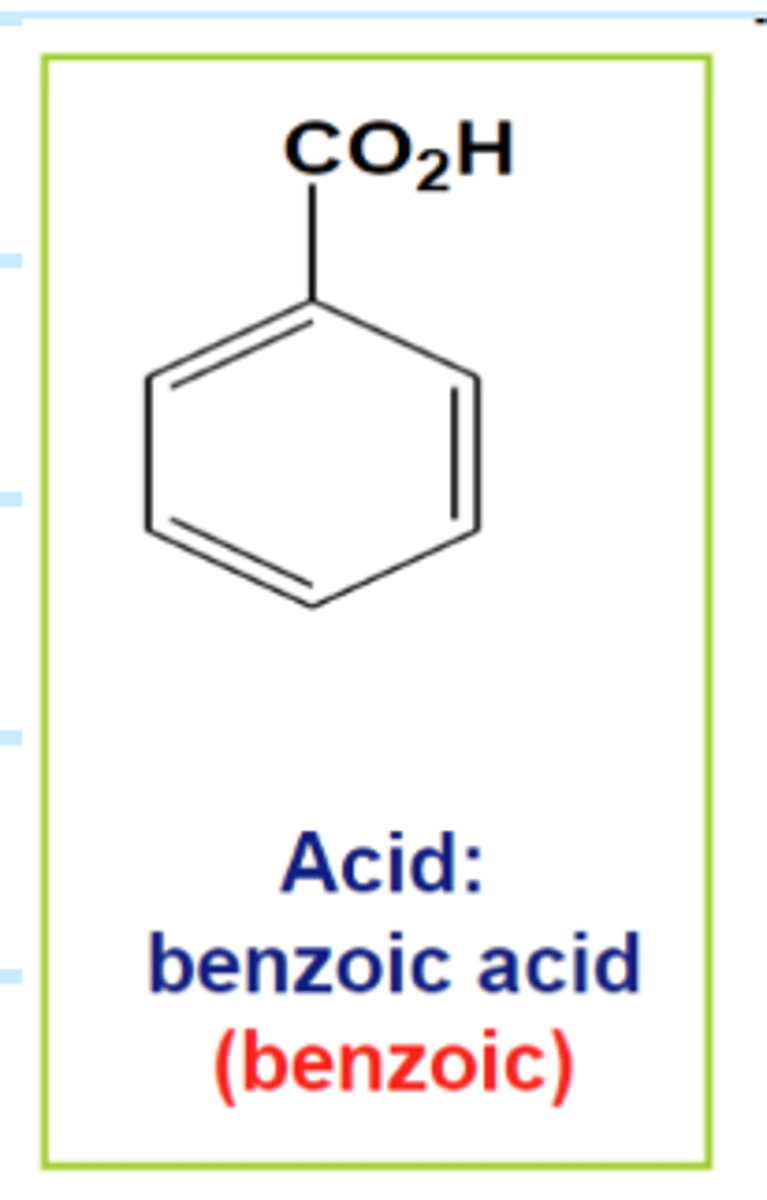
Solvent Extraction
What was the acid
benzoic acid
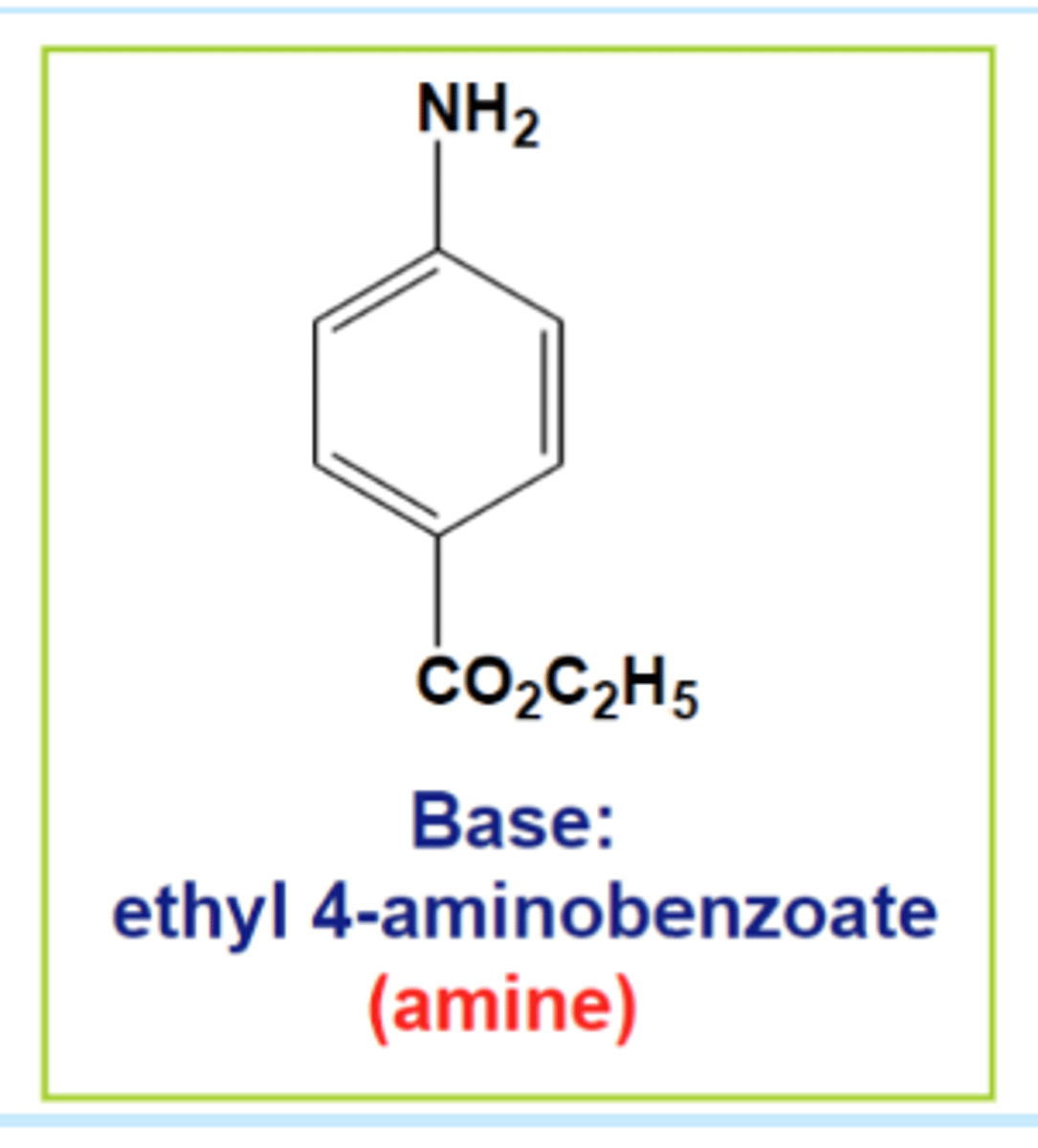
Solvent Extraction
What was the base
ethyl-4-aminobenzoate
Solvent Extraction
What was the neutral compoenent
9-fluorenone
looks like double bond O in between 3 rings
solvent extraction
T or f: The acid, base and neutral compound we use are all INSOLUBLE in water
Solvent Extraction:
Know the reaction that occurs when aqueous HCl or aqueous NaOH is added to a water insoluble base or acid
.....
Solvent Extraction:
What was an indication of the complete extraction of the basic component? (Be specific)
The basic component was considered fully extracted when no spot appeared at its specific Rf value on the TLC plate, indicating it had been completely separated from the mixture. For example in lab when looking at the TLC plate, the basic component ethyl-4-aminobenzoate which was the bottom spot disappeared which indicated proper separation of the compound.
Solvent Extraction
In an extraction...which layer is top/bottom when extracting withether and aqueous solution
ether is the top layer, aqeous solution is the bottom layer
solvent extraction
What is the purpose of adding sodium sulfate?
dry the organic layer
solvent extraction
what is mobile, stationayr phase?
In TLC, stationary phase used is a solid (e. g. silicagel) and mobile phase is a liquid (e. g. organicsolvent such as chloroform, hexane, etc.).
solvent extraction
which compound will have the highest rf, lowest, intermediate?
highest: neutral
intermediate: acid/benzoic
lowest: amine
Look over waste disposal and safety
.........