HAP Brain Quiz
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Meninges
membrane layer located between bone & soft tissue of the NS (brain)
Dura Mater (layer of meninges)
the thick, outermost membrane w/ blood vessels protecting and providing structural support to the brain and spinal cord
Arachnoid (layer of meninges)
no blood vesicles, middle mem, keeps the brain in place
Pia Mater (layer of meninges)
innermost membrane, contains nerves & blood vesicles to nourish cells
Subdura hematoma
Brain injury that causes tissues to bleed & cause pressure
spinal tap
medical professionals insert a needle into the subarachnoid space of the lower lumbar spine, usually between L3/L4 or L4/L5 to collect and test CSF for proteins, cells, & bacteria
Cerebum
large wrinkly part off the brain (cerebral cortex) for higher mental functions + solving problems
Cerebellum
for balance and coordination (has Arbor Vitae- white matter)
brain stem
regulates visceral functions (controls involuntary functions and homeostasis_
Cerebral Hemispheres
right and left sides separated by corpus callosum
corpus callosum
White matter that separates the left and right hemispheres
convolutions of the brain
wrinkles and grooves of the brain
Fissures (convolution of the brain)
deep grooves that separate the lobes of the brain
longitudinal fissures
separate the right and left hemisphere
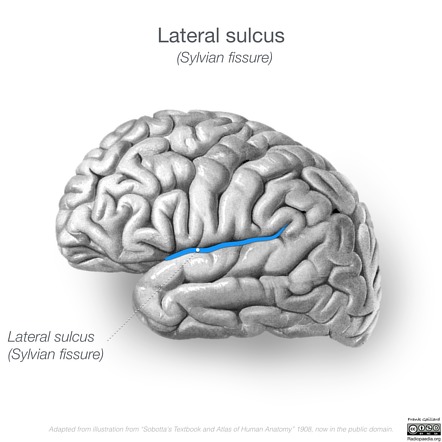
Lateral Fissures
Separates temporal and parietal lobe (not as deep, can be seen)
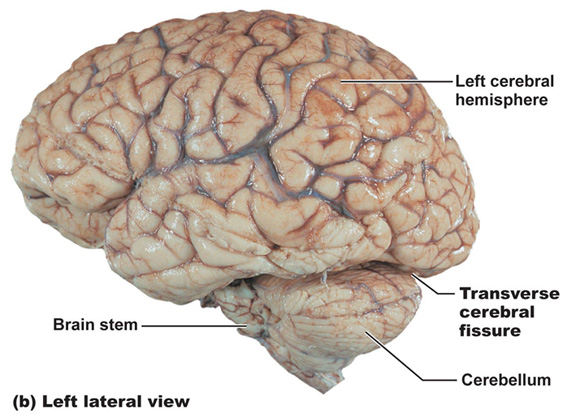
transverse Fissures
separates occipital ad cerebellum (can be seen)
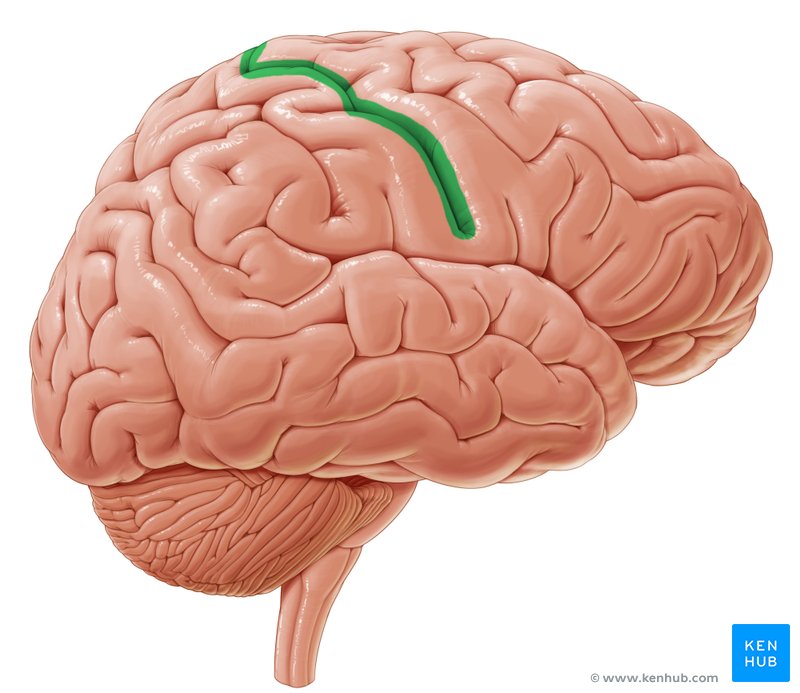
sulcus (convolution of the brain)
shallow groove
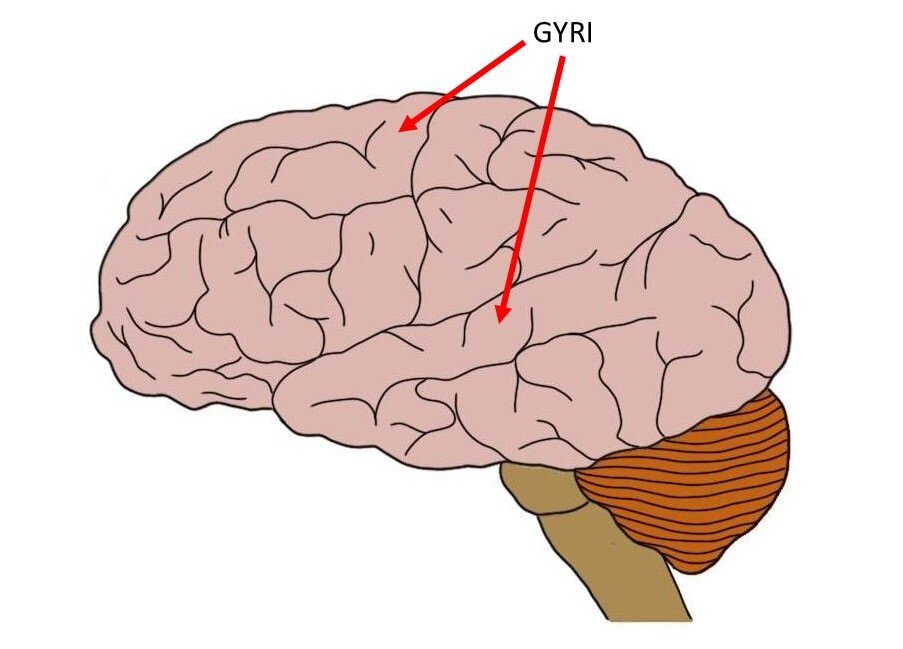
Gyrus
A ridge/fold between two clefs on the cerebral surface of the brain
frontal lobe
executive function, thinking, planning behavioral control
motor cortex
Control movement
Sensory Cortex
process sensations (physical)
Parietal lobe
processes perception, arithmetic, and spelling
occipital lobe
processes vision
Temporal lobe
memory, understanding, language
Ventricles
cavities that are filled w/ fluid & CSF
Limbic System
Hypothalamus, hippocampus, amygdala = plays a role in emotion
What is in Diencephalon?
Hypothalamus, thalamus (subthalamus, epithalamus)
Hypothalamus
maintains homeostasis, control hormones, heart rate, temp, ect
thalamus
relay station for sensory and motor signals
hippocampus
Formation of memories
amygdala
Storage of memories associated with emotional events
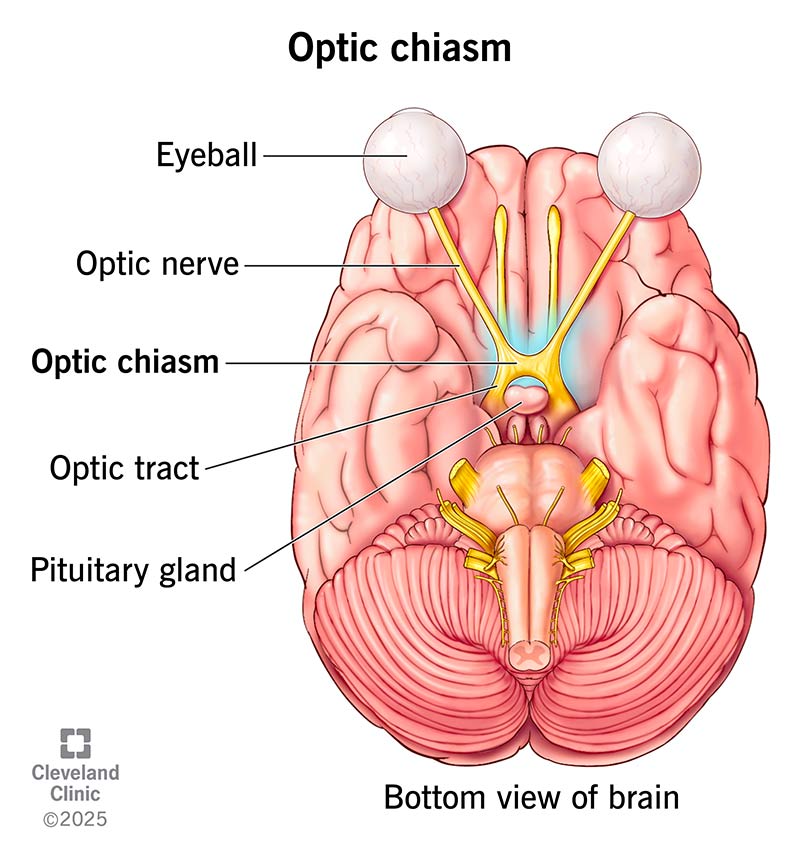
Optic Tract/Chiasm
were the optic nerves cross over eachother
brain stem
midbrain,pons,medulla
midbrain
Visual reflexes, eye movements
Pons
bridge for motor and sensory information to pass between the forebrain and cerebellum
Medulla
Regulates heart rate, respiration, blood pressure
pituitary glad
Master gland of endocrine system controlling hormones
Ascending tract of spinal cord
Receiving sensory info form body (senses and body position)
descending tract of spinal cord
sending motor commands to body