Biology 30 - Unit 3 Booklet 2: Development (Questions)
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
What are the three steps of fertilization?
Capacitating, acrosomal reaction, fertilization
Describe what happens during the capacitating step of fertilization.
Acidic environment of the female reproductive tract causes small pores to open in the acrosome of the sperm. The egg releases chemicals that are detected by receptors on the membrane of sperm, allowing the sperm to swim directionally
Describe what happens during acrosomal reaction.
Enzymes released from the acrosome digest the outer membrane surrounding the egg cell
Describe what happens during fertilization.
A single sperm cell fuses with the plasma membrane of the ovum, creating an electrochemical reaction in the egg and making the egg membrane impermeable to other sperm
During what time can fertilization occur?
Must occur within a specific window of opportunity because egg is only fertile for 10-15 hours and sperm are only fertile for 48 hours
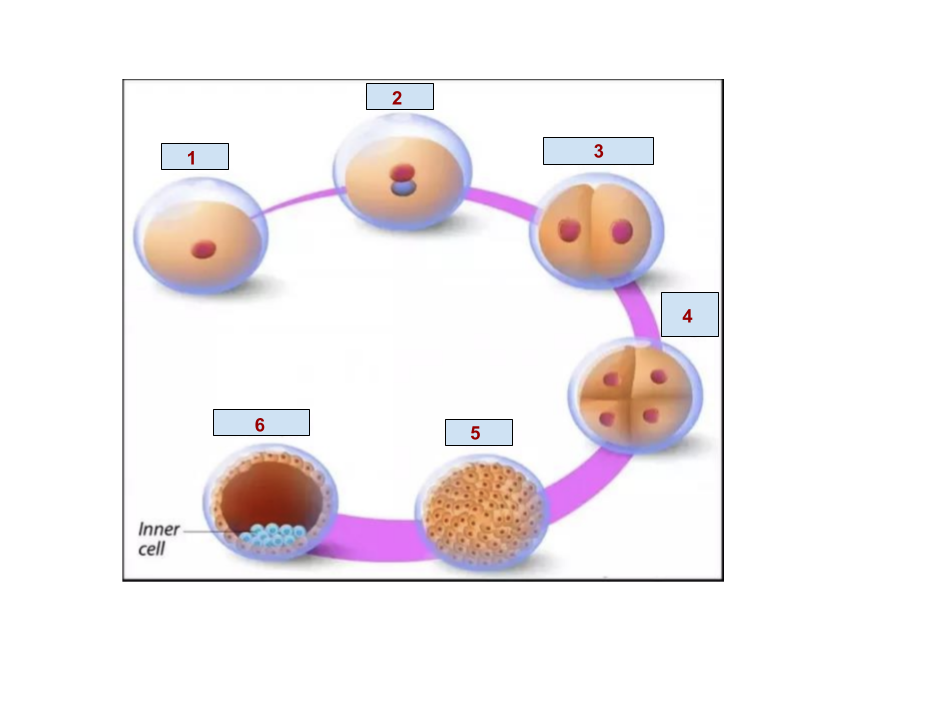
1
Egg
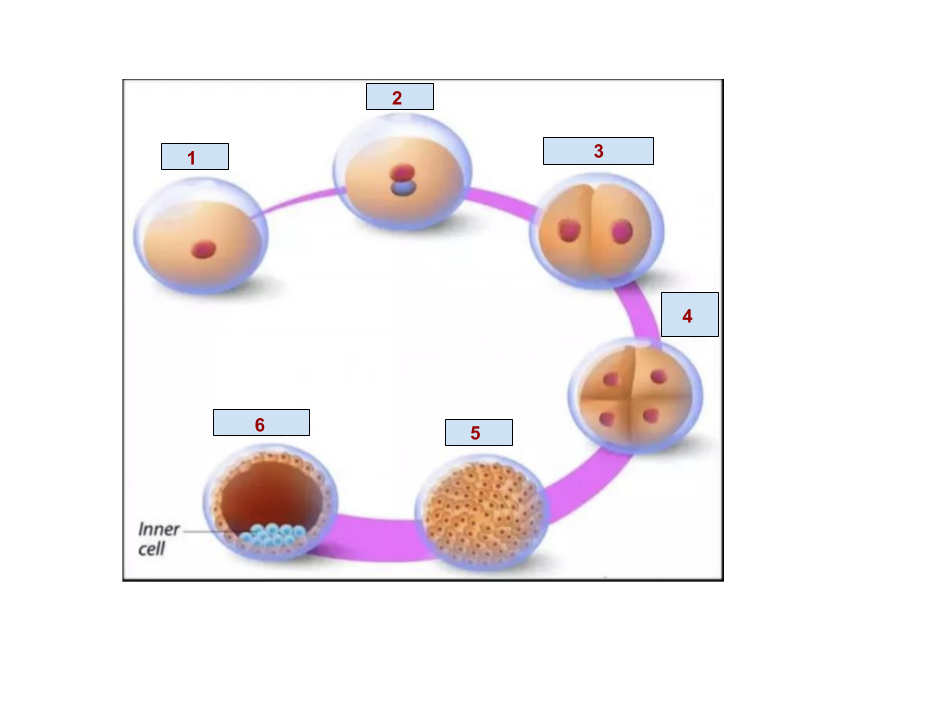
2
Zygote
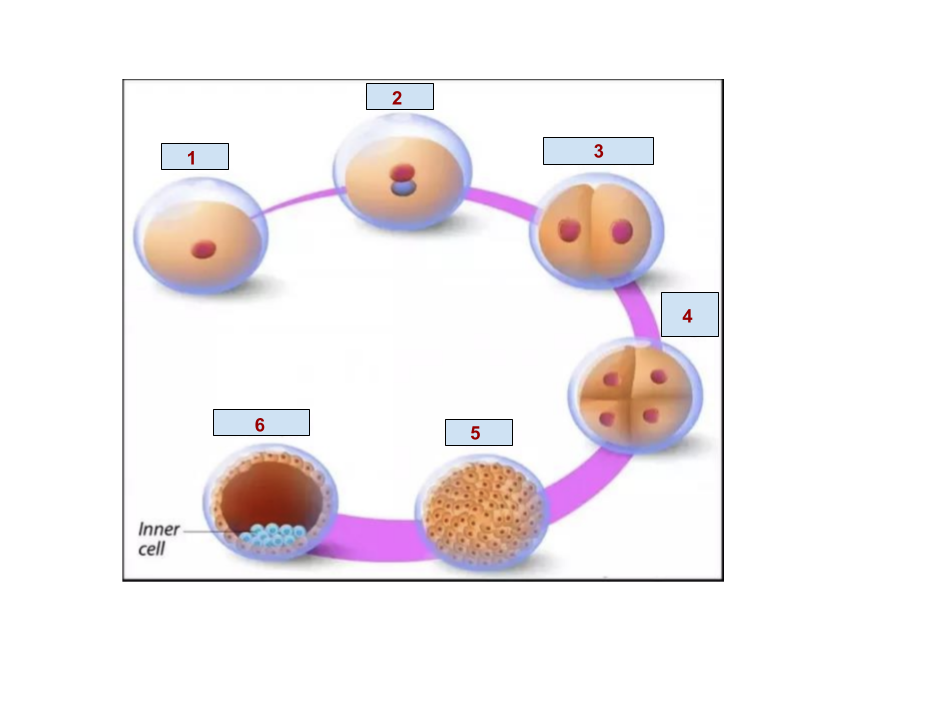
5
Morula
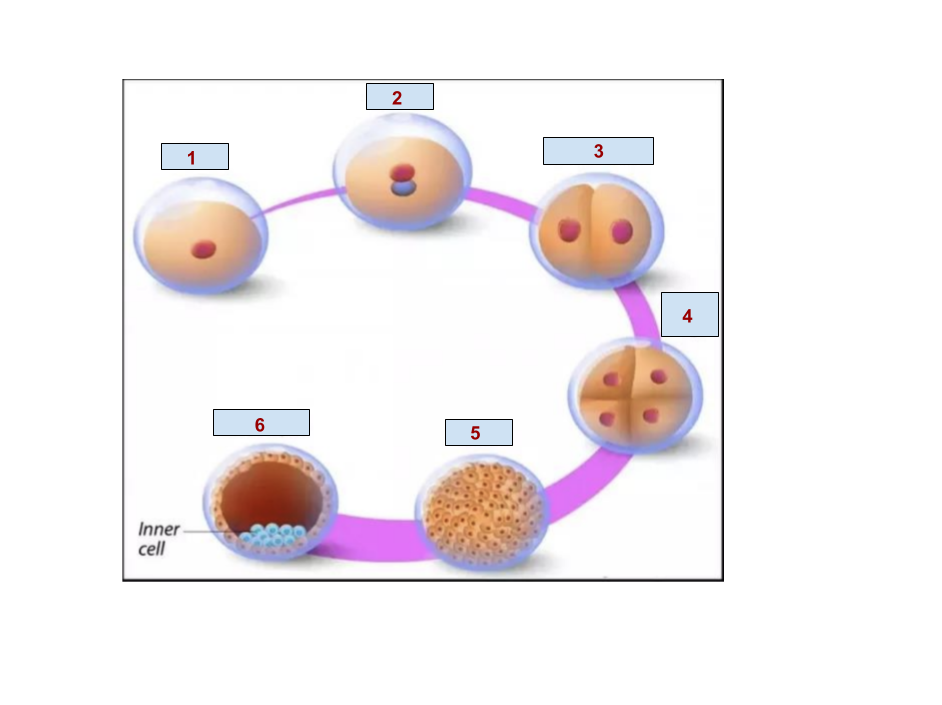
6
Blastocyst
Where does the blastocyst imbed?
Endometrium with sufficient thickness
What needs to be released upon implantation and why?
hCG prevents the corpus luteum from developing for 3 months, causing progesterone and estrogen to continually be made. The endometrium is maintained and contractions are prevented, making sure the embryo can safely develop
What are the hormonal relationships between menstruation and pregnancy?
If pregnancy is established, menstruation does not occur because estrogen and progesterone from the corpus luteum have a negative feedback on the hypothalamus and no GnRH is released. Thus, no secretion of FSH means no new follicles mature and no secrertion of LH means no ovulation
Does maternal and fetal blood mix in the placenta? Why or why not?
Maternal and fetal blood don’t mix because the possibility of incompatible blood types harming the fetus
Do the placenta and corpus luteum function at the same time?
No, after 3 months the placenta is formed and produces enough estrogen and progesterone to keep the fetus healthy and maintain negative feedback to prevent production FSH and LH. Thus the corpus luteum is not needed and dissolves
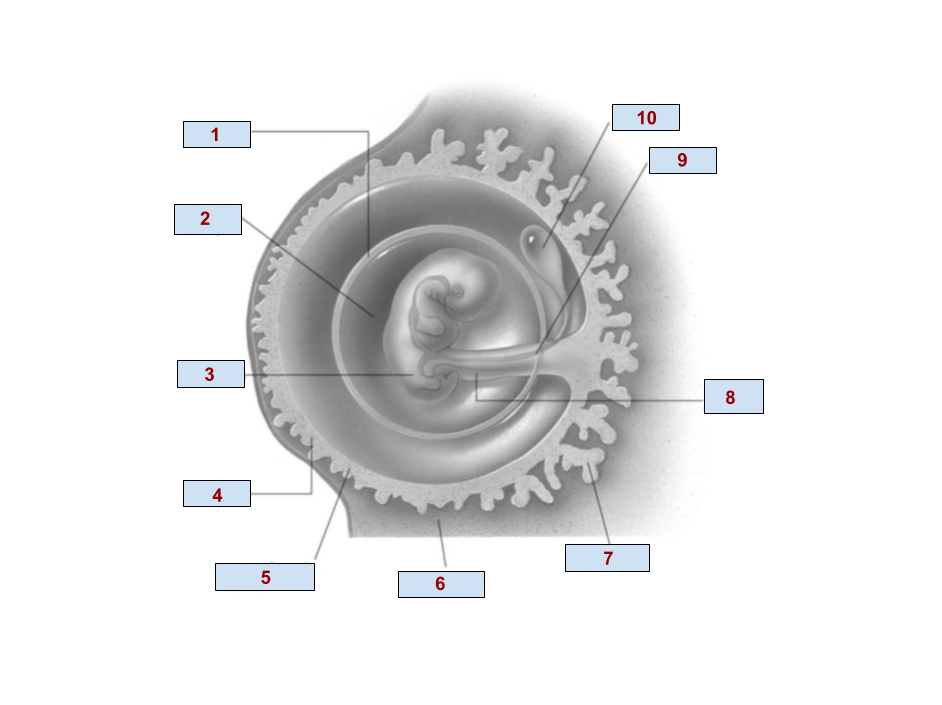
1
Amnion
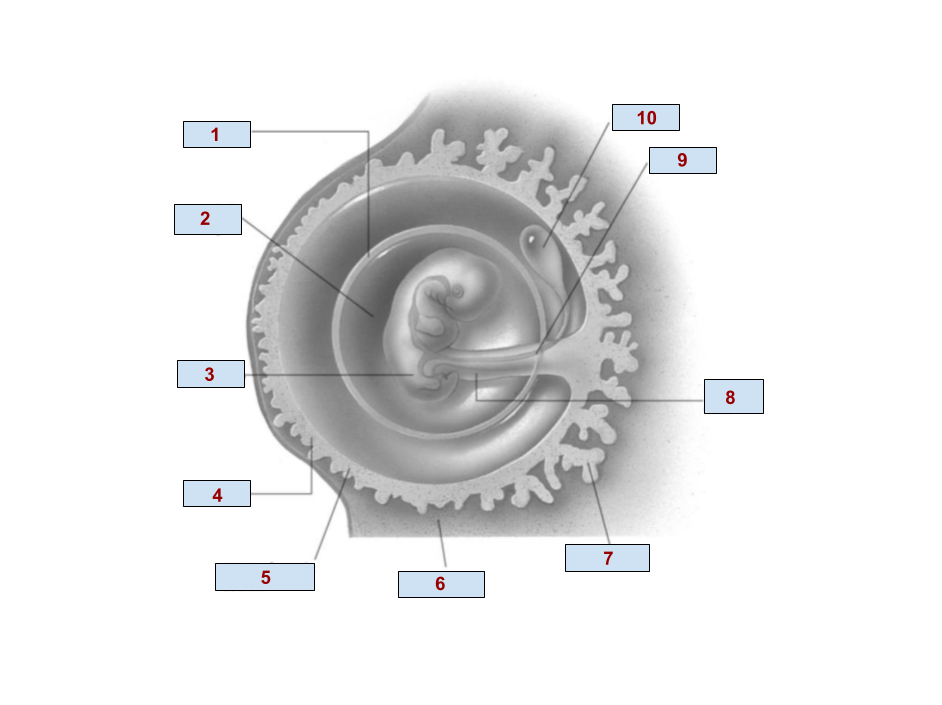
2
Amniotic cavity
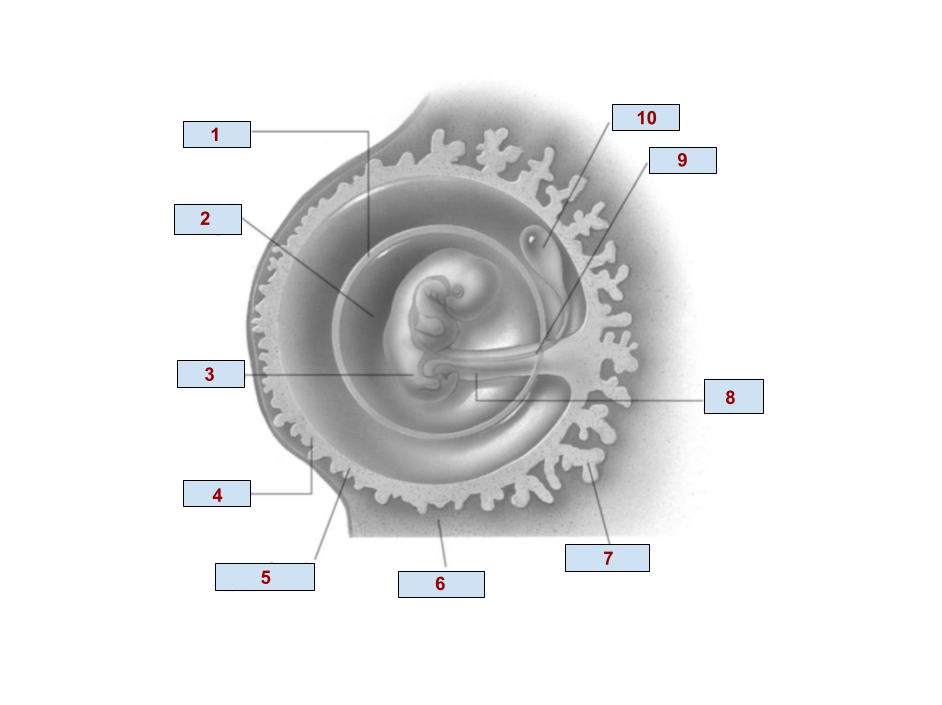
3
Embryo
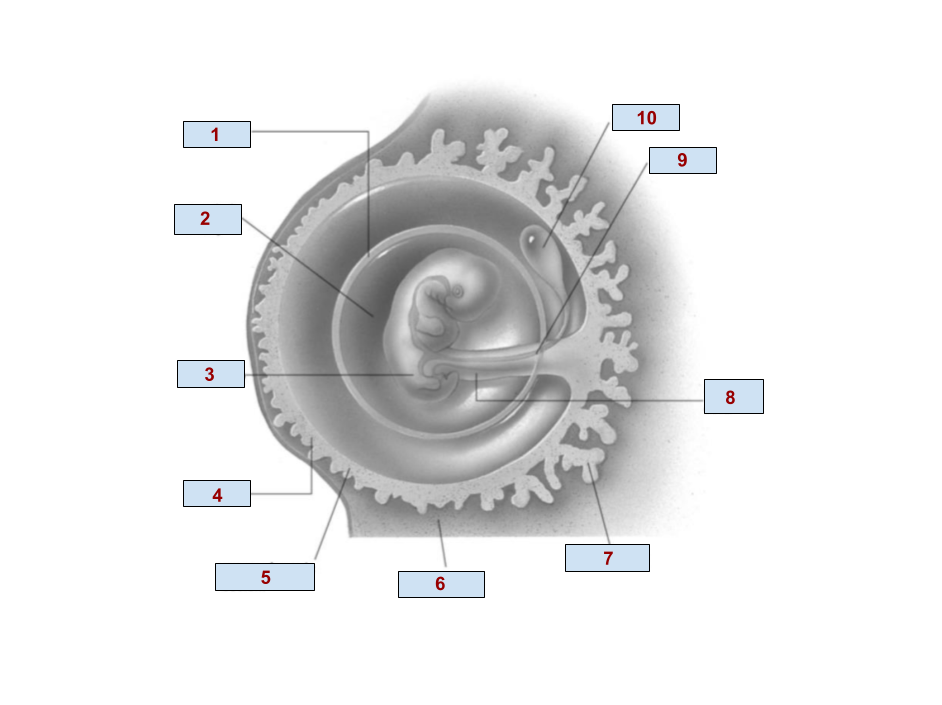
4
Chorion
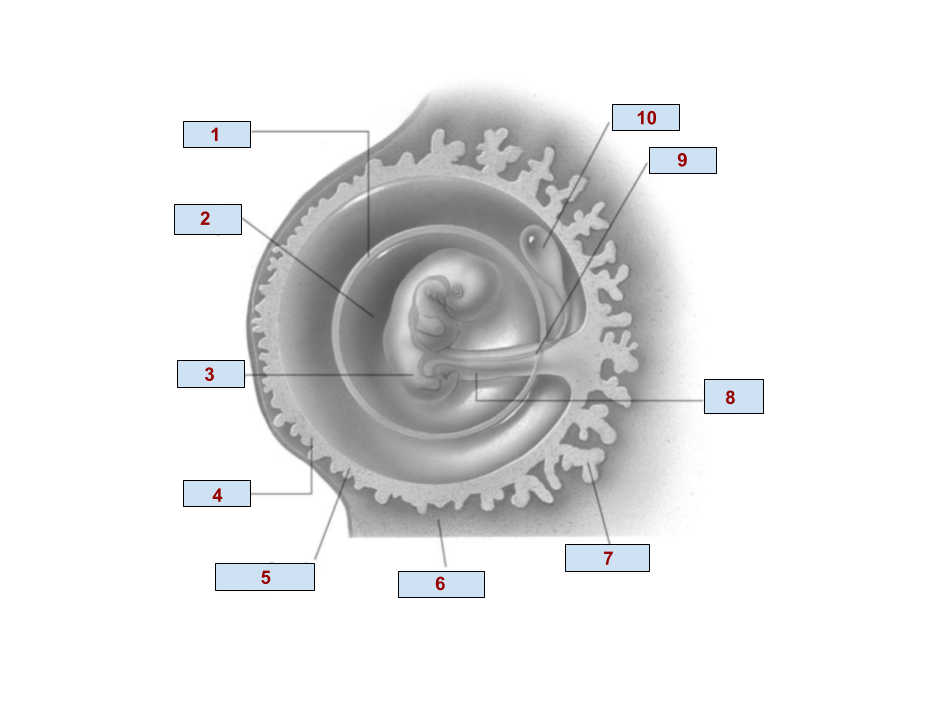
6
Endometrium
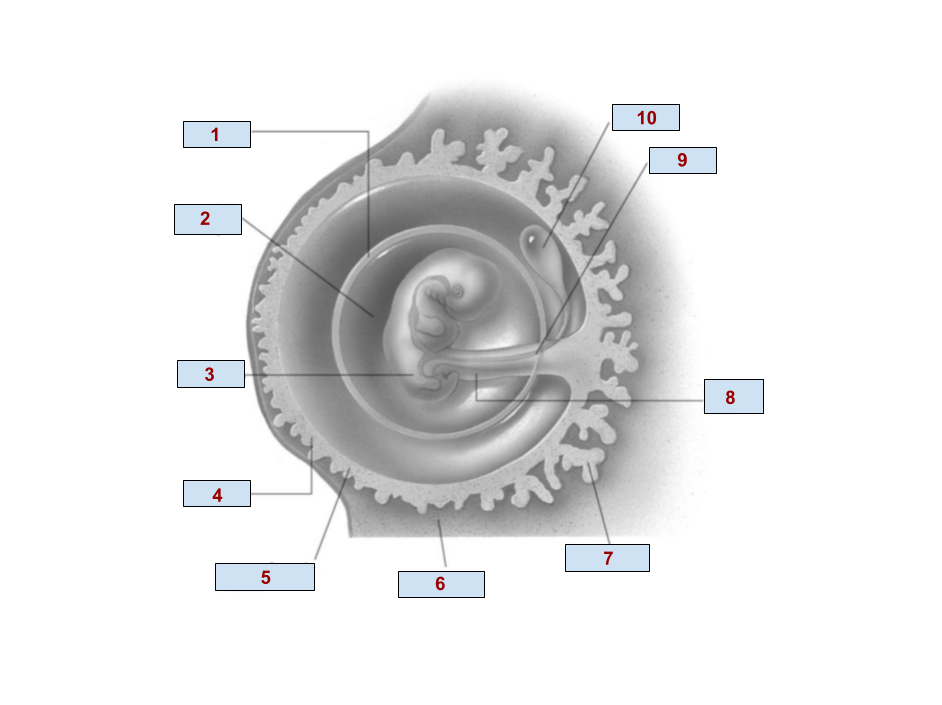
7
Chorionic villi
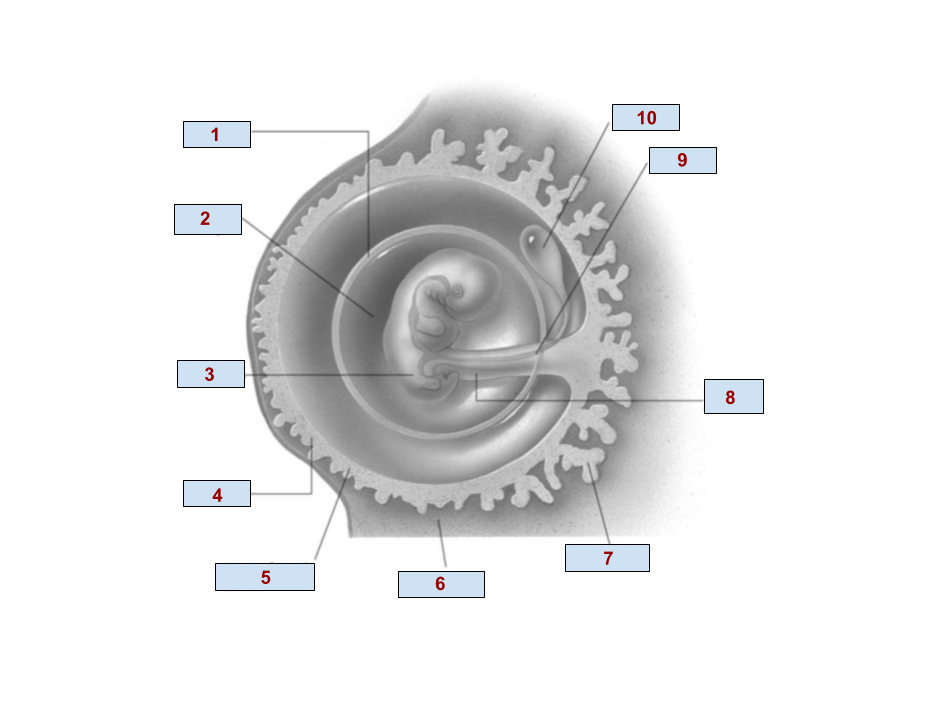
8
Umbilical cord
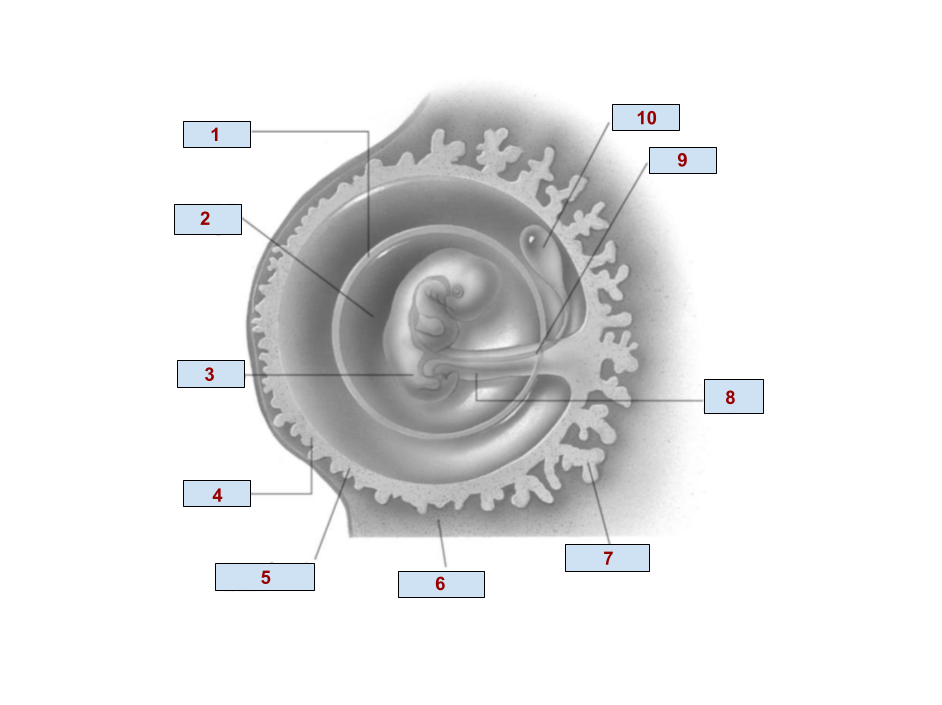
9
Allantois
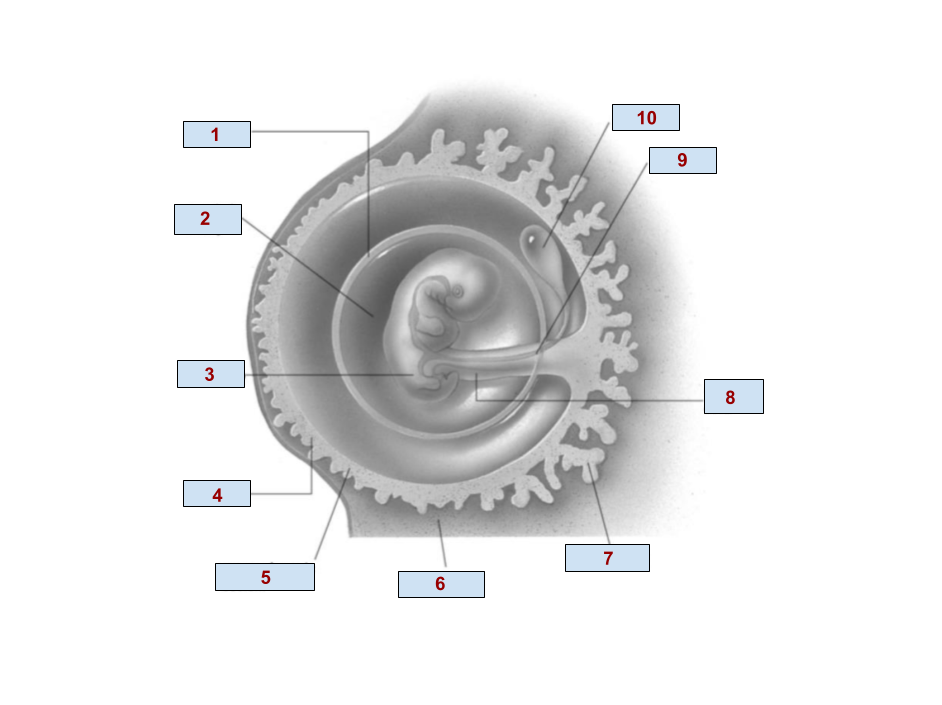
10
Yolk Sac
How are the trimesters of human gestation divided?
1st trimester - weeks 1-12 (fertilization to end of 3rd month), 2nd trimester - weeks 13-24, 3rd trimester - weeks 25-28
What happens during the first trimester (stages of embryonic/fetal development, activity of fetus)?
Zygote undergoes cell division in fallopian tube, becomes a blastocyst and implants in uterus. Develops into a fetus by week 8. Body organs such as anterior brain, limb buds, and heart start to develop. Nervous system development is shown through an evident sucking reflex. Fetus is very sensitive to teratogens and other disturbances
How and when are males and females differentiated during development?
During the first trimester (week 7), testosterone begins to be secreted if Y-chromosomes are present in the embryo, which changes the precursory ovaries into precursory testes
What happens during the second trimester (relative growth of fetus, activity of fetus)?
Rapid growth of fetus. Fetus is actively moving in order to develop muscles. Hair begins to develop and cartilage of skeleton is replaced by bone
What happens during the third trimester (relative growth of fetus, activity of fetus)?
Rapid growth of fetus. Fetal activity decreases due to its size limiting its movement space. Fetus has fully matured and is ready for birth
What will each of the three layers of gastrulation differentiate into?
Ectoderm: skin and nervous system; mesoderm: muscles, skeleton, reproductive structures; endoderm: respiratory and digestive lining, endocrine glands
What are the three stages of childbirth?
Labour, delivery, afterbirth
Describe what happens during labour.
Involuntary, rhythmic contractions of the uterus cause the cervix to open to a diameter of 10 cm
Describe what happens during delivery.
Involuntary uterine contractions (“contractions”) and voluntary abdominal contractions (“pushing”) forces baby out through the cervix and vagina
Describe what happens during afterbirth.
Immediately after delivery, blood vessels in the placenta contract and the placenta separates from the uterine wall, expelled out by muscle contractions
What hormones play a role in childbirth and how?
Progesterone levels decrease to allow the uterus to contract. Oxytocin initiates a positive feedback loop to intensify and accelerate stronger uterine contractions. Relaxin causes the ligaments of the pelvis to loosen to create a larger passageway for the baby. Prostaglandins also help with uterine contractions
How and when does lactation begin?
During pregnancy, high levels of estrogen and progesterone are thought the inhibit the release of prolactin. The expulsion of the placenta during afterbirth causes the mother’s pituitary to secrete prolactin that initiates lactation
When is breast milk produced? Why at this time?
During the first few days of lactation, colostrum is produced instead of breastmilk as the fat in breast milk makes it too difficult to digest for a newborn infant. After a few days of colostrum production, milk is produced
Describe the hormonal feedback process of lactation.
When an infant suckles on the nipple of the mother, prolactin is created and released by the anterior pituitary which causes milk production, while oxytocin is created by the hypothalamus and released by the posterior pituitary causing milk to be released from the mammary into the milk ducts so that the baby can nurse. If suckling continuously occurs, lactation will continue to occur
Where is the tissue sample used for chorionic villi sampling taken from?
The chorion, specifically fetal tissues in the placenta
What are the similarities and differences of using chorionic villi sampling and amniocentesis?
Both are used to prenatally detect chromosomal defects. Chorionic villi sampling can be performed earlier in the pregnancy and results can be obtained within a few days but CVS is much more intensive and thus has a greater risk of spontaneous abortion