Chemical Reactions and Stoichiometry in Year 11 Chemistry
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Chemical Reaction
A process where one or more substances, called reactants, change to form new substances known as products, involving a chemical change.
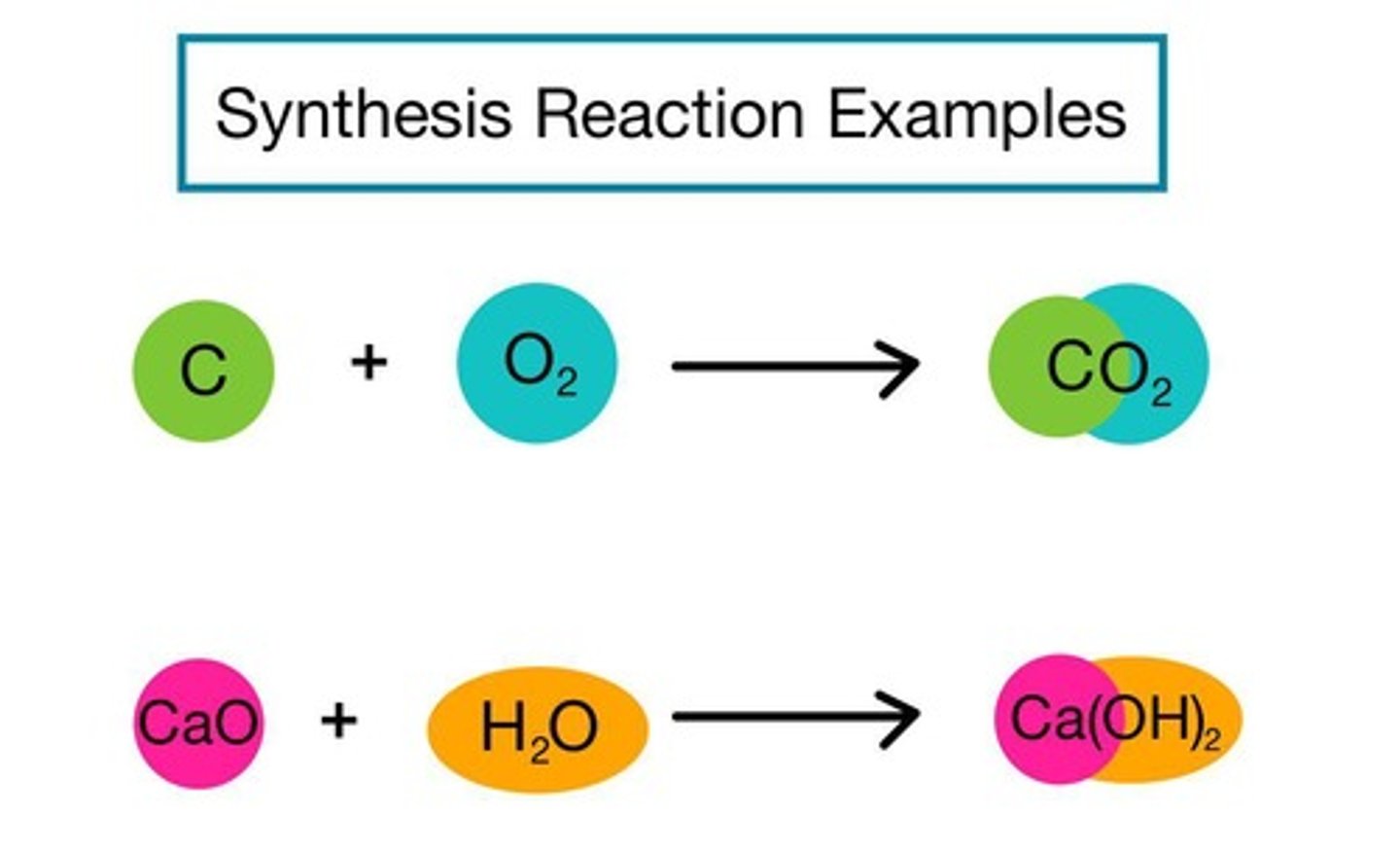
Synthesis Reaction
A chemical process in which simple elements or compounds combine to form a more complex product.
Combustion Reaction
A reaction when a substance reacts with oxygen to release energy in the form of light and heat.
Example of Combustion Reaction
CH4(g) + 2 O2(g) → CO2(g) + 2 H2O(g)
Precipitation Reaction
A chemical reaction occurring in an aqueous solution where two ionic bonds combine, resulting in the formation of an insoluble salt (precipitate).
Example of Precipitation Reaction
Reaction of Potassium Iodide and Lead Nitrate.

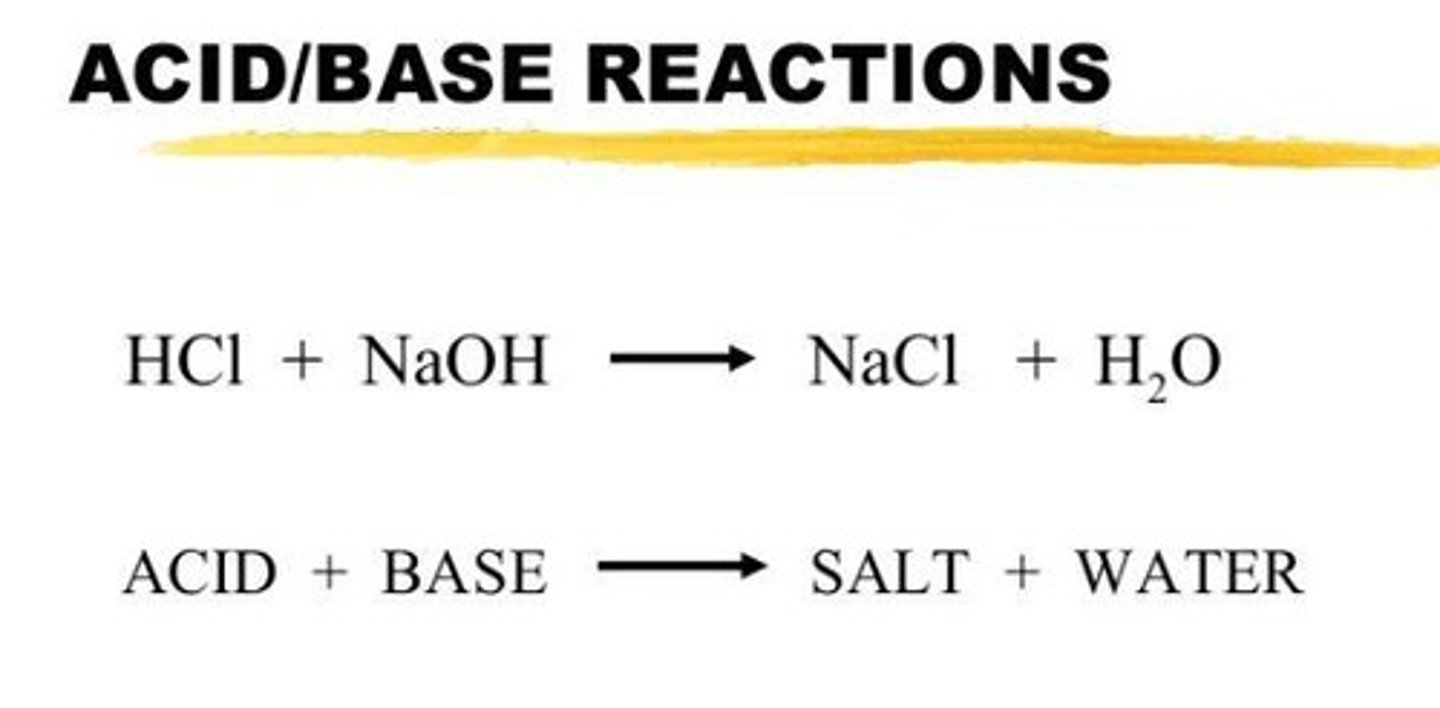
Acid and Base Reaction
Also known as a neutralisation reaction, it involves the reaction of an acid and a base, resulting in the formation of a salt and water.
Example of Acid and Base Reaction
Reaction between HCl and NaOH.
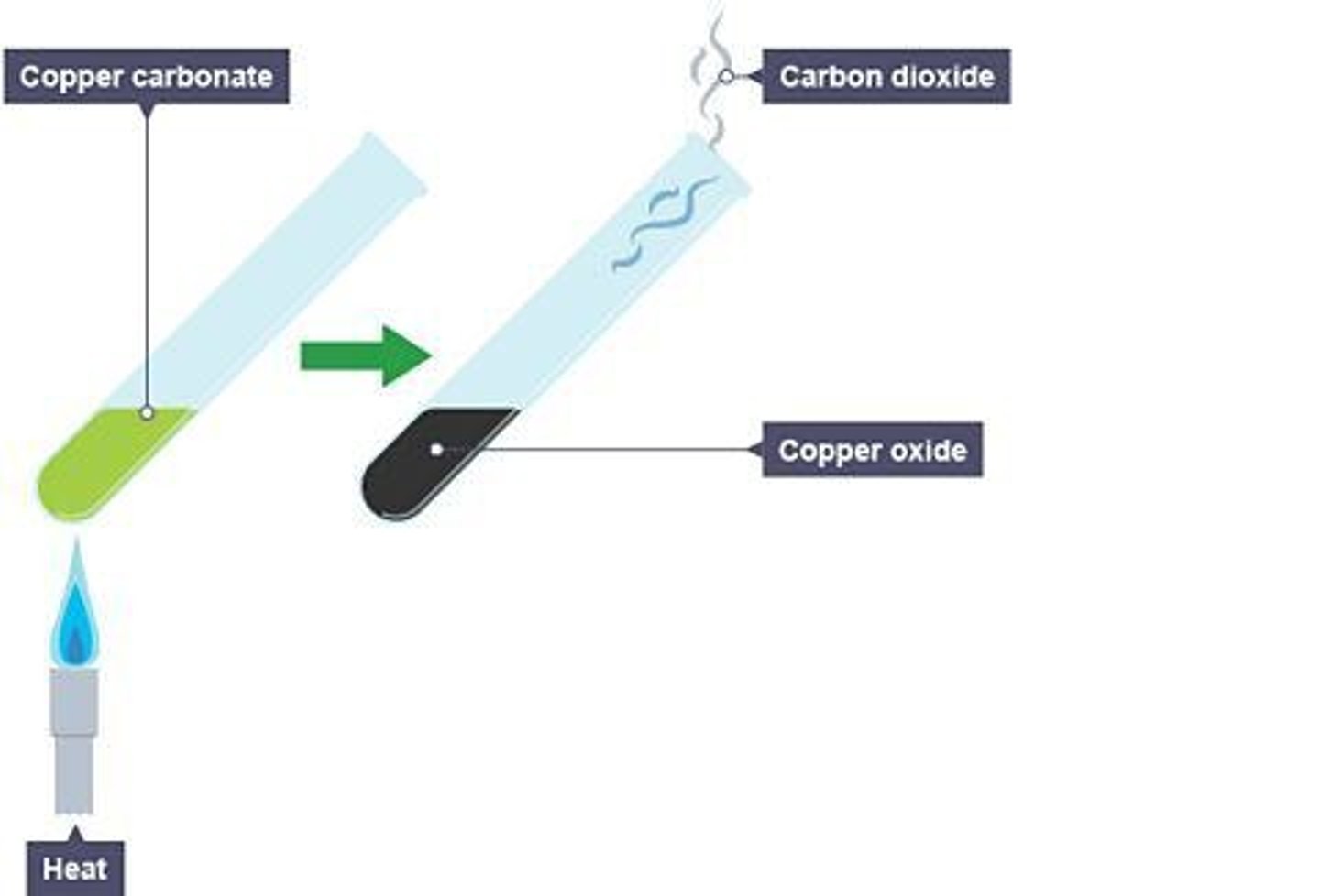
Decomposition Reaction
A reaction in which a compound breaks down into two or more simpler substances, requiring heat or electricity to break the bonds within the compound.
Example of Decomposition Reaction
Decomposition of Copper Carbonate into copper oxide and carbon dioxide when heated.
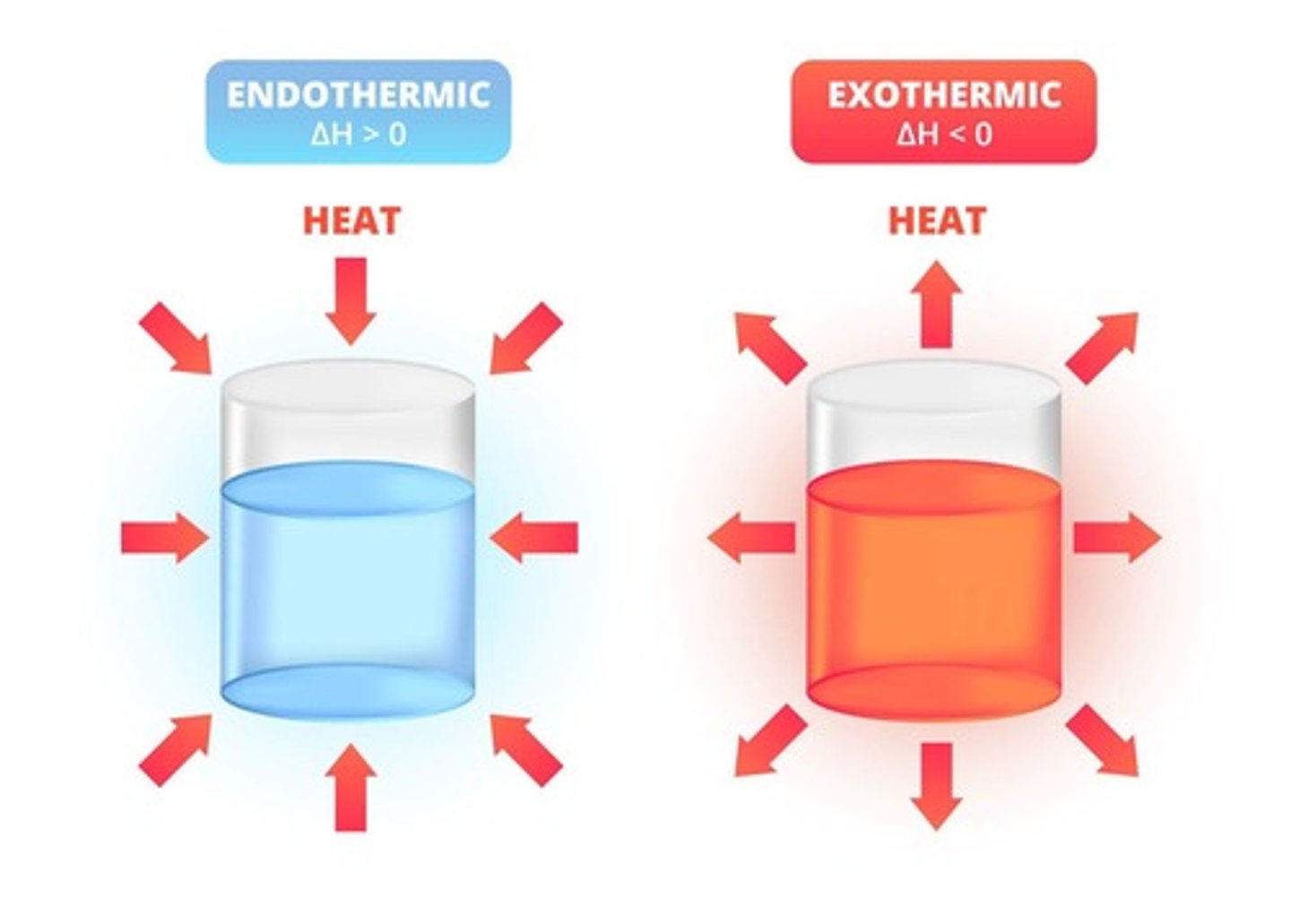
Endothermic Reaction
A reaction that absorbs energy from the surroundings, resulting in a decrease in temperature.
Example of Endothermic Reaction
Thermal decomposition.
Exothermic Reaction
Reactions that release energy to the surroundings, typically in the form of heat, causing an increase in temperature.
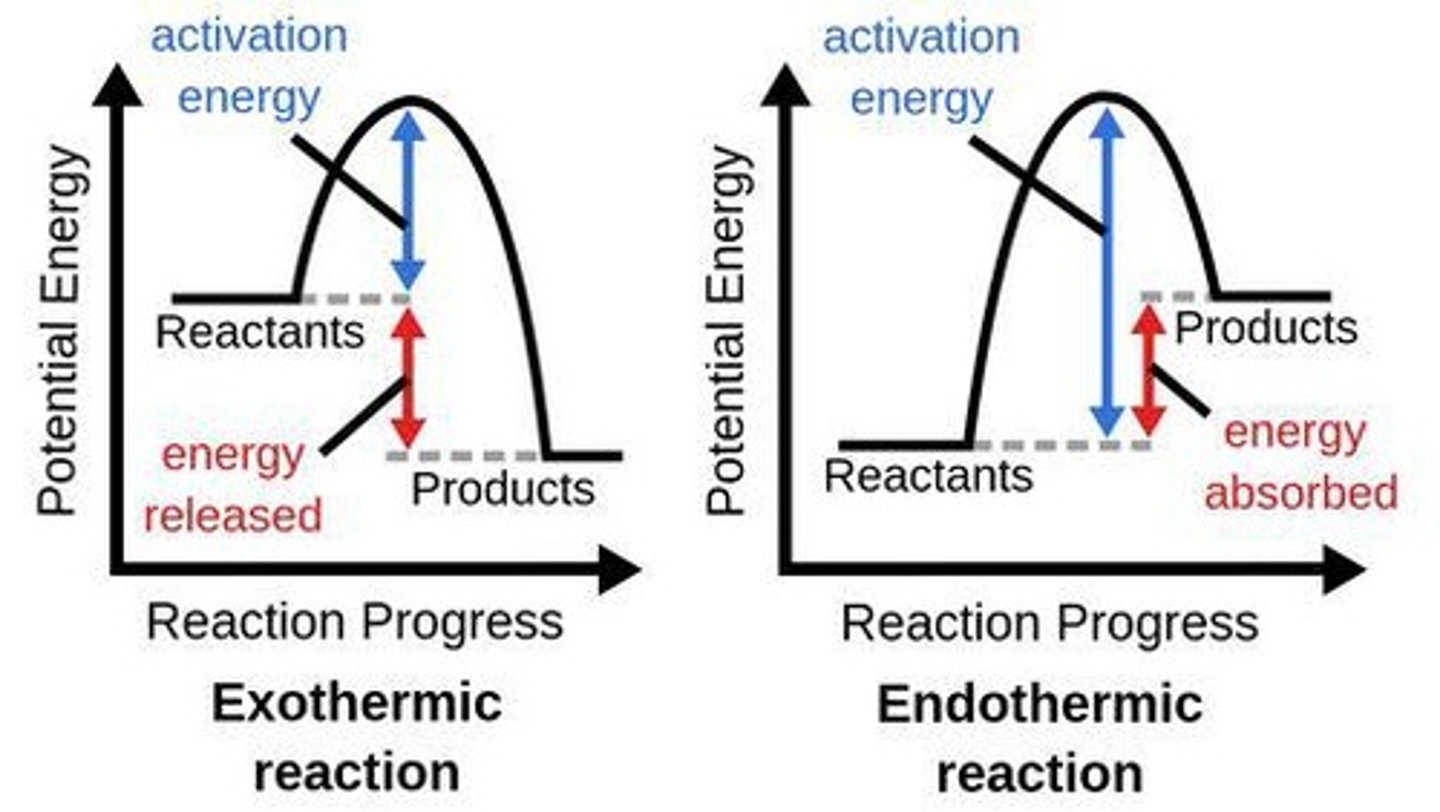
Example of Exothermic Reaction
Combustion, acid-base reactions.
Chemical Energy
The energy of chemical substances that is released when the substances undergo a chemical reaction and transform into other substances.
Stoichiometry
The quantitative relationships of chemical reactions, including masses of solids and/or liquids and volumes of gases.
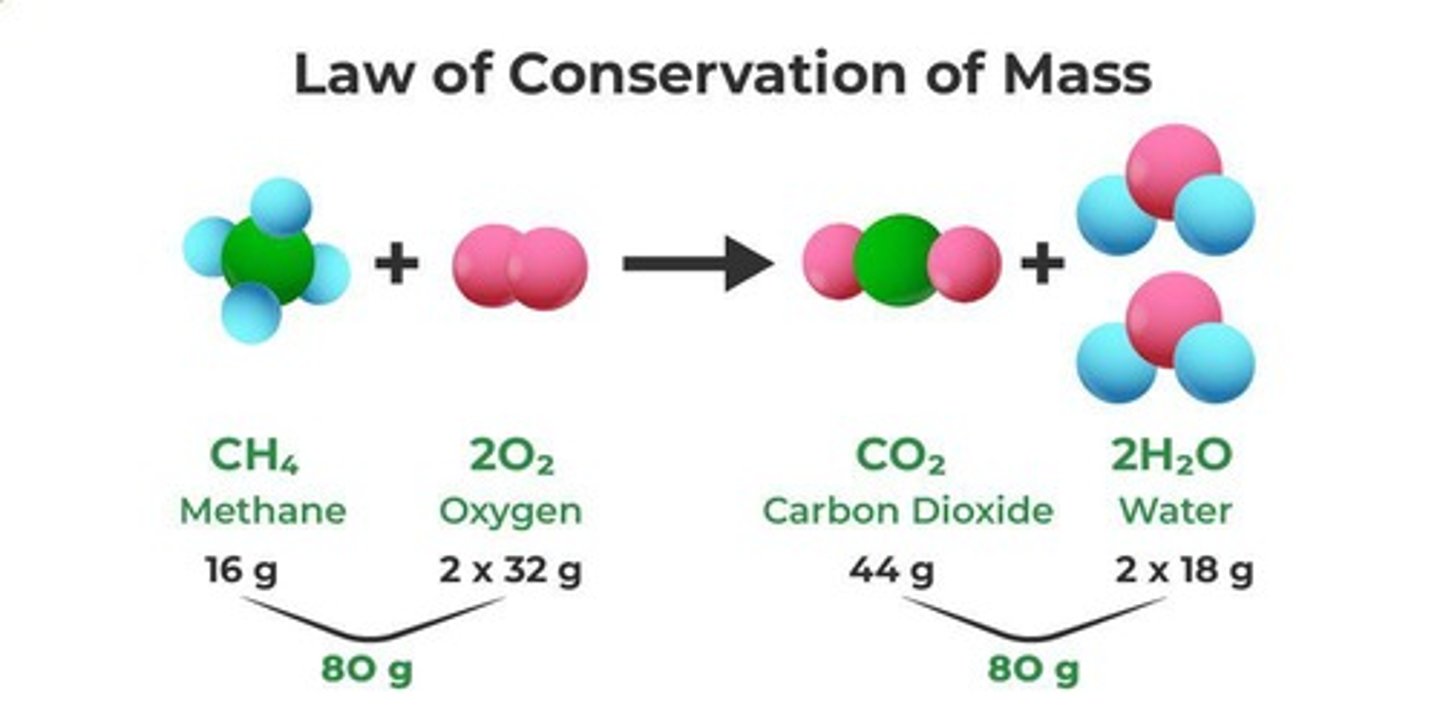
Law of Conservation of Mass
Mass is conserved during a chemical reaction.
Balancing Chemical Equations
The process of ensuring that the number of atoms for each element is the same on both sides of a chemical equation.
Mass Changes in Chemical Reactions
Problems regarding the changes in mass that occur during chemical reactions.
Matter
Anything that has mass and volume (takes up space).
Mass Conservation in Reactions
In a closed system, the mass will stay the same during a chemical reaction.
Open System Reaction
In an open system, the mass may change as it uses up oxygen from the air or releases a gas product to the air.
Reaction Equation for Copper Carbonate
CuCO3 (s)→CuO(s)+CO2 (g)
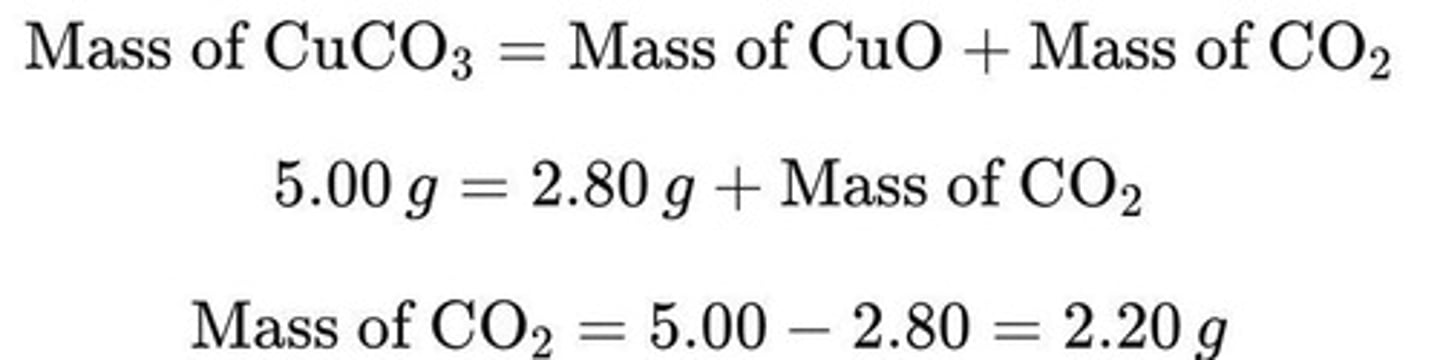
Initial Mass of CuCO₃
5.00 g
Mass of CuO Produced
2.80 g
Mass of Gas Produced
The mass of CuCO₃ decomposed is equal to the sum of the mass of CuO and the mass of CO₂ produced.
Reaction Equation for Magnesium
2Mg(s)+O2 (g)→2MgO(s)
Mass of Magnesium Used
0.24 g
Mass of Magnesium Oxide Produced
0.40 g
Mass Before Reaction
Includes only the mass of magnesium.
Mass After Reaction
Includes the mass of magnesium plus the mass of oxygen that combined with it.
Mass of Reacted Oxygen
0.16 g
Calculation of Mass of O2
Mass of O2 = Mass of MgO − Mass of Mg = 0.40 g−0.24g = 0.16 g
Diagram Illustration of Conservation of Mass
Visually represents the same number and type of atoms on both the reactant and product sides of a chemical equation.