IGSCE Biology - Transport in Humans
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
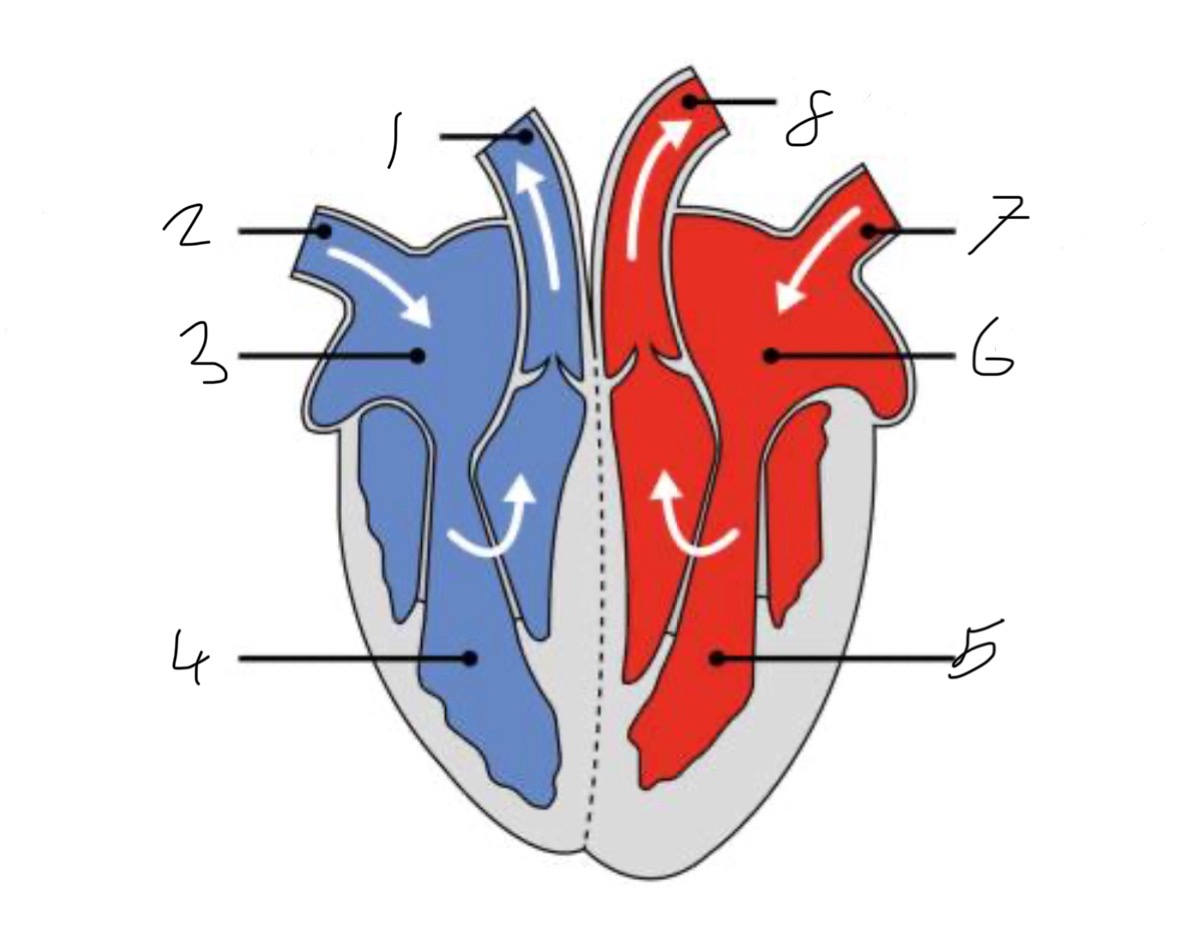
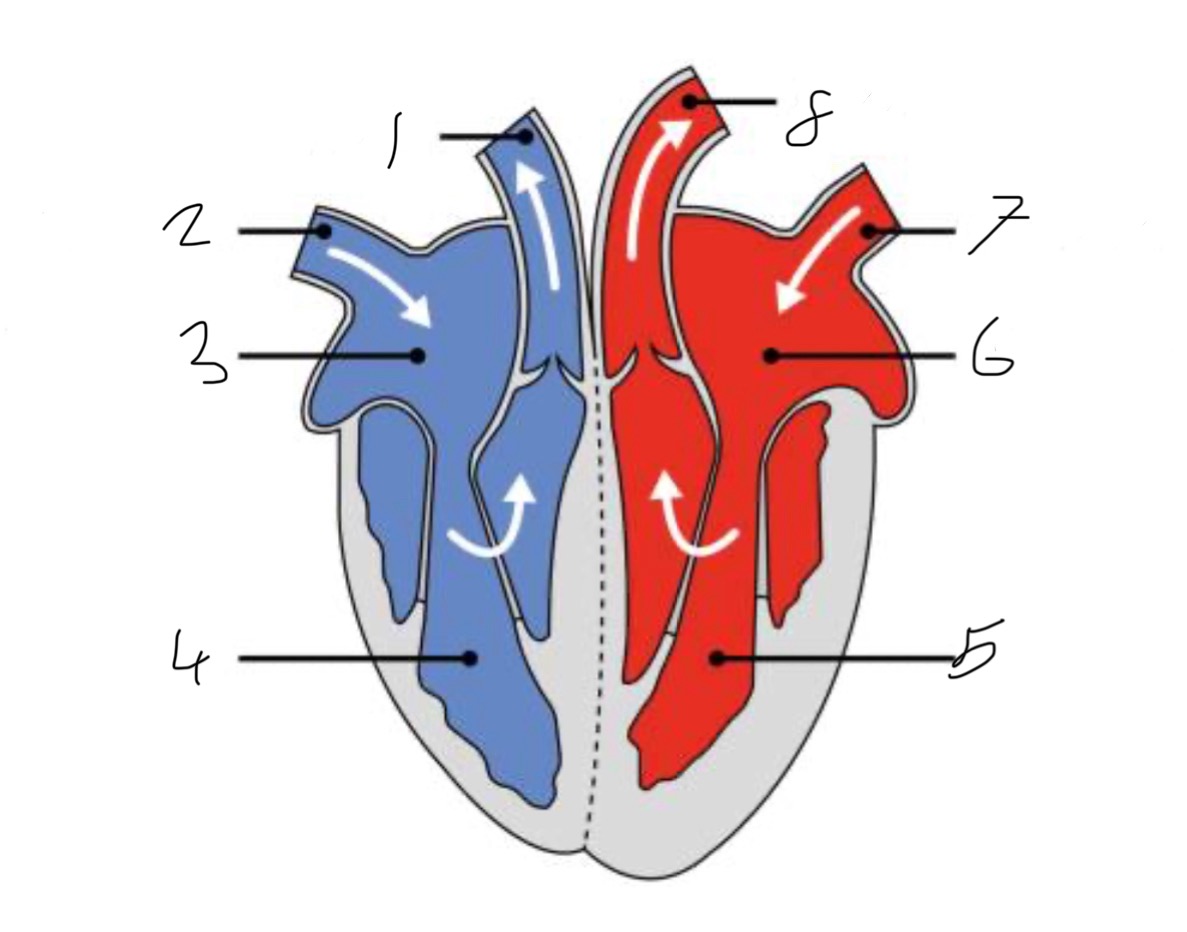
What is the name of the part of the heart labelled as 1?
Pulmonary artery
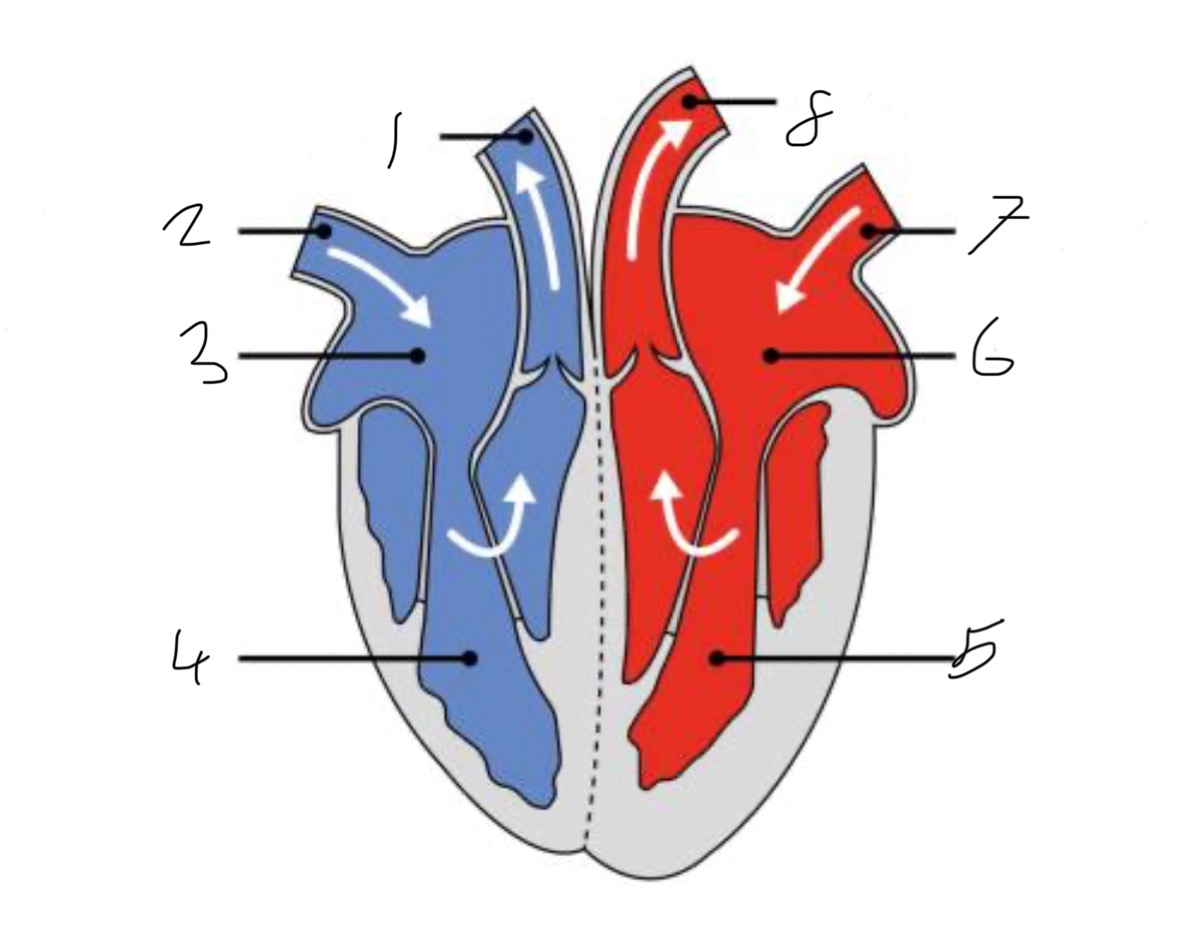
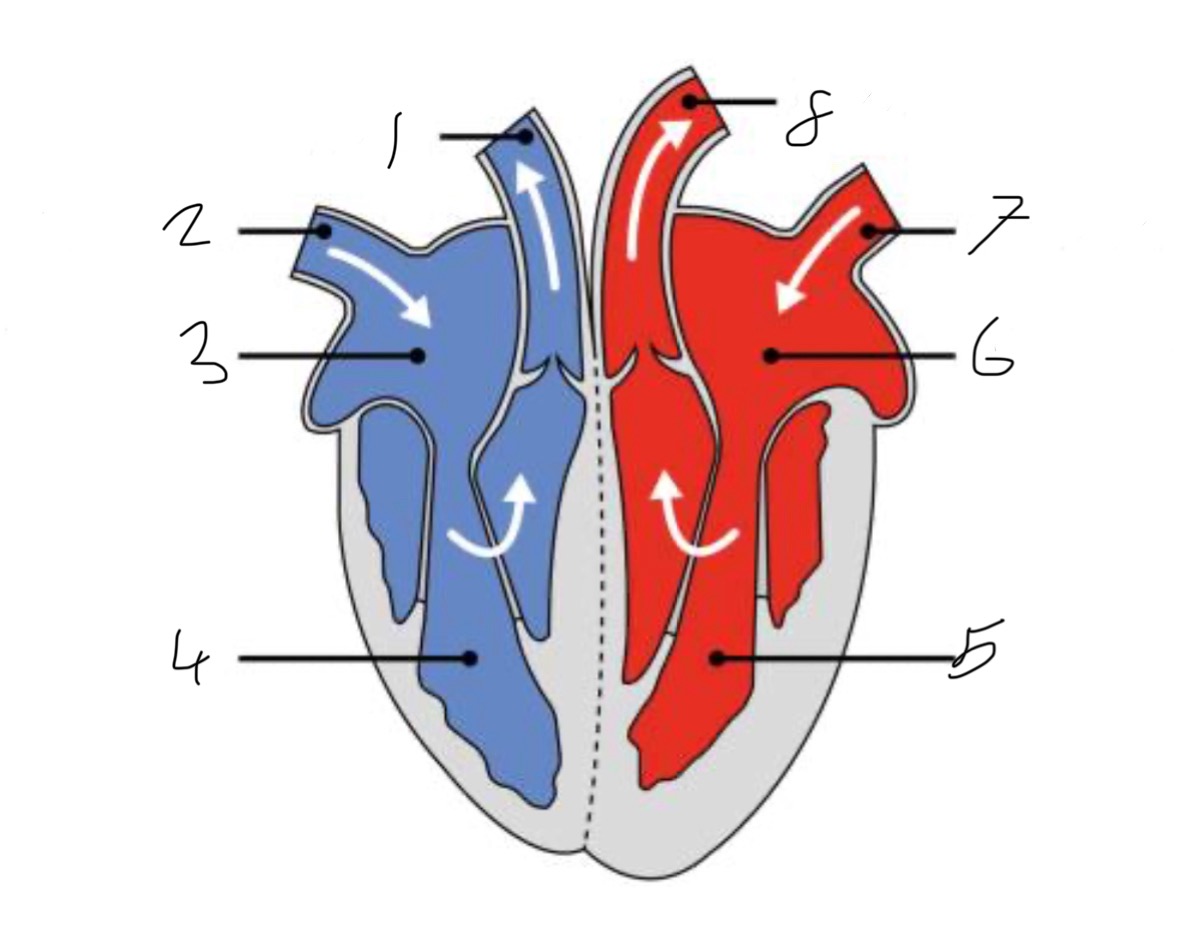
What is the name of the part of the heart labelled as 2?
Vena cava.
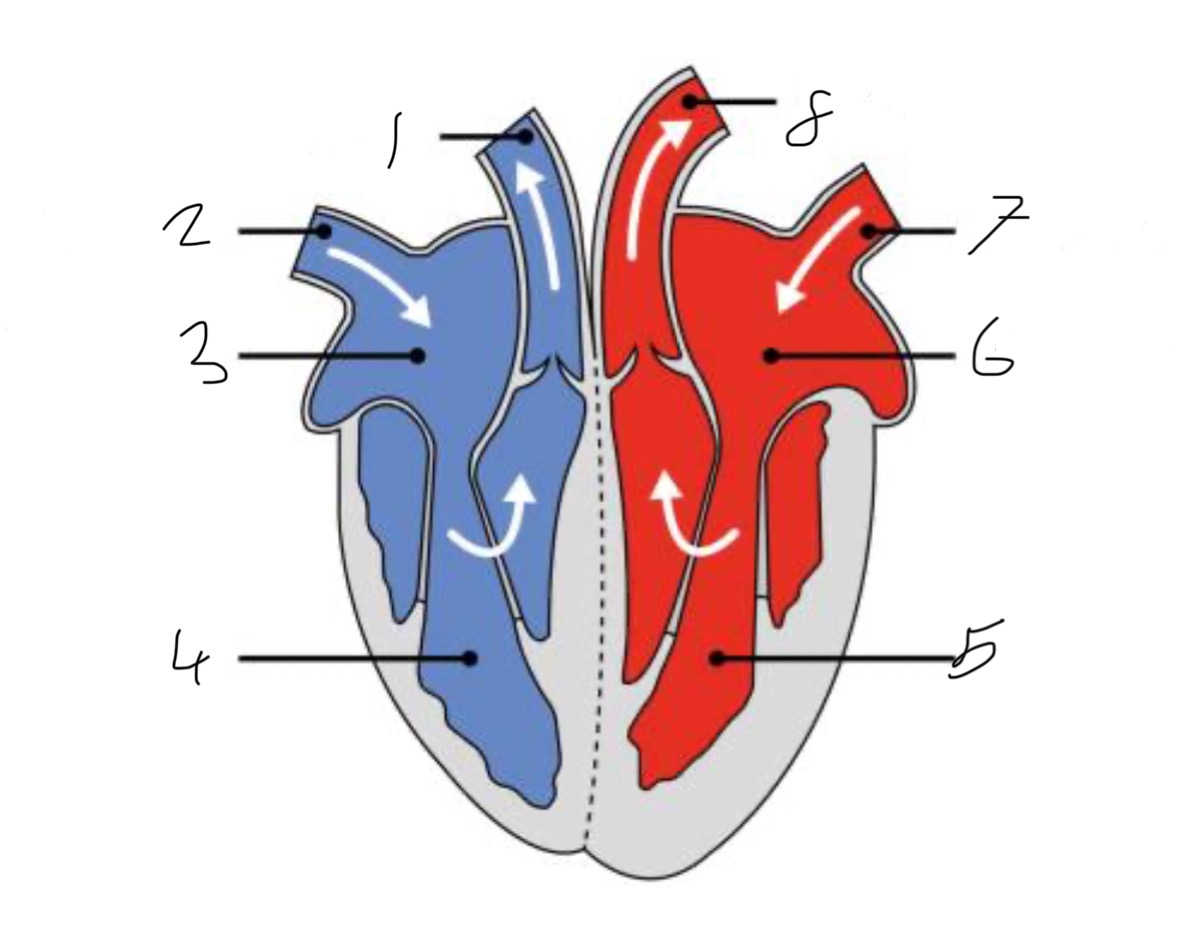
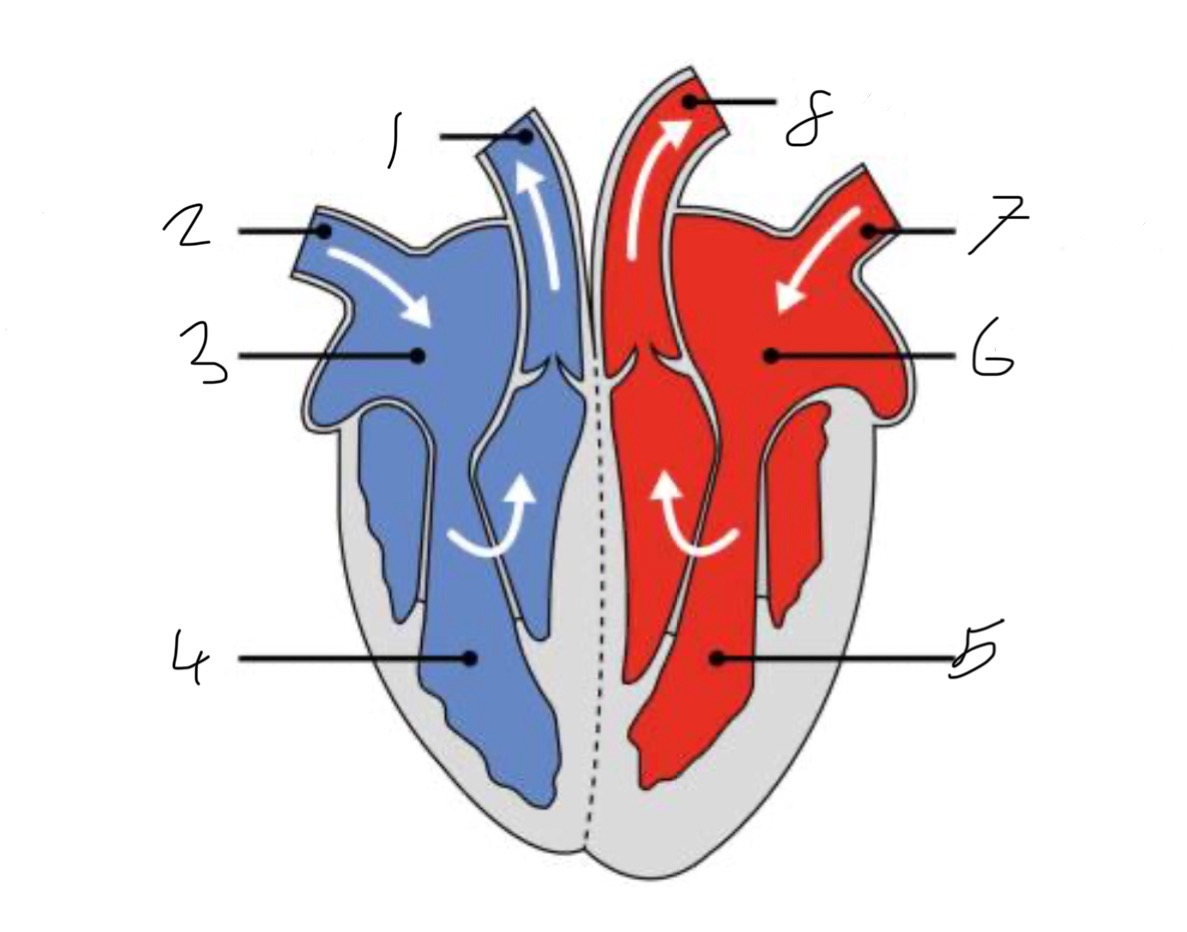
What is the name of the part of the heart labelled as 3?
Right atrium.
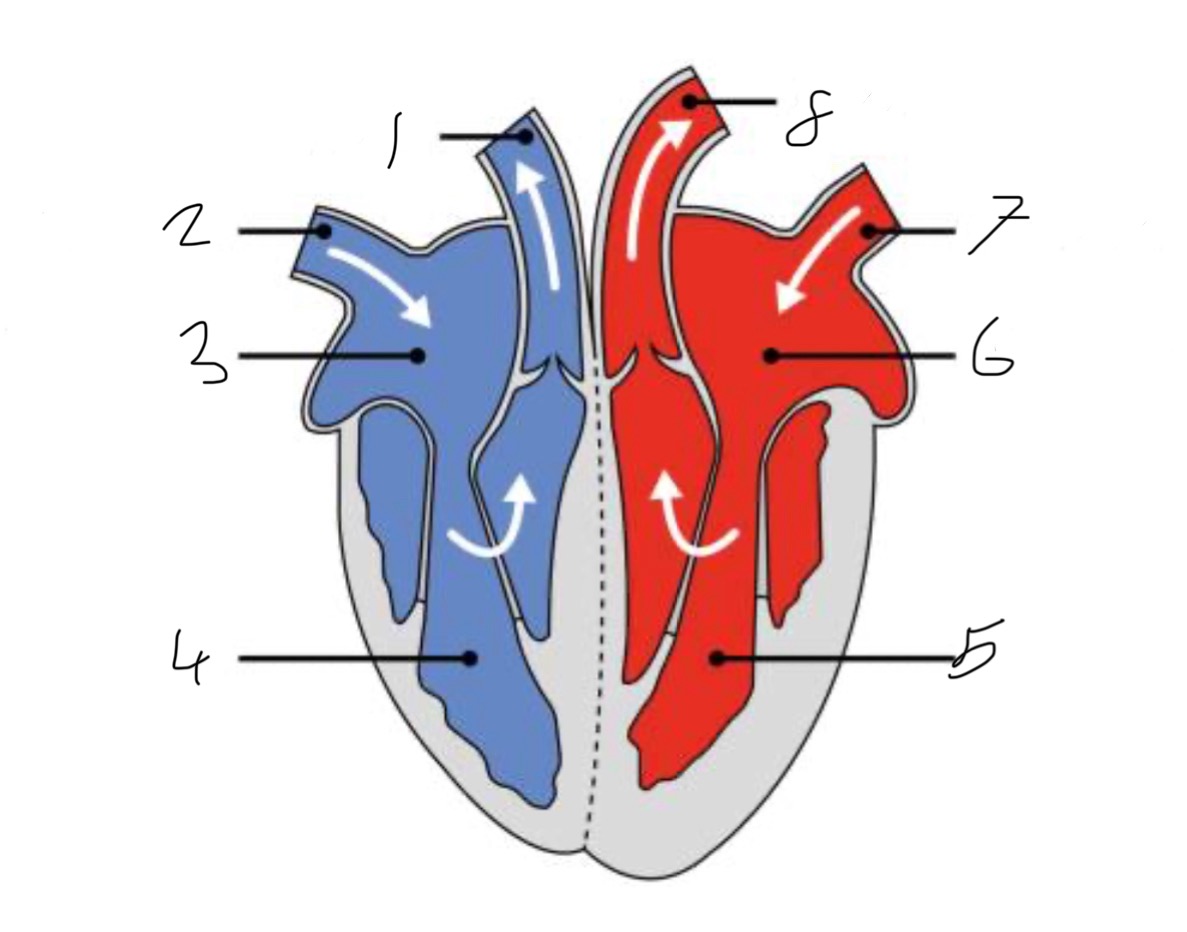
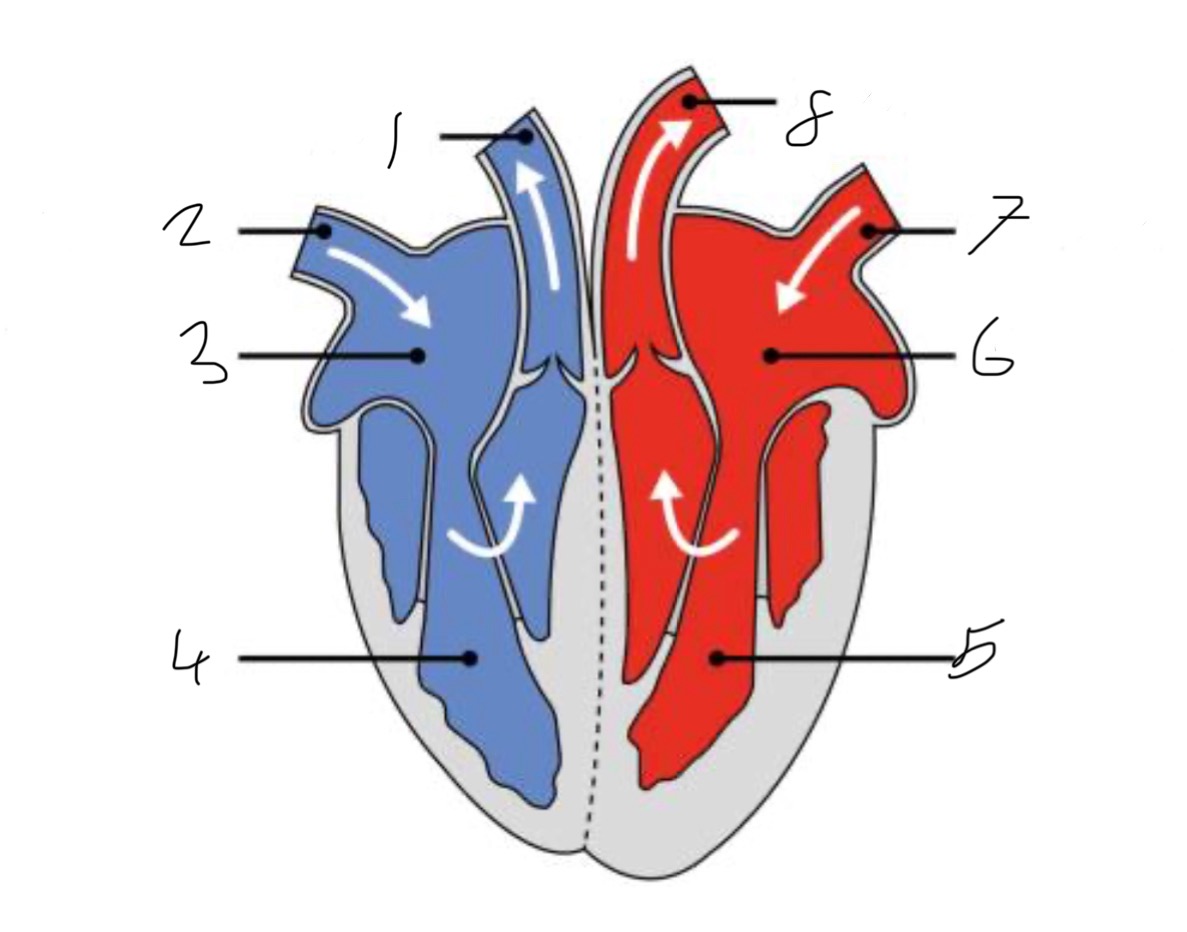
What is the name of the part of the heart labelled as 4?
Right ventricle.
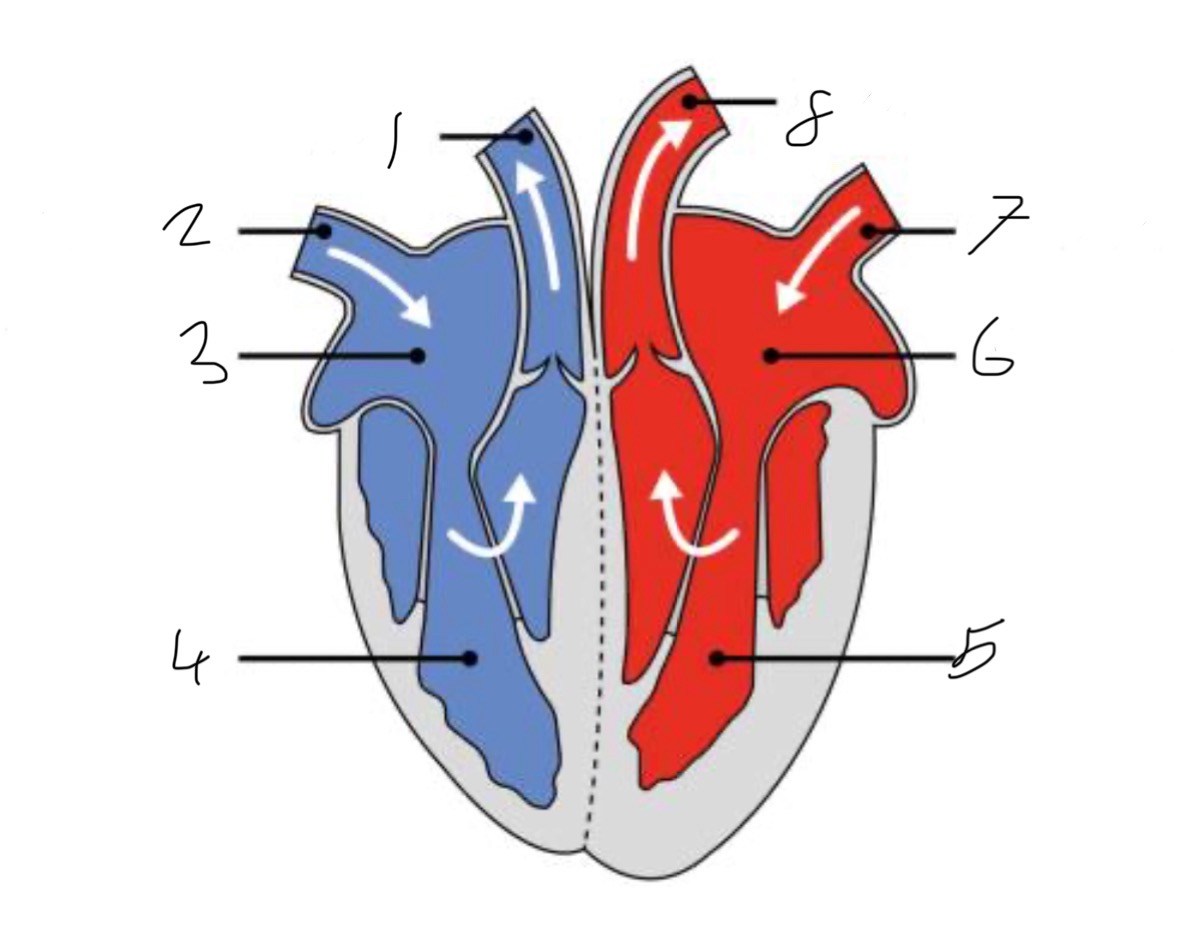
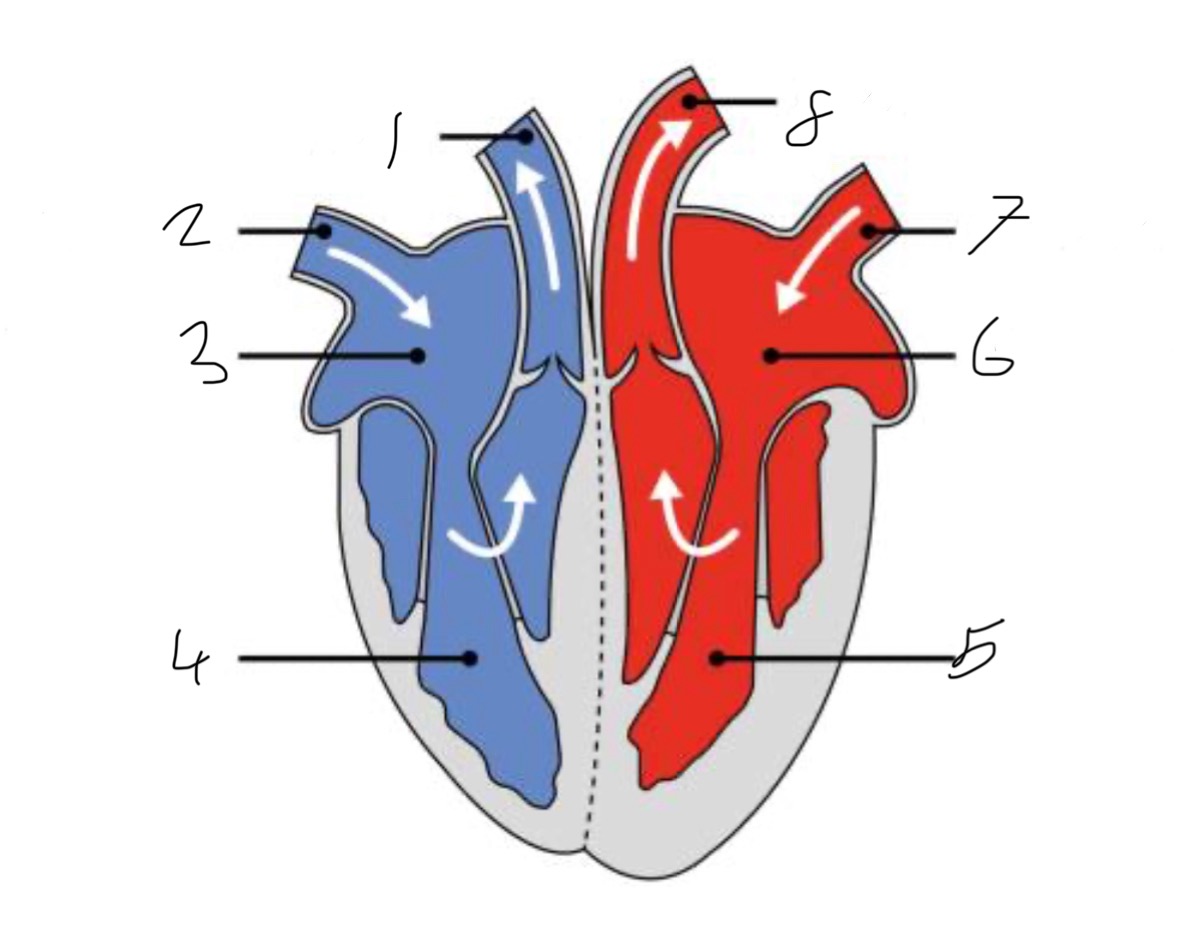
What is the name of the part of the heart labelled as 5?
Left ventricle.
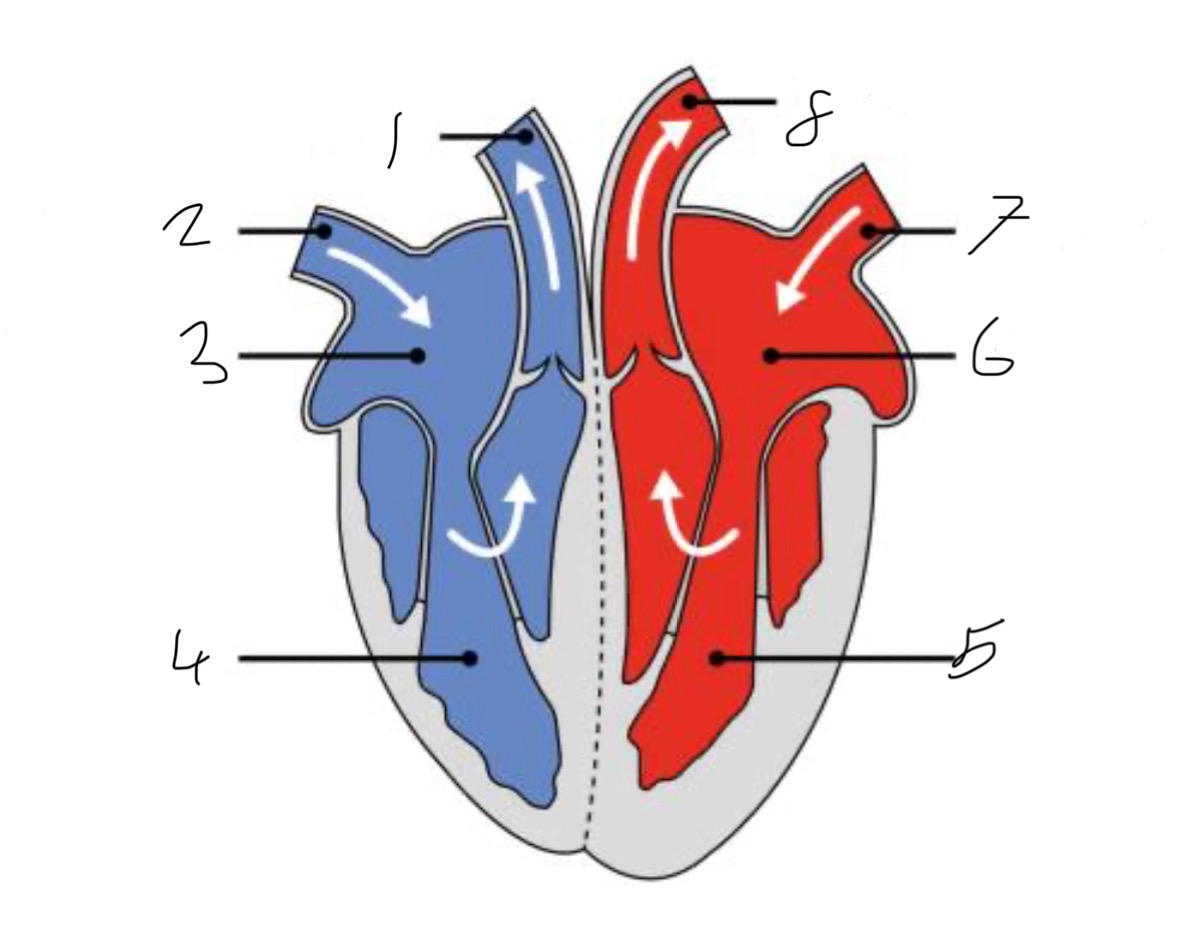
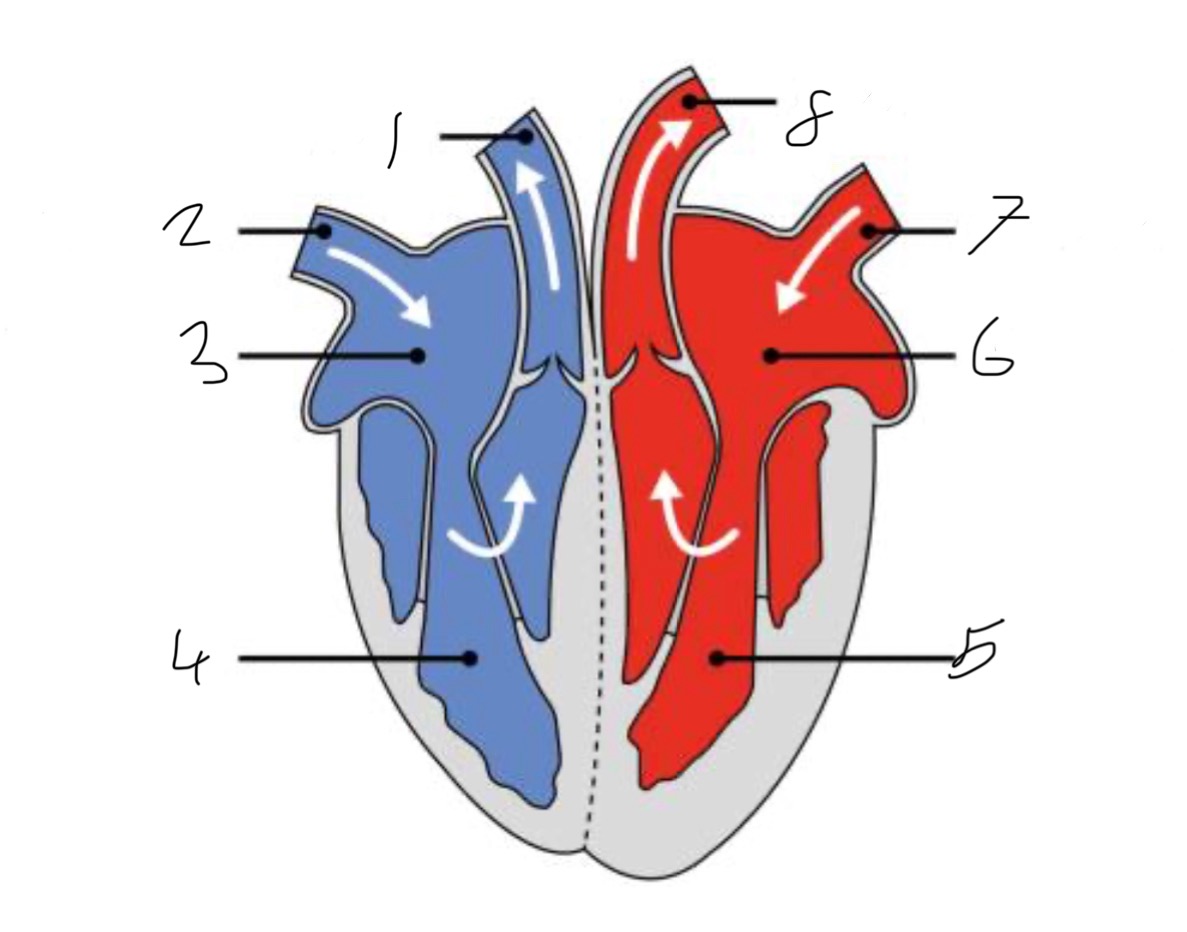
What is the name of the part of the heart labelled as 6?
Left atrium.
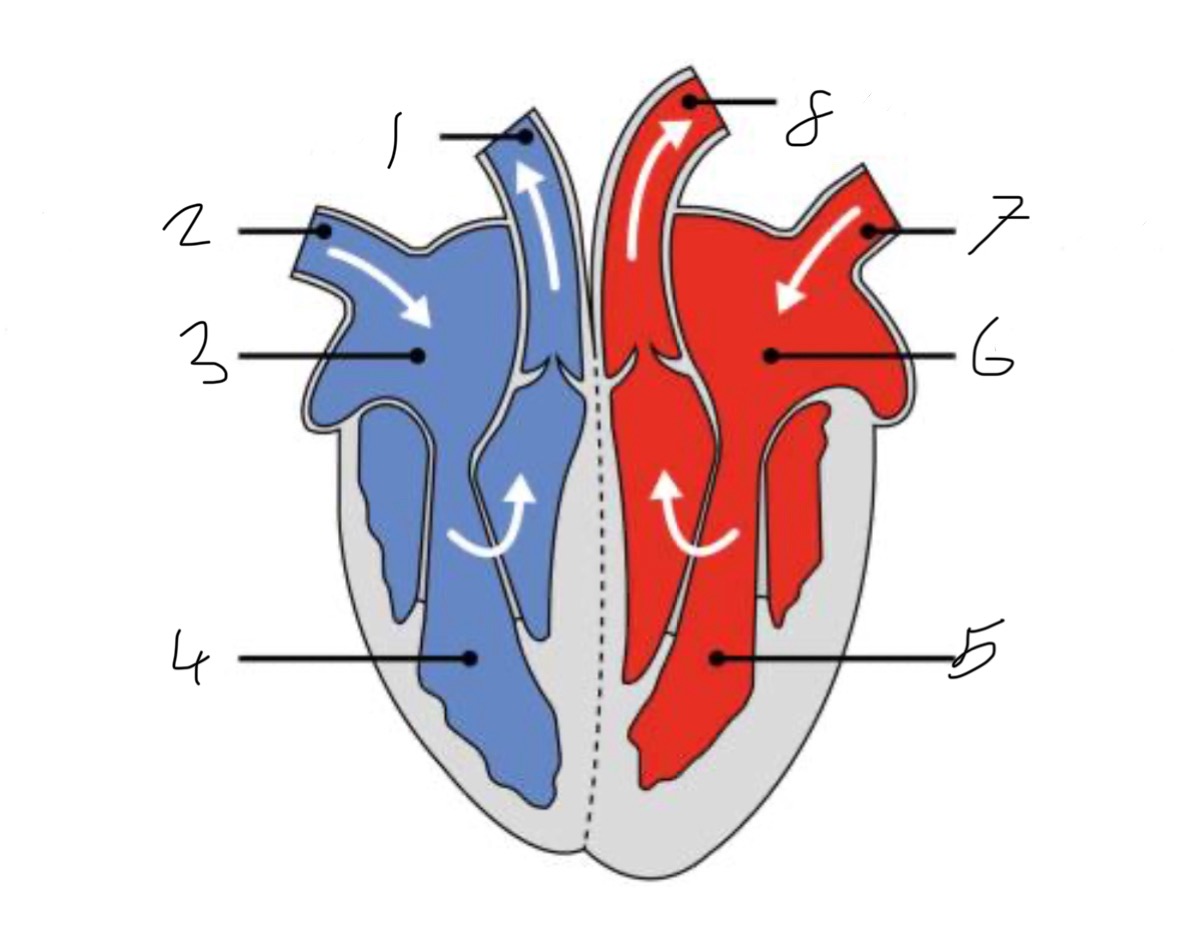
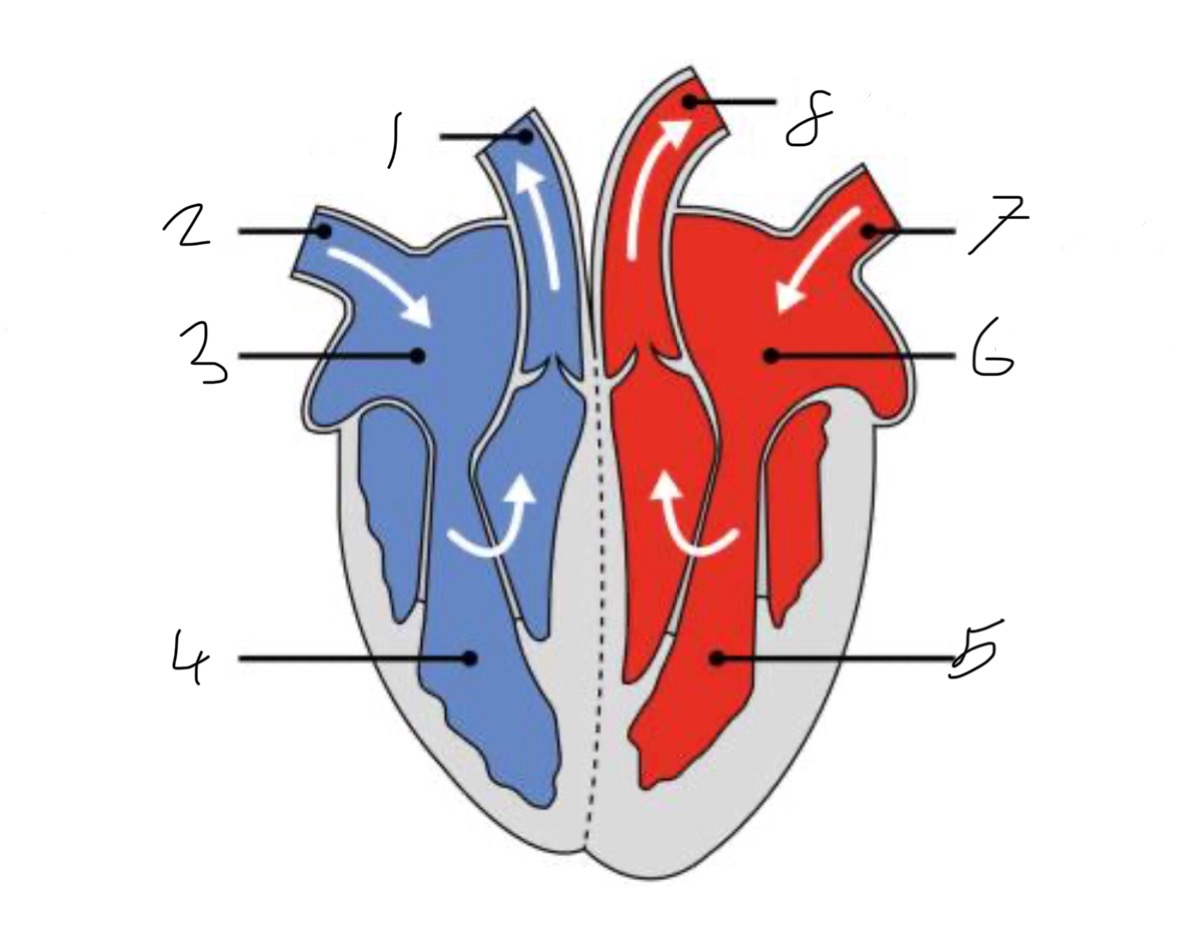
What is the name of the part of the heart labelled as 7?
Pulmonary vein
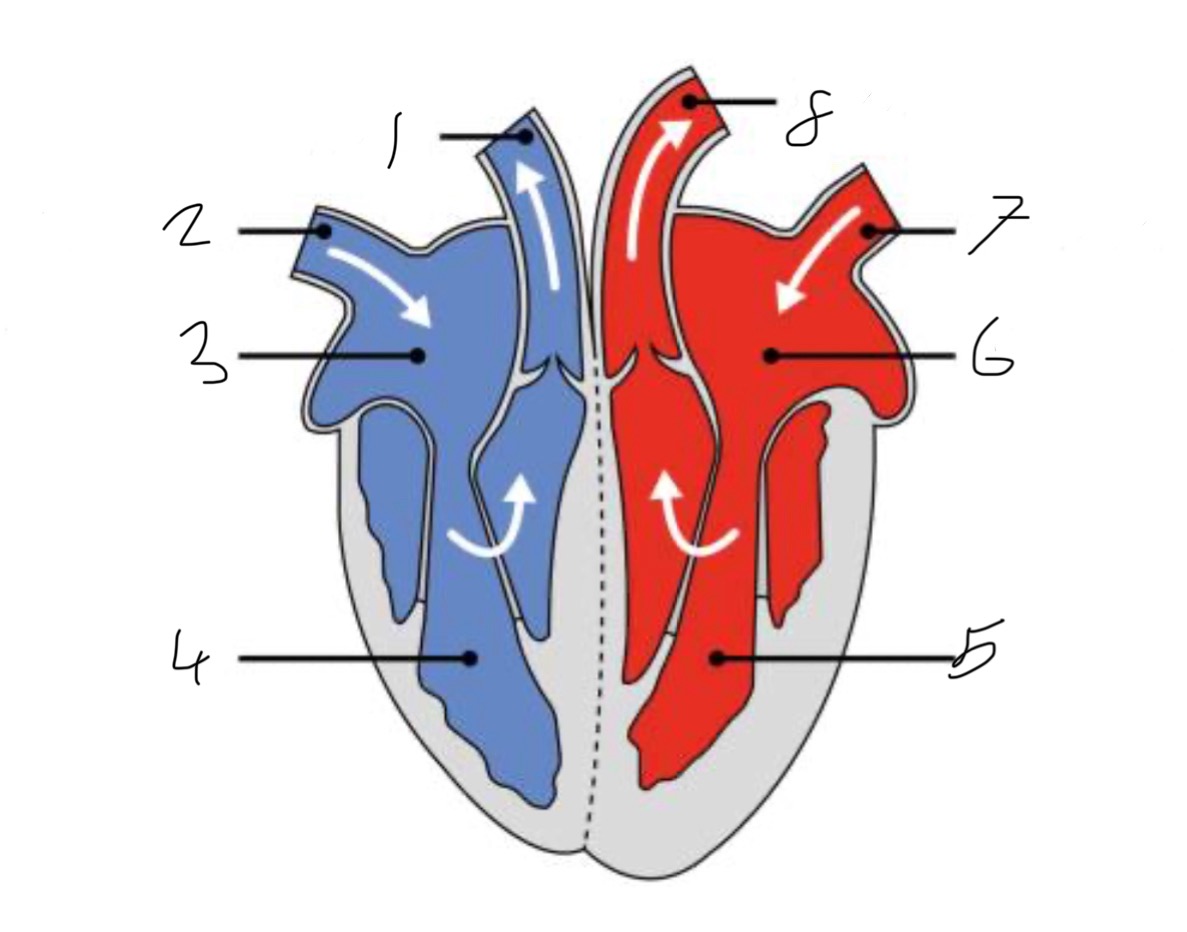
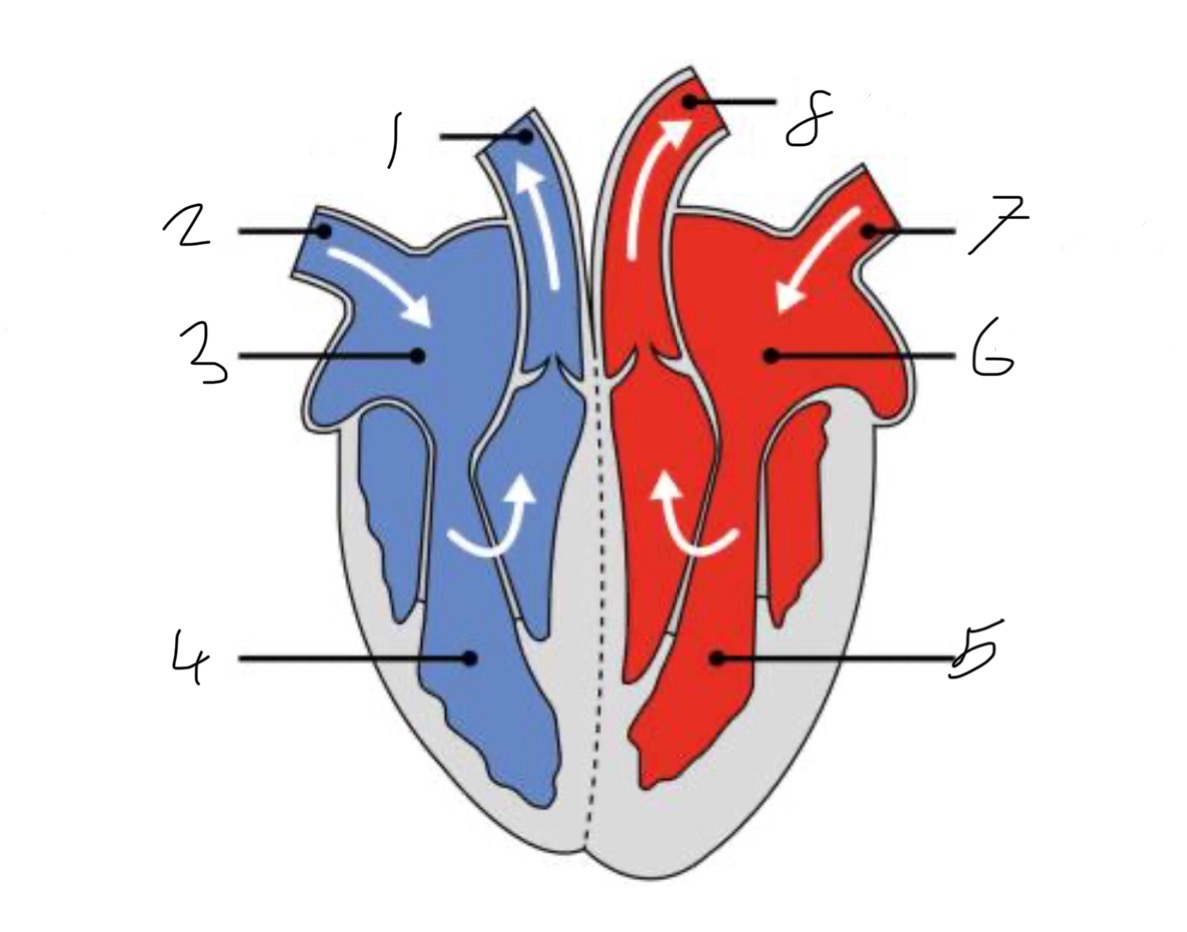
What is the name of the part of the heart labelled as 8?
Aorta.
Blood is made from:
red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and plasma. 55% of blood is plasma.
White blood cells contain:
Lymphocytes and phagocytes.
What is the role of platelets?
To help blood clotting and prevent bleeding.
What per cent of plasma is water?
About 90%
The plasma transports the following things:
glucose
Amino acids
Antibodies
Chlosterol
CO2
Urea
Lactic acid
Hormones
The plasma also distributes heat around the body.
What is the function of red blood cells?
To transport oxygen from the lungs to body tissues and carry carbon dioxide back to the lungs.
How are red blood cells adapted for their role?
They have a biconcave shape to increase surface area for gas exchange, lack a nucleus to maximize haemoglobin content, and contain haemoglobin to bind oxygen to form oxyhaemoglobin.
The innate immune system:
first line of defence (immediate)
Non-specific
No immunological memory
It doesn’t respond differently the second time you come into contact with a pathogen
It includes physical barriers like skin and mucous membranes, as well as immune cells such as phagocytes that respond quickly to pathogens.
How does a phagocyte remove bacteria?
A phagocyte removes bacteria by engulfing them through a process called phagocytosis, where the bacteria are enclosed in a vessel and then destroyed by enzymes.
Example of a physical defence:
Ear wax = has acidic environment that kills bacteria. It traps dirt, dust and small object from damaging your ear.
Adaptive immune system
second line of defence (5-7 days)
Has immunological memory - your immmune system responds better the second time.
Just cellular defence - T and B cells (lymphocytes)
B cells produce antibodies
T cells kill virally infected cells.
Antigens
Fact 1: they are found on the surface of all cells
Fact 2: there are hundreds of thousands of different antigens
Lymphocytes recognise antigens and when they do they:
Make more of themselves
Cause inflammation
The B cells will produce antibodies.
What is the role of antibodies?
Antibodies lock onto invading pathogens and mark them out for destruction by other white cells.
They stick to antigens
They can clump bacteria together and this makes them difficult to reproduce
They stick to viruses and this makes them difficult to get inside cells.
What is a vaccine?
Typically, either alive microbe, mild or weakened, or a dead microbe
Therefore, the antigens are present but the ability to cause the disease is not.
the antigens are present
Therefore, the lymphocytes multiply
Some become memory cells.
If theses memory cells meet the actual pathogens (antigens), they multiply quickly, produce more antibodies and fight the pathogens before you even feel the effects.
Active immunity
You make an immune response either following a real infection or following a vaccine
Passive immunity
You are given antibodies either naturally (in utero) or artificially.
Order of the cardiac cycle.
Atrial systole
Ventricular systole
Diastole
Atrial systole
Atria contract
Ventricular systole
Ventricles contact
Bicuspid/tricuspid open
Blood → ventricles
Bicuspid/tricuspid will close
Blood leaves the heart
Semi-lunar valves open
Diastole
Both relay
Semi-lunar valves close
Blood enters atria
How does the heart rate change during exercise?
More energy so there is more respiration
More carbon dioxide in your blood stream and your brain detects this
The brain sends a signal to your heart so it beats faster and more forcefully.
More blood is sent out from the heart (stroke volume) in each heart beat the blood arrives at the lungs and muscles quickeR
More oxygen arrives at the muscles and more CO2 is removed
Therefore, the muscles contract more.
How does the heart rate change under the influence of adrenaline?
adrenaline is released from the adrenal glands
It increases the heart rate (more oxygen and glucose arrive at the muscles)
The muscles can therefore contract more
Risk factors for coronary heart disease:
Smoking is a risk factor as blood is more likely to clot
Lack of exercise can be a risk factor
stress can affect the heart
Bad diet is a risk factor
saturate fats increase the risk.
What are the three types of blood vessels?
Arteries, veins and capillaries
Arteries
carry blood away from the heart to the organs
The blood is under high pressure so the walls must be able to stretch and recoil
Generally carry oxygenated blood
Veins
carry blood from the organs back towards the heart
Under low pressure
Must allow blood to pass through easily and prevent it flowing backwards
Veins generally carry deoxygenated blood
They have ‘watch-pocket’ valves to prevent back flow
Capillaries
carry blood through organs, bringing the blood close to the cells in the organ
They are permeable so that substances are transferred between the blood and the cells
Their walls are only one cell thick
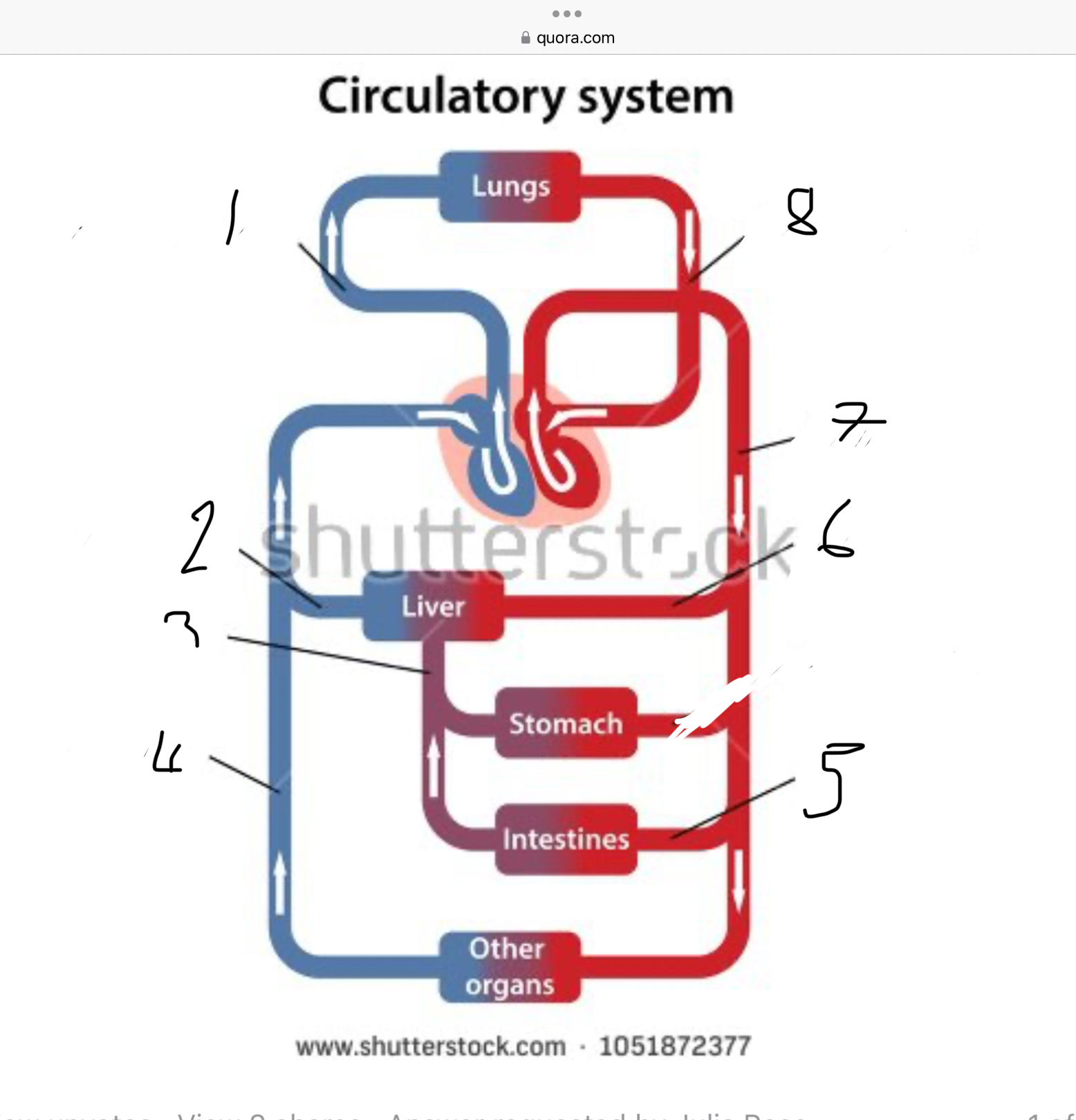
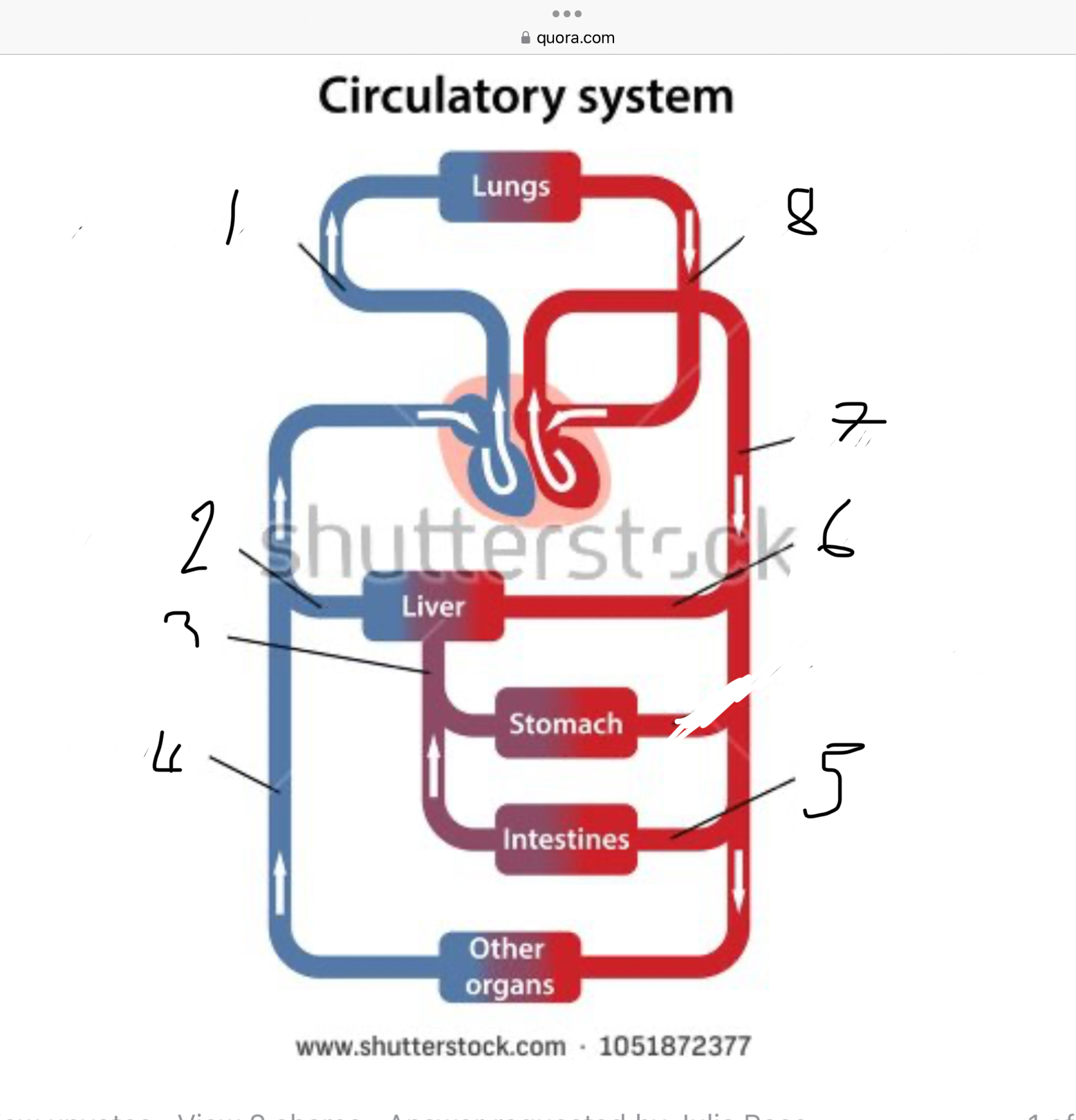
What does 1 represent?
Pulmonary artery
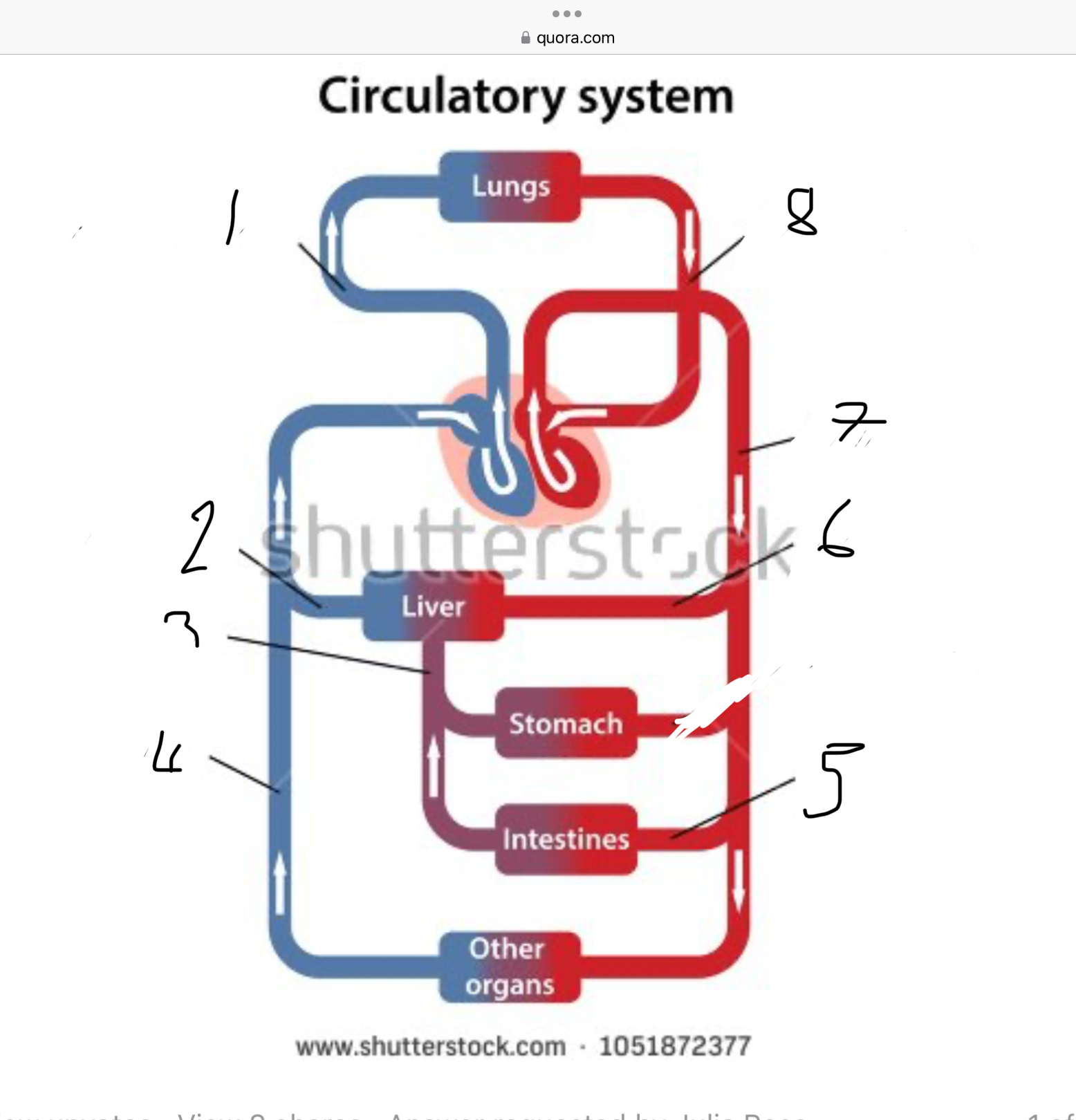
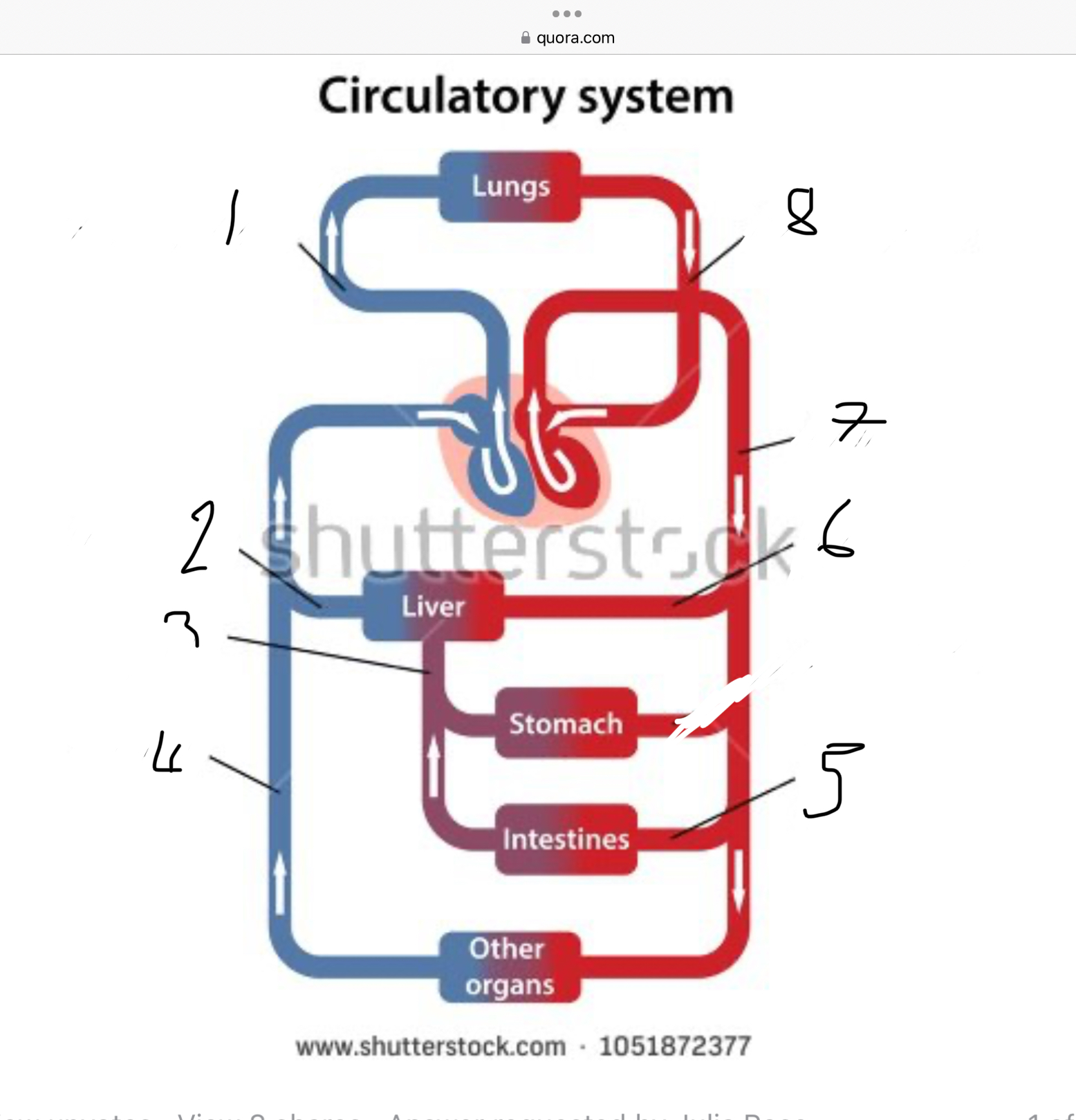
What does 2 represent?
Hepatic vein
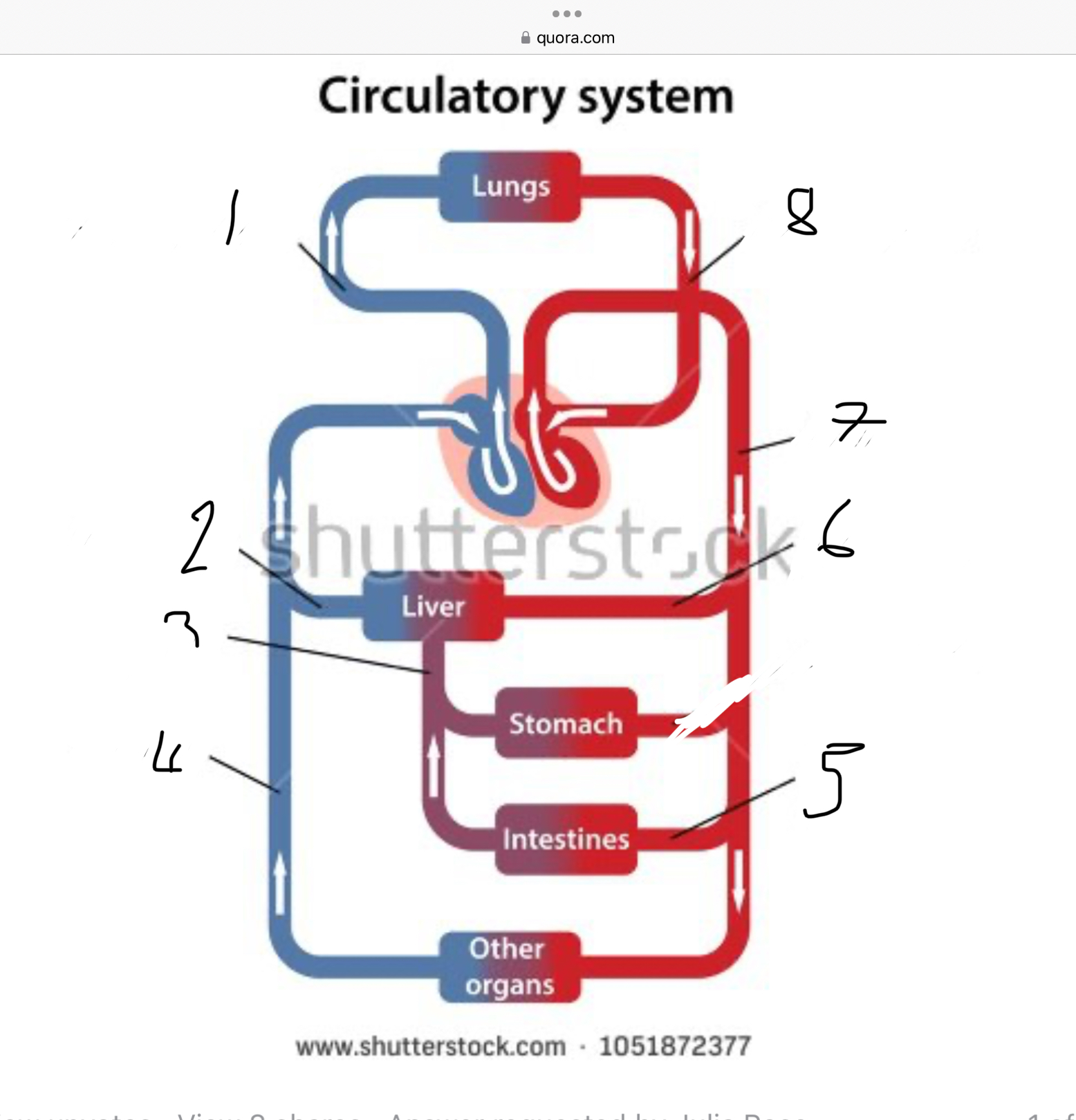
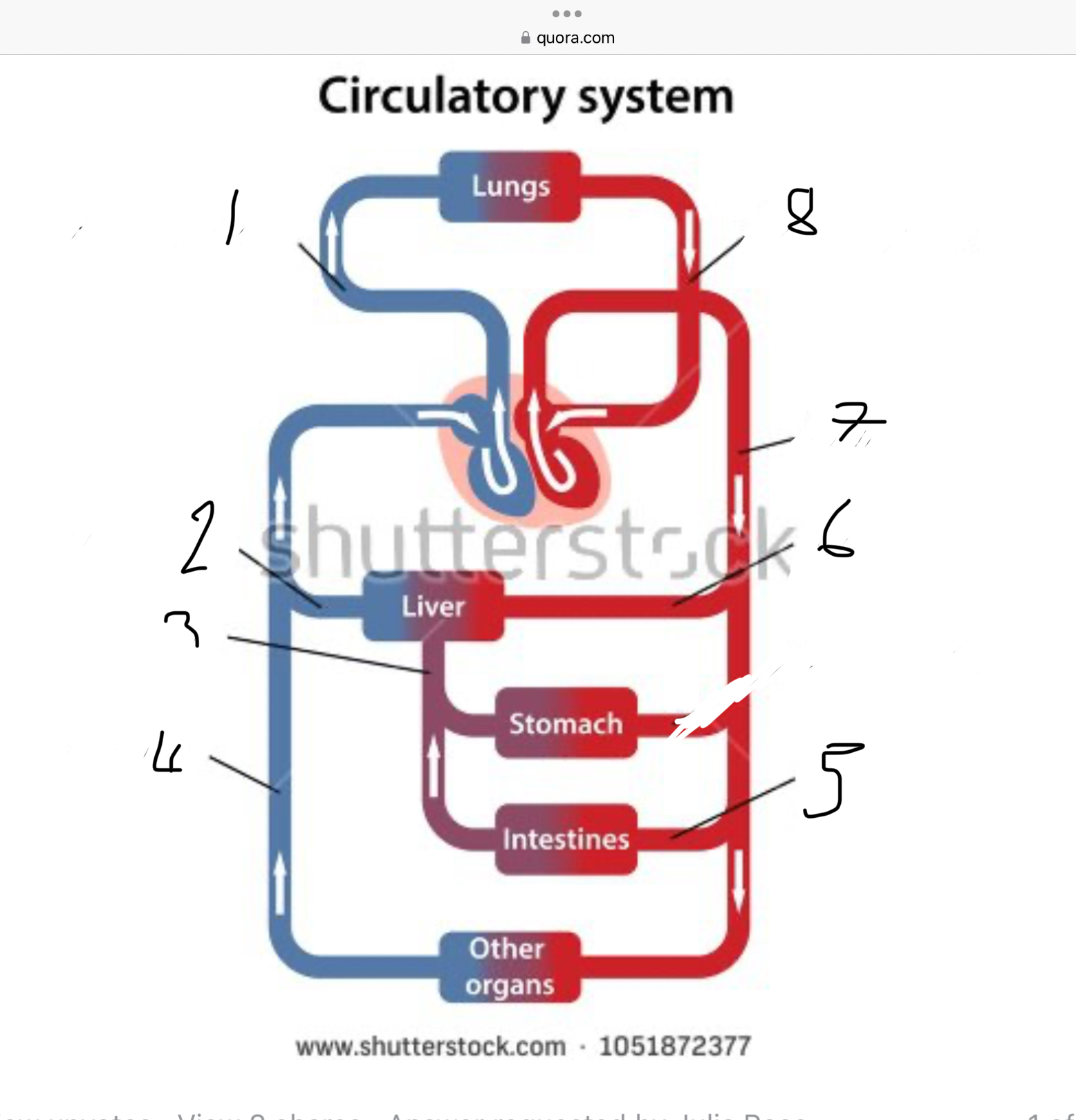
What does 3 represent?
Mesentric vein
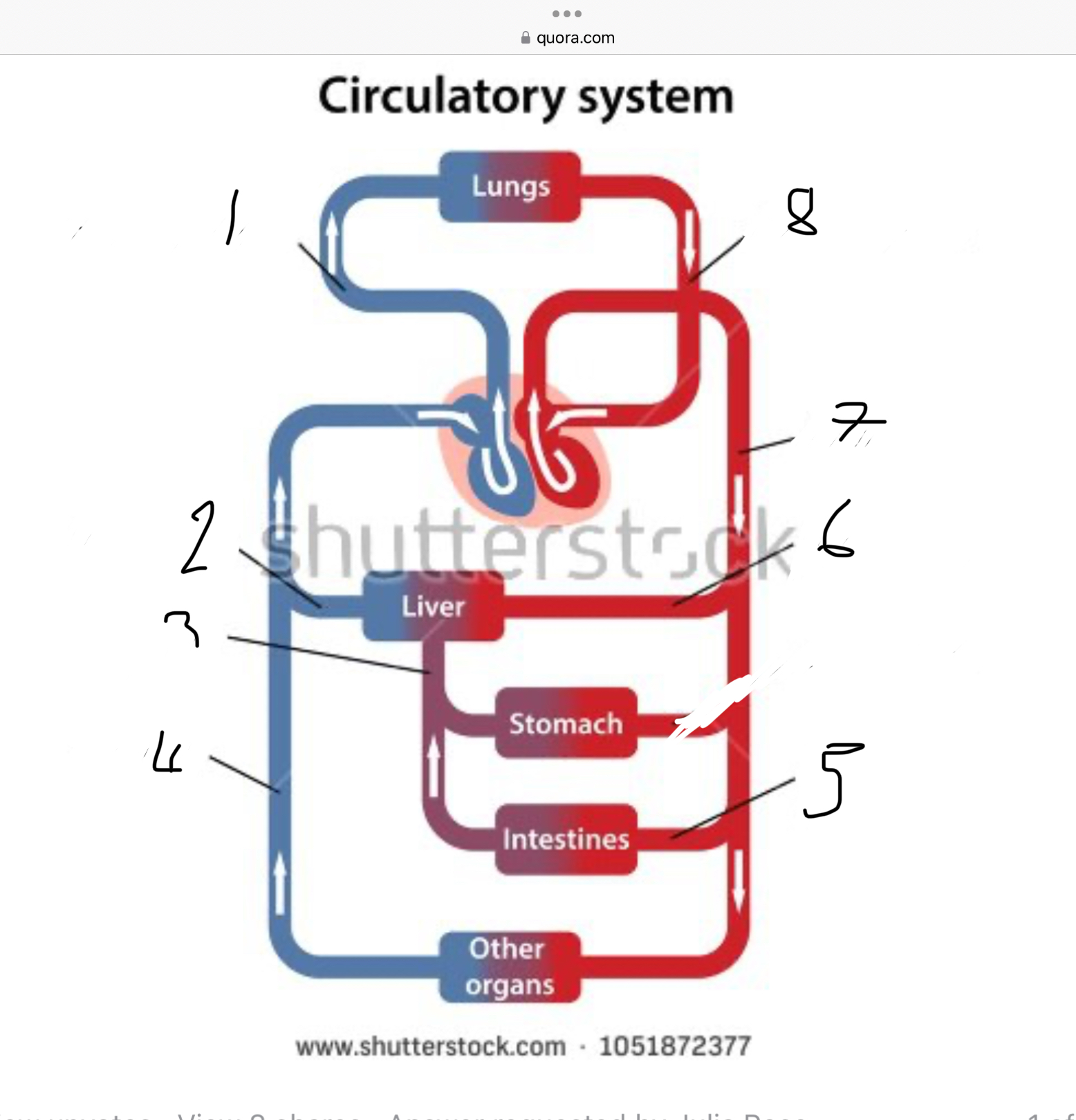
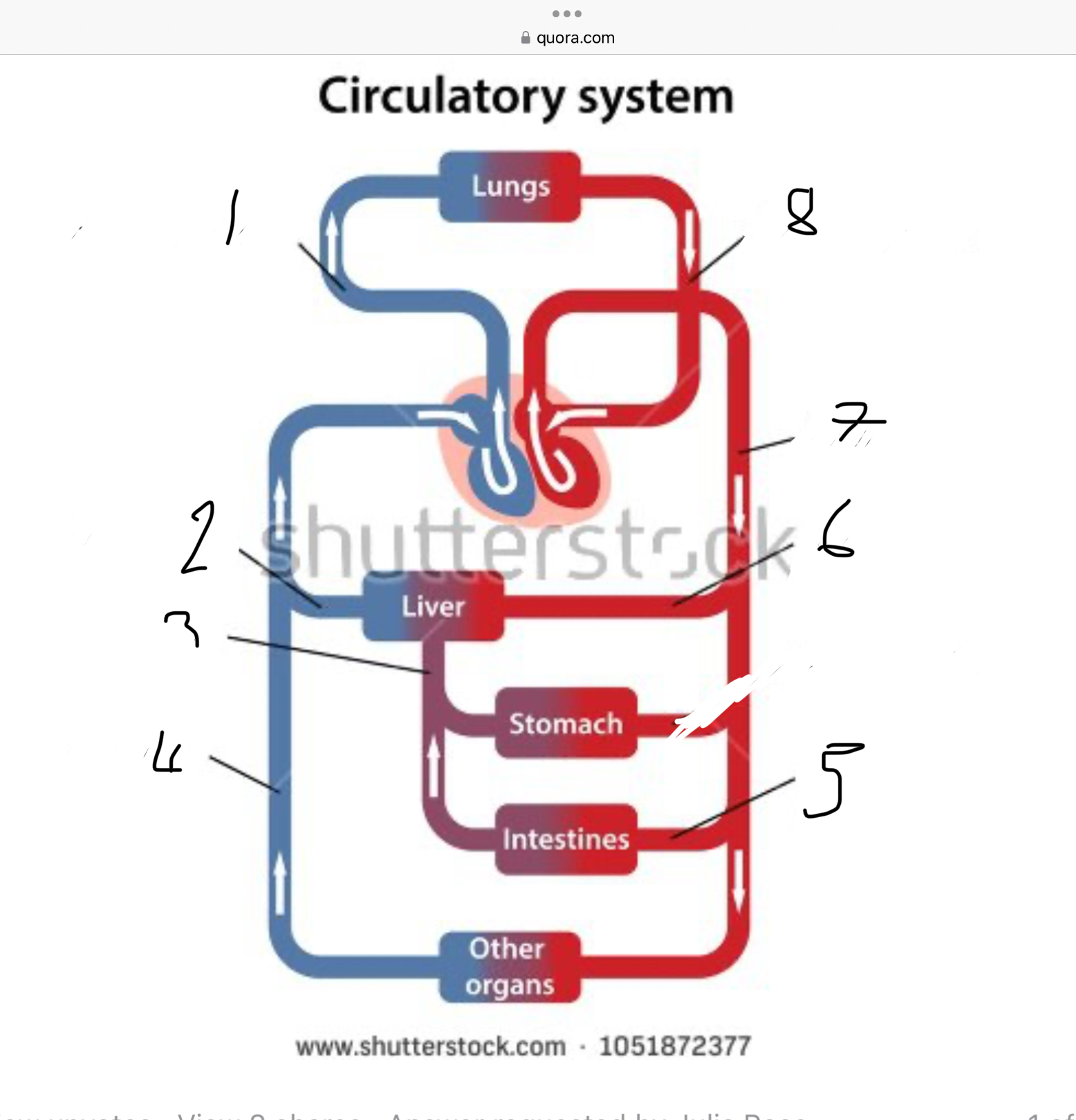
What does 4 represent?
Infenar vena cava
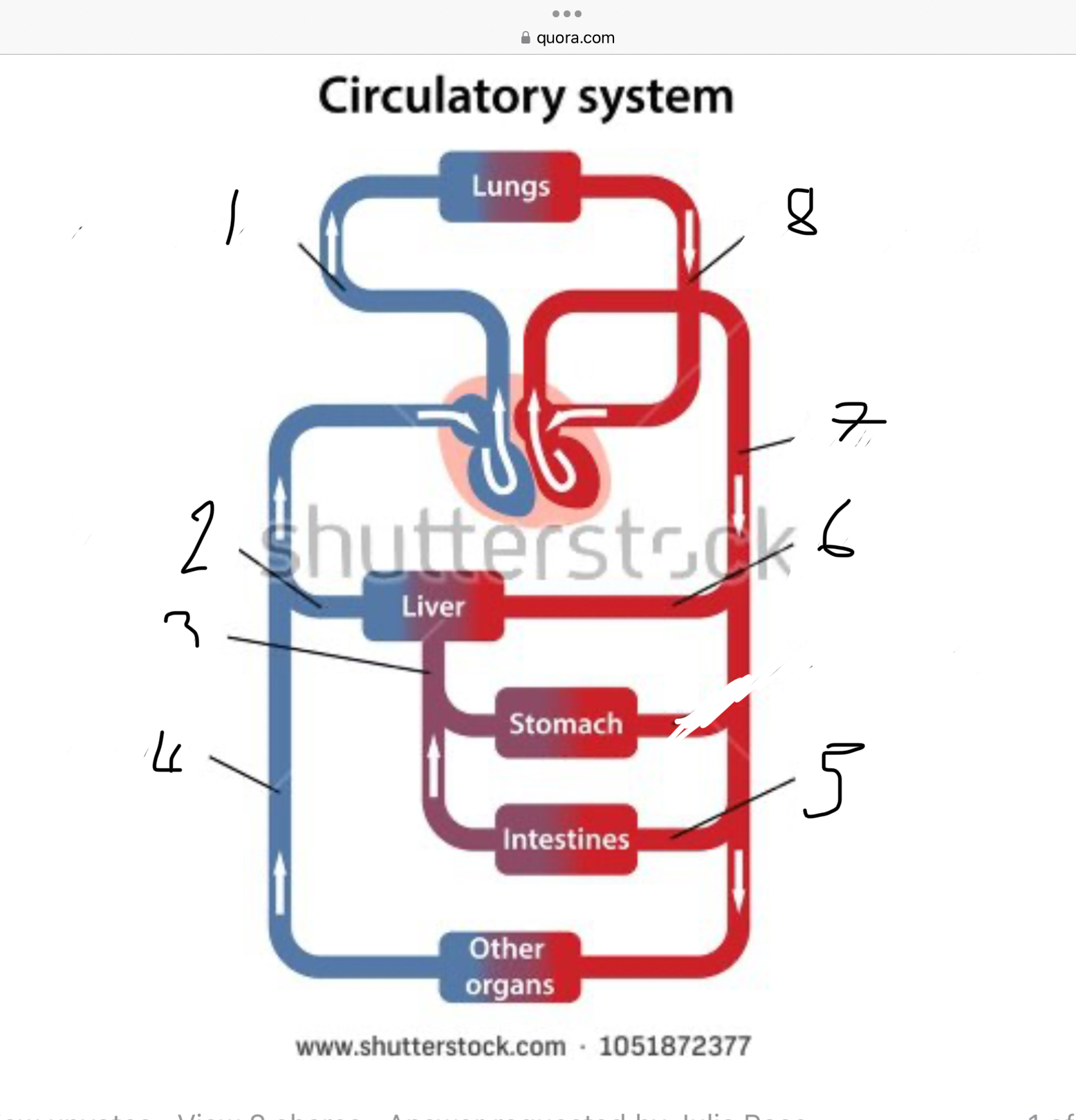
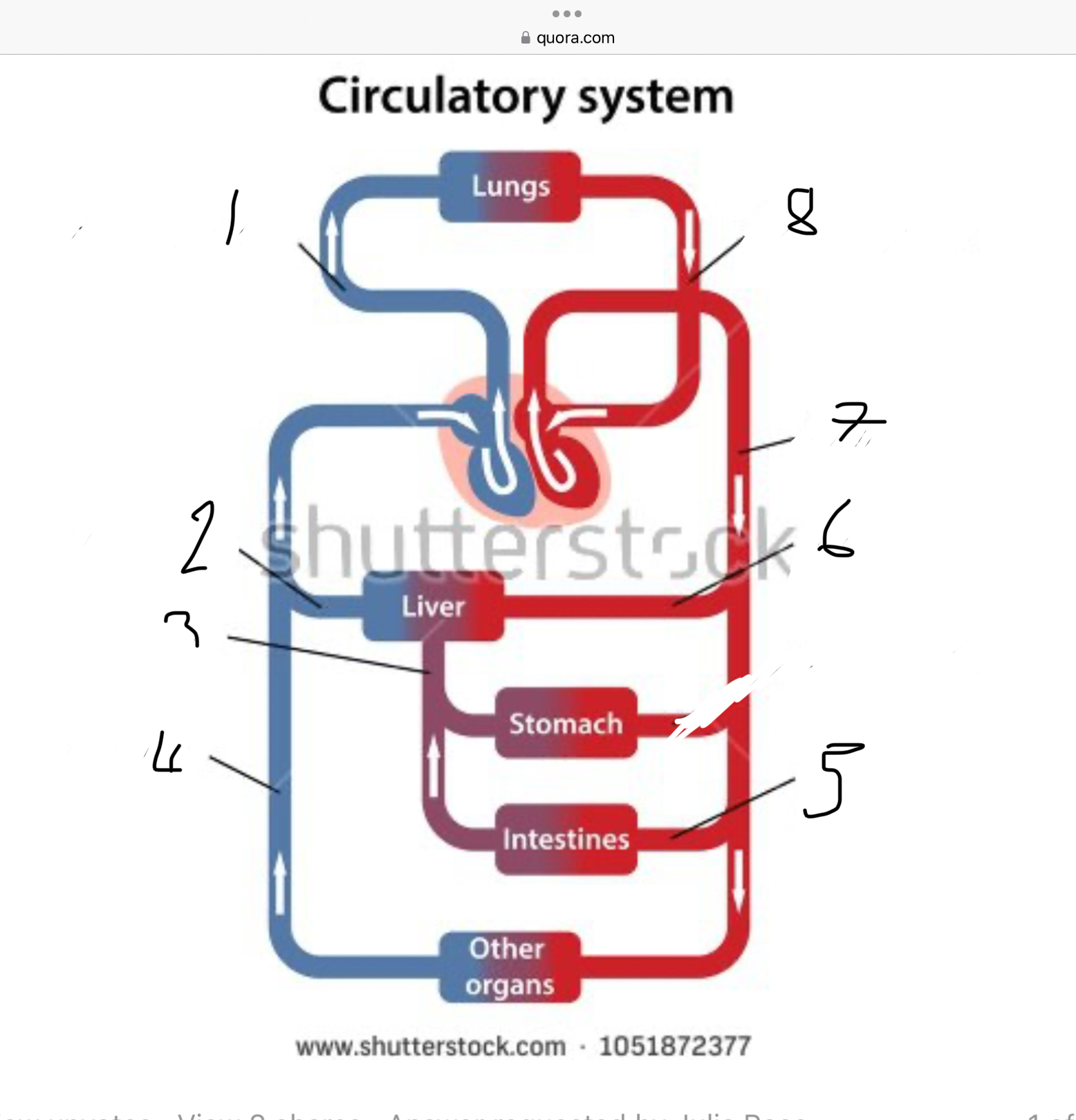
What does 5 represent?
Mesentric artery
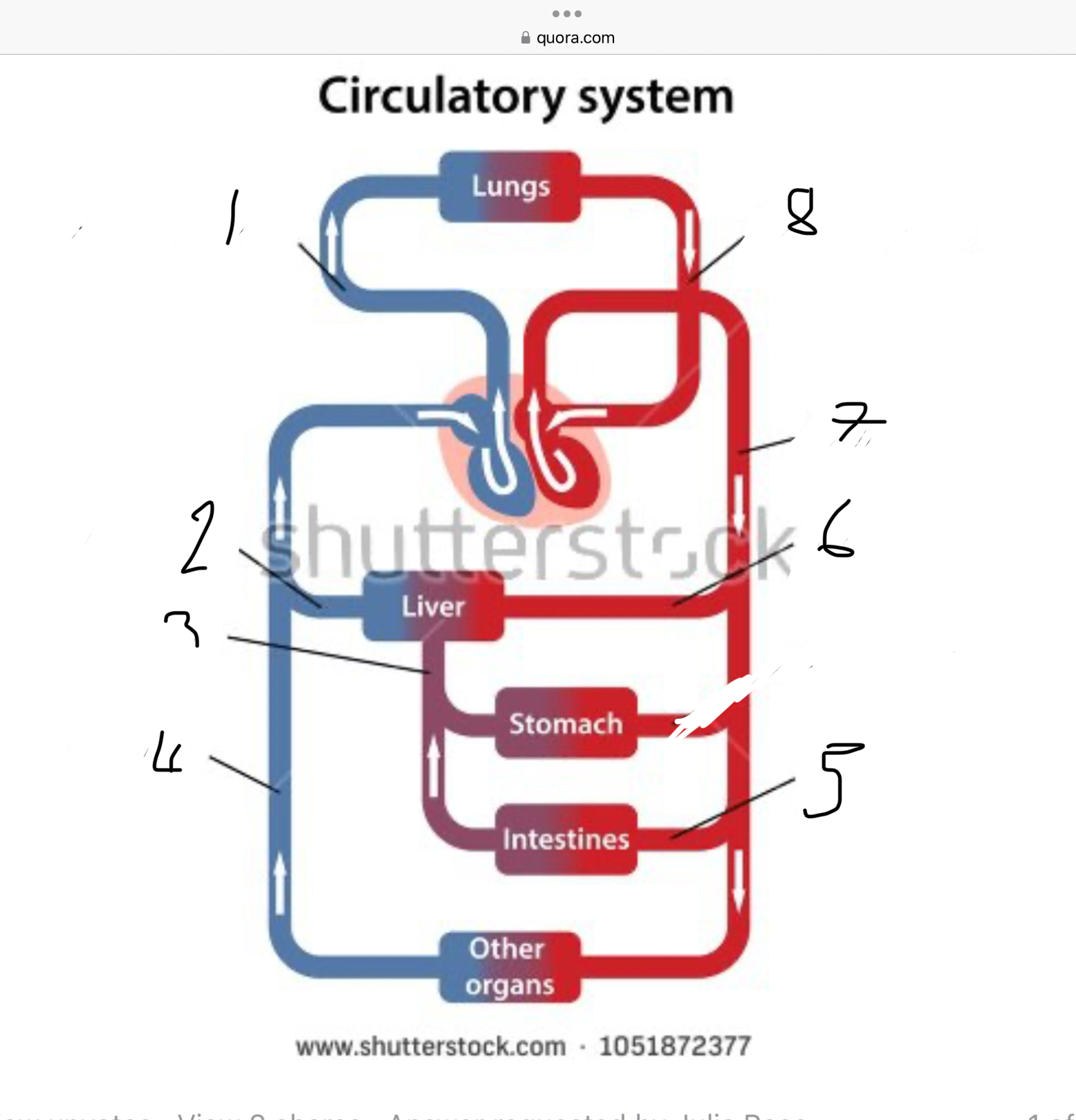
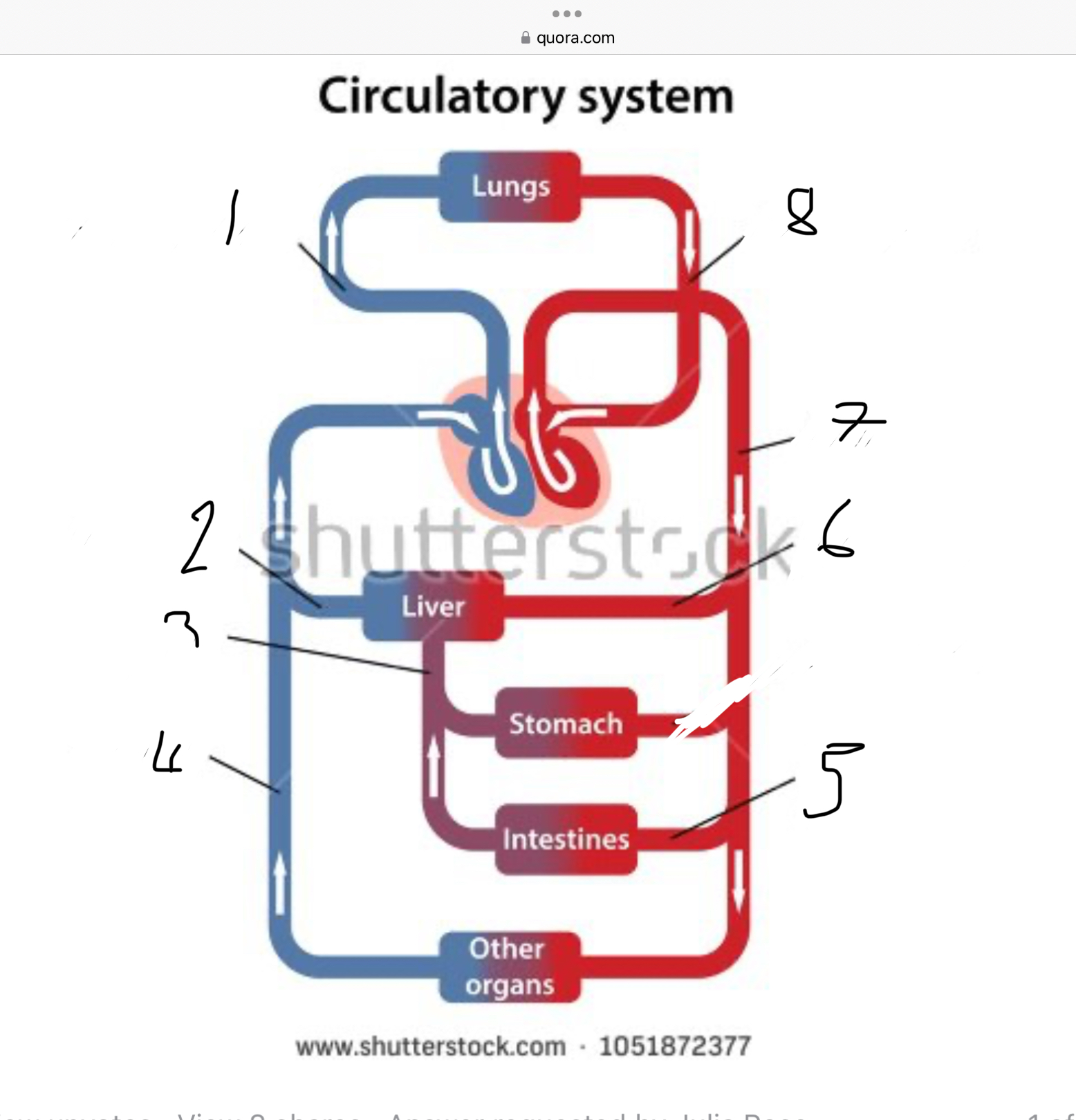
What does 6 represent?
Hepatic artery
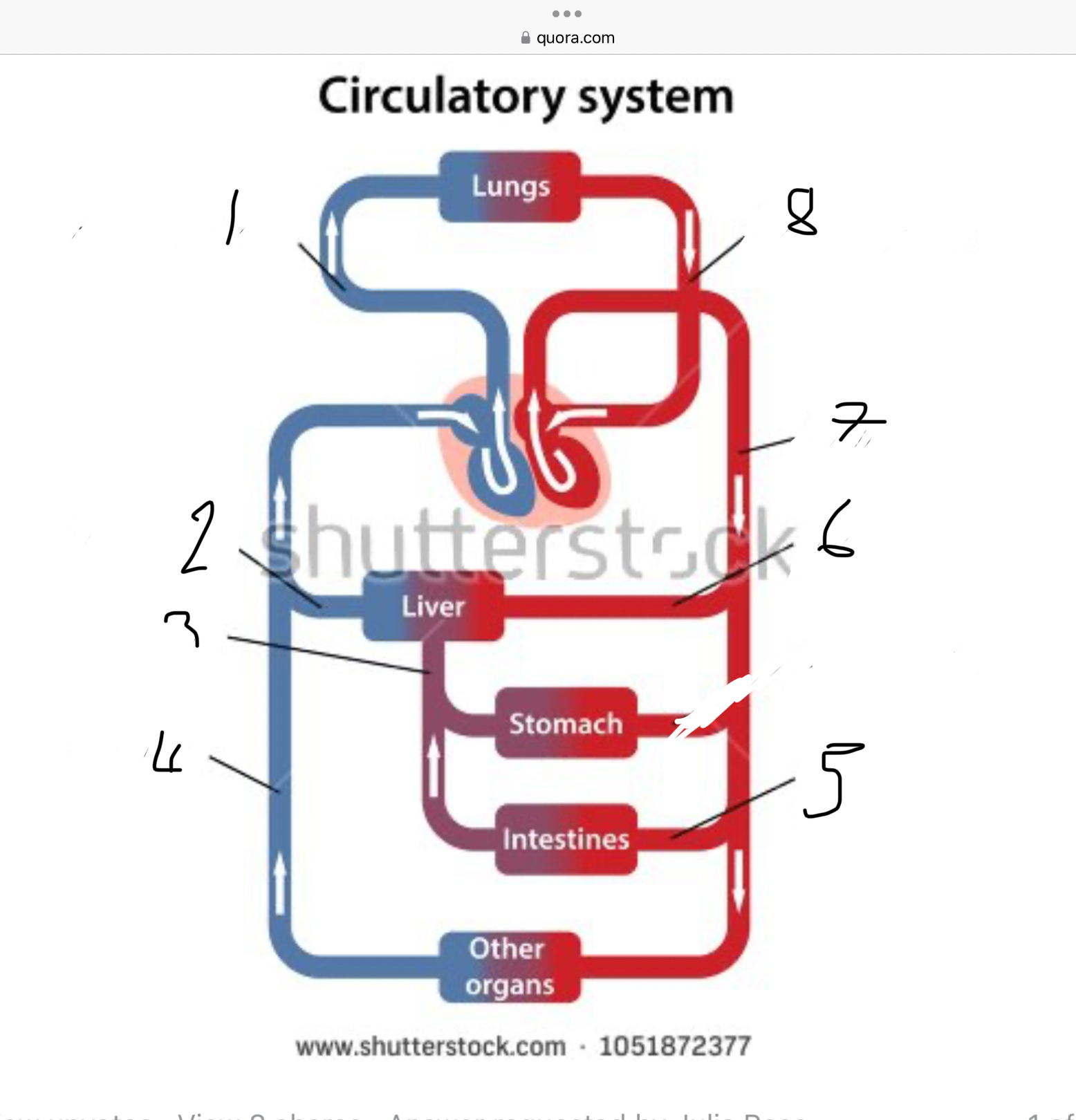
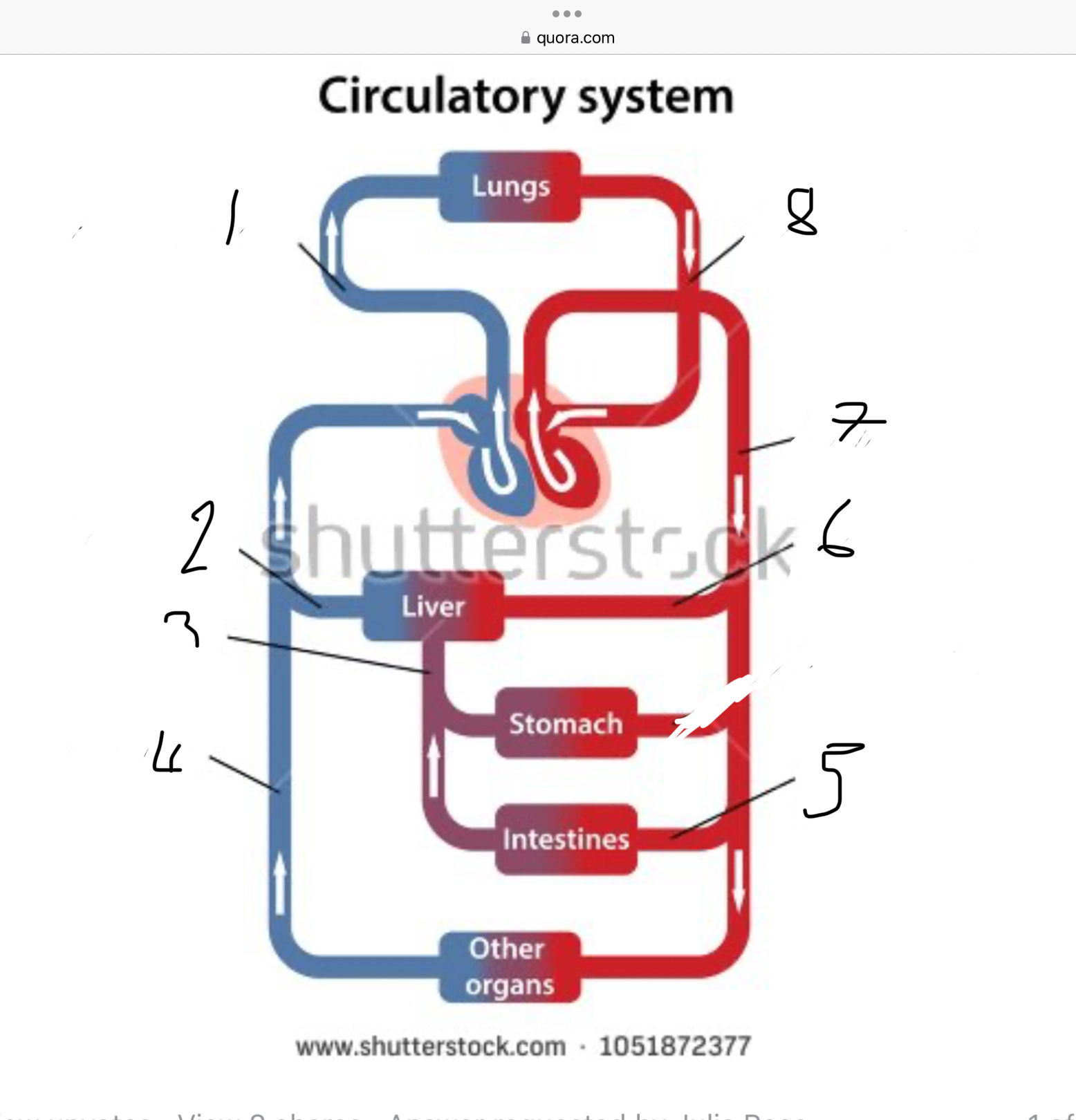
What does 7 represent?
Aorta

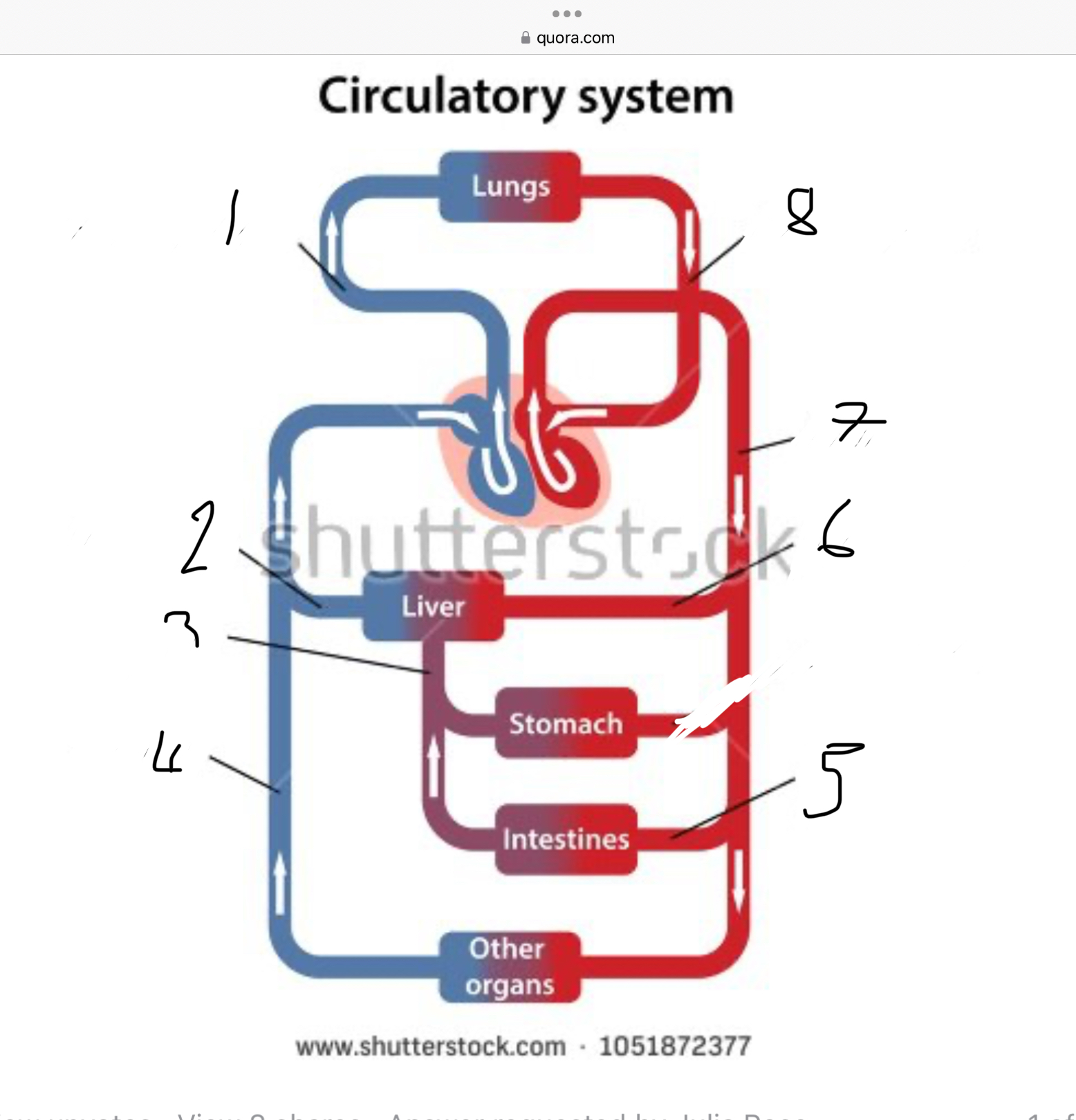
What does 8 represent?
Pulmonary veins