3. blood circulation (vessels)
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
ARTERIES
carry blood away from heart to cells of body
almost all arteries carry oxygenated blood
ARTERIES- EXCEPTIONS
pulmonary artery- carry deoxygenated blood from heart to lungs
umbilical artery- during pregnancy, carry deoxygenated blood from fetus to placenta
ARTERIAL SYSTEM
arteries leaving heart branch off in every direction, and diameter of lumen (central space inside blood vessel) gets smaller the further it is from heart
very smallest branches of arterial system, furthest from heart, are arterioles
ARTERIES- DIAGRAM
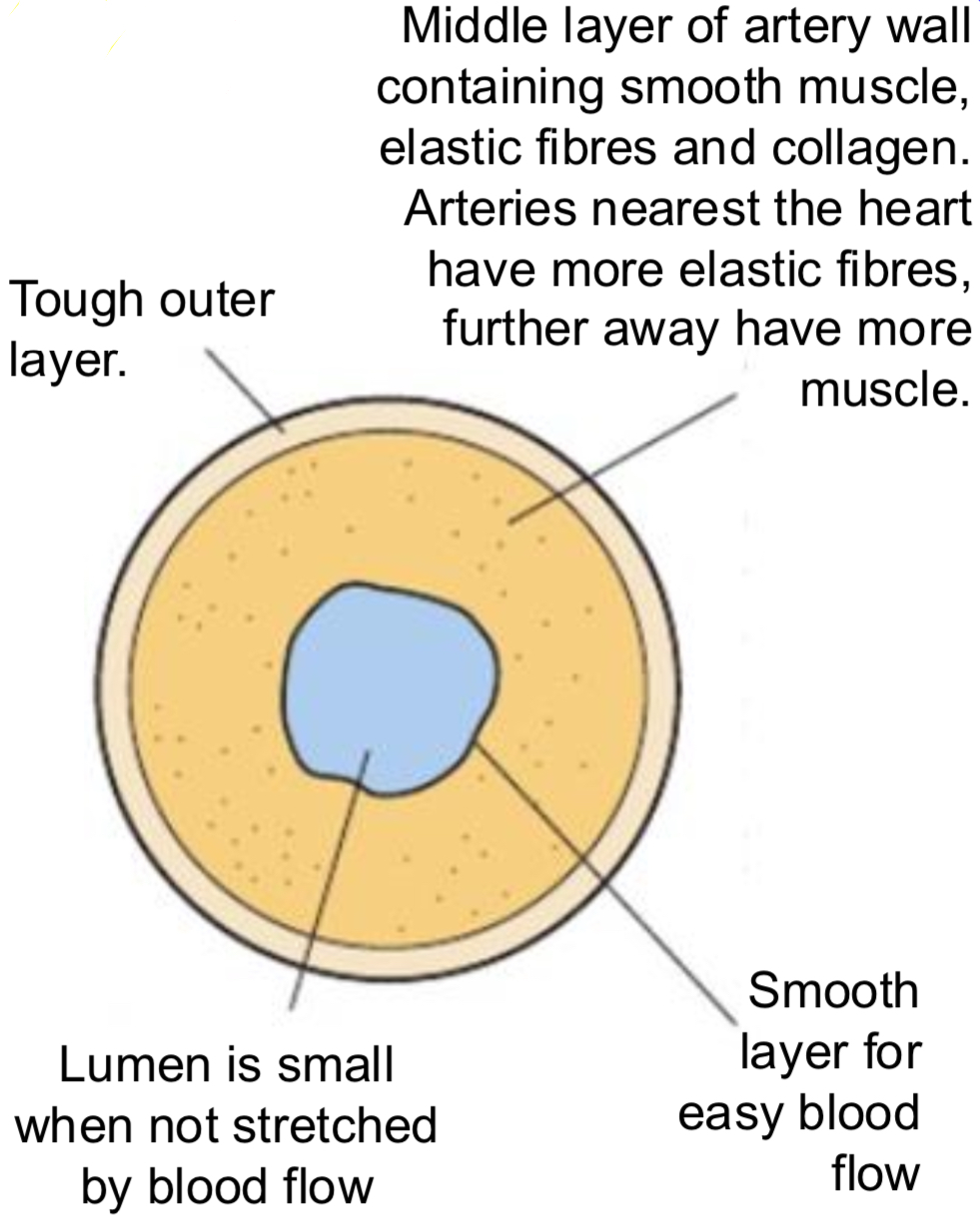
ARTERIES- LAYERS
elastic fibres allow vessels to stretch then recoil– vessels can accommodate a greater vol of blood w/out being damaged
helps as pressure surges in vessels as heart beats
between surges recoil of elastic fibres squeezes blood and keeps it flowing
collagen fibres provide general strength/support so that vessels don’t burst and allow flexibility- can be found in middle and outer layer
PERIPHERAL ARTERIES/ARTERIOLES
small arteries further away from heart
have the same basic structure as other arteries except…
have a greater proportion of smooth muscle in relation to size which allows constriction of lumen to restrict blood flow into capillaries supplying tissues with blood (vasoconstriction)
have a smaller proportion of elastic fibres in relation to size bc blood pressure is lower
VEINS
carry blood back towards heart
most veins carry deoxygenated blood
VEINS- EXCEPTIONS
pulmonary vein- carry oxygenated blood from lungs back to heart
umbilical vein- during pregnancy, carry oxygenated blood from placenta to fetus
VEINS- DIAGRAM
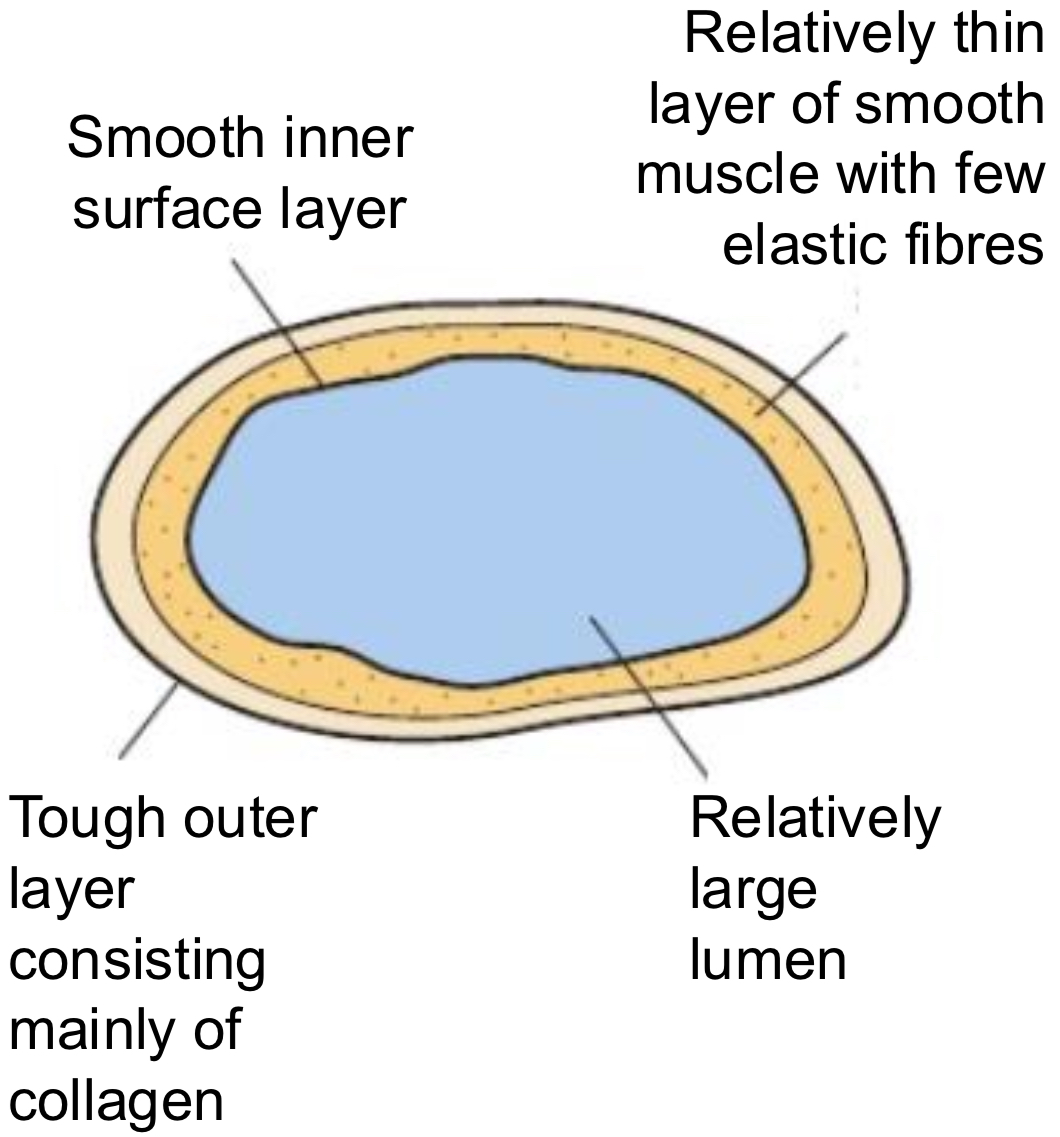
VEINS- CHARACTERISTICS
hold large vol of blood
low blood pressure in veins- blood surges from heart are eliminated as blood passes from capillary beds
this blood at low pressure must be returned to heart to be oxygenated again and recirculated
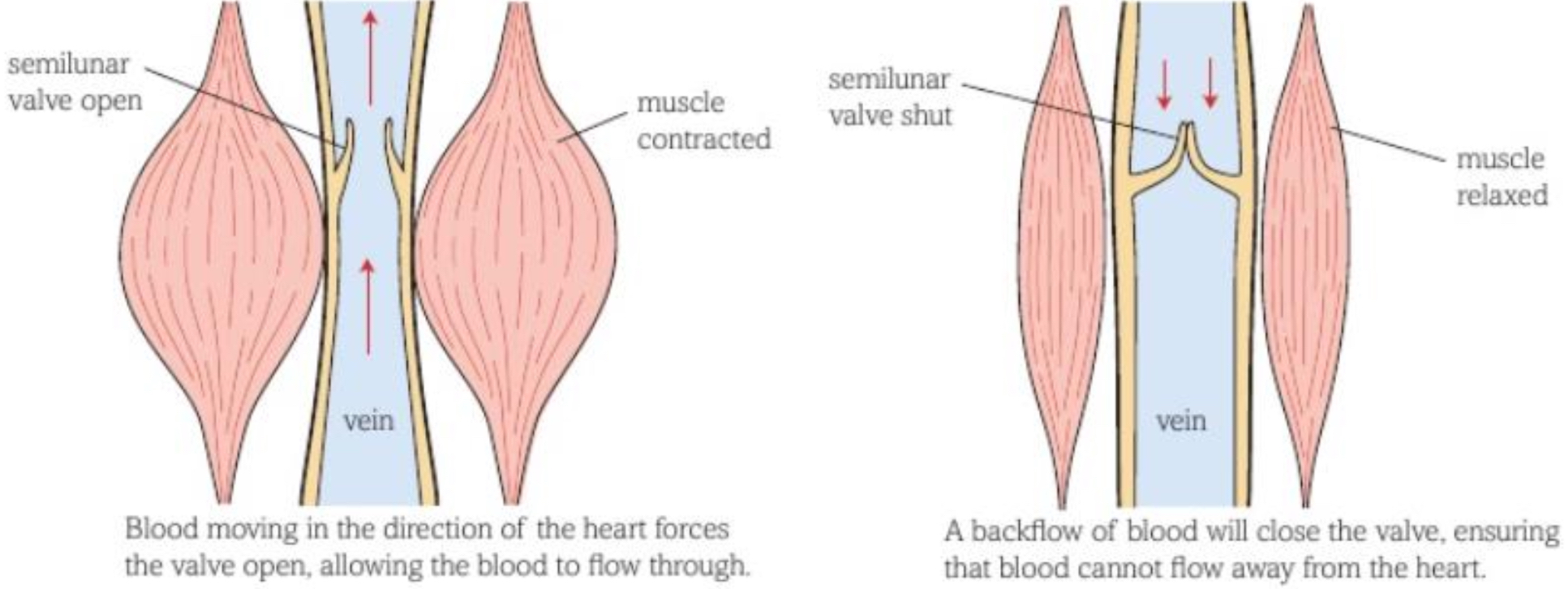
VEINS- VALVES
when blood moves in right direction, valve (semilunar) is forced open
but if blood tries to flow in wrong direction, it gets trapped in curved ‘doors’ of valve, closing the valve (prevents backflow)
many larger veins are surrounded by skeletal muscle– when we move our arms/legs muscles contract and squeeze veins, helping force blood through in right direction
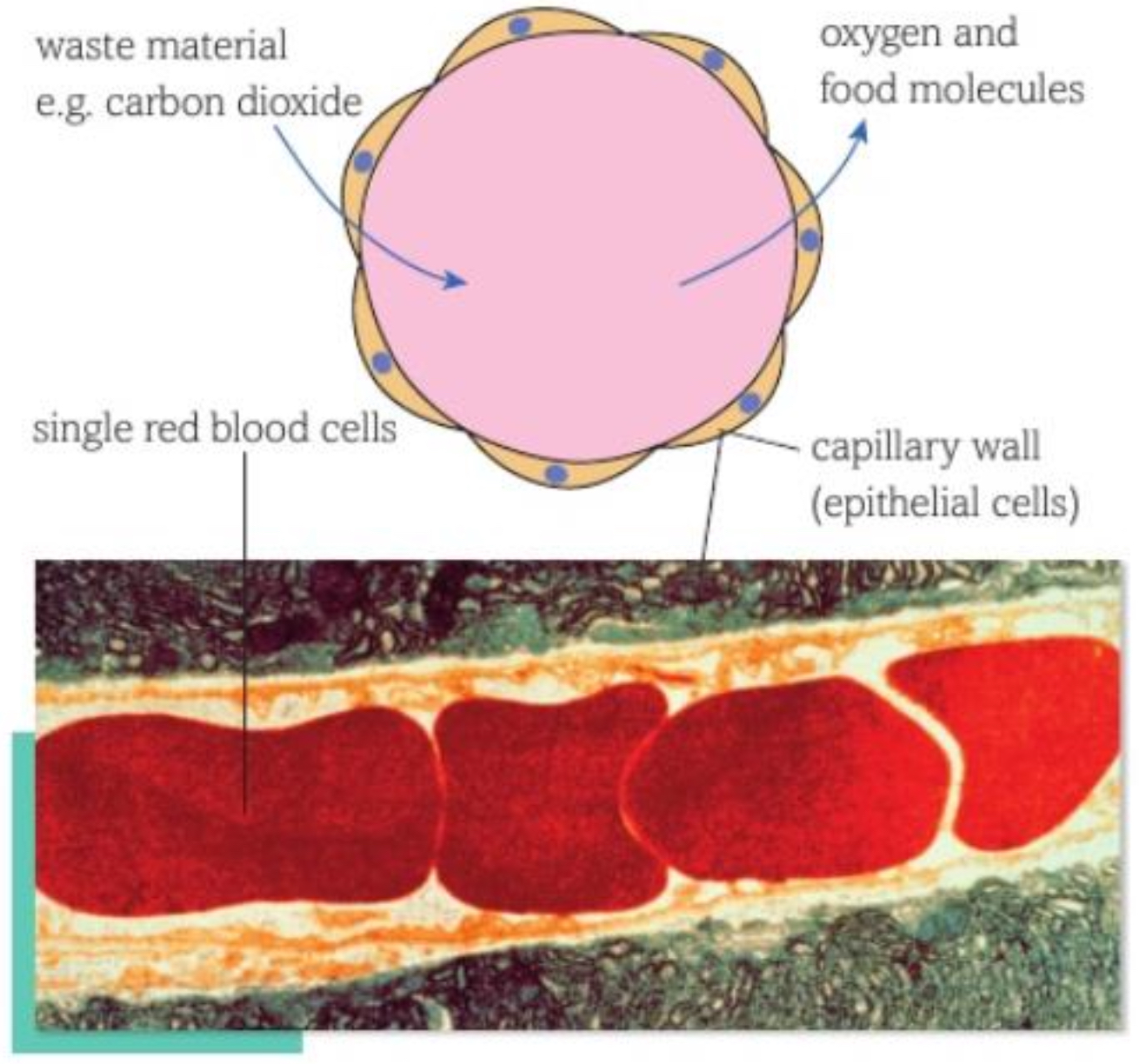
CAPILLARIES
capillaries branch between cells- no cell is far from capillary, so substances can diffuse between cells and blood quickly
small diameter- blood travels slowly through them- gives more opportunity for diffusion to occur
smallest capillary no wider than single red blood cell
CAPILLARIES- ADAPTATIONS
thin walls (one cell thick) and contain no elastic fibres, smooth muscle or collagen- helps fit between individual cells and allows rapid diffusion of substances between blood and cells
O2 and other molecules quickly diffuse out of blood in capillaries into body cells
CO2 and other waste molecules diffuse in
blood entering capillary network from arteries is oxygenated- by time it leaves, carries less O2 and more CO2
CAPILLARIES- DIAGRAM
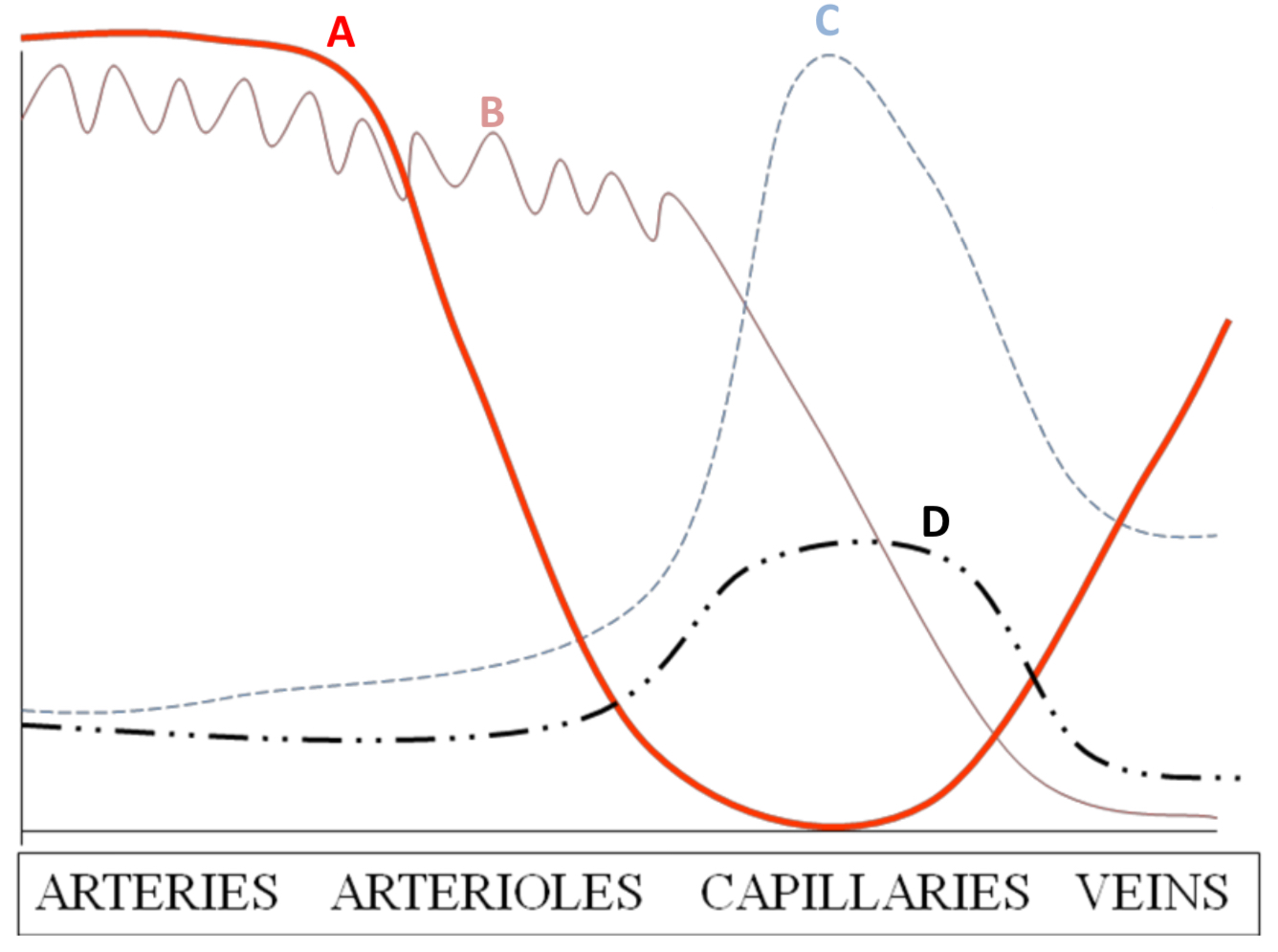
GRAPHS AND BLOOD VESSELS
velocity (A)
highest in arteries as blood pumped out of heart at high pressure so travels faster
lowest in capillaries as these vessels are so narrow and offer most resistance
velocity increases in veins as they are wider so offer less resistance than capillaries
cross-sectional area (C)
highest in capillaries as these vessels are the most numerous by far– thus providing a large SA for diffusion
permeability (D)
highest in capillaries as walls are only one cell thick so diffusion pathway is short
other vessels are not permeable
pressure (B)
highest in arteries since these lead out of the heart
pressure fluctuates in arteries w/ every beat due to elastic nature of arteries
pressure decreases further away from heart the blood goes