Organic Chemistry Reactions + VSEPR
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Types of addition
Hydrogenation
Halogenation
Hydration
Hydrohalogenation
Hydrogenation
Addition of H2 to alkene/alkyne to saturate and break double/triple bond
Halogenation
Addition of halogen to alkene/alkyne to increase reactivity and break double/triple bond. Forms haloalkene
Hydration
Addition of water to alkene/alkyne to produce alcohol and break double/triple bond (Markovnikov’s)
Hydrohalogenation
Addition of hydrogen halide to form Haloalkane (Markovnikov’s)
Substitution (Benzene only)
Replace H2 with others (ex. Cl2). Produces H + remaining compound as byproduct. Bonds with lower EN if 2 non-identical atoms are subbed.
Elimination (dehydration)
Removal of hydrogen atom and hydroxyl group from alcohol to form alkene and water
Condensation
alcohol + alcohol → ester + water. Hydroxyl of 1st alcohol bonds with Hydrogen of 2nd, connecting molecules by oxygen and forming water.
Oxidation
Primary alcohol + (O) → Aldehyde + water
Secondary alchohol + (O) → Ketone + water
Aldehyde + (O) → Carboxylic acid
Reduction (Hydrogenation)
Aldehyde + H2 → Primary alcohol
Ketone + H2 → Secondary alcohol
Esterification (condensation)
Carboxylic acid + Alcohol → Ester + water
Hydrolysis
Ester + Water → Carboxylic Acid + alcohol
Forming Amines
Alkyl Halide + Ammonia → Primary Amine
Alkyl Halide + Primary Amine → Secondary Amine
Forming Amides
Carboxylic acid + Ammonia → Primary Amide + water
Carboxylic acid + Primary Amide → Secondary Amide + water
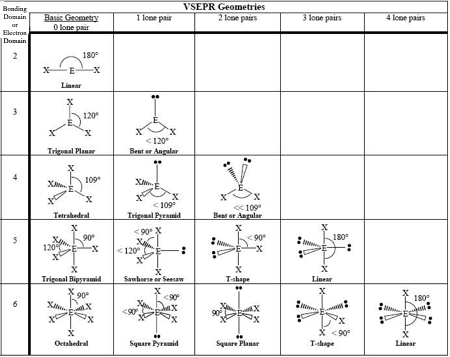
0 LP, Steric # 2
Linear
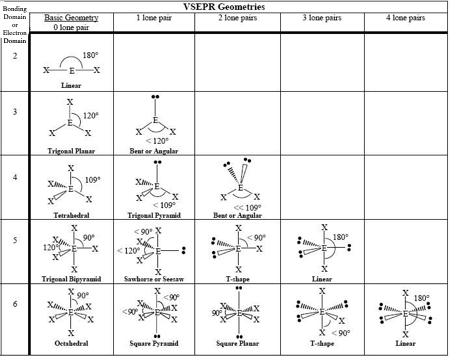
0 LP, Steric #3
Trigonal Planar
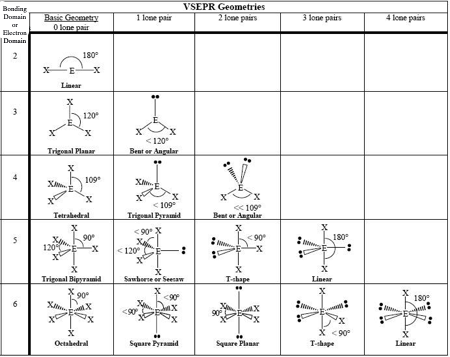
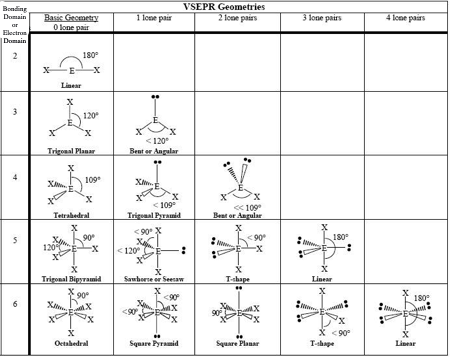
1 LP, Steric #3
Bent
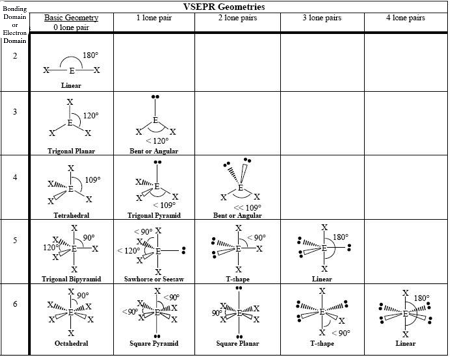
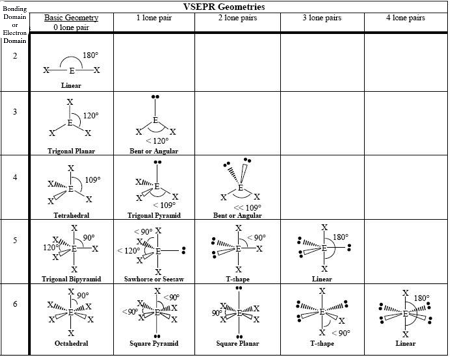
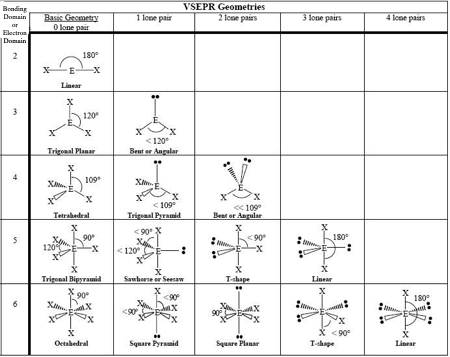
0 LP, Steric #4
Tetrahedral
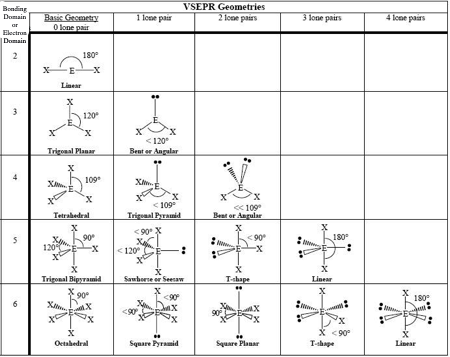
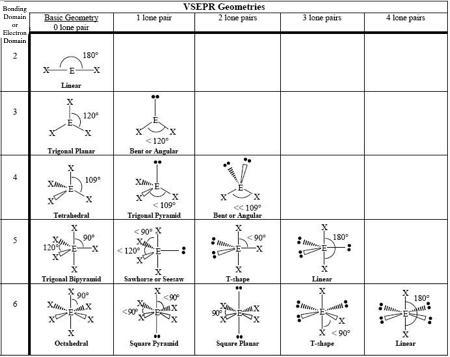
1 LP, Steric #4
Trigonal Pyramid
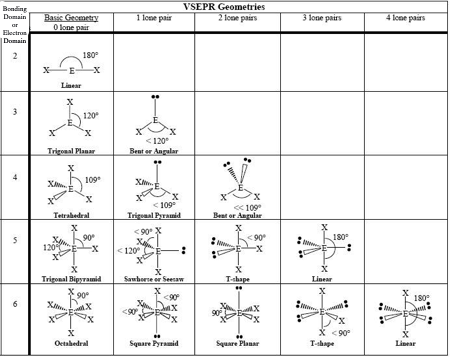
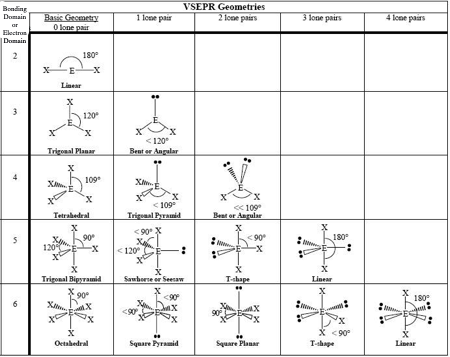
2 LP, Steric # 4
Bent