OZONE STORY - OCR B A-LEVEL CHEMISTRY.
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:18 PM on 9/27/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
1
New cards
what is electronegativity
is a measure of the ability of an atom to attract electrons in a chemical bond to itself
2
New cards
explain the qualitative trends of electronegativity in the periodic table
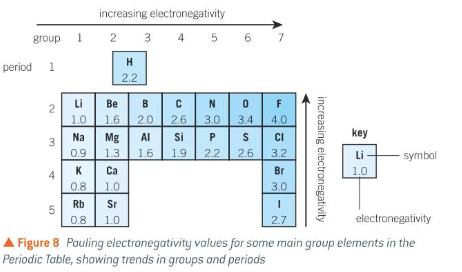
3
New cards
use of relative electronegativity values to predict bond polarity in a covalent bond;

4
New cards
relation of overall polarity of a molecule to its shape and the polarity of its individual bonds

5
New cards
what is an instantaneous dipole-induced dipole?
when an instantaneous dipole induces a dipole disturbing the electron arrangement in the non polar species.
6
New cards
explain dependence on branching and chain length of organic molecules and Mr)
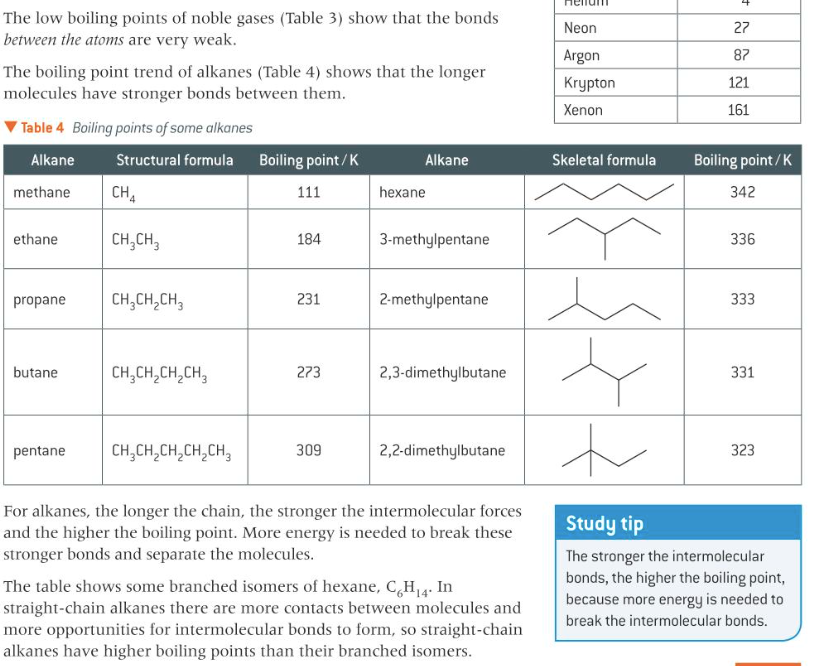
7
New cards
what is the weakest type of intermolecular bonding
instantaneous dipole-induced dipole
8
New cards
what is permanent dipole-permanent dipole?
a permanent dipole is polar e.g hydrogen chloride. H-CL - H-CL, this is a permanent dipole-permanent dipole bond. stronger than instantaneous dipole-induced dipole bonding.
9
New cards
describe the formation of hydrogen bonds

10
New cards
hydrogen bonding in ice

11
New cards
hydrogen bonding in water

12
New cards
describe the boiling points of the halogens
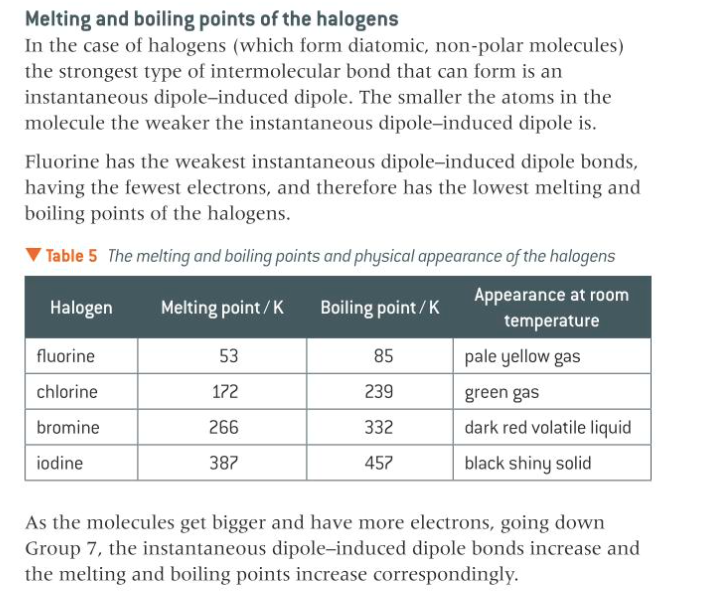
13
New cards
what is activation enthalpy
the minimum amount of kinetic energy needed between two particles before a reaction will occur
14
New cards
what is an enthalpy profile
useful for picturing what energy changes are happening throughout the reaction, the highest point on the pathway corresponds to the transition state.
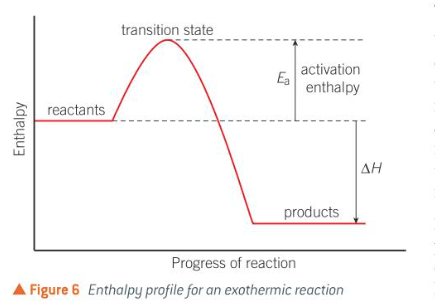
15
New cards
The effect of concentration and pressure on the rate of a reaction explained in terms of the collision theory

16
New cards
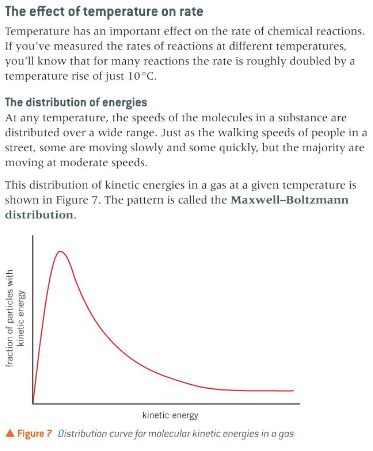
use of the concept of activation enthalpy and the Boltzmann distribution to explain the qualitative effect of temperature changes and catalysts on rate of reaction; techniques and procedures
for experiments in reaction kinetics including plotting graphs to follow the course of a reaction
for experiments in reaction kinetics including plotting graphs to follow the course of a reaction
17
New cards
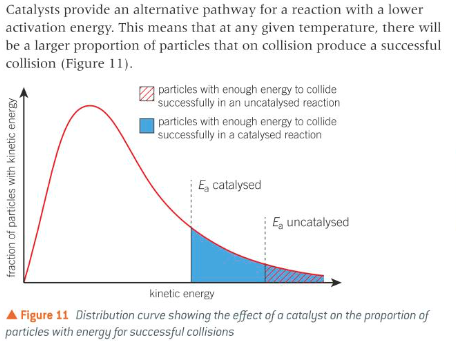
the role of catalysts in providing alternative routes of lower activation enthalpy
18
New cards
what is a homogenous catalyst

19
New cards
describe the formation of intermediates

20
New cards
calculations, from given data, of values for composition by volume of a component in a gas mixture measured in percentage concentration and in parts per million (ppm)
