Molecular Biology: DNA, RNA, and Genetic Processes
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Nucleic acids
Composed of nucleotides, essential for genetic information.
Phosphate groups
Part of nucleotides, links nucleic acids together.
Pentose sugars
Five-carbon sugars in DNA and RNA nucleotides.
Deoxyribose
Sugar in DNA, lacks one oxygen atom.
Ribose
Sugar in RNA, contains one more oxygen than deoxyribose.
Nitrogenous bases
A, T, C, G, and U; building blocks of nucleic acids.
Purines
Adenine and guanine, two-ring nitrogenous bases.
Pyrimidines
Cytosine, thymine, and uracil; single-ring bases.
Transformation
Genetic alteration of a cell by external DNA.
Griffith's experiment
Demonstrated transformation using Streptococcus pneumoniae.
Avery's experiment
Identified DNA as the transforming agent.
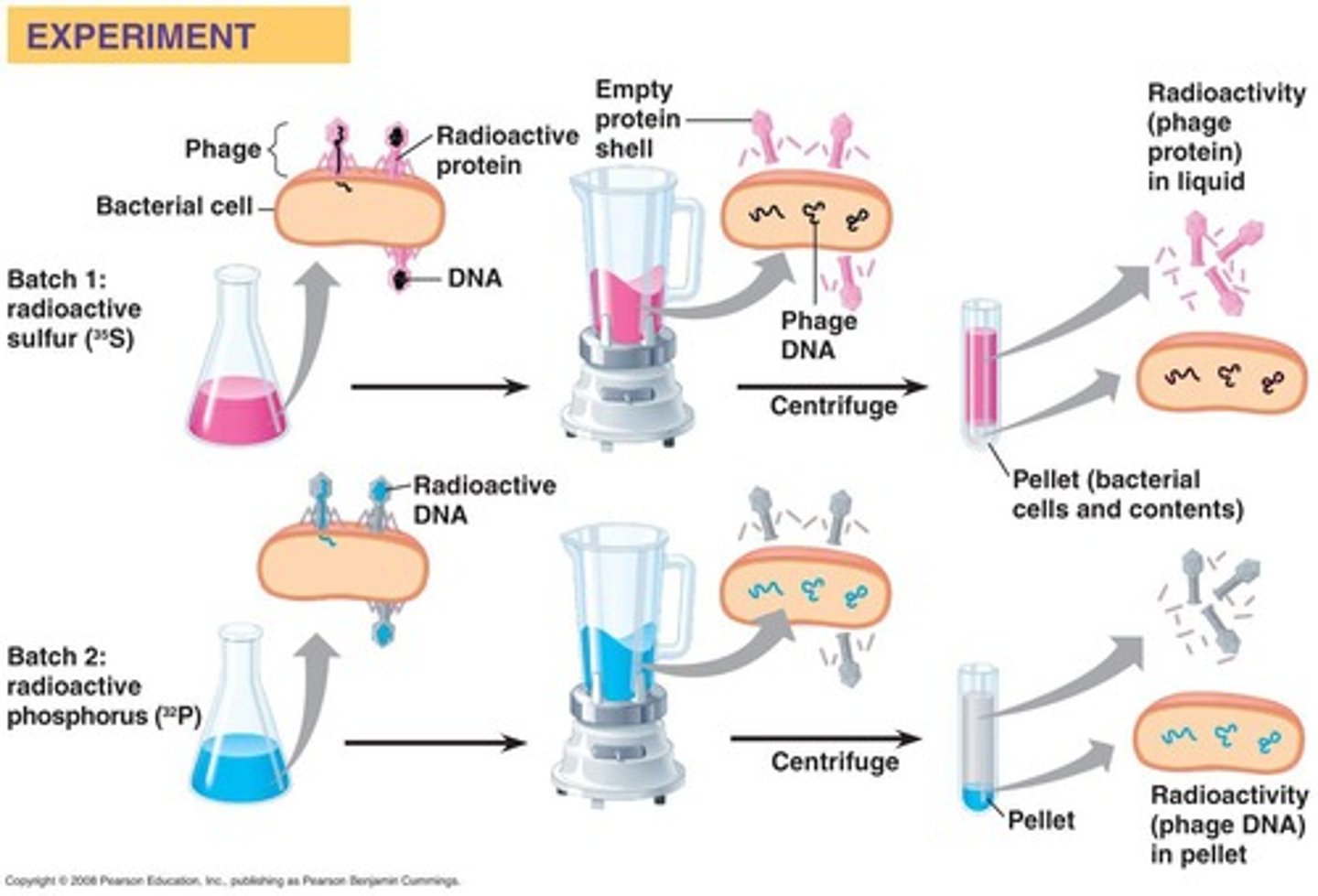
Bacteriophages
Viruses that infect bacteria, used in Hershey-Chase experiment.
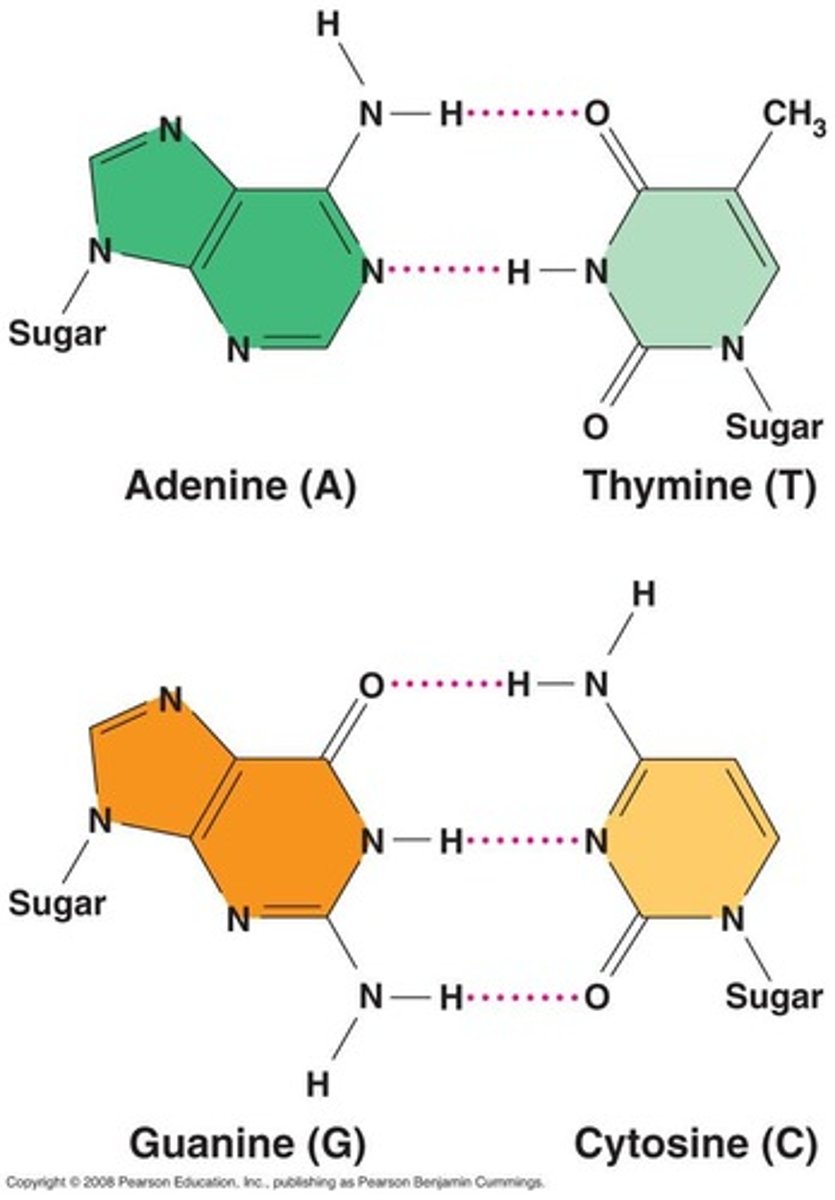
Chargaff's Rule
A=T and G=C in DNA molecules.
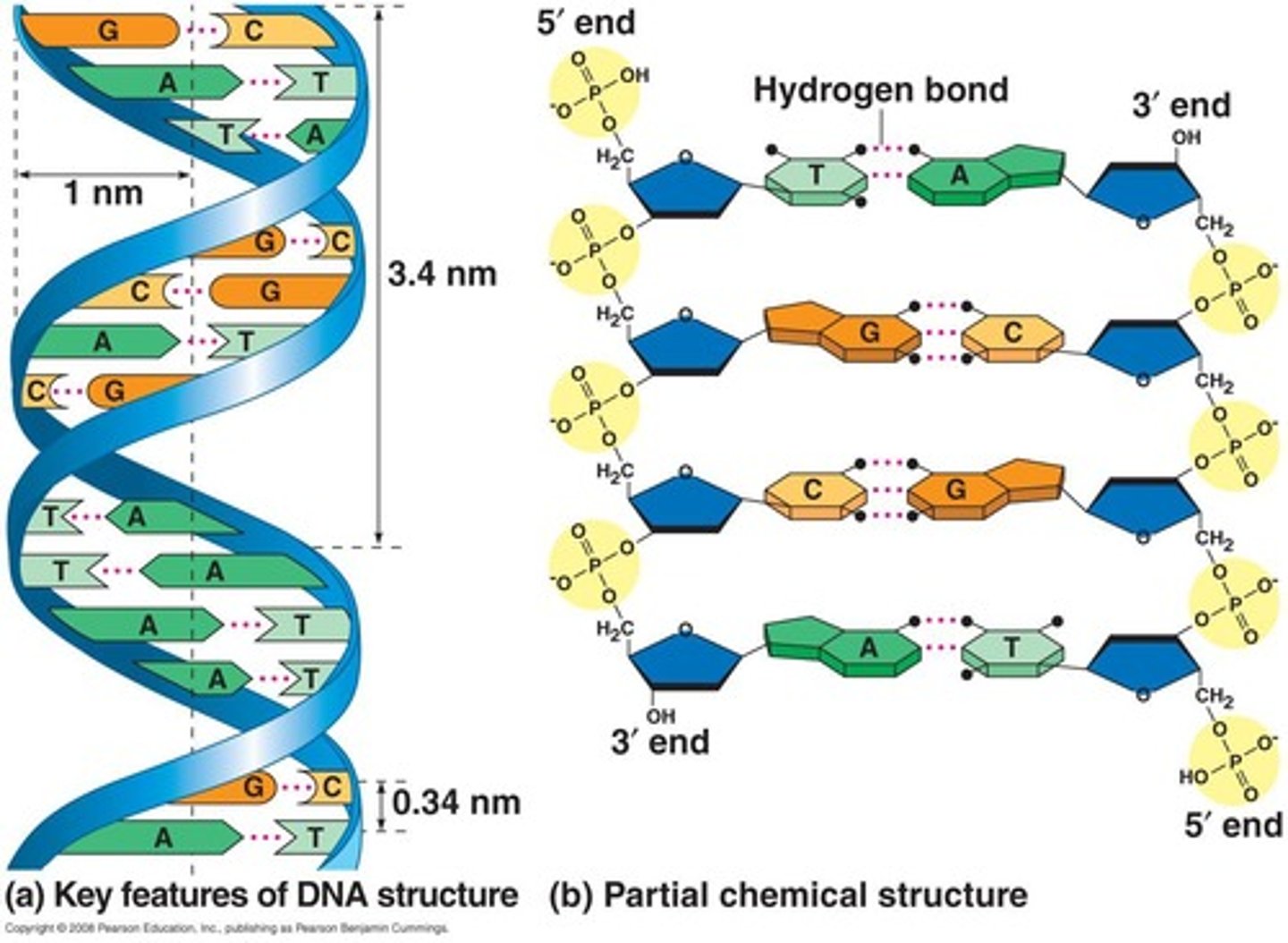
Double helix
Three-dimensional structure of DNA, twisted ladder shape.
DNA replication
Process of copying DNA during cell division.
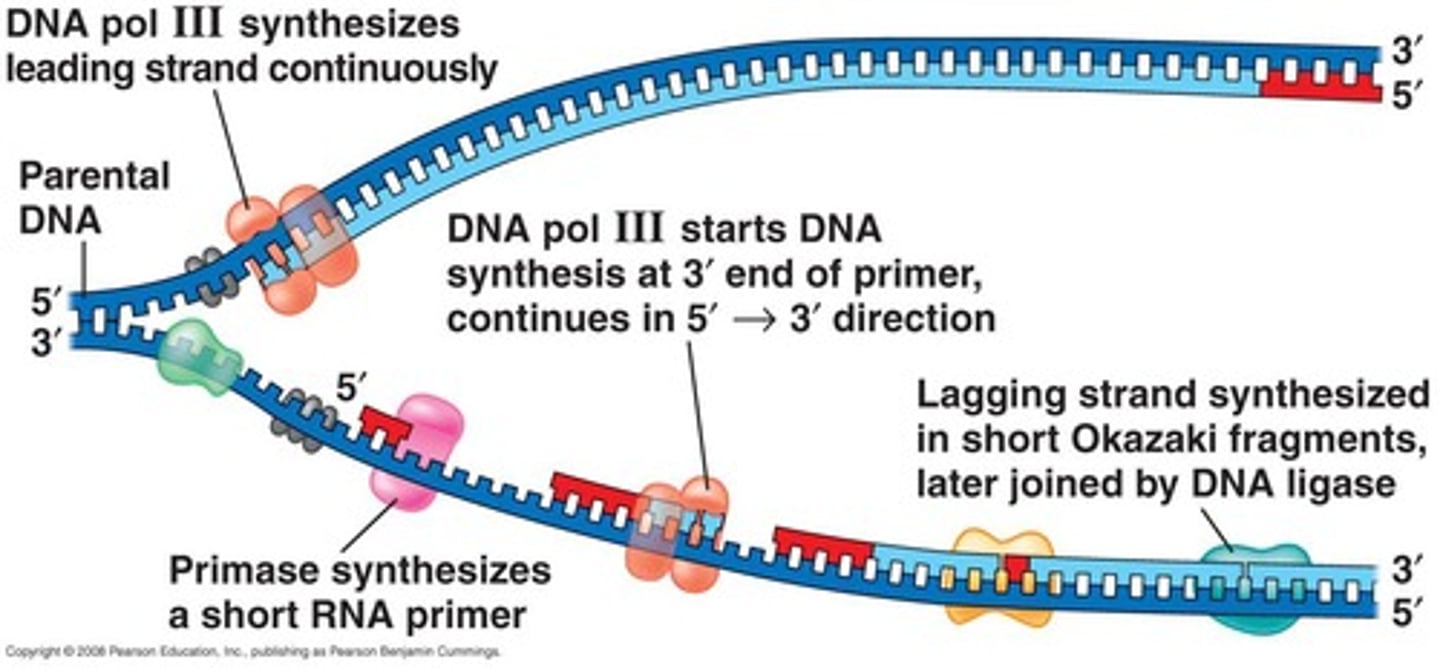
Helicase
Enzyme that unwinds and separates DNA strands.
DNA polymerase
Enzyme that synthesizes new DNA strands.
Leading strand
Continuously synthesized DNA strand during replication.
Lagging strand
Discontinuously synthesized DNA strand with Okazaki fragments.
DNA ligase
Enzyme that joins Okazaki fragments together.
Central Dogma
Flow of genetic information: DNA to RNA to Protein.
Transcription
Synthesis of RNA from a DNA template.
Translation
Synthesis of protein from mRNA at ribosomes.
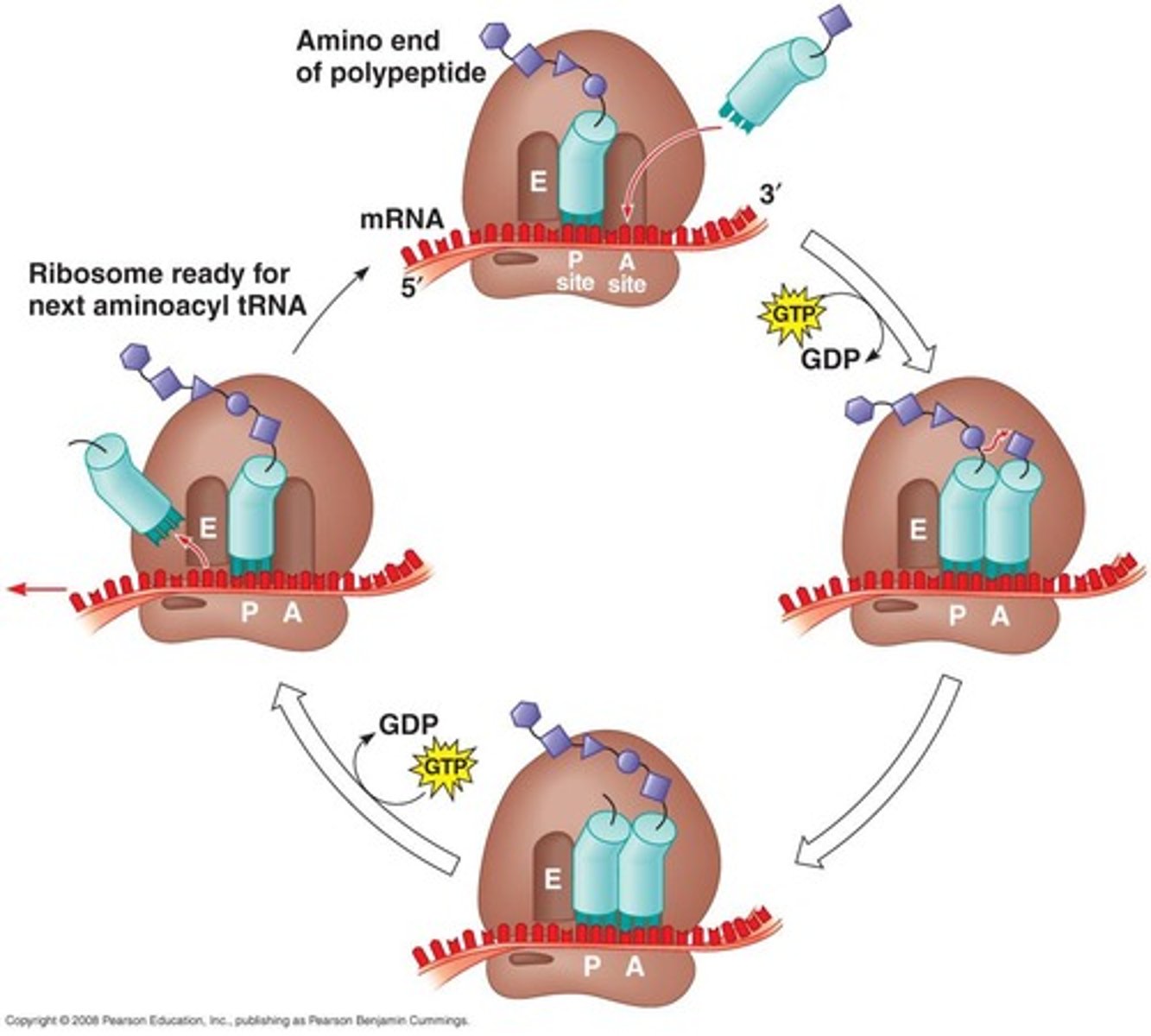
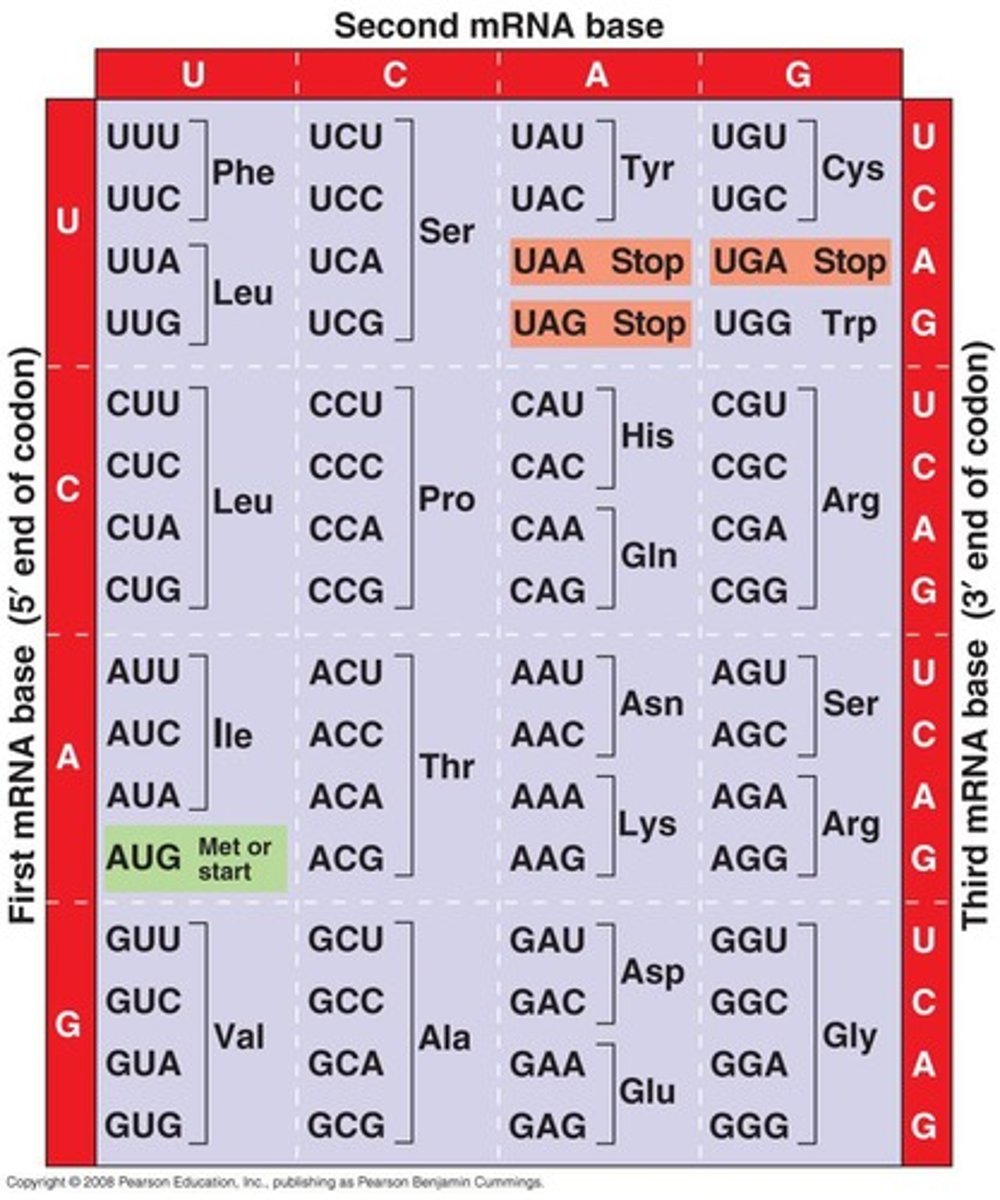
Codon
Sequence of three nucleotides coding for an amino acid.
Point mutations
Alterations at a specific base in DNA.
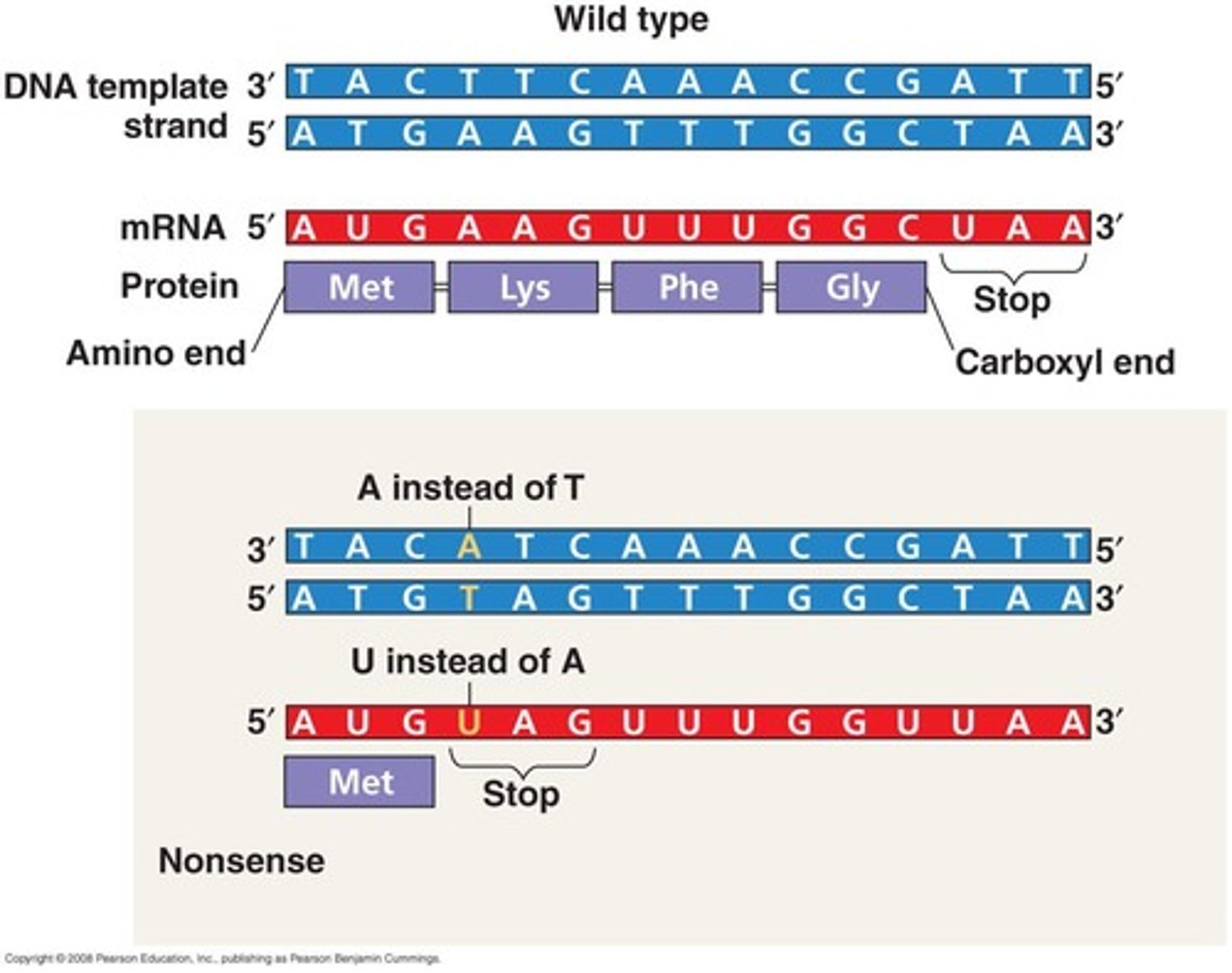
Frame shift mutations
Mutations that shift the reading frame of codons.