P6 - Waves
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
Define amplitude.
The maximum displacement of a point from its rest position.

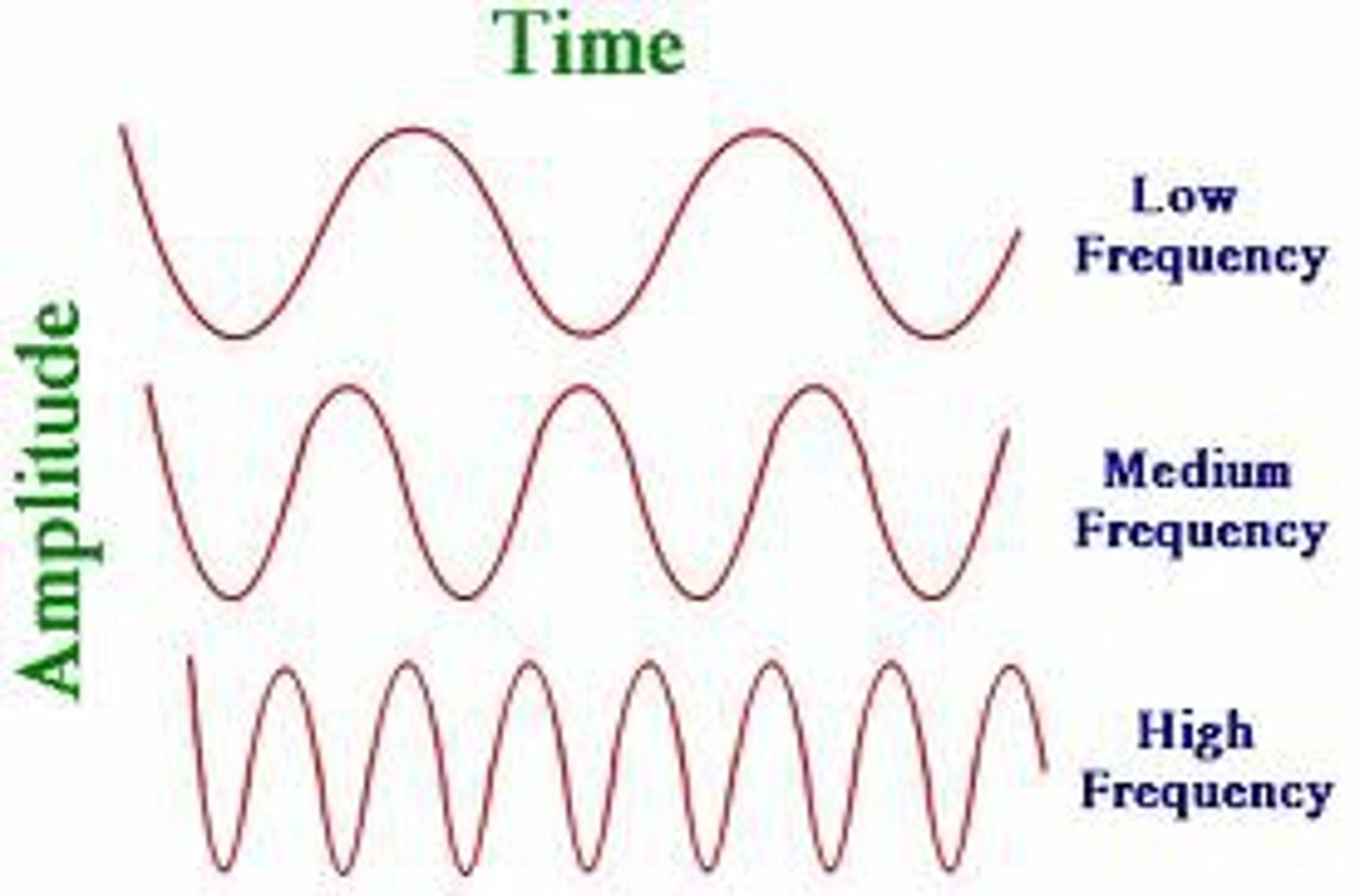
Define frequency.
The number of waves passing a point per second
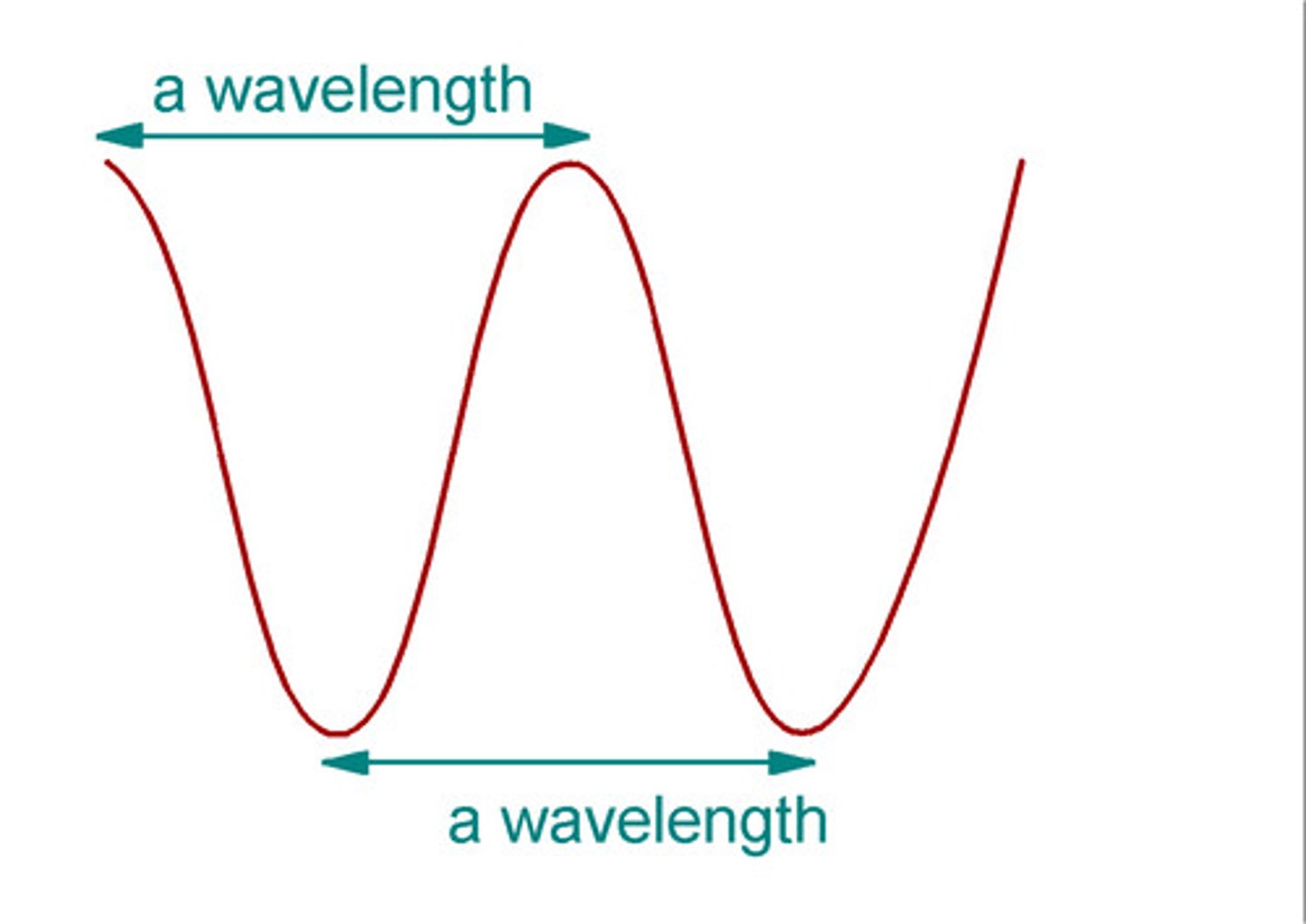
Define wavelength
The distance between two corresponding parts of a wave
What direction do the longitudinal waves vibrate
Parallel to the direction of wave travel
What direction do the transverse waves vibrate
Right angles/perpendicular to the direction of wave travel.
Define angle of incidence
The angle between the incident ray and the normal.
Define angle of reflection.
The angle between the reflected ray and the normal
Define wave speed.
The speed which the waves travel through the medium.
Define medium
Material in which a wave travels.
Define time period
The time for one complete oscillation
Wave speed units
m/s.
Wave speed =
frequency x wavelength
Frequency =
1/time period
time period =.
1/frequency.
Frequency units
Hz (Hertz.)
Wavelength unit
m.
wave speed symbol =
V.
Frequency symbol =
F.
Wavelength symbol
λ(lambda).
λ =
wavelength
Where do sound waves enter the ear
outer ear structures
After hitting the ear flap, where do sound waves travel down
Vibrate down the ear canal
Define ultrasound
A frequency above the threshold of human hearing.
What frequency is ultrasound above
2x10^4
What do sound waves consist of?
Pressure waves.
What vibrates after the eardrum?
Small bones in the middle ear
Where do the pressure waves move to in the ear?
The cochlear.
How is an electrical impulse generated from the cochlear
Hair and fibres stimulate a response.
What do s-waves travel through
Only solids
What do p-waves travel through
Solids and liquids
What causes the s-wave "shadow zone"?
Being stopped entirely by the liquid core
Which of the electromagnetic spectrum has the longest wavelength
Radio waves
Which of the electromagnetic spectrum has the shortest wavelength?
gamma rays.
Which of the electromagnetic spectrum has are ionising radiation
Ultraviolet.
Xrays
Gamma Rays.
What visible light is refracted the least?
Red.
What visible light is refracted the most
Violet
What is the speed of sound?
340 m/s
What is the speed of light?
3x10^8 m/s.
Maximum displacement=
Amplitude.
Distance of one entire oscillation
Wavelength
Time it takes for one complete oscillation
Time period
Number of complete oscillations per second=
Frequency.
What do waves transfer from one location to another?
Energy
Is sound long or trans?
Longitudinal
The distance from the lens to the principal focus is called the...
focal length
Which type of electromagnetic waves are the most penetrating?
gamma
What kind of object returns to its original shape when the force stops acting on it?
elastic
What is the upper limit of frequencies able to be heard by humans?
20 000 hz
A wave where the oscillations are perpendicular to the direction of energy transfer is a:
transverse wave
A wave where the oscillations are parallel to the direction of energy transfer is a:
longitudinal wave
What type of image will specular reflection produce?
A clear image
Light travels more ________ in a more dense material.
slowly
Light travelling from a less dense material, into a more dense material, will bend ________ the normal.
towards
Are longitudinal waves p or s?
primary (p)
Are transverse waves p or s?
secondary (s)
What type of wave are sound waves?
longitudinal
What type of wave are all electromagnetic waves?
transverse
What unit is used for frequency?
Hz
When will light reflect?
when the object is opaque and not absorbed by the material
When will light transmit?
when waves pass through a transparent material
When will waves be absorbed?
If the frequency of light matches the energy levels of the electrons
What is white light?
A combination of all wavelengths of visible light
What determines how transparent / translucent an object is?
The proportion of transmitted light
What is an opaque object?
An object that does not transmit any light
Objects that are hotter than their surroundings emit ________ radiation than they absorb.
more
Define intensity (for radiation)
power of the radiation per unit area
What happens to the wavelength emitted as an object gets hotter?
It decreases
What are oscilloscopes used for?
To display the frequency of an alternating current
Can transverse waves travel through a vacuum?
Yes
What type of waves are electromagnetic waves?
transverse waves
What property of the light wave changes when it is refracted?
wave speed (and so wavelength)
What happens to the speed of a wave if it passes through a more dense material?
slows
What happens to the direction of a slower moving wave in a denser material?
bends towards the normal
Define visible light
Spectrum of wavelengths that our eyes can detect
What type of reflection occurs as visible light travels through optical fibres?
Specular
Define fluorescence
UV light being absorbed and re-emitted as visible light
True or false: s-waves are longitudinal and p-waves are transverse
False