Chemistry ✿ Bonding, structure, and the properties of matter
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
how are ions formed?
when an atom loses or gains an electron
why are elements from groups 1, 2, 5 and 6 more likely to form ions?
elements from groups 1 and 2 can easily lose an electron to gain a full outer shell
elements from groups 5 and 6 easily gain an electron to gain a full outer shell
ionic bonding
when a metal and non-metal reacts
electrons are transferred
caused by oppositely charged atoms
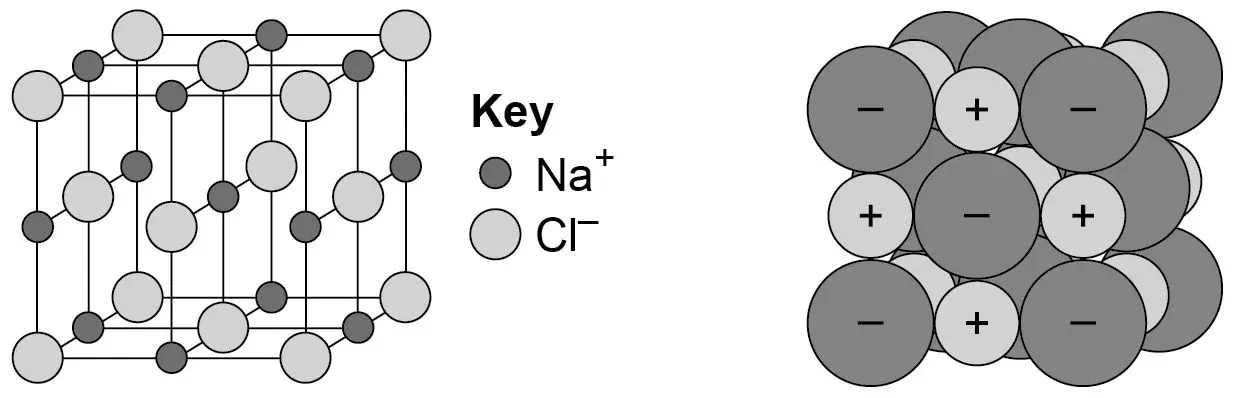
give 3 features of the structure of an iconic compound
held together by strong electrostatic forces between oppositely charged ions
regular lattice
conductors ONLY when melted
why do ionic compounds have high boiling points?
due to strong electrostatic forces, they need more energy to be broken
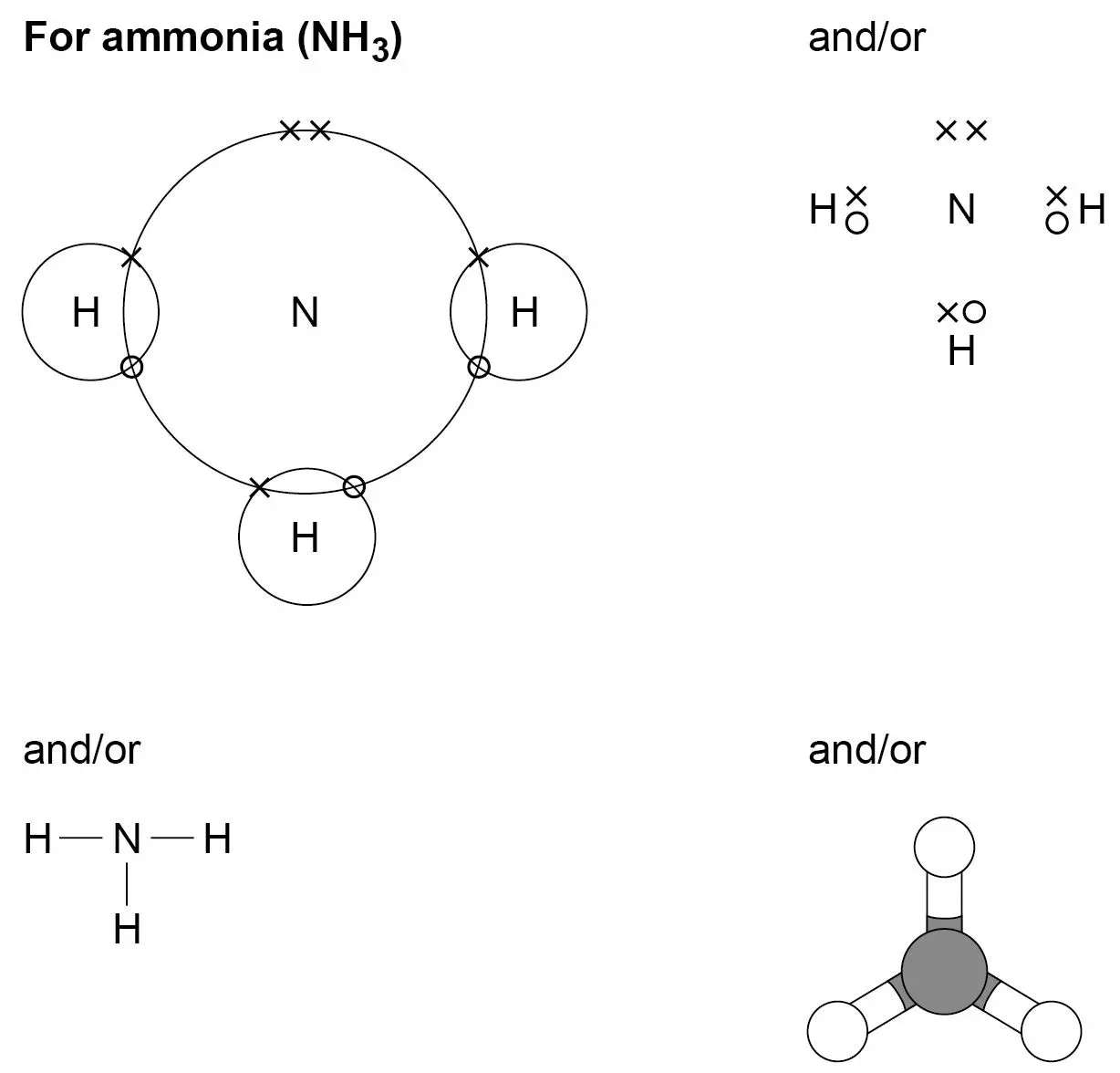
covenant bonding
when non-metal and metals react
electrons are shared
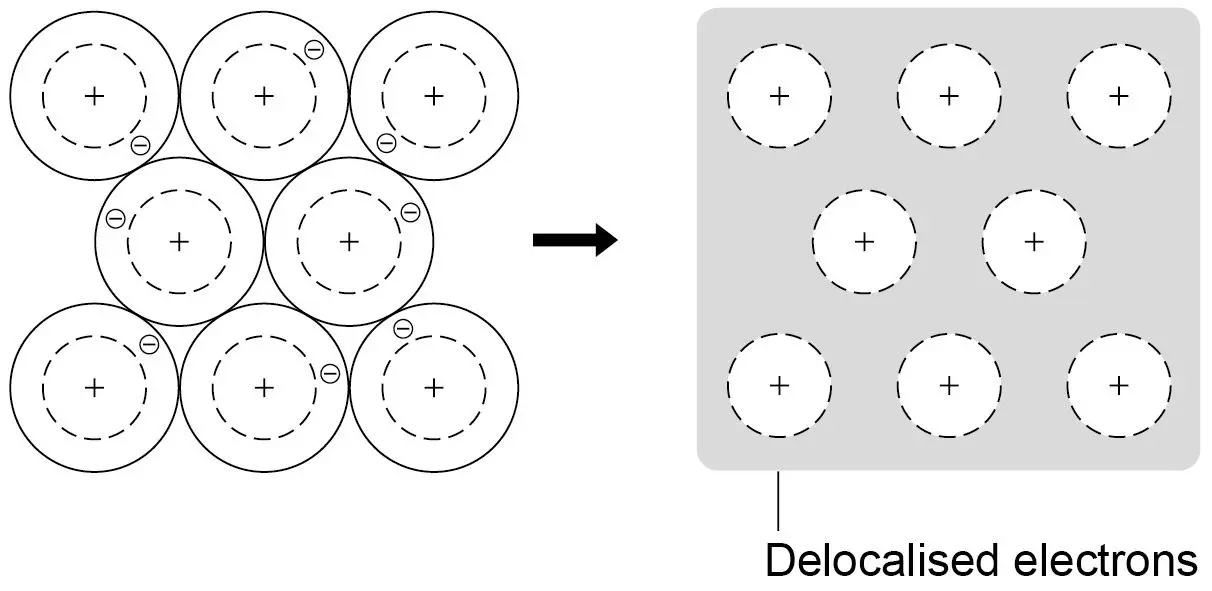
metallic bonding
when 2 metals react
sharing delocalised electrons
give 4 features of a simple molecular substance
usually gases or liquids
low melting points and boiling points
weak intermolecular forces between the molecules
as molecules get bigger the higher their melting and boiling points will be
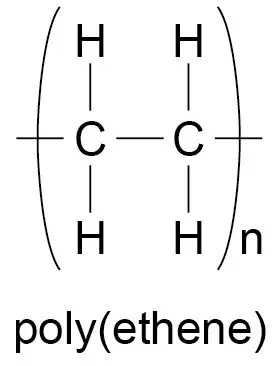
polymers
long chains of molecules joined by covalent bonds
give 3 features of a polymer
large intermolecular forces
solid at room temperature
lower boiling points than ionic or giant molecular compounds
give 3 features of a giant covalent structure
strong covenant bonds
high melting and boiling points
no charged particles, cannot conduct
give 3 examples of giant covalent structures
diamond
graphite
silicon dioxide
allotropes
elements in different structural forms
eg diamond and graphite
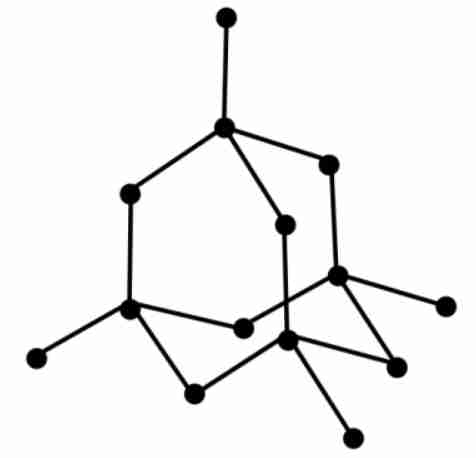
give 3 reasons why diamond is hard
each carbon atom forms 4 strong covalent bonds
giant covalent structure
bonds require a lot of energy to break
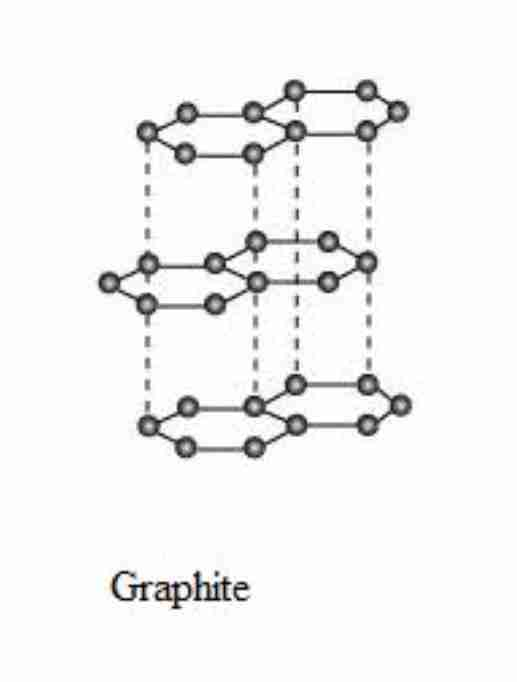
Give 3 properties of graphite
each carbon atom has 3 covalent bonds, creating layers
layers held by weak forces, they slide over each other
one electron from each carbon atom is delocalised
why does graphite conduct electricity?
has delocalised electrons which carry electricity
give 4 properties of an alloy
low melting point
malleable
distorted layers
rust resistant
fullerenes
molecules of carbon shaped like hollow balls
nanotubes
tiny carbon cylinders
give 2 properties of a nanotube and some uses of them
conduct electricity and heat
not broken when stretched
used in electronics and to strengthen materials
why are most metals malleable?
layers of atoms can slide over each other
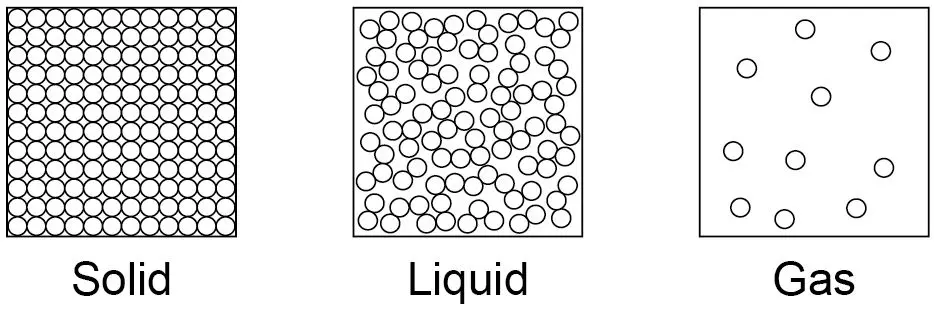
what are the limitations of the simple model shown?
no forces shown
all particles are represented as spheres
spheres are solid
why do ionic compounds only conduct electricity when molten?
when molten, ions are free to move so charge can easily flow