MCAT BIOLOGY
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
Proximal Convoluted Tubule
Where does 75% of sodium get reabsorbed?
Ascending Loop of Henle
Where does 25% of salts get reabsorbed?
Distal Convoluted Tubule
Where does a small amount of sodium get absorbed
Renin
Enzyme that is increased during low salt levels in the body. Detected by baroreceptors. Leads to a increase in aldosterone
Aldosterone
Hormone released from adrenal cortex. Increases reabsorption of sodium in the collecting duct and water (passively)
ADH/Vasopressin
Hormone produced by the hypothalamus. Released due to low water levels in the body. Increases reabsorption of water in the collecting duct.
Where are steroid hormones stored in the cell
Nowhere
Where are protein hormones stored in the cell?
Granules
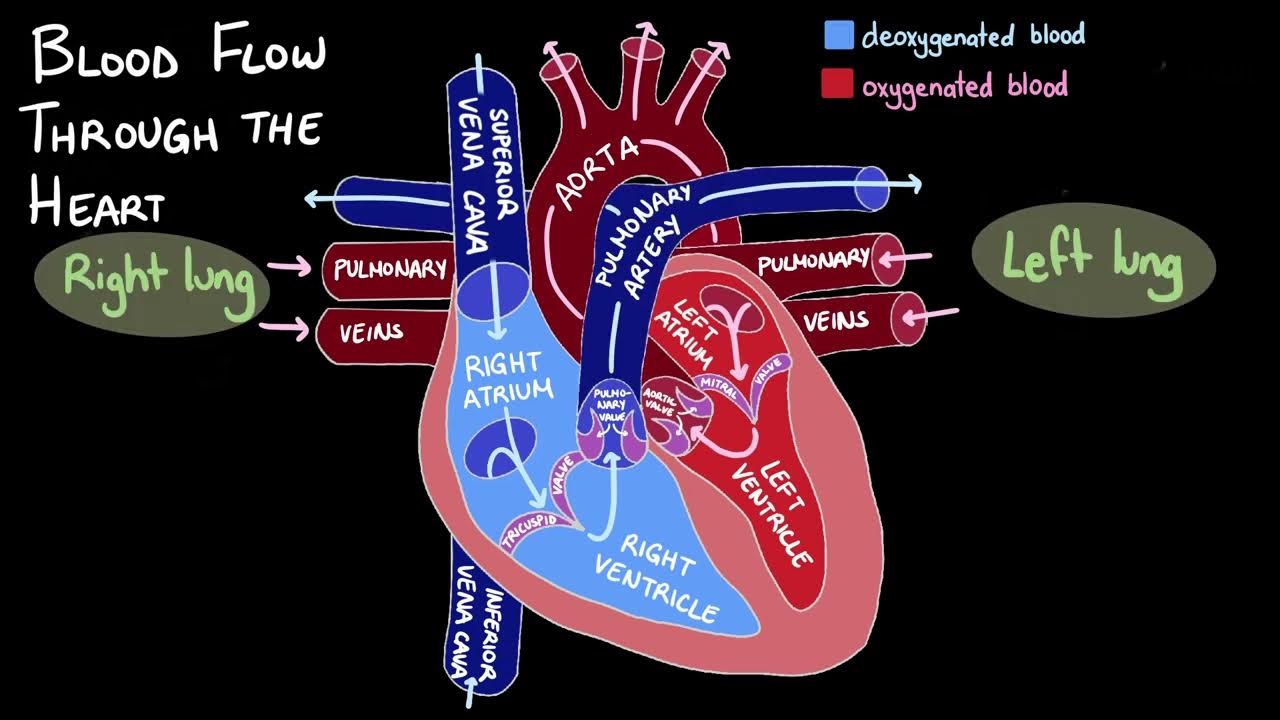
Flow of blood through the heart
Apoptosis of the webbing in-between digits
What process prevents Syndactyly
What is a brush border enzyme
enzyme that is present in the luminal surface of cells lining the duodenum. Includes disaccharidases (maltase/isomaltase/lactase/sucrase) and peptidases (dipeptidase/enteropeptidase)
What is a epigenome and what does it do
Chemicals that surround the DNA and can change the gene expression without changing the DNA itself
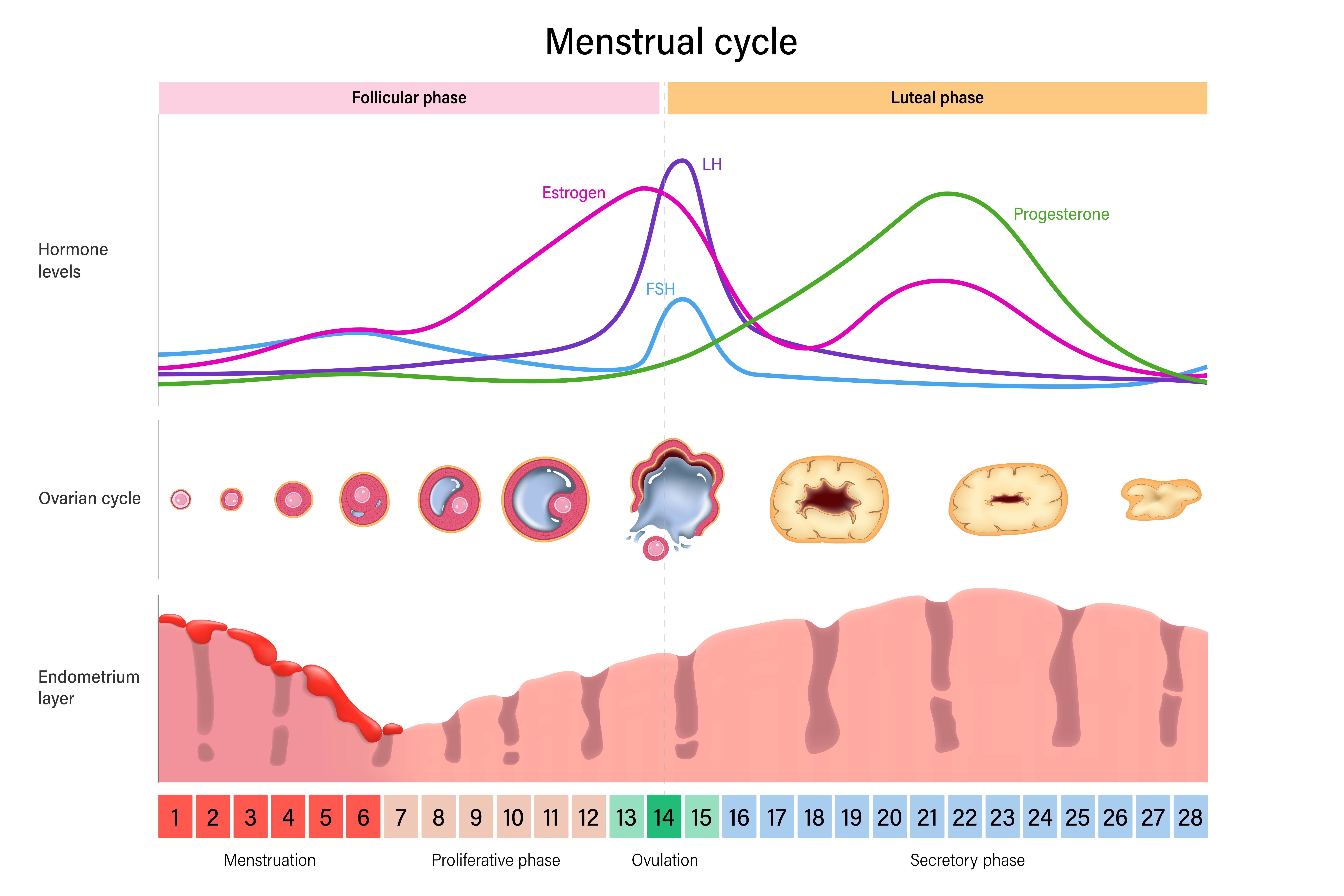
Describe the menstural cycle as a whole (ovarian/hromones’’/endometrium)
Ectopic pregnancy
When a fertilized egg implants in the wrong area AKA not in the endometrium (usually the fallopian tubes)
Myosin is ____, and actin is _____
Myosin is thick, and actin is thin
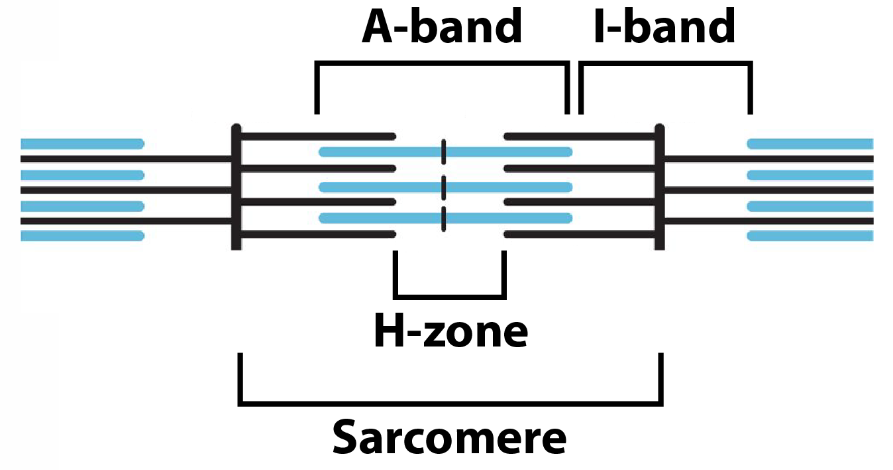
Parts of a sarcomere
Z line- end of sarcomere
M line- middle of sarcomere
I band- thIn filaments only
H band- only tHick filaments
A band- All of the thick filament, including the overlapped portions with thin filaments
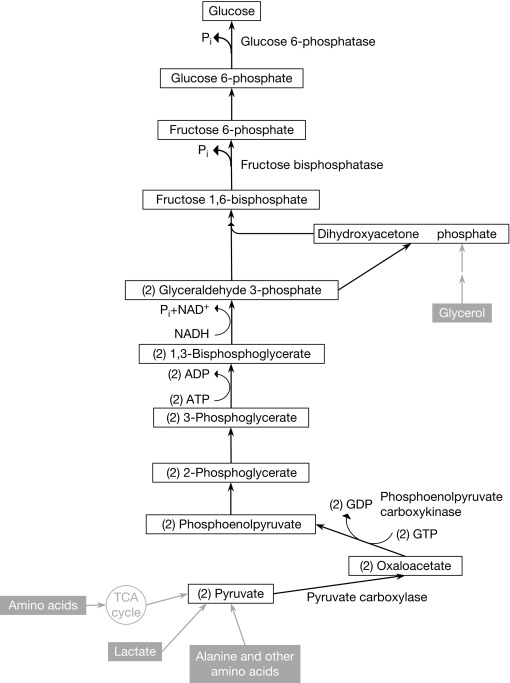
Describe the path of gluconeogenesis
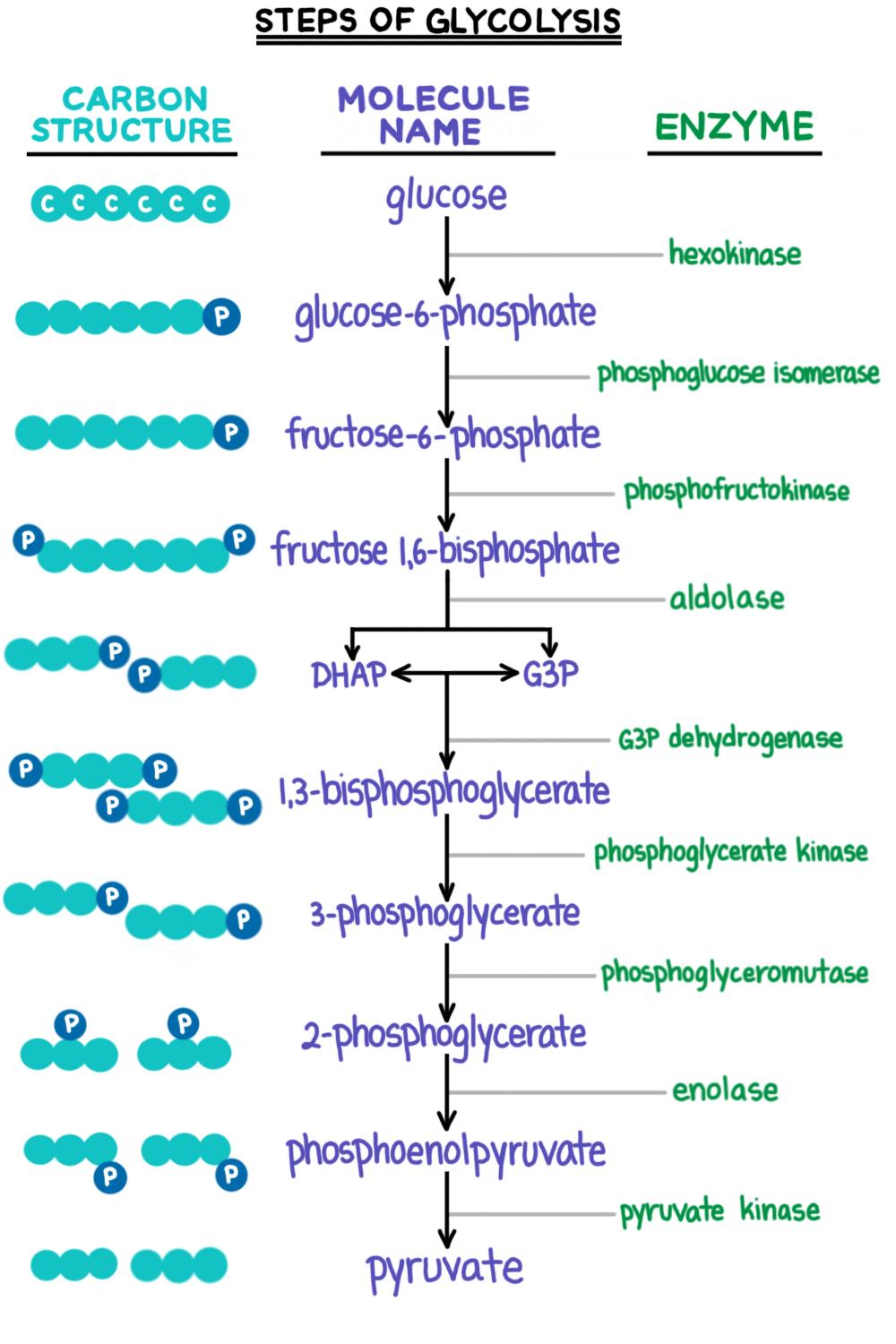
Describe the path of glycolysis
Describe the path of CAC
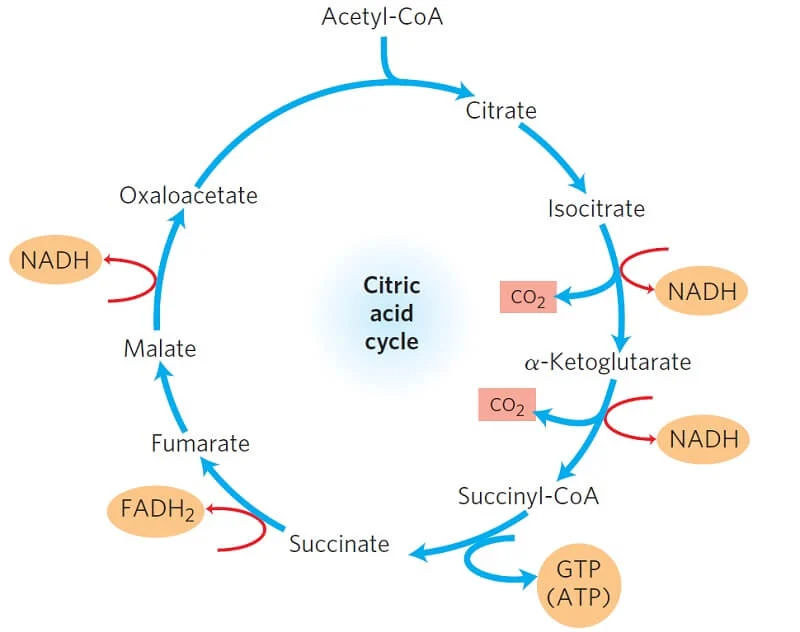
What is the rate determining step of CAC
The conversion of isocitrate to alpha-ketoglutarate
3 NADH and 1 FADH2
How much NADH and FADH2 is produced from 1 cycle of CAC
How much ATP is made from 1 NADH
2.5 ATP
How much ATP is made from 1 FADH2
1.5
How much ATP is produced from 1 cycle of CAC
7.5 from NADH + 1.5 from FADH2 + 1 from GTP= 10 ATP TOTAL
Thymus is a immune organ that matures and creates T cells
What is the function of the thymus
What is the function of T cells
Destroys an infected cells that contain foreign antigens
Where are B cells produced and what do they do
Be cells are matured and created in bone marrow and are involved in antibody production
contain large fragments of DNA and include both coding (exon) and non coding (introns) regions of genome
Genomic library
cDNA library
constructed by reverse transcription and lacks the non coding regions (introns)
What are the three steps of PCR
Denaturation- heat up DNA to unwind double helix
Annealing- lower temperatures slightly so primers can bind
Elongation- DNA polymerase uses primers to add the new complementary strand
Why can’t human polymerase be used in the PCR process
The high temperatures needed in denaturation will also denature human polymerase. Taq comes from a extremophile so its polymerase will be able to remain intact during denaturation
When carbohydrates are not available, what energy resources are used instead
Fats and proteins but fats are prioritized over proteins
What is hydrostatic pressure
pressure of liquids pushing against each other
What is oncotic pressure
Pressure that develops due to differences in osmotic gradients due to solutes
What are the three parts of a bacterial growth curve
Lag phase, log phase and death phase
In conjugation how is DNA transferred
Genetic material is transferred from F+ to F- unidirectionally (only F- gets new genetic info)
Variable expressivity
people with the same genotype that have different phenotype
the proportion of people with a certain genotype that express the phenotype is usually less than those who have the gene
Reduced penetrance
when a heterozygote expresses a phenotype that is a mix of two homozygous genotypes
Incomplete dominance
Codominance
when more than one dominant allele exists for a given gene
What are the subunits of eukaryotic ribosomes
60S and 40S (80S)
What are the subunits of prokaryotic ribosomes
50S and 30S (70S)
Where does a repressor bind
at the operator
Positive inducible
No transcription occurs until a inducer binds
Positive repressible
Transcription occurs until a inhibitor binds
Negative inducible
Repressor is normally bound but a inducer deactivates it
Negative repressible
Transcription occurs until a repressor binds
Describe movement of water and solutes in the loop of Henle
Descending limb- water exits
Ascending limb- solute exits
What alleles do people of different blood types pass
AB passes A and B
A passes A
B passes B
O passes O
What is nondisjunction
When chromosomes do not properly separate in meiosis. Can result in trisomy or monosomy
Germline vs somatic cells
Germline cells can be used to make gametes while somatic cells do not
What comes from the ectoderm
Skin, eyes, nervous system
What comes from the mesoderm
Skeletal system, notochord, excretory system, circulatory system, reproductive system
What comes from the endoderm
Lining of digestive tract, repsiratory system excretory system, productive system and liver, prancreas, thymus, thyroid gland, parathyroid gland
What is a energy source used in translation
GTP