Pregnancy, Labor, Delivery- Higgins
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
The # of times a woman has been pregnant is called _________.
idk how imp
gravidity
The # of pregnancies exceeding 20 weeks gestation is called ___________.
idk how imp
parity
Early symptoms and signs of pregnancy?
early s
fatigue
increased urination
n/V
“morning sickness”
signs:
missed period
change in cervical mucus
bluish discoloration of vaginal mucosa
increased skin pigmentation
breast changes

In pregnant women:
what should be supplemented in pregnancy to prevent neural tube defects?
multivitamin with ______+_______ should be given.
minimize consumption of what stimulant?
what intake should be limited due to mercury content?
can you drink alcohol?
folic acid 0.4mg PO daily
multivitamin with calcium and iron
minimize caffeine consumption
limit seafood intake (12 oz)
don’t drink alcohol 😑
What vaccines should be given during pregnancy? which shouldn’t?
give inactivated influenza vaccine
give Tdap vaccine ~27-36 weeks gestation
NO LIVE vaccines
What PK changes occur during pregnancy?
Absorption
Distribution
Metabolism
Excretion
Absorption
decrease GI motility and gastric acid secretion
altered bioavailability due to n/v
increased skin absorption
Distribution
blood volume increases 30-50%
increased TBW
body fat increases
albumin conc decreases
Metabolism
hepatic perfusion increases
hepatic metabolism altered (CYP implications)
Excretion
renal blood flow increases 25-50%
GFR increases by 50%
renally excreted drugs should be adjusted up
lower SCr concentrations
Definition of teratogen:
substance (drug or environmental agent) that has the potential to produce abnormal development in the fetus
Difference btwn Congenital vs Congenital malformation vs Congenital anomaly:
idk how important
congenital—> any condition existing at birth, regardless of cause
congenital malformation—> structural defect in an organ or body part arising during fetal development
congenital anomaly—> broader term for any deviation from normal development, including structural, functional, or metabolic abnormalities (includes malformations)
What medications are associated with teratogenic effects during organogenesis?
chemo drugs, sex hormones, lithium, retinoids, thalidomide, warfarin, antiseizure medications
NSAIDs and tetracyclines—> effects in 2nd and 3rd trimester
How does drug exposure effect each period of pregnancy?
first 4 weeks of gestation
embryonic period
2nd/3rd trimester
I do NOT think important!!!!!!!!
first 4 weeks of gestation= all-or-none phenomenon
embryonic period= structural anomalies
2nd/3rd trimester= growth restriction, CNS abnormalities, impaired organ fxn, fetal demise
What antiseizure medication should be avoided during pregnancy?
valproic acid
What resources are available to assess medication safety in pregnant individuals?
FDA
package inserts
fact sheets
Brigg’s Drugs in pregnancy and lactation
can volunteer to sign up for a pregnancy exposure registry
What are the most common pregnancy-influenced GI issues?
n/v
constipation
acid reflux
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is
diagnosed when?
what happens to carbohydrate tolerance? b-cells? insulin resistance?
RFs? idk how important
diagnosed between 24-28 weeks
carbohydrate intolerance, pancreatic b cell dysfunction, insulin resistance
RFs:
history of GDM
high-risk race
BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2
TGs >250 mg/dL
indications of insulin resistance
history of diabetes
physical inactivity
Polycystic ovary syndrome
A1c >5.7%
previous birth of an infant weight ≥4 kg
HTN
HDL <35 mg/dL
What’s the one step and two step method for screening and diagnosis of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM)?
one step method
75-gram oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT)
draw plasma glucose at fasting, 1 and 2 hrs after admin
GDM diagnosis when 1 or more of the following met:
fasting: 92 mg/dl
1hr: 180 mg/dl
2hr: 153 mg/dl
two step method
step 1
50-gram oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) in a non-fasting state
draw plasma glucose 1 hr after admin
if plasma glucose ≥140 mg/dL then move to step 2
step 2
100-gram OGTT with fasting 1-,2-, and 3-hr levels
GDM diagnosis when 2 or more of the following met:
fasting: 95 mg/dl
1hr: 180 mg/dl
2hr: 155 mg/dl
3hr: 140 mg/dl
What is the first line tx for GDM?
dietary and exercise changes
at least 4 times daily
What pharmacotherapy can be used for GDM pts. if diet and exercise fail?
WHAT IS 1st LINE?
BASAL INSULIN w/ bolus if needed
alternatives: metformin, glyburide
How is preeclampsia diagnosed?
elevated blood pressure + proteinuria
if no proteinuria:
new onset of thrombocytopenia + serum creatine >1.1 mg/dl
OR
doubling of creatinine + elevated LFTs + pulmonary edema
OR
new onset HA
Preeclampsia risk factors:
idk how important
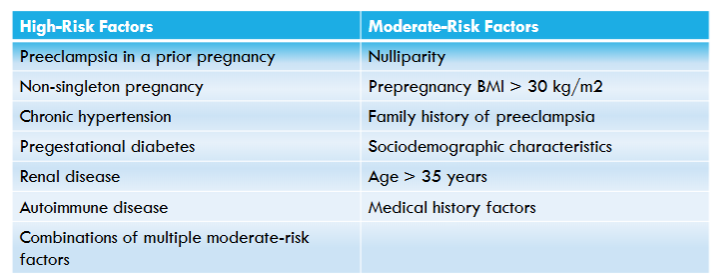
Preeclampsia may progress rapidly to what? Main symptom?
Eclampsia—> seizures!!
What are the complications of uncontrolled HTN?
pregnant individuals:
fetus:
chronic HTN:
IDK HOW IMPORTANT
pregnant individuals:
preeclampsia
eclampsia
stroke
labor induction
placental abruption
fetus:
intrauterine growth restriction
preterm delivery
low birth weight
still birth
chronic HTN:
death
pulmonary edema
renal insufficiency/failure
myocardial infarction
cesarean delivery
postpartum hemorrhage
GDM
congenital anomalies
treatment of preeclampsia with pharmacotherapy is recommended when blood pressure is ≥______ mmHg.
160/110 mmHg
What antihypertensives are preferred for tx of preeclampsia?
What antihypertensives are preferred if there is a urgent need?
preferred: labetalol and nifedipine XR
urgent need: IV labetalol, IM hydralazine, or nifedipine IR
2nd line: nicardipine or esmolol infusion
______________ is recommended with severe hypertension with preeclampsia to prevent progression to eclampsia and treat eclamptic seizures.
magnesium
HELLP syndrome is an acronym for what?
H= hemolysis
EL= elevated liver enzymes
LP= low platelet count
Postpartum hemorrhage is losing how much blood?
What should be administered before placental delivery to reduce blood loss?
blood loss >1000ml or blood loss with s/sx of hypovolemia
oxytocin should be administered
Initial tx for postpartum depression?
Pharm tx?
What drug has a specific indication for postpartum?
initial: psychotherapy, CBT, group/family therapy
pharm tx: sertraline, paroxteine, fluoxetine, nortriptyline
brexanolone is FDA approved for tx of postpartum
What is the BBW for Brexanolone?
Admin?
REMs program
BBW—> excessive sedation and sudden loss of consciousness
IV admin as 60 min continuous infusion
Preterm labor is uterine contractions before ____ weeks gestation with changes in cervical dilation and/or effacement.
37
RFs for preterm labor?
idk how imp

Tocolytic therapy is used to postpone delivery long long enough to do what?
allow for max effect of antenatal corticosteroid and Mg admin
allow for transport of pregnant pt. to high-risk hospital
What drugs can be used for tocolytic therapy?
b adrenergic receptor agonist (terbutaline)
CCBs (nifedipine)
NSAIDs (indomethacin)
Mg for fetal neuroprotection
10-30% of pregnant individuals are colonized with Group B Strep (GBS) which leads to pregnancy risks.
What abx are given until delivery for pts. with GBS?
IV ampicillin q4 hrs until delivery
Prelabor rupture of membranes (PROM) before 34 weeks prophylactic antibiotics should be initiated to prolong pregnancy, reduce infection in patient and neonate and reduce major morbidities and mortality.
What abx should be given for PROM pts.?
7 day course of:
IV ampicillin + erythromucin for 2 days followed by oral amoxicillin + erthromycin for 5 days
amoxillin-clavulanate not rec
The ACOG recommends antenatal corticosteroids for fetal lung maturation in what pts.?
What are the most common antenatal corticosteroid regimens?
rec for 24-34 weeks gestation and at high risk for preterm delivery
most common regimens:
betamethasone IM, 2 doses 24 hrs apart
dexamethasone, 4 doses 12 hrs apart
HIGGINS REVIEW:
PK changes in pregnancy- ADME
Resources for drug information in pregnancy
Which medications are teratogens and what can you do to reduce risk
Preterm labor medication considerations
Focus on what needs to be given to protect baby
Treatment of pregnancy complications
Focus on nonpharmacologic and first line pharmacologic management
most imp PK changes:
plasma volume, cardiac output, and eGFR increase 30-50%
body fat increases= increase Vd
plasma albumin decreases
hepatic perfusion increases
absorption: n/v, delayed gastric emptying, and increase in gastric pH
increased levels of estrogen/progesterone= affect the liver enzyme activity
resources:
FDA and package inserts
fact sheets
Brigg’s drugs in pregnancy and lactation
FDA pregnancy registry
key medications that are teratogens
chemo drugs, sex hormones, lithium, retinoids, thalidomide, warfarin
NSAIDs and tetracyclines—> 2nd and 3rd trimester
antiseizure meds—> no VALPROIC ACID
preterm labor medication considerations
tocolytic therapy
b-adrenergic receptor agonists (terbutaline)
CCBs
NSAIDs
Mg (for neuroprotection)
abx
EBS—> IV ampicillin q4hrs
PROM—> 7 day regimen
antenatal corticosteroids
betamethasone IM, 2 doses 24 hrs apart
dexamethasone, 4 doses 12 hrs apart
what needs to be given to protect baby
in general: folic acid supplements, multivitamins with Ca and Fe
vaccines: Tdap, inactivated influenza
tx of pregnancy complications
GDM
1st line: diet and exercise
pharm tx: INSULIN
alt: metformin or glyburide
preeclampsia
labetalol and nifedipine XR preferred
if urgent need: IV labetalol, IM hydralazine, IR nifedipine —> 1st line
must also give Mg
postpartum hemorrhage
oxytocin
postpartum depression
initial tx: nonpharm
pharm tx: sertraline, paroxetine, fluoxetine, nortriptyline
brexanolone
PRACTICE:
JC is a 25-year-old Black female who is pregnant with her first child. She is currently 28 weeks gestational age and begins to have contractions and bleeding. Which of the following medications can be used to attempt to postpone delivery?
a. Terbutaline
b. Magnesium
c. Dexamethasone
d. Ampicillin
a.